Abstract
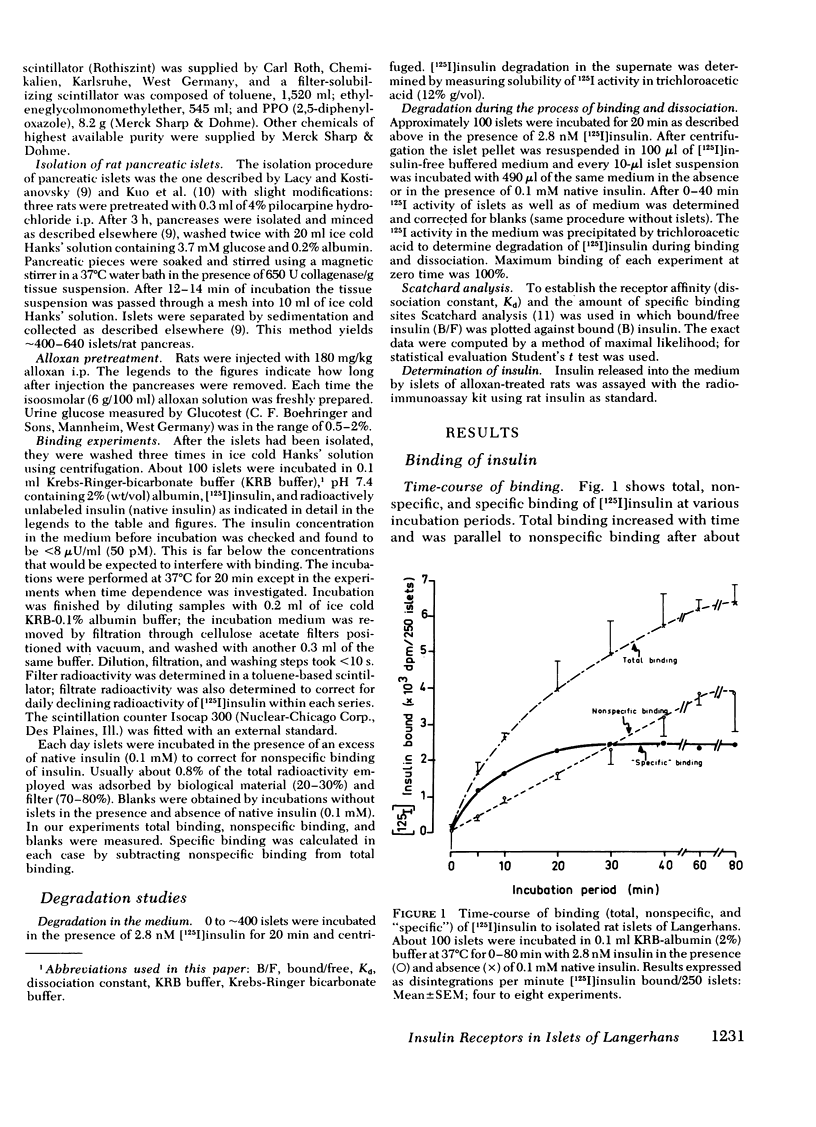
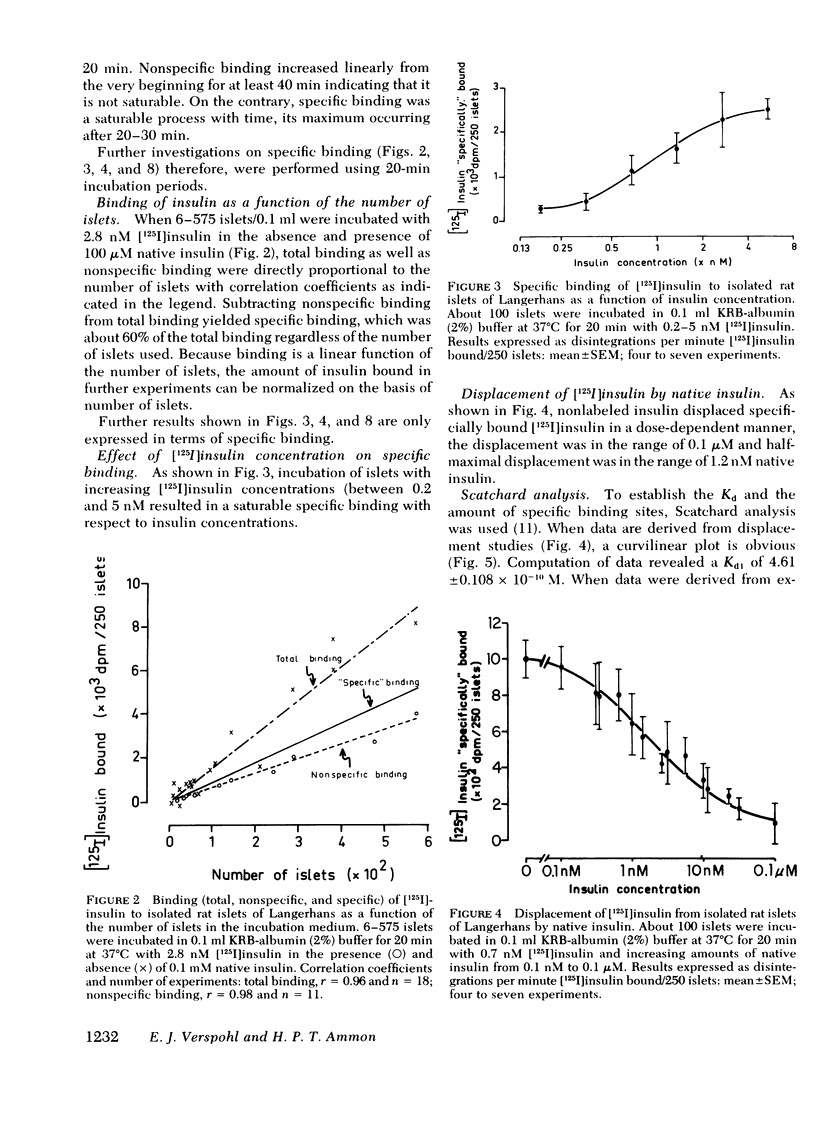
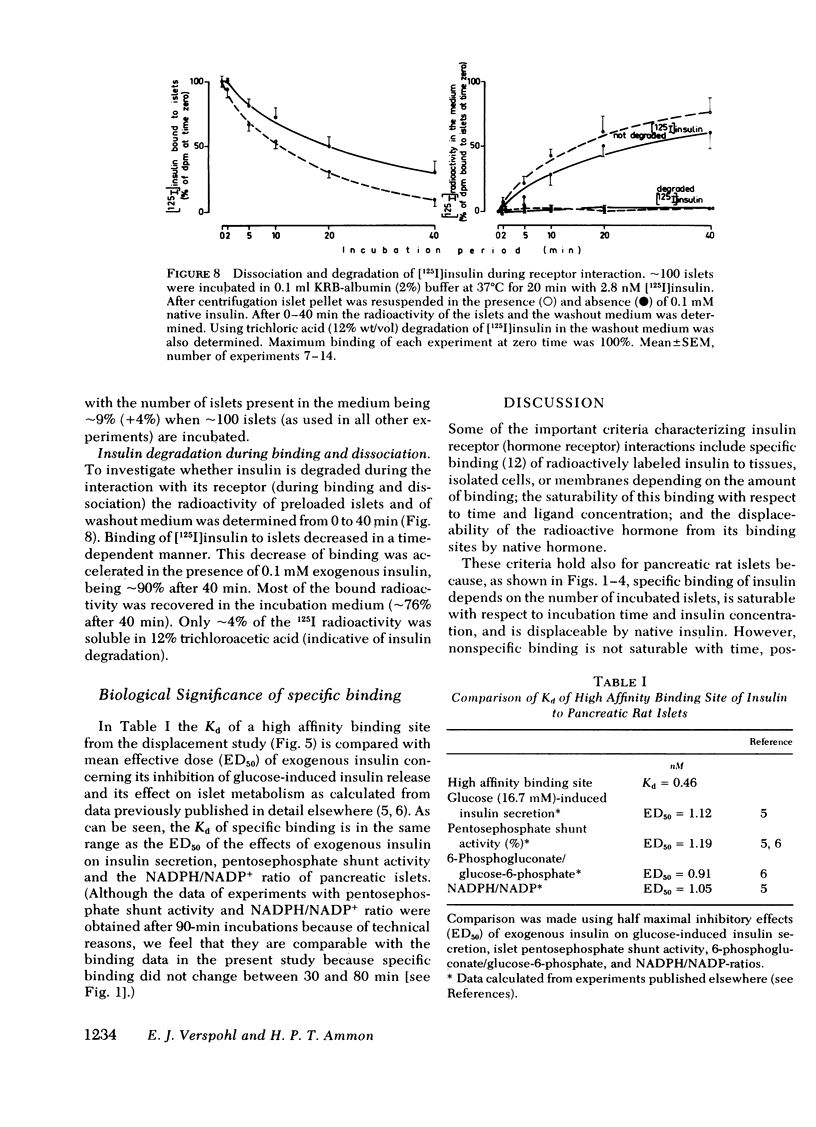
Binding of insulin to islets of Langerhans was studied. It was found that "specific" binding of [125I]insulin ("specific" binding equals total binding minus nonspecific binding) was saturable with respect to time and insulin concentration and depended on the number of incubated islets. Furthermore, bound insulin was displaced by native insulin in a dose-dependent manner. Bound [125I]insulin was easily dissociated and there was little [125I]insulin degradation both in the incubation medium and during the processes of binding and dissociation. Scatchard analysis of experiments with increasing [125I]insulin concentration and with displacement of insulin binding by native insulin revealed "high affinity" binding sites with a dissociation constant of 0.461 +/- 0.08 n M and 3.5 X 10(6) high affinity binding sites per islet. There also existed "low affinity" binding sites with dissociation constant (Kd) of 43.9 +/- 11.6 nM and 5.9 X 10(7) low affinity binding sites. High affinity binding sites of islets from rats pretreated with alloxan decreased by about one half, whereas Kd was unaffected. Because the Kd of specific high affinity binding and mean effective dose (ED50) of the biological effects of insulin on normal pancreatic islets are in the same range (between 0.46 and 1.19 nM), the insulin-receptor interaction may be biologically significant.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akhtar M. S., Verspohl E., Hegner D., Ammon H. P. 6-Phosphogluconate/glucose-6-phosphate ratio in rat pancreatic islets during inhibition of insulin release by exogenous insulin. Diabetes. 1977 Sep;26(9):857–863. doi: 10.2337/diab.26.9.857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ammon H. P., Steinke J. 6-Amnionicotinamide (6-AN) as a diabetogenic agent. In vitro and in vivo studies in the rat. Diabetes. 1972 Mar;21(3):143–148. doi: 10.2337/diab.21.3.143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ammon H. P., Verspohl E. Pyridine nucleotides in pancreatic islets during inhibition of insulin release by exogenous insulin. Endocrinology. 1976 Dec;99(6):1469–1476. doi: 10.1210/endo-99-6-1469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P. Commentary. Insulin receptors, cell membranes and hormone action. Biochem Pharmacol. 1974 Sep 1;23(17):2353–2361. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(74)90224-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P., Desbuquois B., Krug F. Insulin-receptor interactions in liver cell membranes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Jul 16;44(2):333–339. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90604-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P. Insulin--receptor interactions in adipose tissue cells: direct measurement and properties. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jun;68(6):1264–1268. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.6.1264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P. Properties of the insulin receptor of isolated fat cell membranes. J Biol Chem. 1971 Dec 10;246(23):7265–7274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeMeyts P., Bainco A. R., Roth J. Site-site interactions among insulin receptors. Characterization of the negative cooperativity. J Biol Chem. 1976 Apr 10;251(7):1877–1888. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRERICHS H., REICH U., CREUTZFELDT W. INSULINSEKRETION IN VITRO. I. HEMMUNG DER GLUCOSEINDUZIERTEN INSULINABGABE DURCH INSULIN. Klin Wochenschr. 1965 Feb 1;43:136–140. doi: 10.1007/BF01484504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fussganger R. D., Kahn C. R., Roth J., De Meyts P. Binding and degradation of insulin by human peripheral granulocytes. Demonstration of specific receptors with high affinity. J Biol Chem. 1976 May 10;251(9):2761–2769. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fussganger R. D., Kahn C. R., Roth J., De Meyts P. Binding and degradation of insulin by human peripheral granulocytes. Demonstration of specific receptors with high affinity. J Biol Chem. 1976 May 10;251(9):2761–2769. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gammeltoft S., Gliemann J. Binding and degradation of 125I-labelled insulin by isolated rat fat cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Aug 17;320(1):16–32. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(73)90161-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldfine I. D., Gardner J. D., Neville D. M., Jr Insulin action in isolated rat thymocytes. I. Binding of 125 I-insulin and stimulation of -aminoisobutyric acid transport. J Biol Chem. 1972 Nov 10;247(21):6919–6926. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOUSE E. L. A histological study of the pancreas, liver and kidney both during and after recovery from alloxan diabetes. Endocrinology. 1958 Feb;62(2):189–200. doi: 10.1210/endo-62-2-189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammond J. M., Jarett L., Mariz I. K., Daughaday W. H. Heterogeneity of insulin receptors on fat cell membranes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Nov 15;49(4):1122–1128. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90329-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatfield H. H., Banasiak M. F., Driscoll T., Kim H. J., Kalkhoff R. K. Glucose suppression of glucagon: relationship to pancreatic beta cell function? J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1977 Jun;44(6):1080–1087. doi: 10.1210/jcem-44-6-1080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iversen J., Miles D. W. Evidence for a feedback inhibition of insulin on insulin secretion in the isolated, perfused canine pancreas. Diabetes. 1971 Jan;20(1):1–9. doi: 10.2337/diab.20.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn C. R., Freychet P., Roth J., Neville D. M., Jr Quantitative aspects of the insulin-receptor interaction in liver plasma membranes. J Biol Chem. 1974 Apr 10;249(7):2249–2257. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo W. N., Hodgins D. S., Kuo J. F. Adenylate cyclase in islets of Langerhans. Isolation of islets and regulation of adenylate cyclase activity by various hormones and agents. J Biol Chem. 1973 Apr 25;248(8):2705–2711. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacy P. E., Kostianovsky M. Method for the isolation of intact islets of Langerhans from the rat pancreas. Diabetes. 1967 Jan;16(1):35–39. doi: 10.2337/diab.16.1.35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lernmark A. The preparation of, and studies on, free cell suspensions from mouse pancreatic islets. Diabetologia. 1974 Oct;10(5):431–438. doi: 10.1007/BF01221634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olefsky J. M., Jen P., Reaven G. M., Alto P. Insulin binding to isolated human adipocytes. Diabetes. 1974 Jul;23(7):565–571. doi: 10.2337/diab.23.7.565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patton G. S., Ipp E., Dobbs R. E., Orci L., Vale W., Unger R. H. Pancreatic immunoreactive somatostatin release. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 May;74(5):2140–2143. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.5.2140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toyota T., Abe K., Kudo M. Inhibitory action of rat insulin and synthetic rat C-peptide on insulin secretion in the perfused rat pancreas. Acta Diabetol Lat. 1977 Sep-Dec;14(5-6):250–256. doi: 10.1007/BF02580973. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zawalich W. S., Karl R. C., Ferrendelli J. A., Matschinsky F. M. Factors governing glucose induced elevation of cyclic 3'5' AMP levels in pancreatic islets. Diabetologia. 1975 Jun;11(3):231–235. doi: 10.1007/BF00422327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


