Abstract
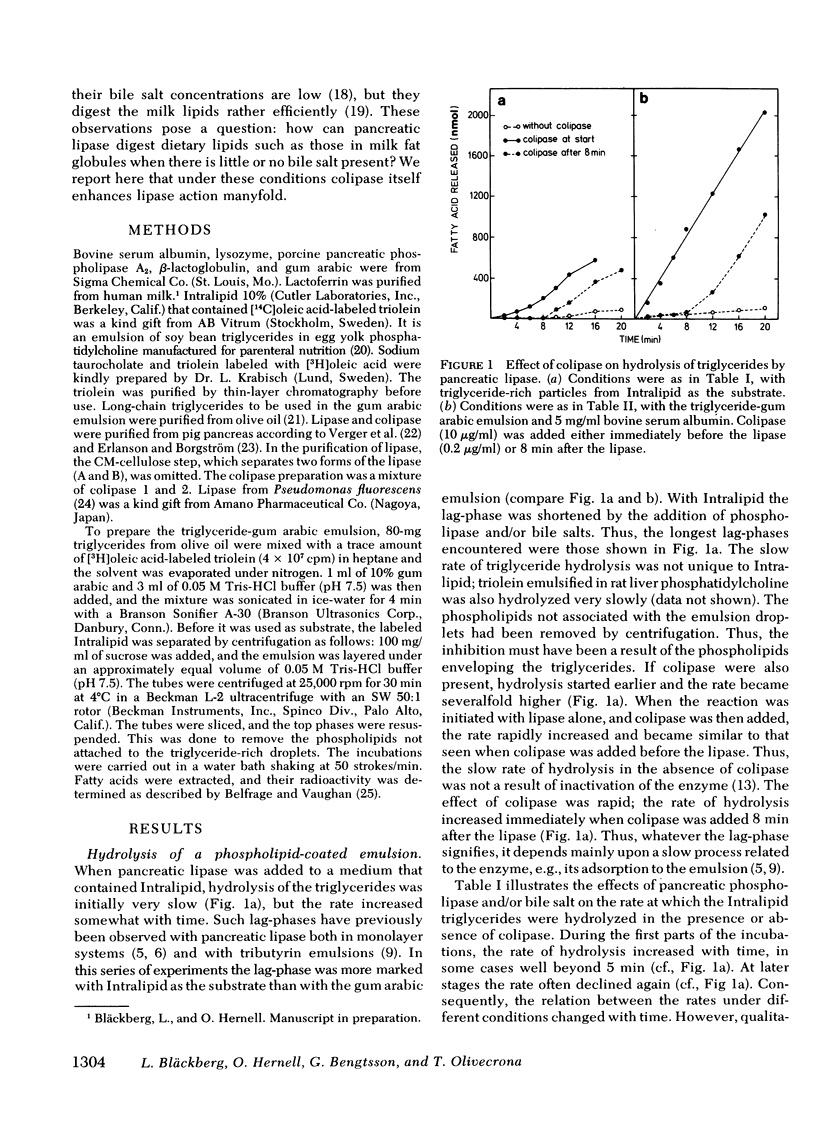
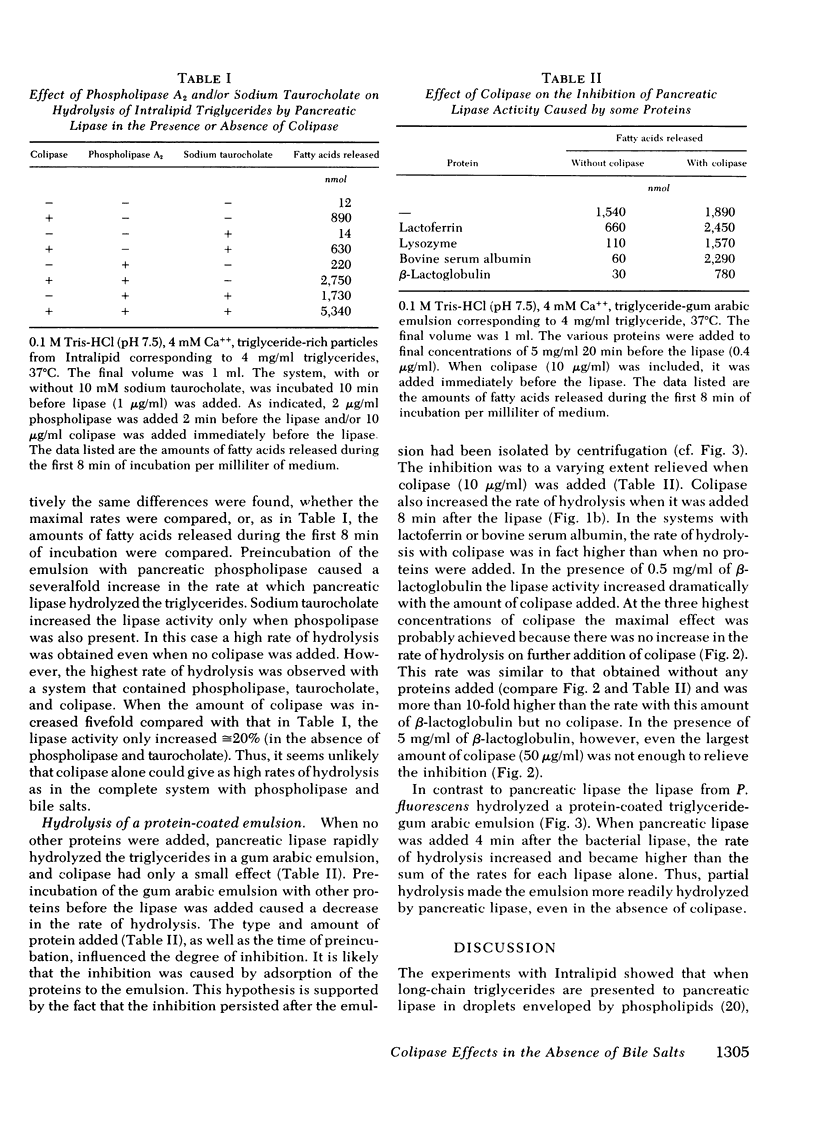
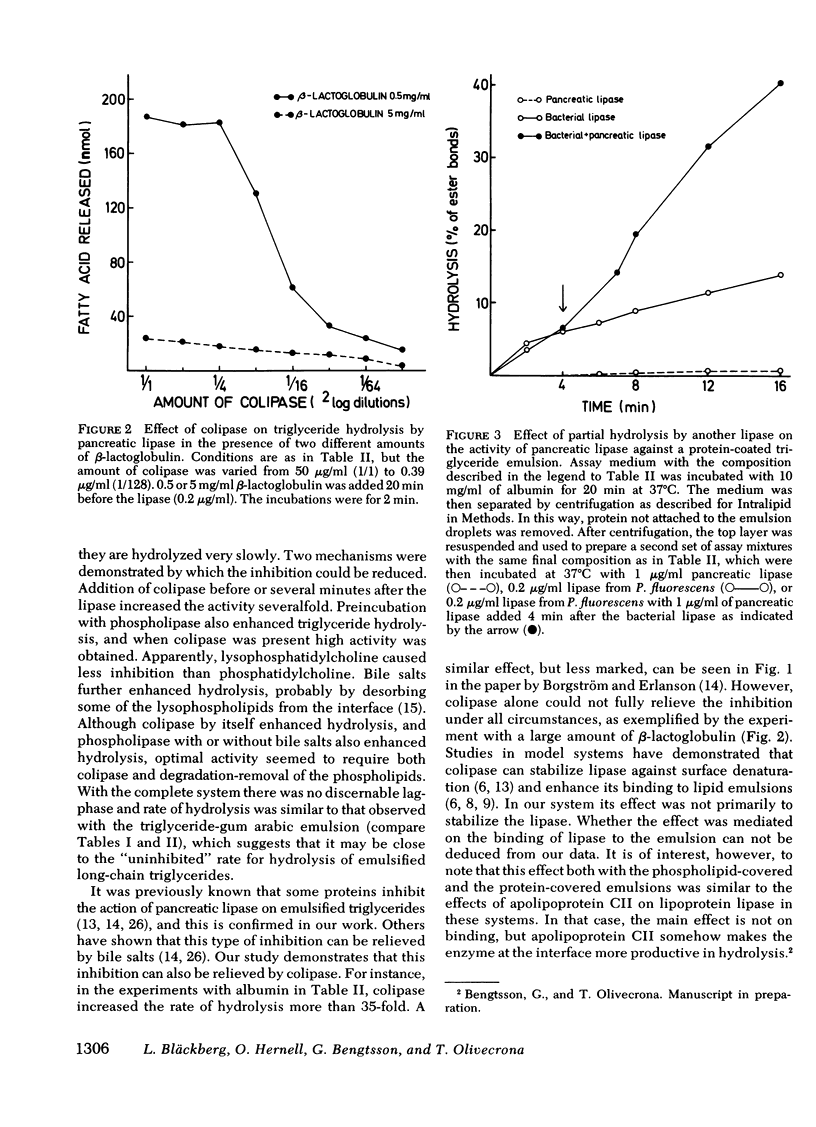
This study explores how dietary lipids are digested when intraduodenal bile salts are low or absent. Long-chain triglycerides emulsified with phosphatidylcholine were found to be hydrolyzed very slowly by pancreatic lipase alone, as if the surface layer of phospholipids enveloping the triglycerides impeded the action of the enzyme. Colipase enhanced triglyceride hydrolysis severalfold, both when added before or after the lipase. Hydrolysis became even more rapid when the emulsion was first incubated with pancreatic phospholipase. Hydrolysis of long-chain triglycerides was also severely impeded when other proteins were added to the system, probably because they adsorbed to the oil-water interface of the emulsion droplets. It was previously known that bile salts can relieve such inhibition, presumably by desorbing the adsorbed proteins. Colipase was found to enhance hydrolysis severalfold in a dose-dependent manner even in the absence of bile salts, i.e., it could partially or completely relieve the inhibition depending upon the amount and the type of inhibitory protein added to the system. Prior exposure of a protein-coated triglyceride emulsion to another lipase also enhanced the rate at which pancreatic lipase could then hydrolyze the lipids. Most dietary triglycerides are probably presented for intestinal digestion in emulsions covered by proteins and/or phospholipids. These emulsions would be hydrolyzed slowly by pancreatic lipase alone. However, through the action of the lipase in stomach contents and of pancreatic phospholipase and through the lipolysis-promoting effects of collipase, these triglycerices can be rather efficiently hydrolyzed, even in the absence of bile salts.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Belfrage P., Vaughan M. Simple liquid-liquid partition system for isolation of labeled oleic acid from mixtures with glycerides. J Lipid Res. 1969 May;10(3):341–344. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borgström B., Erlanson C. Pancreatic lipase and co-lipase. Interactions and effects of bile salts and other detergents. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Aug 1;37(1):60–68. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02957.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borgström B. The action of bile salts and other detergents on pancreatic lipase and the interaction with colipase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Sep 28;488(3):381–391. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(77)90197-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brockerhoff H. On the function of bile salts and proteins as cofactors of lipase. J Biol Chem. 1971 Sep 25;246(18):5828–5831. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brockman H. L., Kézdy F. J., Law J. H. Isobaric titration of readine monolayers: kinetics of hydrolysis of glycerides by pancreatic lipase B. J Lipid Res. 1975 Jan;16(1):67–74. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brogström B., Hildebrand H. Lipase and co-lipase activities of human small intestinal contents after a liquid test meal. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1975;10(6):585–591. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapus C., Sémériva M., Bovier-Lapierre C., Desnuelle P. Mechanism of pancreatic lipase action. 1. Interfacial activation of pancreatic lipase. Biochemistry. 1976 Nov 16;15(23):4980–4987. doi: 10.1021/bi00668a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen M., Morgan R. G., Hofmann A. F. Lipolytic activity of human gastric and duodenal juice against medium and long chain triglycerides. Gastroenterology. 1971 Jan;60(1):1–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards-Webb J. D., Thompson S. Y. Studies on lipid digestion in the preruminant calf. 2. A comparison of the products of lipolysis of milk fat by salivary and pancreatic lipases in vitro. Br J Nutr. 1977 May;37(3):431–440. doi: 10.1079/bjn19770046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekman R., Nilsson-Ehle P. Effects of apolipoproteins on lipoprotein lipase activity of human adipose tissue. Clin Chim Acta. 1975 Aug 18;63(1):29–35. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(75)90374-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erlanson C., Borgström B. Carboxyl ester hydrolase and lipase of human pancreatic juice and intestinal content. Behaviour in gel filtration. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1970;5(5):395–400. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erlanson C., Borgström B. Purification and further characterization of co-lipase from porcine pancreas. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jul 21;271(2):400–412. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(72)90215-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser G. P., Nicol A. D. Studies on human pancreatic lipase. Clin Chim Acta. 1966 May;13(5):552–562. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(66)90158-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fredrikzon B., Olivecrona T. Decrease of lipase and esterase activities in intestinal contents of newborn infants during test meals. Pediatr Res. 1978 May;12(5):631–634. doi: 10.1203/00006450-197805000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garner C. W., Smith L. C. Hydrolysis of monomolecular films of trioctanoin by porcine pancreatic lipase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 May 22;39(4):672–682. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90258-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamosh M., Klaeveman H. L., Wolf R. O., Scow R. O. Pharyngeal lipase and digestion of dietary triglyceride in man. J Clin Invest. 1975 May;55(5):908–913. doi: 10.1172/JCI108019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanna F. M., Navarrete D. A., Hsu F. A. Calcium-fatty acid absorption in term infants fed human milk and prepared formulas simulating human milk. Pediatrics. 1970 Feb;45(2):216–224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helenius A., Simons K. Solubilization of membranes by detergents. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Mar 25;415(1):29–79. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(75)90016-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lairon D., Nalbone G., Lafont H., Leonardi J., Domingo N., Hauton J. C., Verger R. Possible roles of bile lipids and colipase in lipase adsorption. Biochemistry. 1978 Nov 28;17(24):5263–5269. doi: 10.1021/bi00617a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Momsen W. E., Brockman H. L. Effects of colipase and taurodeoxycholate on the catalytic and physical properties of pancreatic lipase B at an oil water interface. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jan 25;251(2):378–383. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy G. M., Signer E. Bile acid metabolism in infants and children. Gut. 1974 Feb;15(2):151–163. doi: 10.1136/gut.15.2.151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olivecrona T., Billström A., Fredrikzon B., Johnson O., Samuelson G. Gastric lipolysis of human milk lipids in infants with pyloric stenosis. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1973 Sep;62(5):520–522. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1973.tb08149.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patton J. S., Albertsson P. A., Erlanson C., Borgström B. Binding of porcine pancreatic lipase and colipase in the absence of substrate studies by two-phase partition and affinity chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jun 25;253(12):4195–4202. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patton J. S., Donnér J., Borgström B. Lipase-colipase interactions during gel filtration. High and low affinity binding situations. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Apr 28;529(1):67–78. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(78)90104-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patton S., Keenan T. W. The milk fat globule membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Oct 31;415(3):273–309. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(75)90011-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter H. P., Saunders D. R., Tytgat G., Brunser O., Rubin C. E. Fat absorption in bile fistula man. A morphological and biochemical study. Gastroenterology. 1971 Jun;60(6):1008–1019. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rietsch J., Pattus F., Desnuelle P., Verger R. Further studies of mode of action of lipolytic enzymes. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jun 25;252(12):4313–4318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Semeriva M., Dufour C. Further studies on the exocellular lipase of Rhizopus arrhizus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Mar 23;260(3):393–400. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(72)90054-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugiura M., Oikawa T., Hirano K., Inukai T. Purification, crystallization and properties of triacylglycerol lipase from Pseudomonas fluorescens. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Sep 28;488(3):353–358. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(77)90194-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandermeers A., Vandermeers-Piret M. C., Rathé J., Christophe J. Effect of colipase on adsorption and activity of rat pancreatic lipase on emulsified tributyrin in the presence of bile salt. FEBS Lett. 1975 Jan 1;49(3):334–337. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80779-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandermeers A., Vandermeers-Piret M. C., Rathé J., Christophe J. On human pancreatic triacylglycerol lipase: isolation and some properties. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Nov 25;370(1):257–268. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(74)90050-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verger R. Interfacial enzyme kinetics of lipolysis. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1976;5:77–117. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.05.060176.000453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verger R., Rietsch J., Desnuelle P. Effects of colipase on hydrolysis of monomolecular films by lipase. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jun 25;252(12):4319–4325. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verger R., de Haas G. H., Sarda L., Desnuelle Purification from porcine pancreas of two molecular species with lipase activity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969;188(2):272–282. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(69)90075-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


