Abstract
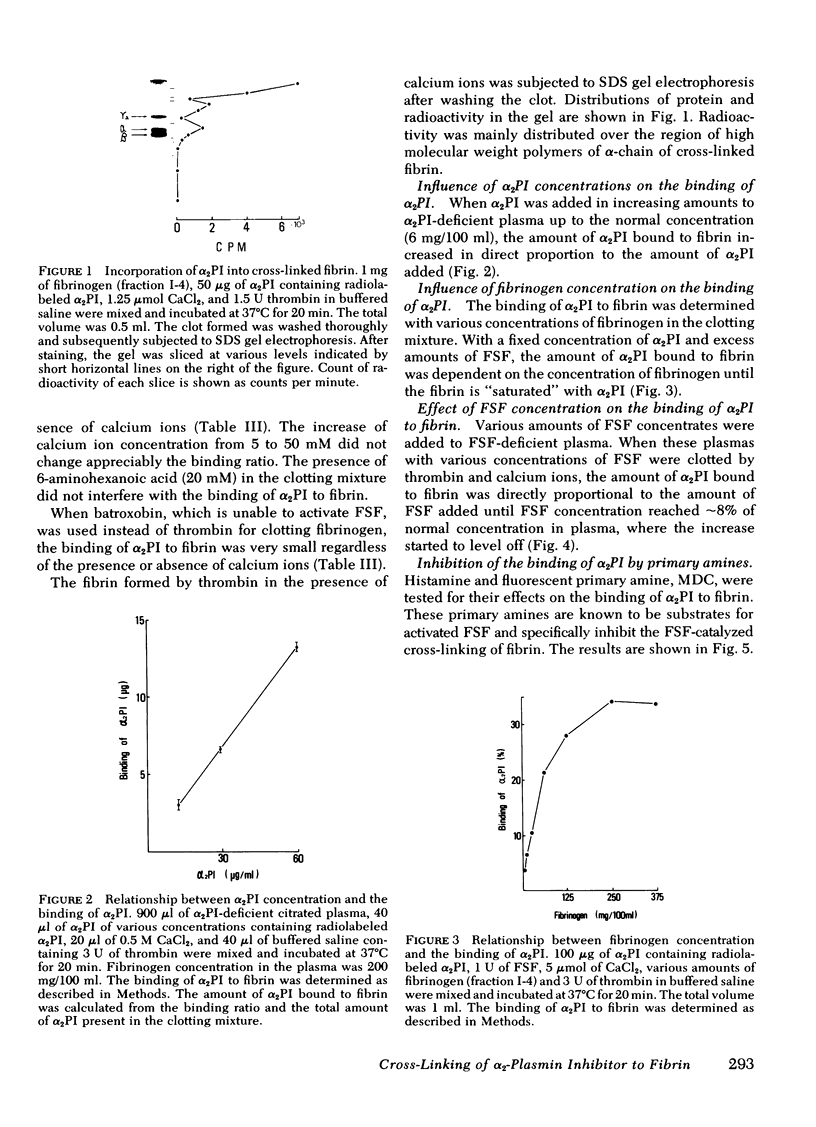
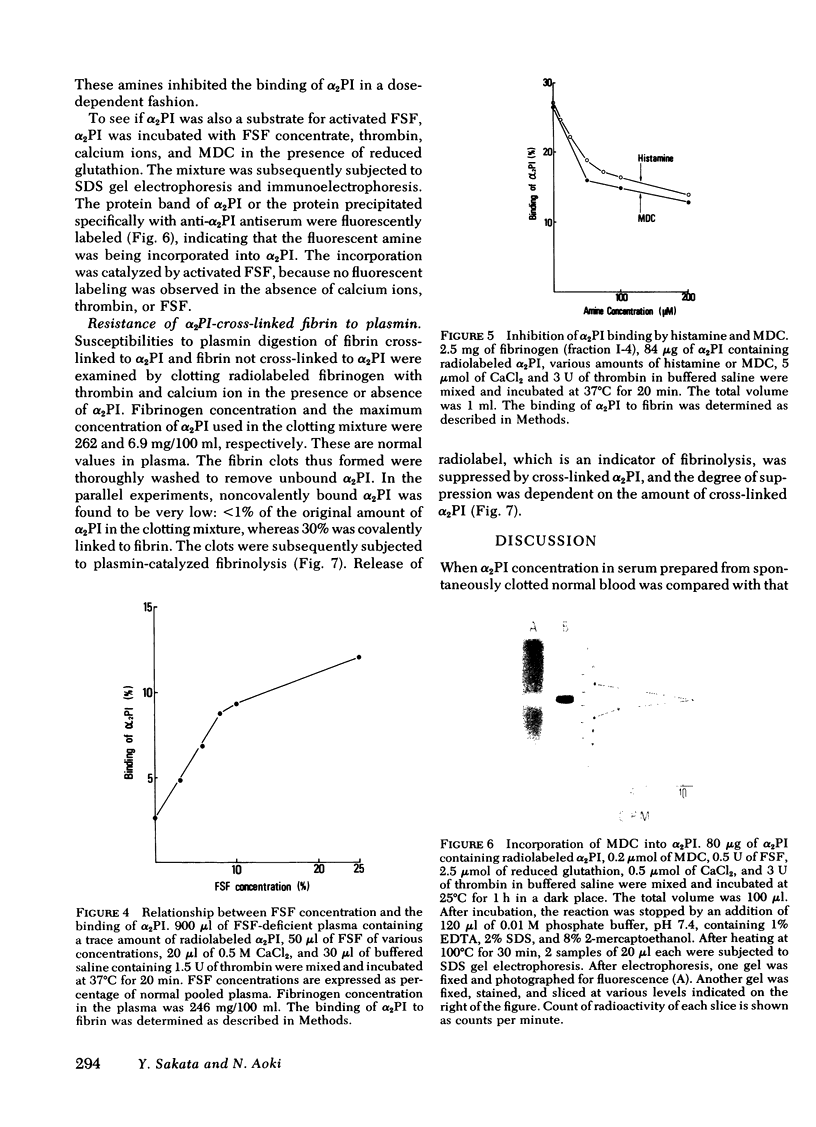
The concentration of alpha 2-plasmin inhibitor in blood plasma is higher than that in serum obtained from the blood clotted in the presence of calcium ions, but is the same as that in serum obtained in the absence of calcium ions. Radiolabeled alpha2-plasmin inhibitor was covalently bound to fibrin only when calcium ions were present at the time of clotting of plasma or fibrinogen. Whereas, when batroxobin, a snake venom enzyme that lacks the ability to activate fibrin-stabilizing factor, was used for clotting fibrinogen, the binding was not observed. When fibrin-stablizing, factor-deficient plasma was clotted, the specific binding of alpha 2-plasmin inhibitor to fibrin did not occur even in the presence of calcium ions and the concentration of alpha 2-plasmin inhibitor in serum was the same as that in plasma. Monodansyl cadaverine, a fluorescent substrate of the fibrin-stablizing factor, was incorporated into alpha 2-plasmin inhibitor by activated fibrin-stablizing factor. All these findings indicate that alpha 2-plasmin inhibitor is cross-linked to fibrin by activated fibrin-stabilizing factor when blood is clotted. Analysis of alpha 2-plasmin inhibitor-incorporated fibrin by sodium dodecyl sulfate gel electrophoresis showed that the inhibitor was mainly cross-linked to polymerized alpha-chains of cross-linked fibrin. Cross-linking of alpha 2-plasmin inhibitor to fibrin renders fibrin clot less susceptible to fibrinolysis by plasmin.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aoki N., Moroi M., Matsuda M., Tachiya K. The behavior of alpha2-plasmin inhibitor in fibrinolytic states. J Clin Invest. 1977 Aug;60(2):361–369. doi: 10.1172/JCI108784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aoki N., Moroi M., Tachiya K. Effects of alpha2-plasmin inhibitor on fibrin clot lysis. Its comparison with alpha2-macroglobulin. Thromb Haemost. 1978 Feb 28;39(1):22–31. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aoki N. Natural inhibitors of fibrinolysis. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 1979 Jan-Feb;21(4):267–286. doi: 10.1016/0033-0620(79)90014-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aoki N., Saito H., Kamiya T., Koie K., Sakata Y., Kobakura M. Congenital deficiency of alpha 2-plasmin inhibitor associated with severe hemorrhagic tendency. J Clin Invest. 1979 May;63(5):877–884. doi: 10.1172/JCI109387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aoki N., Yamanaka T. The alpha2-plasmin inhibitor levels in liver diseases. Clin Chim Acta. 1978 Mar 1;84(1-2):99–105. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(78)90481-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohn H., Haupt H. Eine quantitative Bestimmung von Faktor 13 mit Anti-Faktor-13-Serum. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1968 Jul 31;19(3):309–315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brockway W. J., Castellino F. J. Measurement of the binding of antifibrinolytic amino acids to various plasminogens. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1972 Jul;151(1):194–199. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(72)90488-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis C. G., Brown K. L., Credo R. B., Domanik R. A., Gray A., Stenberg P., Lorand L. Calcium-dependent unmasking of active center cysteine during activation of fibrin stabilizing factor. Biochemistry. 1974 Aug 27;13(18):3774–3780. doi: 10.1021/bi00715a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- David G. S. Solid state lactoperoxidase: a highly stable enzyme for simple, gentle iodination of proteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Jul 25;48(2):464–471. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(72)80074-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaffney P. J., Whitaker A. N. Fibrin crosslinks and lysis rates. Thromb Res. 1979 Jan;14(1):85–94. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(79)90027-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haverkate F. Proceedings: Lysis of crosslinked and non-crosslinked purified fibrin. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1975 Nov 15;34(2):584–585. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedner U. Studies on an inhibitor of plasminogen activation in human serum. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1973 Nov;30(2):414–424. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson K. W., Nussbaum M. Mechanism of enhanced streptokinase-induced clot lysis following in-vitro factor-XIII inactivation. Br J Haematol. 1969 Nov;17(5):445–453. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1969.tb01392.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LORAND L., JACOBSEN A. Accelerated lysis of blood clots. Nature. 1962 Sep 1;195:911–912. doi: 10.1038/195911b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorand L., Rule N. G., Ong H. H., Furlanetto R., Jacobsen A., Downey J., Oner N., Bruner-Lorand J. Amine specificity in transpeptidation. Inhibition of fibrin cross-linking. Biochemistry. 1968 Mar;7(3):1214–1223. doi: 10.1021/bi00843a043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundblad R. L. A rapid method for the purification of bovine thrombin and the inhibition of the purified enzyme wtih phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2501–2506. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda M., Yoshida N., Aoki N., Wakabayashi K. Distribution of cold-insoluble globulin in plasma and tissues. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1978 Jun 20;312:74–92. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1978.tb16794.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonagh R. P., Jr, McDonagh J., Duckert F. The influence of fibrin crosslinking on the kinetics of urokinase-induced clot lysis. Br J Haematol. 1971 Sep;21(3):323–332. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1971.tb03444.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moroi M., Aoki N. Isolation and characterization of alpha2-plasmin inhibitor from human plasma. A novel proteinase inhibitor which inhibits activator-induced clot lysis. J Biol Chem. 1976 Oct 10;251(19):5956–5965. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosher D. F. Action of fibrin-stabilizing factor on cold-insoluble globulin and alpha2-macroglobulin in clotting plasma. J Biol Chem. 1976 Mar 25;251(6):1639–1645. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosher D. F. Cross-linking of cold-insoluble globulin by fibrin-stabilizing factor. J Biol Chem. 1975 Aug 25;250(16):6614–6621. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REMMERT L. F., COHEN P. P. Partial purification and properties of a proteolytic enzyme of human serum. J Biol Chem. 1949 Nov;181(1):431–448. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rampling M. W. Factor XIII cross-linking and the rate of fibrinolysis induced by streptokinase and urokinase. Thromb Res. 1978 Feb;12(2):287–295. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(78)90299-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakata Y., Tateno K., Tamaki T., Aoki N. Calcium-dependent binding of alpha 2-plasmin inhibitor to fibrin. Thromb Res. 1979;16(1-2):279–282. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(79)90291-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorell J. I., Johansson B. G. Enzymatic iodination of polypeptides with 125I to high specific activity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Dec 28;251(3):363–369. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(71)90123-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]