Abstract
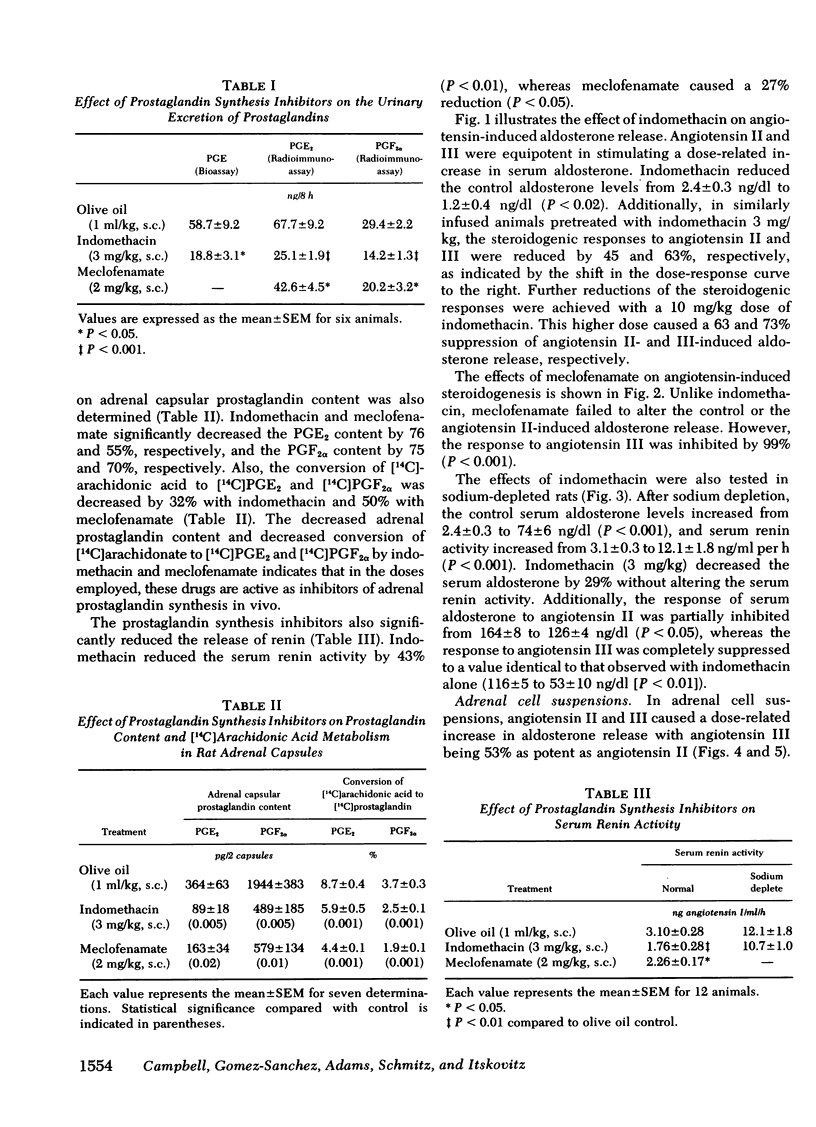
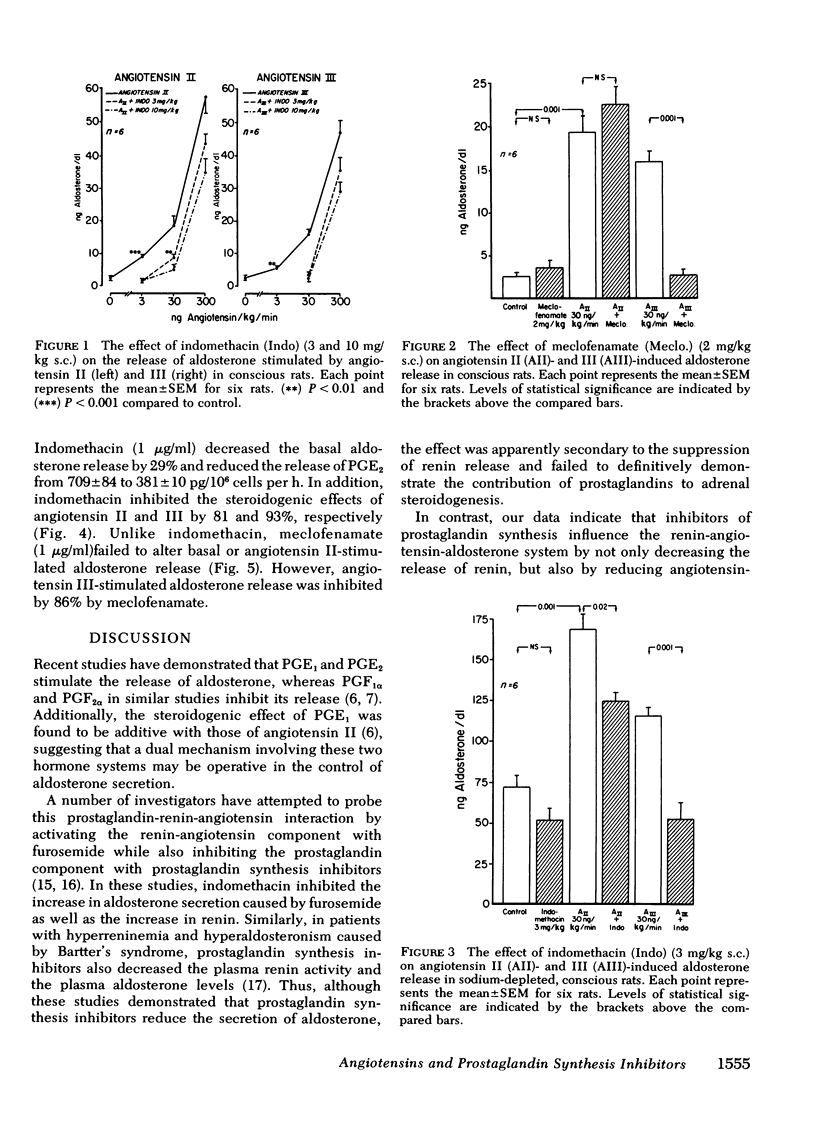
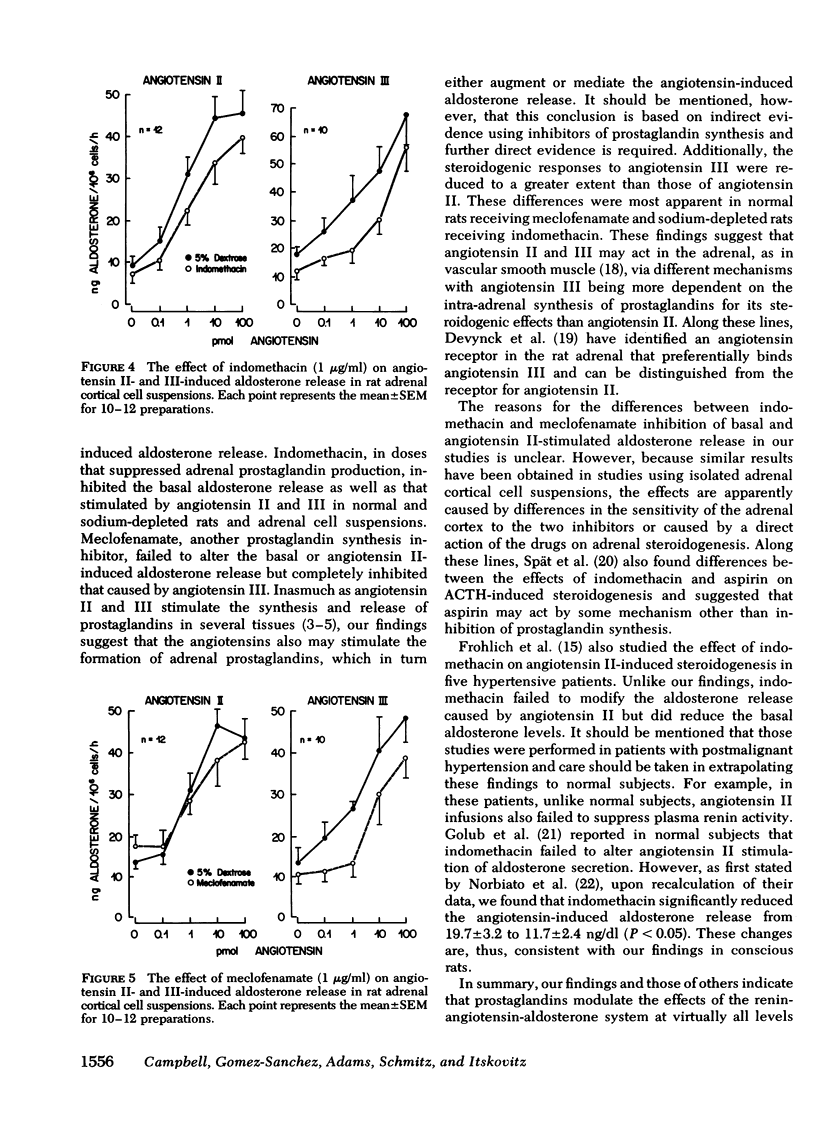
The effect of two prostaglandin synthesis inhibitors, indomethacin and meclofenamate, on angiotensin II (AII)- and III (AIII)-induced aldosterone release was studied in normal and sodium-depleted conscious rats and in adrenal capsular cell suspensions obtained from normal rats. In normal rats, in vivo AII and AIII were equipotent in causing dose-related increases in serum aldosterone concentrations. Indomethacin decreased the basal serum aldosterone levels by 50% and serum renin levels by 43%. In addition, the steroidogenic effects of AII and AIII were reduced by 45 and 63% with 3 mg/kg of indomethacin and 63 and 73% with 10 mg/kg, respectively. In contrast, meclofenamate failed to alter basal serum levels of aldosterone or AII-stimulated aldosterone release but inhibited serum renin levels by 27% and the aldosterone-stimulating effect of AIII by 99%. Indomethacin (3 mg/kg) and meclofenamate (2 mg/kg) inhibited urinary prostaglandin (PG)E2 and PGF2α excretion by 63 and 52% and 37 and 31%, respectively. Both inhibitors significantly decreased the adrenal capsular PGE2 and PGF2α content and the conversion of [14C]arachidonate to [14C]PGE2 and [14C]PGF2α. In sodium-depleted rats, indomethacin produced similar effects reducing the control serum aldosterone levels by 29%, AII-stimulated aldosterone by 47%, and completely suppressing the aldosterone response to AIII without altering serum renin activity. In adrenal cell suspensions, similar results were observed with indomethacin inhibiting basal and AII- and AIII-stimulated aldosterone release by 29, 81, and 93%, respectively. Meclofenamate failed to alter basal and AII-stimulated aldosterone release but inhibited that stimulated by AIII by 86%. The present findings suggest that prostaglandins modulate the effects of the renin-angiotensin system by stimulating the release of renin from the kidney and augmenting the steroidogenic effects of AII and AIII in the adrenal cortex.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ackerly J. A., Moore A. F., Peach M. J. Demonstration of different contractile mechanisms for angiotensin II and des-Asp1-angiotensin II in rabbit aortic strips. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5725–5728. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aiken J. W., Vane J. R. Intrarenal prostaglandin release attenuates the renal vasoconstrictor activity of angiotensin. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1973 Mar;184(3):678–687. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumberg A. L., Nishikawa K., Denny S. E., Marshall G. R., Needleman P. Angiotensin (A I, A II, A III) receptor characterization. Correlation of prostaglandin release with peptide degradation. Circ Res. 1977 Aug;41(2):154–158. doi: 10.1161/01.res.41.2.154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumberg A., Denny S., Nishikawa K., Pure E., Marshall G. R., Needleman P. Angiotensin III-induced prostaglandin (PG) release. Prostaglandins. 1976 Jan;11(1):195–197. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(76)90184-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell W. B., Graham R. M., Jackson E. K. Role of renal prostaglandins in sympathetically mediated renin relase in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1979 Aug;64(2):448–456. doi: 10.1172/JCI109482. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell W. B., Schmitz J. M., Itskovitz H. D. (Des-Asp1) angiotensin I: a study of its pressor and steroidogenic activities in conscious rats. Endocrinology. 1977 Jan;100(1):46–51. doi: 10.1210/endo-100-1-46. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell W. B., Schmitz J. M., Itskovitz H. D. Effect of sodium depletion on the steroidogenic and pressor actions of angiotensin in the rat. Clin Sci (Lond) 1979 Apr;56(4):325–333. doi: 10.1042/cs0560325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devynck M. A., Pernollet M. G., Matthews P. G., Khosla M. C., Bumpus F. M., Meyer P. Specific receptors for des-Asp1-angiotensin II (("angiotensin III") in rat adrenals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):4029–4032. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.4029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dray F., Charbonnel B., Maclouf J. Radioimmunoassay of prostaglandins Falpha, E1 and E2 in human plasma. Eur J Clin Invest. 1975 Jul 29;5(4):311–318. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1975.tb00459.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frölich J. C., Hollifield J. W., Dormois J. C., Frölich B. L., Seyberth H., Michelakis A. M., Oates J. A. Suppression of plasma renin activity by indomethacin in man. Circ Res. 1976 Sep;39(3):447–452. doi: 10.1161/01.res.39.3.447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill J. R., Jr, Frölich J. C., Bowden R. E., Taylor A. A., Keiser H. R., Seyberth H. W., Oates J. A., Bartter F. C. Bartter's syndrome: a disorder characterized by high urinary prostaglandins and a dependence of hyperreninemia on prostaglandin synthesis. Am J Med. 1976 Jul;61(1):43–51. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(76)90029-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golub M. S., Speckart P. F., Zia P. K., Horton R. The effect of prostaglandin A1 on renin and aldosterone in man. Circ Res. 1976 Oct;39(4):574–579. doi: 10.1161/01.res.39.4.574. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomez-Sanchez C., Kem D. C., Kaplan N. M. A radioimmunoassay for plasma aldosterone by immunologic purification. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1973 Apr;36(4):795–798. doi: 10.1210/jcem-36-4-795. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honn K. V., Chavin W. Role of prostaglandins in aldosterone production by the human adrenal. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Oct 18;72(4):1319–1326. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(76)80159-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGiff J. C., Crowshaw K., Terragno N. A., Lonigro A. J. Release of a prostaglandin-like substance into renal venous blood in response to angiotensin II. Circ Res. 1970 Jul;27(1 Suppl 1):121–130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norbiato G., Bevilacqua M., Raggi U., Micossi P., Moroni C., Fasoli A. Effect of prostaglandin synthetase inhibitors on renin and aldosterone in man on a normal or low sodium diet. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1978 Mar;87(3):577–588. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0870577. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patak R. V., Mookerjee B. K., Bentzel C. J., Hysert P. E., Babej M., Lee J. B. Antagonism of the effects of furosemide by indomethacin in normal and hypertensive man. Prostaglandins. 1975 Oct;10(4):649–659. doi: 10.1016/s0090-6980(75)80012-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulsen K., Jorgensen J. An easy radioimmunological microassay of renin activity, concentration and substrate in human and animal plasma and tissues based on angiotensin I trapping by antibody. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1974 Nov;39(5):816–825. doi: 10.1210/jcem-39-5-816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarstedt C. A., Vaughan E. D., Jr, Peach M. J. Selective inhibition by des-1-Asp-8-lle-angiotensin ii of the steroidogenic response to restricted sodium intake in the rat. Circ Res. 1975 Sep;37(3):350–358. doi: 10.1161/01.res.37.3.350. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saruta T., Kaplan N. M. Adrenocortical steroidogenesis: the effects of prostaglandins. J Clin Invest. 1972 Sep;51(9):2246–2251. doi: 10.1172/JCI107033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spät A., Siklós P., Antoni F. A., Nagy K., Szirányi K. Effect of prostaglandin synthetase inhibitors of basal and ACTH-stimulated steroid synthesis by separated adrenocortical zones. J Steroid Biochem. 1977 Apr;8(4):293–298. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(77)90022-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vane J. R. Inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis as a mechanism of action for aspirin-like drugs. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jun 23;231(25):232–235. doi: 10.1038/newbio231232a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yorio T., Bentley P. J. Phospholipase A and the mechanism of action of aldosterone. Nature. 1978 Jan 5;271(5640):79–81. doi: 10.1038/271079a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


