Abstract
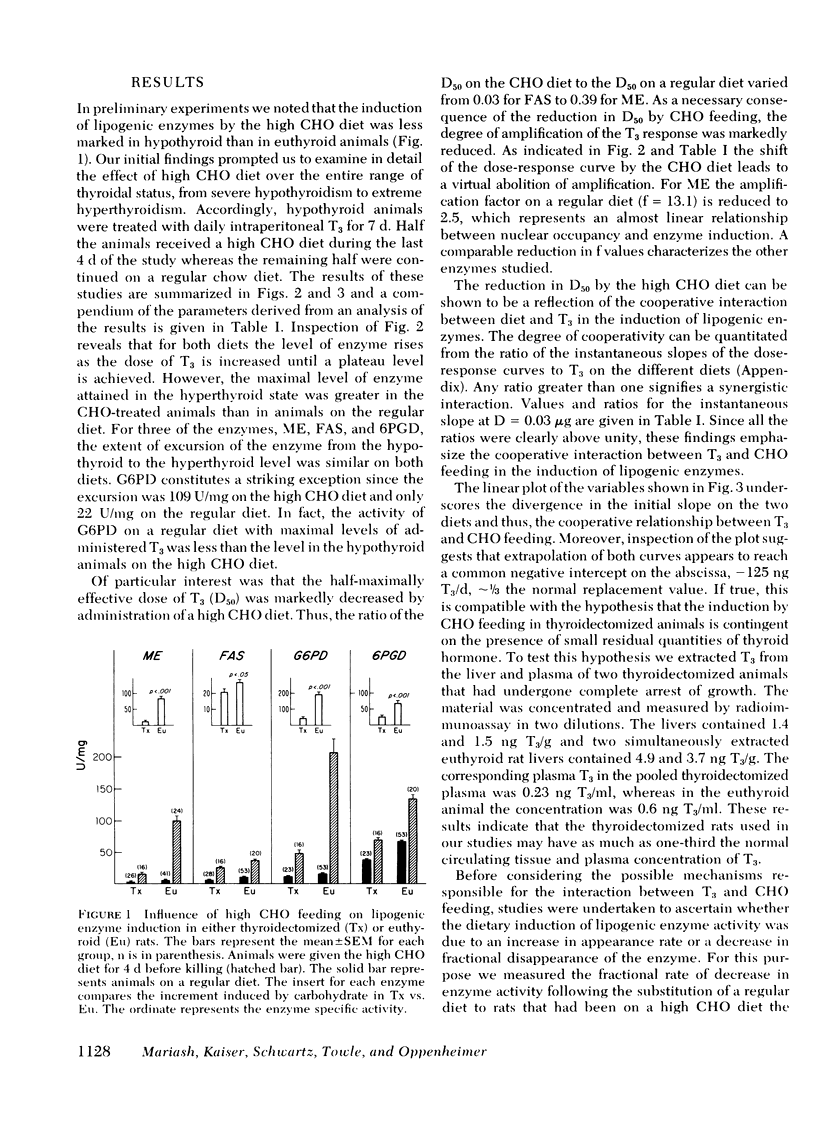
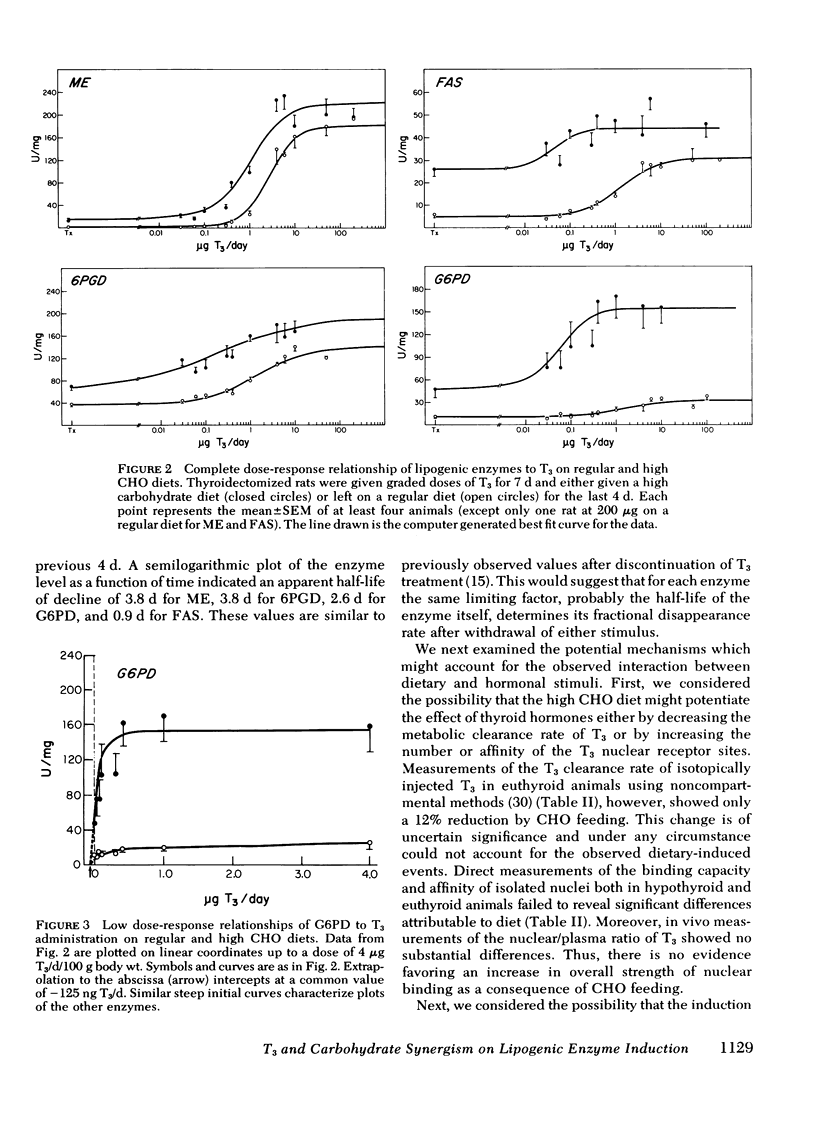
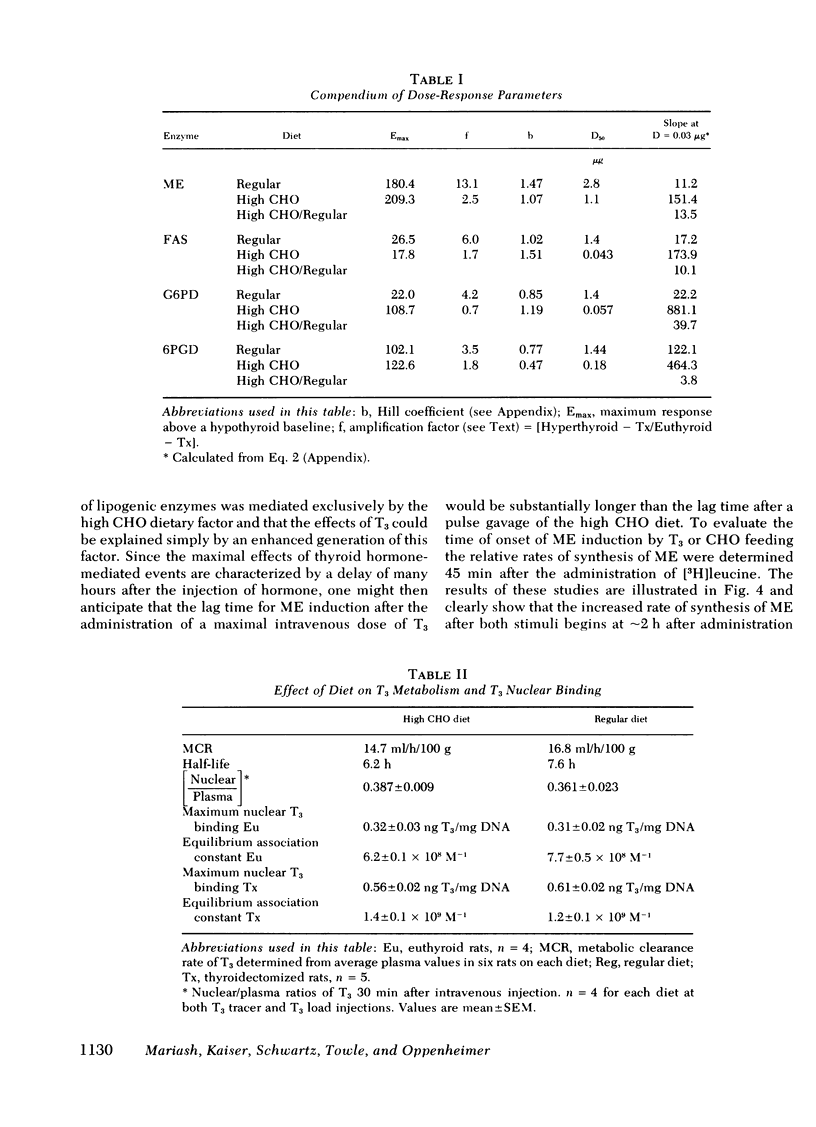
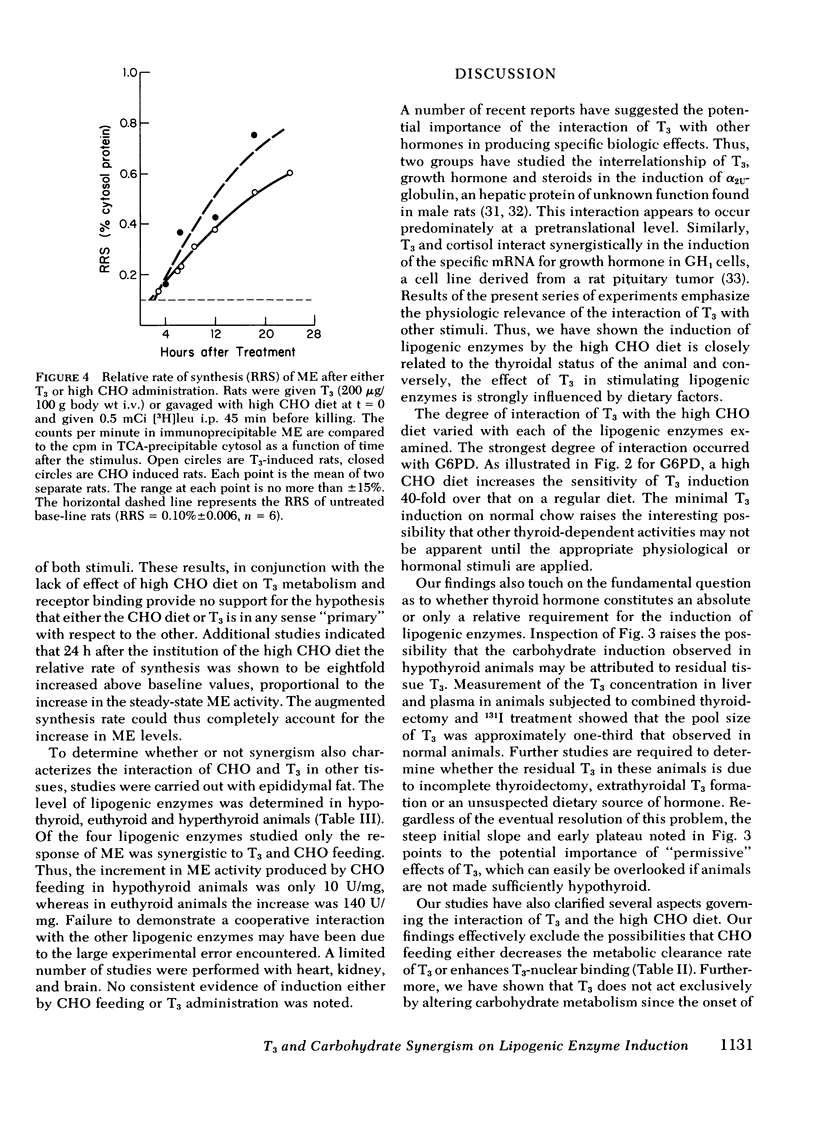
We have investigated the relationship between the administration of triiodothyronine (T3) and a high carbohydrate (CHO) fat-free diet in the induction of lipogenic enzymes in two rat tissues, liver, and fat. Male thyroidectomized rats were treated with graded daily doses of T3 and either supplemented with a high CHO diet or left on a regular diet. Enzymes studied included malic enzyme (ME), fatty acid synthetase, glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase, and 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase. In the liver, all four lipogenic enzymes showed a synergistic response between T3 administration and high CHO feeding. In fat, ME also responded synergistically. The interaction was reflected in an increased sensitivity to T3. The dose of T3 required to achieve 50% maximal response was reduced three- to seven-fold by the high CHO diet. This phenomenon could not be attributed to a dietary-induced alteration either in T3 metabolism or in number or affinity of the T3-nuclear receptors. Moreover, studies of the relative rate of synthesis of ME suggested a simultaneous time of onset in the induction of ME, within 2 h after the application of either T3 or CHO. Thus, it is unlikely that either stimulus is secondary to the other. Since parallel experiments from this laboratory (Towle, Mariash, and Oppenheimer,1980.Changes in hepatic levels of messenger ribonucleic acid for malic enzyme during induction by thyroid hormone or diet. Biochemistry. 19: 579-585.) show that ME induction both by CHO and T3 is mediated by an increase in specific messenger RNA for ME, the interaction of T3 and the dietary factor occurs at a pretanslational level.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BOTTOMLEY R. H., PITOT H. C., POTTER V. R., MORRIS H. P. Metabolic adaptations in rat hepatomas. V. Reciprocal relationship between threonine dehydrase and glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase. Cancer Res. 1963 Mar;23:400–409. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamant S., Gorin E., Shafrir E. Enzyme activities related to fatty-acid synthesis in liver and adipose tissue of rats treated with triiodothyronine. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Apr 24;26(4):553–559. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01798.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dillmann W. H., Schwartz H. L., Oppenheimer J. H. Selective alterations in hepatic enzyme response after reduction of nuclear triiodothyronine receptor sites by partial hepatectomy and starvation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Jan 13;80(1):259–266. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91131-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELRICK H., HLAD C. J., Jr, ARAI Y. Influence of thyroid function on carbohydrate metabolism and a new method for assessing response to insulin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1961 Apr;21:387–400. doi: 10.1210/jcem-21-4-387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flick P. K., Chen J., Alberts A. W., Vagelos P. R. Translation of rat liver fatty acid synthetase mRNA in a cell-free system derived from wheat germ. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Feb;75(2):730–734. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.2.730. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLOCK G. E., MCLEAN P., WHITEHEAD J. K. Pathways of glucose catabolism in rat liver in alloxan diabetes and hyperthyroidism. Biochem J. 1956 Jul;63(3):520–524. doi: 10.1042/bj0630520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia D. R., Holten D. Inhibition of rat liver glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase synthesis by glucagon. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):3960–3965. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson D. M., Lyons R. T., Scott D. F., Muto Y. Synthesis and degradation of the lipogenic enzymes of rat liver. Adv Enzyme Regul. 1972;10:187–204. doi: 10.1016/0065-2571(72)90014-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutchison J. S., Holten D. Quantitation of messenger RNA levels for rat liver 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jan 10;253(1):52–57. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koerner D., Surks M. I., Oppenheimer J. H. In vitro demonstration of specific triiodothyronine binding sites in rat liver nuclei. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1974 Apr;38(4):706–709. doi: 10.1210/jcem-38-4-706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar S., Das D. K., Dorfman A. E., Asato N. Stimulation of the synthesis of hepatic fatty acid synthesizing enzymes of hypophysectomized rats by 3,5,3'-l-triiodothyronine. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1977 Jan 30;178(2):507–516. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(77)90221-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mariash C. N., Kaiser F. E., Oppenheimer J. H. Comparison of the response characteristics of four lipogenic enzymes to 3,5,3'-triiodothyronine administration: evidence for variable degrees of amplification of the nuclear 3,5,3'-triiodothyronine signal. Endocrinology. 1980 Jan;106(1):22–27. doi: 10.1210/endo-106-1-22. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nepokroeff C. M., Lakshmanan M. R., Porter J. W. Fatty-acid synthase from rat liver. Methods Enzymol. 1975;35:37–44. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(75)35136-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nepokroeff C. M., Porter J. W. Translation and characterization of the fatty acid synthetase messenger RNA. J Biol Chem. 1978 Apr 10;253(7):2279–2283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheimer J. H., Schwartz H. L., Surks M. I. Determination of common parameters fo iodothyronine metabolism and distribution in man by noncompartmental analysis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1975 Aug;41(2):319–324. doi: 10.1210/jcem-41-2-319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheimer J. H., Silva E., Schwartz H. L., Surks M. I. Stimulation of hepatic mitochondrial alpha-glycerophosphate dehydrogenase and malic enzyme by L-triiodothyronine. Characteristics of the response with specific nuclear thyroid hormone binding sites fully saturated. J Clin Invest. 1977 Mar;59(3):517–527. doi: 10.1172/JCI108667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheimer J. H. Thyroid hormone action at the cellular level. Science. 1979 Mar 9;203(4384):971–979. doi: 10.1126/science.218285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodbard D. Apparent positive cooperative effects in cyclic AMP and corticosterone production by isolated adrenal cells in response to ACTH analogues. Endocrinology. 1974 May;94(5):1427–1437. doi: 10.1210/endo-94-5-1427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roncari D. A., Murthy V. K. Effects of thyroid hormones on enzymes involved in fatty acid and glycerolipid synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jun 10;250(11):4134–4138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy A. K., Dowbenko D. J. Role of growth hormone in the multihormonal regulation of messenger RNA for alpha2u globulin in the liver of hypophysectomized rats. Biochemistry. 1977 Aug 23;16(17):3918–3922. doi: 10.1021/bi00636a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudack D., Chisholm E. M., Holten D. Rat liver glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase. Regulation by carbohydrate diet and insulin. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 10;246(5):1249–1254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudack D., Gozukara E. M., Chisholm E. M., Holten D. The effect of dietary carbohydrate and fat on the synthesis of rat liver 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Nov 12;252(2):305–313. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(71)90011-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruegamer W. R., Newman G. H., Richert D. A., Westerfeld W. W. Specificity of the alpha-glycerophosphate dehydrogenase and malic enzyme response to thyroxine. Endocrinology. 1965 Oct;77(4):707–715. doi: 10.1210/endo-77-4-707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHIMKE R. T., SWEENEY E. W., BERLIN C. M. THE ROLES OF SYNTHESIS AND DEGRADATION IN THE CONTROL OF RAT LIVER TRYPTOPHAN PYRROLASE. J Biol Chem. 1965 Jan;240:322–331. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro L. E., Samuels H. H., Yaffe B. M. Thyroid and glucocorticoid hormones synergistically control growth hormone mRNA in cultured GH1 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jan;75(1):45–49. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.1.45. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surks M. I., Oppenheimer J. H. Concentration of L-thyroxine and L-triiodothyronine specifically bound to nuclear receptors in rat liver and kidney. Quantitative evidence favoring a major role of T3 in thyroid hormone action. J Clin Invest. 1977 Sep;60(3):555–562. doi: 10.1172/JCI108807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surks M. I., Schadlow A. R., Oppenheimer J. H. A new radioimmunoassay for plasma L-triiodothyronine: measurements in thyroid disease and in patients maintained on hormonal replacement. J Clin Invest. 1972 Dec;51(12):3104–3113. doi: 10.1172/JCI107137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towle H. C., Mariash C. N., Oppenheimer J. H. Changes in the hepatic levels of messenger ribonucleic acid for malic enzyme during induction by thyroid hormone or diet. Biochemistry. 1980 Feb 5;19(3):579–585. doi: 10.1021/bi00544a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vagenakis A. G., Burger A., Portnary G. I., Rudolph M., O'Brian J. R., Azizi F., Arky R. A., Nicod P., Ingbar S. H., Braverman L. E. Diversion of peripheral thyroxine metabolism from activating to inactivating pathways during complete fasting. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1975 Jul;41(1):191–194. doi: 10.1210/jcem-41-1-191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volpe J. J., Marasa J. C. Hormonal regulation of fatty acid synthetase, acetyl-CoA carboxylase and fatty acid synthesis in mammalian adipose tissue and liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Mar 24;380(3):454–472. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(75)90113-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volpe J. J., Vagelos P. R. Mechanisms and regulation of biosynthesis of saturated fatty acids. Physiol Rev. 1976 Apr;56(2):339–417. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1976.56.2.339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volpe J. J., Vagelos P. R. Regulation of mammalian fatty-acid synthetase. The roles of carbohydrate and insulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Mar;71(3):889–893. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.3.889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winberry L., Holten D. Rat liver glucose-6-p dehydrogenase. Dietary regulation of the rate of synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Nov 10;252(21):7796–7801. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeang K. K., Carrico R. J. Purification of malic enzyme by affinity chromatography on immobilized N6-(6-aminohexyl)-adenosine 2',5'-bisphosphate. Anal Biochem. 1976 Aug;74(2):369–375. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90218-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


