Abstract
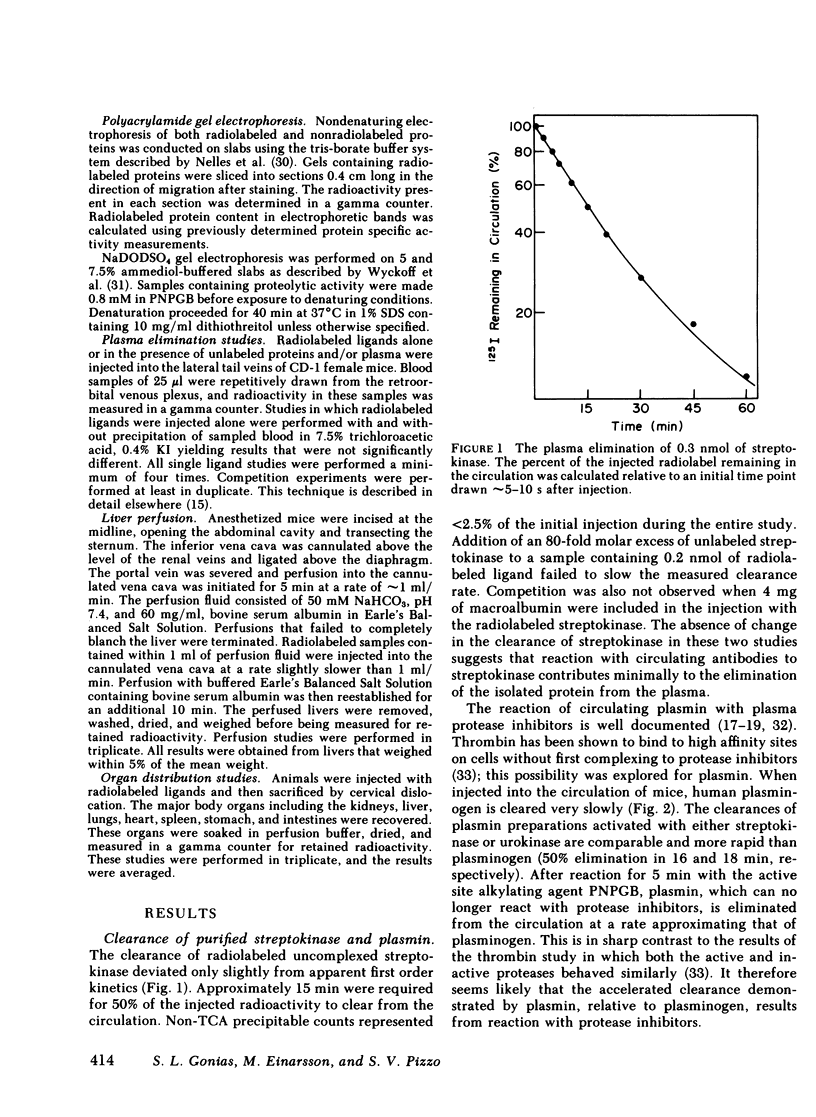
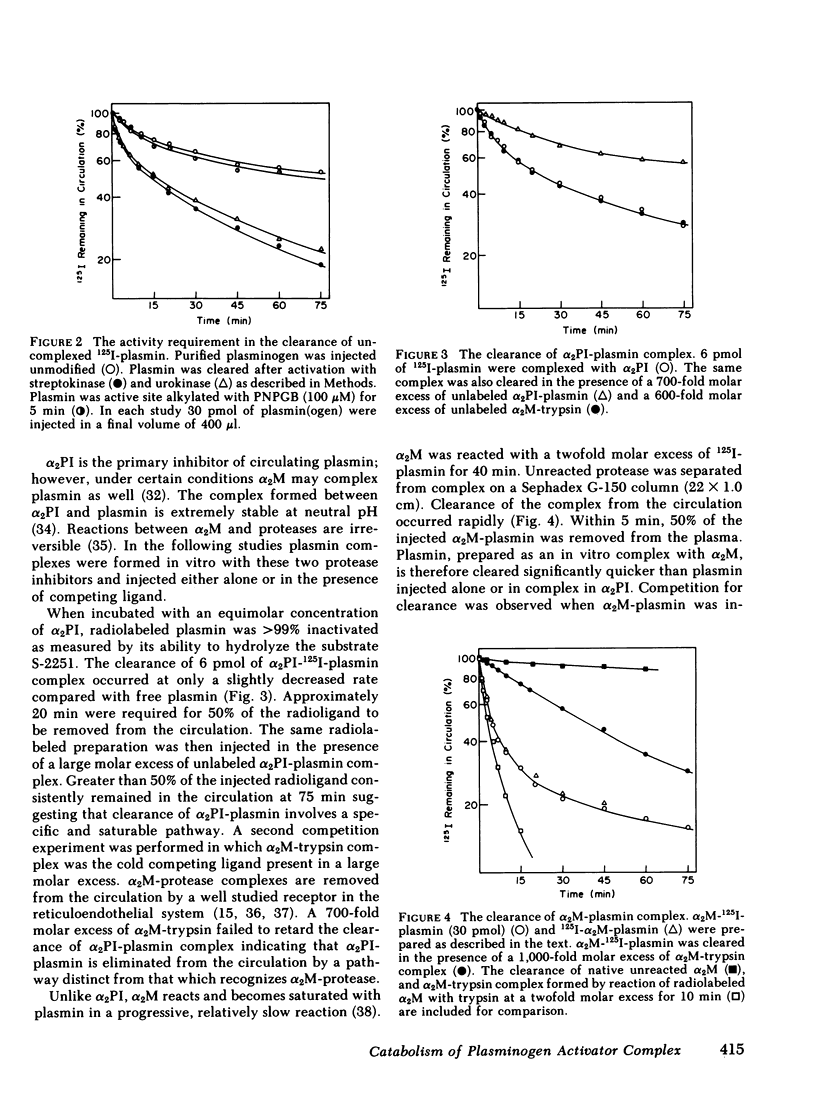
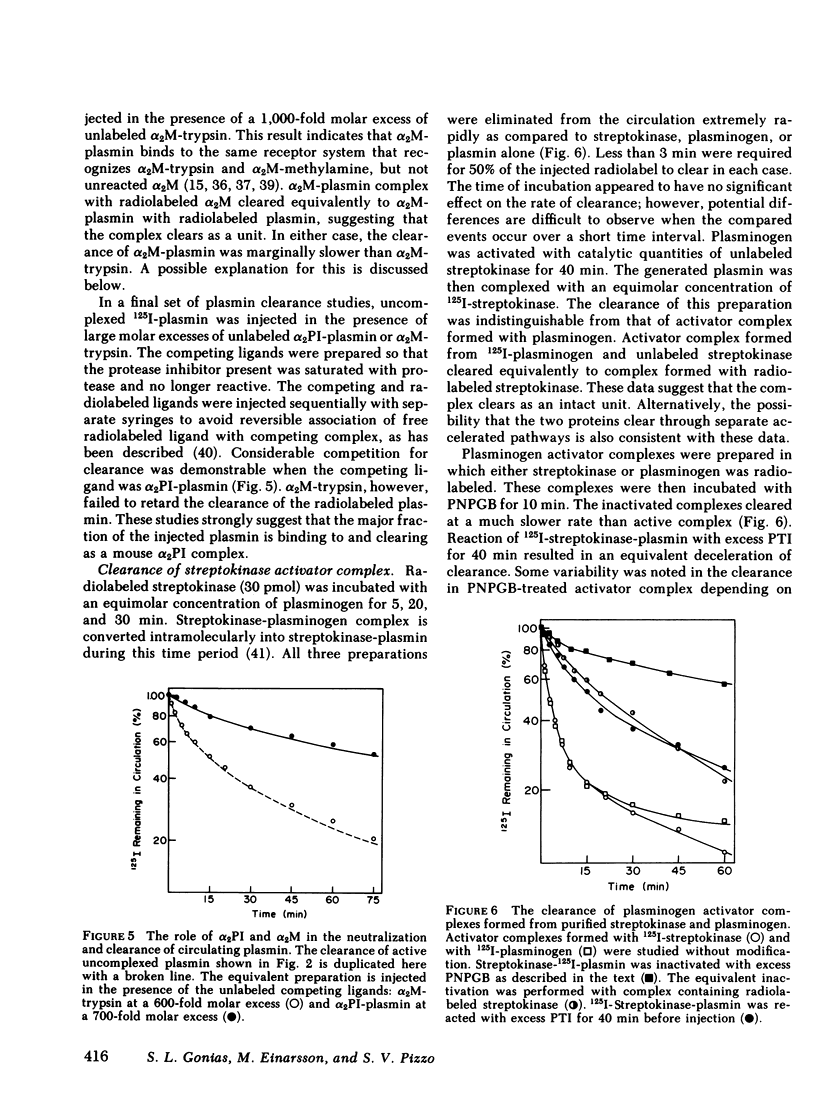
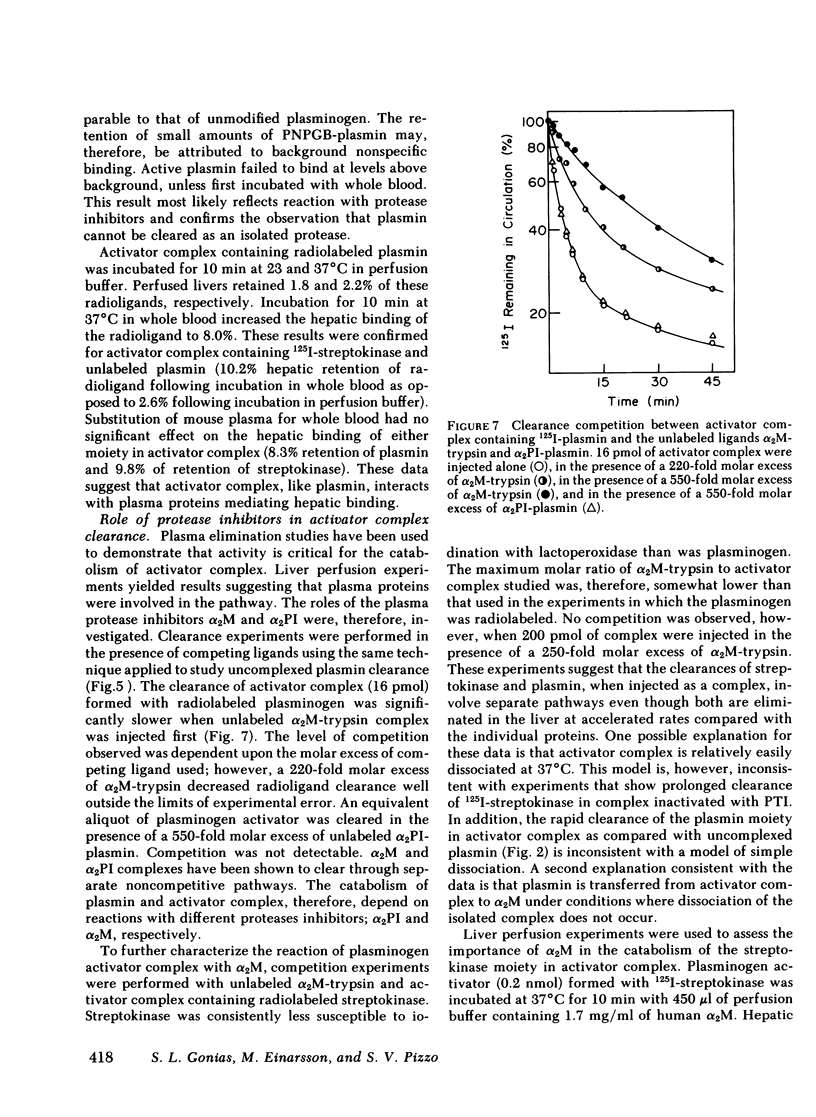
The catabolic pathways of streptokinase, plasmin, and activator complex prepared with human plasminogen were studied in mice. 125I-streptokinase clearance occurred in the liver and was 50% complete in 15 min. Incubation with mouse plasma had no effect on the streptokinase clearance rate. Complexes of plasmin and α2-plasmin inhibitor were eliminated from the plasma by a specific and saturable pathway. Competition experiments demonstrated that this pathway is responsible for the clearance of injected plasmin. Streptokinase-plasminogen activator complex formed with either 125I-plasminogen or 125I-streptokinase cleared in the liver at a significantly faster rate than either of the uncomplexed proteins (50% clearance in <3 min). Streptokinase incubated with human plasma also demonstrated this accelerated clearance. p-Nitrophenyl-p′-guanidinobenzoate-HCl or pancreatic trypsin inhibitor-treated complex cleared slowly compared with untreated complex independent of which protein was radiolabeled. Significant competition for clearance was demonstrated between α2-macroglobulin-trypsin and activator complex only when the plasmin(ogen) was the radiolabeled moiety. Large molar excesses of α2-plasmin inhibitor-plasmin failed to retard the clearance of activator complex. Hepatic binding of streptokinase-plasmin, in liver perfusion experiments, was dependent upon prior incubation with plasma (8-10% uptake compared to a background of ∼ 2.5%). Substitution of human α2-macroglobulin for plasma also resulted in binding when the incubation was performed for 10 min at 37°C (7.5%). Electrophoresis experiments confirmed the transfer of 0.8 mol plasmin/mol α2-macroglobulin when activator complex was incubated at 37°C with α2-macroglobulin for 40 min. Streptokinase transfer from activator complex to α2-macroglobulin was negligible. The in vivo clearance of activator complex is proposed to involve active attack of the complex on the α2-macroglobulin “bait region,” resulting in facilitated plasmin transfer. Dissociated streptokinase is rapidly bound and cleared by sites in the liver.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aoki N., Moroi M., Tachiya K. Effects of alpha2-plasmin inhibitor on fibrin clot lysis. Its comparison with alpha2-macroglobulin. Thromb Haemost. 1978 Feb 28;39(1):22–31. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BACK N., AMBRUS J. L., MINK I. B. Distribution and fate of I-131-labeled components of the fibrinolysin system. Circ Res. 1961 Nov;9:1208–1216. doi: 10.1161/01.res.9.6.1208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bajaj A. P., Castellino F. J. Activation of human plasminogen by equimolar levels of streptokinase. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jan 25;252(2):492–498. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett A. J., Brown M. A., Sayers C. A. The electrophoretically 'slow' and 'fast' forms of the alpha 2-macroglobulin molecule. Biochem J. 1979 Aug 1;181(2):401–418. doi: 10.1042/bj1810401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett A. J., Starkey P. M. The interaction of alpha 2-macroglobulin with proteinases. Characteristics and specificity of the reaction, and a hypothesis concerning its molecular mechanism. Biochem J. 1973 Aug;133(4):709–724. doi: 10.1042/bj1330709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brockway W. J., Castellino F. J. Measurement of the binding of antifibrinolytic amino acids to various plasminogens. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1972 Jul;151(1):194–199. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(72)90488-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cederholm-Williams S. A., De Cock F., Lijnen H. R., Collen D. Kinetics of the reactions between streptokinase, plasmin and alpha 2-antiplasmin. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Oct;100(1):125–132. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb02040.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chase T., Jr, Shaw E. p-Nitrophenyl-p'-guanidinobenzoate HCl: a new active site titrant for trypsin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Nov 30;29(4):508–514. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(67)90513-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coates G., DeNardo S. J., DeNardo G. L., Troy F. A. Pharmacokinetics of radioiodinated streptokinase. J Nucl Med. 1975 Feb;16(2):136–142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- David G. S., Reisfeld R. A. Protein iodination with solid state lactoperoxidase. Biochemistry. 1974 Feb 26;13(5):1014–1021. doi: 10.1021/bi00702a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Renzo E. C., Siiteri P. K., Hutchings B. L., Bell P. H. Preparation and certain properties of highly purified streptokinase. J Biol Chem. 1967 Feb 10;242(3):533–542. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deutsch D. G., Mertz E. T. Plasminogen: purification from human plasma by affinity chromatography. Science. 1970 Dec 4;170(3962):1095–1096. doi: 10.1126/science.170.3962.1095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Einarsson M., Skoog B., Forsberg B., Einarsson R. Characterization of highly purified native streptokinase and altered streptokinase after alkaline treatment. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 May 10;568(1):19–29. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(79)90269-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLETCHER A. P., ALKJAERSIG N., SMYRNIOTIS F. E., SHERRY S. The treatment of patients suffering from early myocardial infarction with massive and prolonged streptokinase therapy. Trans Assoc Am Physicians. 1958;71:287–296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs H. E., Shifman M. A., Pizzo S. V. In vivo catabolism of alpha 1-proteinase inhibitor-trypsin, antithrombin III-thrombin and alpha 2-macroglobulin-methylamine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 May 27;716(2):151–157. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(82)90263-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonias S. L., Pizzo S. V. Altered clearance of human alpha 2-macroglobulin complexes following reaction with cis-dichlorodiamineplatinum(II). Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Dec 4;678(2):268–274. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(81)90216-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez-Gronow M., Siefring G. E., Jr, Castellino F. J. Mechanism of activation of human plasminogen by the activator complex, streptokinase-plasmin. J Biol Chem. 1978 Feb 25;253(4):1090–1094. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall P. K., Roberts R. C. Physical and chemical properties of human plasma alpha2-macroglobulin. Biochem J. 1978 Jul 1;173(1):27–38. doi: 10.1042/bj1730027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harpel P. C. Alpha2-plasmin inhibitor and alpha2-macroglobulin-plasmin complexes in plasma. Quantitation by an enzyme-linked differential antibody immunosorbent assay. J Clin Invest. 1981 Jul;68(1):46–55. doi: 10.1172/JCI110253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harpel P. C., Hayes M. B., Hugli T. E. Heat-induced fragmentation of human alpha 2-macroglobulin. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 10;254(17):8669–8678. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harpel P. C. Plasmin inhibitor interactions. The effectiveness of alpha2-plasmin inhibitor in the presence of alpha2-macroglobulin. J Exp Med. 1977 Oct 1;146(4):1033–1040. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.4.1033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harpel P. C. Studies on human plasma alpha 2-macroglobulin-enzyme interactions. Evidence for proteolytic modification of the subunit chain structure. J Exp Med. 1973 Sep 1;138(3):508–521. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.3.508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- IIO M., WAGNER H. N., Jr, SCHEFFEL U., JABBOUR B. Studies of the reticuloendothelial system (RES). I. Measurement of the phagocytic capacity of the RES in man and dog. J Clin Invest. 1963 Mar;42:417–426. doi: 10.1172/JCI104729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imber M. J., Pizzo S. V. Clearance and binding of two electrophoretic "fast" forms of human alpha 2-macroglobulin. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 10;256(15):8134–8139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOHNSON A. J., McCARTY W. R. The lysis of artificially induced intravascular clots in man by intravenous infusions of streptokinase. J Clin Invest. 1959 Sep;38:1627–1643. doi: 10.1172/JCI103941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan J., Nielsen M. L. Analysis of macrophage surface receptors. I. Binding of alpha-macroglobulin . protease complexes to rabbit alveolar macrophages. J Biol Chem. 1979 Aug 10;254(15):7323–7328. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lollar P., Owen W. G. Clearance of thrombin from circulation in rabbits by high-affinity binding sites on endothelium. Possible role in the inactivation of thrombin by antithrombin III. J Clin Invest. 1980 Dec;66(6):1222–1230. doi: 10.1172/JCI109973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClintock D. K., Bell P. H. The mechanism of activation of human plasminogen by streptokinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 May 7;43(3):694–702. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90670-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moroi M., Aoki N. Isolation and characterization of alpha2-plasmin inhibitor from human plasma. A novel proteinase inhibitor which inhibits activator-induced clot lysis. J Biol Chem. 1976 Oct 10;251(19):5956–5965. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müllertz S., Clemmensen I. The primary inhibitor of plasmin in human plasma. Biochem J. 1976 Dec 1;159(3):545–553. doi: 10.1042/bj1590545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelles L. P., Hall P. K., Roberts R. C. Human alpha-2-macroglobulin. Studies on the electrophoretic heterogeneity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 May 29;623(1):46–56. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(80)90006-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohlsson K. Elimination of 125-I-trypsin alpha-macroglobulin complexes from blood by reticuloendothelial cells in dogs. Acta Physiol Scand. 1971 Feb;81(2):269–272. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1971.tb04900.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy K. N., Markus G. Mechanism of activation of human plasminogen by streptokinase. Presence of active center in streptokinase-plasminogen complex. J Biol Chem. 1972 Mar 25;247(6):1683–1691. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renston R. H., Jones A. L., Christiansen W. D., Hradek G. T., Underdown B. J. Evidence for a vesicular transport mechanism in hepatocytes for biliary secretion of immunoglobulin A. Science. 1980 Jun 13;208(4449):1276–1278. doi: 10.1126/science.7375938. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salvesen G. S., Barrett A. J. Covalent binding of proteinases in their reaction with alpha 2-macroglobulin. Biochem J. 1980 Jun 1;187(3):695–701. doi: 10.1042/bj1870695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shifman M. A., Pizzo S. V. The in vivo metabolism of antithrombin III and antithrombin III complexes. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 25;257(6):3243–3248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjöholm I. Studies on the conformational changes of plasminogen induced during activation to plasmin and by 6-aminohexanoic acid. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Nov 15;39(2):471–479. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb03146.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Som P., Rhodes B. A., Bell W. R. Radiolabeled streptokinase and urokinase and their comparative biodistribution. Thromb Res. 1975 Mar;6(3):247–253. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(75)90072-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sottrup-Jensen L., Petersen T. E., Magnusson S. Mechanism of proteinase complex formation with alpha 2-macroglobulin. Three modes of trypsin binding. FEBS Lett. 1981 Jun 1;128(1):127–132. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)81097-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summaria L., Arzadon L., Bernabe P., Robbins K. C. The interaction of streptokinase with human, cat, dog, and rabbit plasminogens. The fragmentation of streptokinase in the equimolar plasminogen-streptokinase complexes. J Biol Chem. 1974 Aug 10;249(15):4760–4769. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tillett W. S., Sherry S. THE EFFECT IN PATIENTS OF STREPTOCOCCAL FIBRINOLYSIN (STREPTOKINASE) AND STREPTOCOCCAL DESOXYRIBONUCLEASE ON FIBRINOUS, PURULENT, AND SANGUINOUS PLEURAL EXUDATIONS. J Clin Invest. 1949 Jan;28(1):173–190. doi: 10.1172/JCI102046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Violand B. N., Castellino F. J. Mechanism of the urokinase-catalyzed activation of human plasminogen. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jul 10;251(13):3906–3912. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiman B., Collen D. On the kinetics of the reaction between human antiplasmin and plasmin. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Mar 15;84(2):573–578. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12200.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiman B., Collen D. On the mechanism of the reaction between human alpha 2-antiplasmin and plasmin. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 25;254(18):9291–9297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiman B. On the reaction of plasmin or plasmin-streptokinase complex with aprotinin or alpha 2-antiplasmin. Thromb Res. 1980 Jan 1;17(1-2):143–152. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(80)90302-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wulf R. J., Mertz E. T. Studies on plasminogen. 8. Species specificity of streptokinase. Can J Biochem. 1969 Oct;47(10):927–931. doi: 10.1139/o69-145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyckoff M., Rodbard D., Chrambach A. Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis in sodium dodecyl sulfate-containing buffers using multiphasic buffer systems: properties of the stack, valid Rf- measurement, and optimized procedure. Anal Biochem. 1977 Apr;78(2):459–482. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90107-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]