Abstract
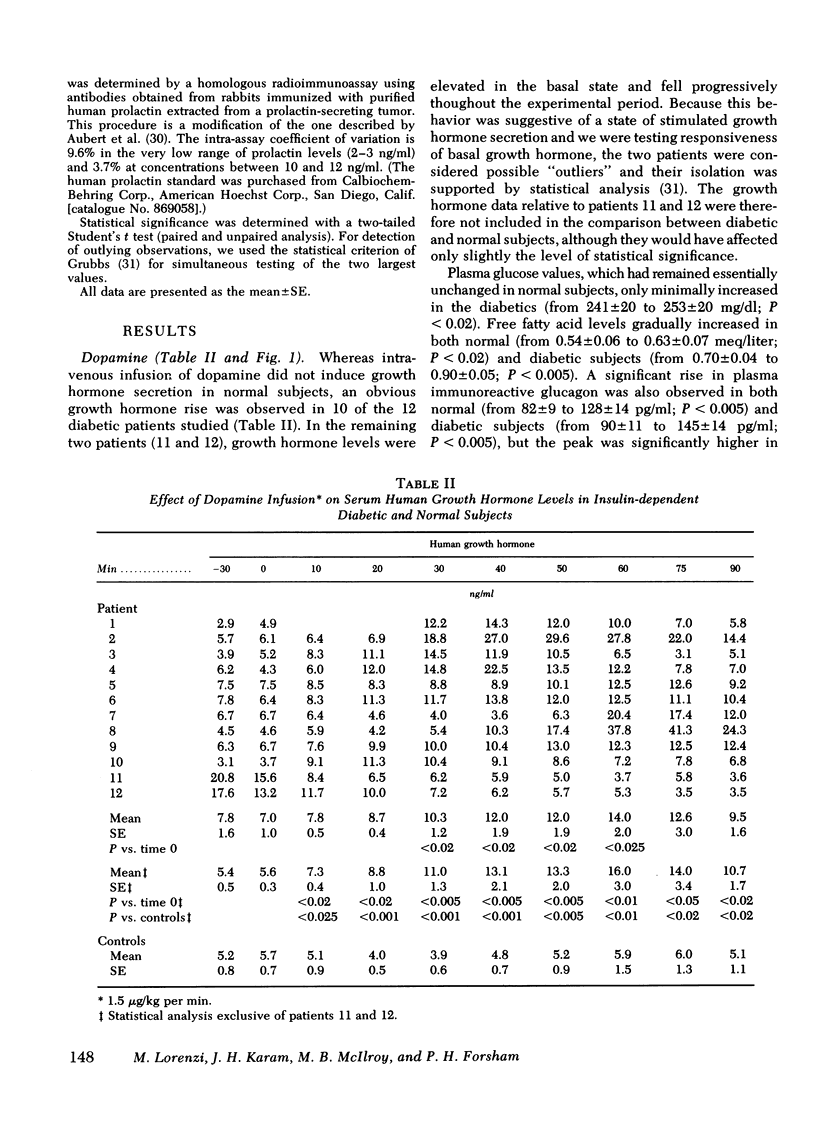
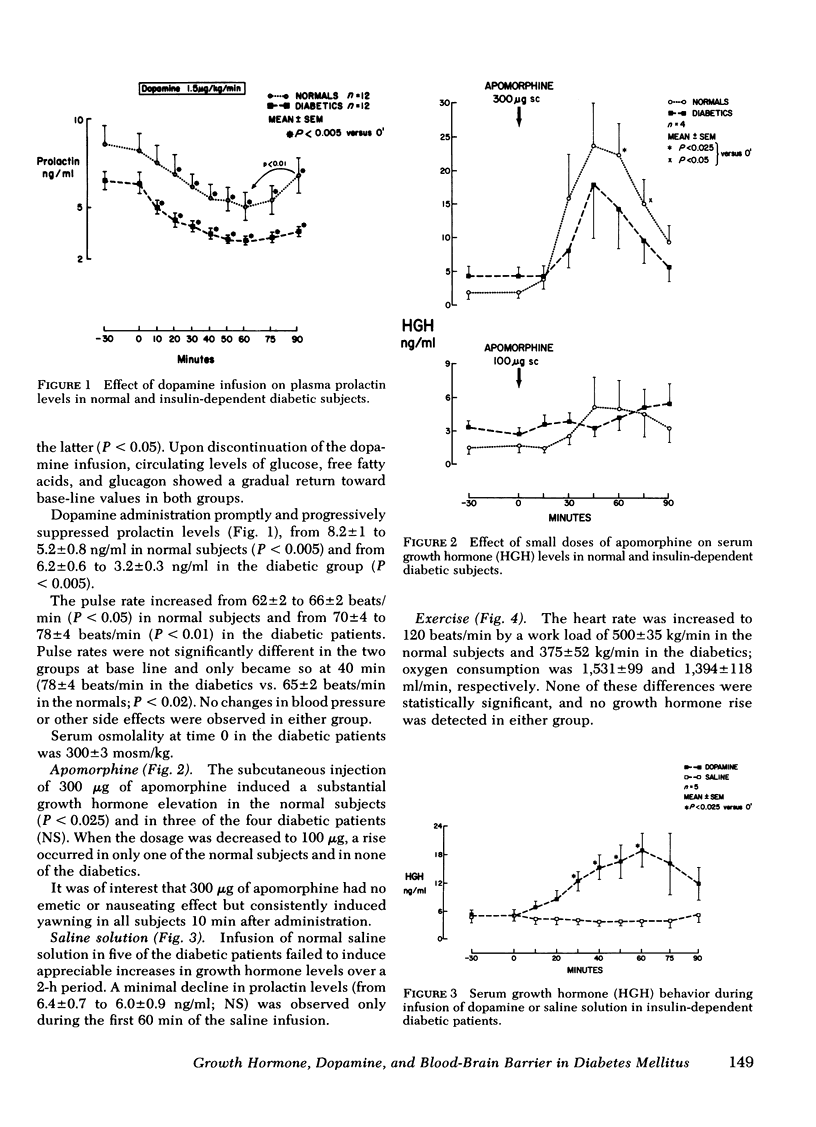
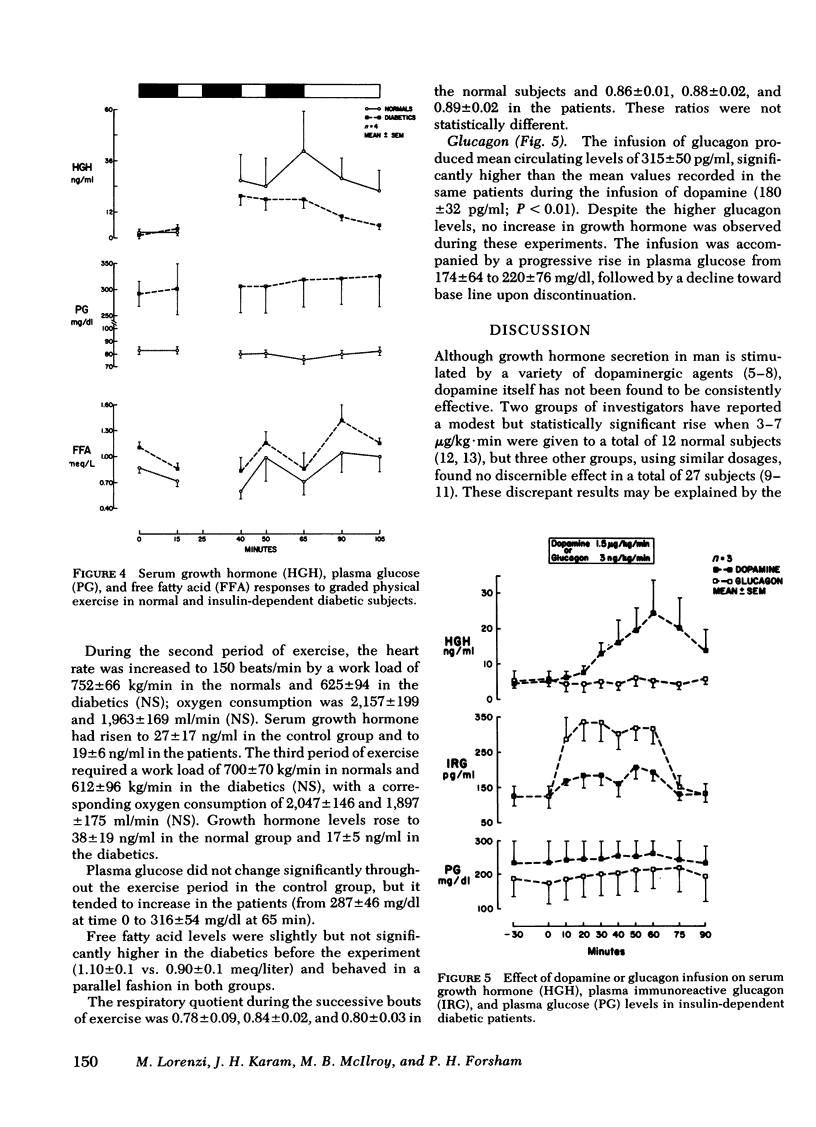
To test the hypothesis that cerebral capillaries, which share the embroyologic and morphologic characteristics of retinal capillaries, might have the same abnormal permeability in diabetic patients, we investigated the growth hormone response to a small amount of peripherally administered dopamine (1.5 microgram/kg.min). Consistent with the known exclusion of systemic dopamine from brain parenchyma, no rise was observed in 12 normal subjects. In 10 of 12 juvenile-onset, insulin-dependent diabetic patients, however, a substantial growth hormone rise occurred (peak value, 19.2 +/- 3.0 ng/ml [mean +/- SE]). Comparision of metabolic and cardiovascular responses to the infusion in both groups did not suggest that higher circulating levels of dopamine had been achieved in the diabetics. Other growth hormone stimuli (apomorphine in decreasing amounts, glucagon, and graded physical exercise) failed to indicate that hypothalamic hypersensitivity could account for the consistent rise. We postulate that an abnormal permeability of the blood-brain barrier in the diabetic patients permitted exposure of the hypothalamic structures regulating growth hormone secretion to a greater fraction of the infused dopamine.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aubert M. L., Grumbach M. M., Kaplan S. L. Heterologous radioimmunoassay for plasma human prolactin (hPRL); values in normal subjects, puberty, pregnancy and in pituitary disorders. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1974 Nov;77(3):460–476. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0770460. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernardis L. L., Frohman L. A. Effect of lesion size in the ventromedial hypothalamus on growth hormone and insulin levels in weanling rats. Neuroendocrinology. 1970;6(5):319–328. doi: 10.1159/000121937. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertler A., Falck B., Owman C., Rosengrenn E. The localization of monoaminergic blood-brain barrier mechanisms. Pharmacol Rev. 1966 Mar;18(1):369–385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burrow G. N., May P. B., Spaulding S. W., Donabedian R. K. TRH and dopamine interactions affecting pituitary hormones secretion. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1977 Jul;45(1):65–72. doi: 10.1210/jcem-45-1-65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cain J. P., Williams G. H., Dluhy R. G. Glucagon stimulation of human growth hormone. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1970 Aug;31(2):222–224. doi: 10.1210/jcem-31-2-222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calne D. B., Teychenne P. F., Leigh P. N., Bamji A. N., Greenacre J. K. Treatment of parkinsonism with bromocriptine. Lancet. 1974 Dec 7;2(7893):1355–1356. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)92219-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camanni F., Massara F., Belforte L., Molinatti G. M. Changes in plasma growth hormone levels in normal and acromegalic subjects following administration of 2-bromo-alpha-ergocryptine. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1975 Mar;40(3):363–366. doi: 10.1210/jcem-40-3-363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camanni F., Massara F., Belforte L., Rosatello A., Molinatti G. M. Effect of dopamine on plasma growth hormone and prolactin levels in normal and acromegalic subjects. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1977 Mar;44(3):465–473. doi: 10.1210/jcem-44-3-465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavagnini F., Peracchi M., Scotti G., Raggi U., Pontiroli A. E., Bana R. Effect of L-dopa administration on growth hormone secretion in normal subjects and Parkinsonian patients. J Endocrinol. 1972 Sep;54(3):425–433. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0540425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christlieb A. R., Assal J. P., Katsilambros N., Williams G. H., Kozak G. P., Suzuki T. Plasma renin activity and blood volume in uncontrolled diabetes. Ketoacidosis, a state of secondary aldosteronism. Diabetes. 1975 Feb;24(2):190–193. doi: 10.2337/diab.24.2.190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cryer P. E., Silverberg A. B., Santiago J. V., Shah S. D. Plasma catecholamines in diabetes. The syndromes of hypoadrenergic and hyperadrenergic postural hypotension. Am J Med. 1978 Mar;64(3):407–416. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(78)90220-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunha-Vaz J. G., Fonseca J. R., Abreu J. F., Ruas M. A. Detection of early retinal changes in diabetes by vitreous fluorophotometry. Diabetes. 1979 Jan;28(1):16–19. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunha-Vaz J., Faria de Abreu J. R., Campos A. J. Early breakdown of the blood-retinal barrier in diabetes. Br J Ophthalmol. 1975 Nov;59(11):649–656. doi: 10.1136/bjo.59.11.649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De la Torre J. C. The blood-brain barrier for L-dopa in the hypothalamus. J Neurol Sci. 1971 Jan;12(1):77–93. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(71)90253-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorchy H., Toussaint D., Devroede M., Ernould C., Loeb H. Diagnostic de la rétinopathie diabétique infantile par angiographie fluorescéinique. Description des lésions initiales. Nouv Presse Med. 1977 Feb 5;6(5):345–347. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drash A., Field J. B., Garces L. Y., Kenny F. M., Mintz D., Vazquez A. M. Endogenous insulin and growth hormone response in children with newly diagnosed diabetes mellitus. Pediatr Res. 1968 Mar;2(2):94–102. doi: 10.1203/00006450-196803000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Düby S. E., Cotzias G. C., Papavasiliou P. S., Lawrence W. H. Injected apomorphine and orally administered levodopa in Parkinsonism. Arch Neurol. 1972 Dec;27(6):474–480. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1972.00490180010004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Earll J. M., Sparks L. L., Forsham P. H. Glucose suppression of serum growth hormone in the diagnosis of acromegaly. JAMA. 1967 Aug 21;201(8):628–630. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLODMARK S., STEINWALL O. A method for study of the interrelation between EEG and blood-brain barrier phenomena. Acta Physiol Scand. 1962 Oct;56:112–119. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1962.tb02488.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerich J. E., Karam J. H., Forsham P. H. Stimulation of glucagon secretion by epinephrine in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1973 Sep;37(3):479–481. doi: 10.1210/jcem-37-3-479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg L. I. The dopamine vascular receptor. Biochem Pharmacol. 1975 Mar 15;24(6):651–653. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(75)90239-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen A. P. Abnormal serum growth hormone response to exercise in juvenile diabetics. J Clin Invest. 1970 Aug;49(8):1467–1478. doi: 10.1172/JCI106364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardebo J. E., Edvinsson L., MacKenzie E. T., Owman C. Regional brain uptake of norepinephrine following mechanical or osmotic opening of the blood-brain barrier. Adv Neurol. 1978;20:303–313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansen K., Hansen A. P. Diurnal serum growth hormone levels in poorly and well-controlled juvenile diabetics. Diabetes. 1971 Apr;20(4):239–245. doi: 10.2337/diab.20.4.239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurell S., Tibbling G. Colorimetric micro-determination of free fatty acids in plasma. Clin Chim Acta. 1967 Apr;16(1):57–62. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(67)90269-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leblanc H., Lachelin G. C., Abu-Fadil S., Yen S. S. Effects of dopamine infusion on pituitary hormone secretion in humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1976 Sep;43(3):668–674. doi: 10.1210/jcem-43-3-668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leebaw W. F., Lee L. A., Woolf P. D. Dopamine affects basal and augmented pituitary hormone secretion. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1978 Sep;47(3):480–487. doi: 10.1210/jcem-47-3-480. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorenzi M., Karam J. H., Tsalikian E., Bohannon N. V., Gerich J. E., Forsham P. H. Dopamine during alpha- or beta-adrenergic blockade in man. Hormonal, metabolic, and cardiovascular effects. J Clin Invest. 1979 Feb;63(2):310–317. doi: 10.1172/JCI109304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorenzi M., Tsalikian E., Bohannon N. V., Gerich J. E., Karam J. H., Forsham P. H. Differential effects of L-dopa and apomorphine on glucagon secretion in man: evidence against central dopaminergic stimulation of glucagon. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1977 Dec;45(6):1154–1158. doi: 10.1210/jcem-45-6-1154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malone J. I., Van Cader T. C., Edwards W. C. Diabetic vascular changes in children. Diabetes. 1977 Jul;26(7):673–679. doi: 10.2337/diab.26.7.673. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell M. L., Byrne M. J., Silver J. Growth-hormone release by glucagon. Lancet. 1969 Feb 8;1(7589):289–290. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)91041-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldendorf W. H. Brain uptake of radiolabeled amino acids, amines, and hexoses after arterial injection. Am J Physiol. 1971 Dec;221(6):1629–1639. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.221.6.1629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powis G. The binding of catecholamines to human serum proteins. Biochem Pharmacol. 1975 Mar 15;24(6):707–712. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(75)90247-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson G. L., Shelton R. L., Athar S. The osmoregulation of vasopressin. Kidney Int. 1976 Jul;10(1):25–37. doi: 10.1038/ki.1976.76. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherwin R. S., Fisher M., Hendler R., Felig P. Hyperglucagonemia and blood glucose regulation in normal, obese and diabetic subjects. N Engl J Med. 1976 Feb 26;294(9):455–461. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197602262940901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unger R. H., Aguilar-Parada E., Müller W. A., Eisentraut A. M. Studies of pancreatic alpha cell function in normal and diabetic subjects. J Clin Invest. 1970 Apr;49(4):837–848. doi: 10.1172/JCI106297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verde G., Oppizzi G., Colussi G., Cremascoli G., Botalla L., Müller E. E., Silvestrini F., Chiodini P. G., Liuzzi A. Effect of dopamine infusion on plasma levels of growth hormone in normal subjects and in agromegalic patients. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 1976 Jul;5(4):419–423. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.1976.tb01971.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallow I. H., Engerman R. L. Permeability and patency of retinal blood vessels in experimental diabetes. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1977 May;16(5):447–461. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waltman S. R., Oestrich C., Krupin T., Hanish S., Ratzan S., Santiago J., Kilo C. Quantitative vitreous fluorophotometry. A sensitive technique for measuring early breakdown of the blood-retinal barrier in young diabetic patients. Diabetes. 1978 Feb;27(2):85–87. doi: 10.2337/diab.27.2.85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner R. I., Ganong W. F. Role of brain monoamines and histamine in regulation of anterior pituitary secretion. Physiol Rev. 1978 Oct;58(4):905–976. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1978.58.4.905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise J. K., Hendler R., Felig P. Evaluation of alpha-cell function by infusion of alanine in normal, diabetic and obese subjects. N Engl J Med. 1973 Mar 8;288(10):487–490. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197303082881003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


