Abstract
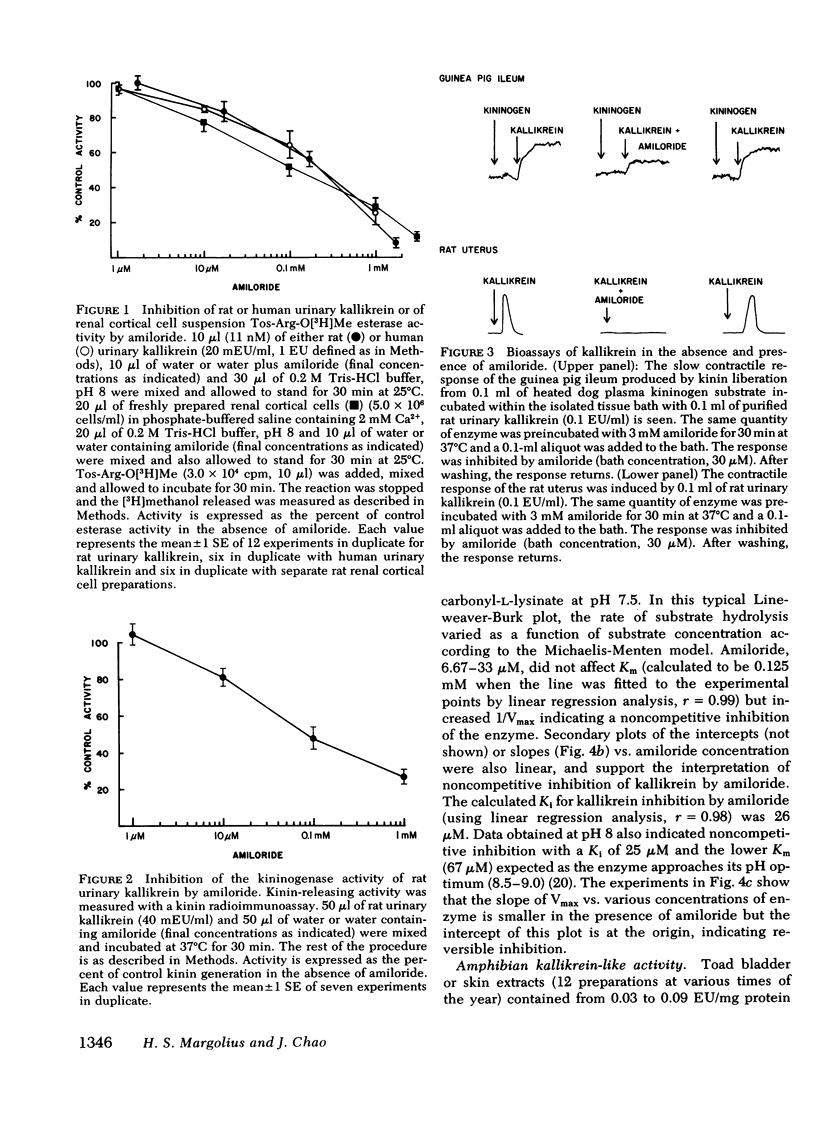
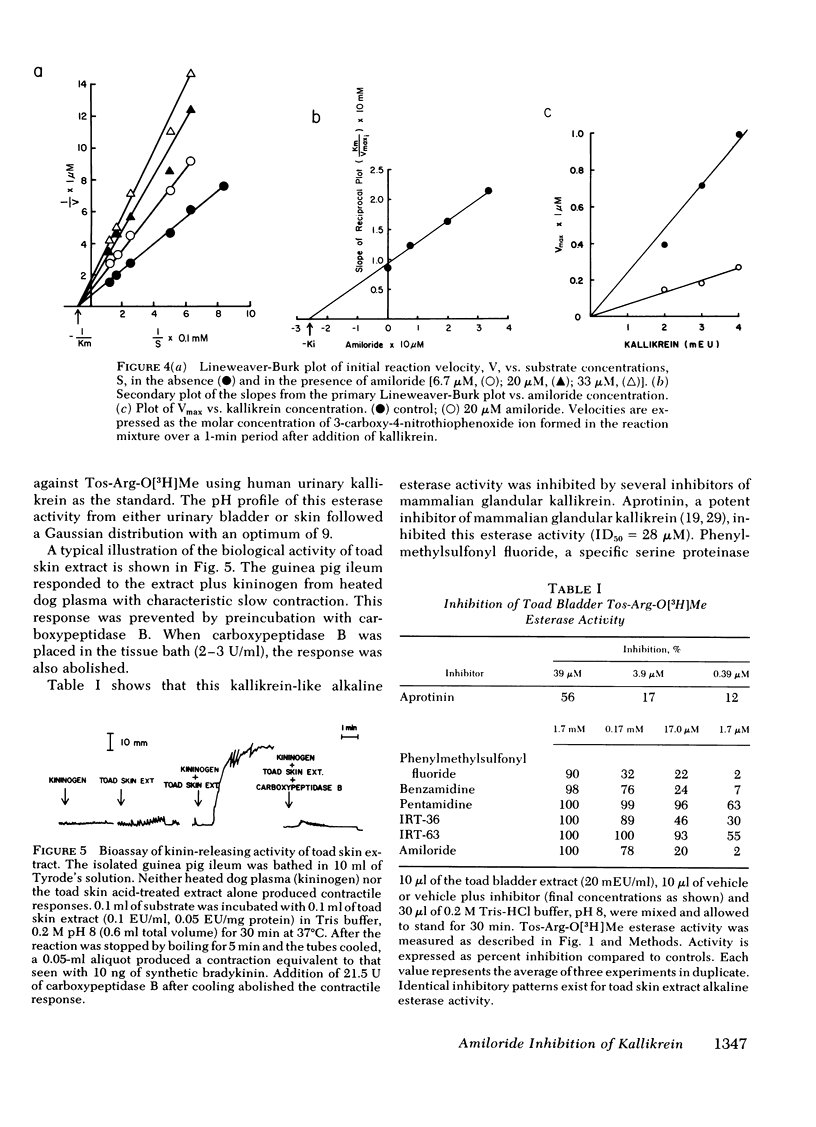
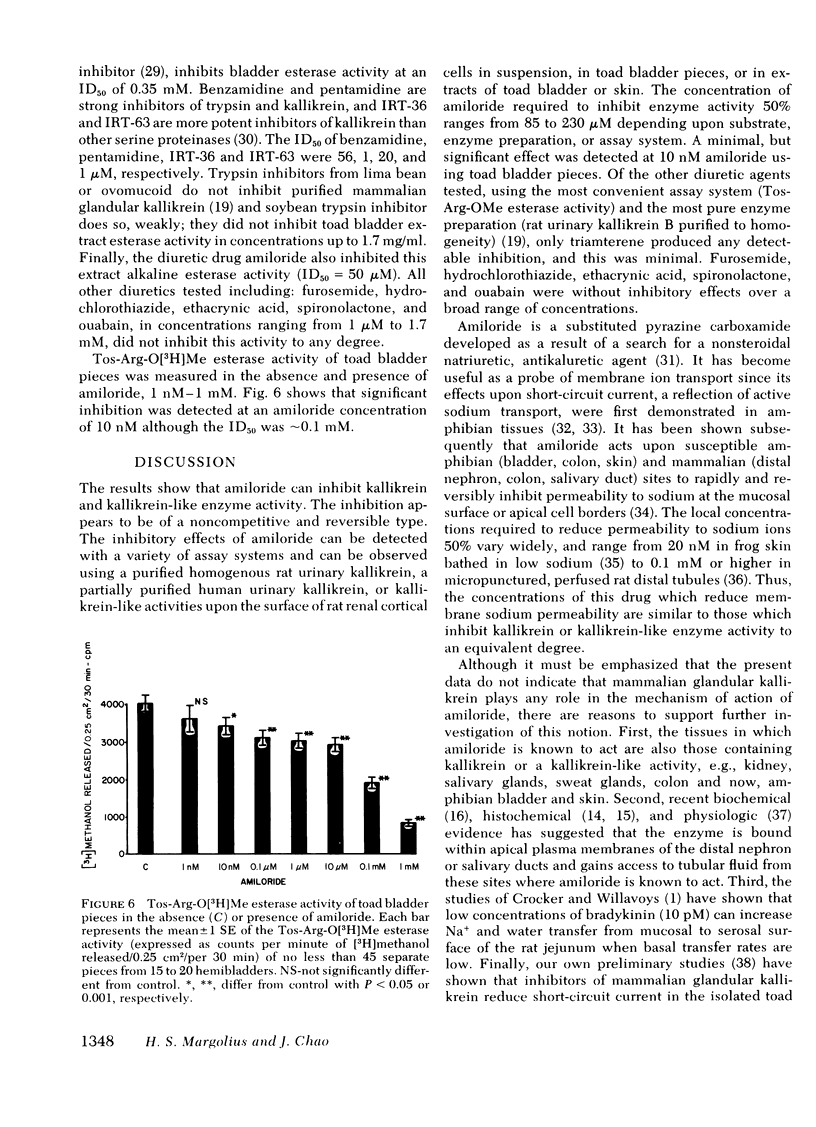
Renal kallikrein is localized in luminal plasma membranes of the mammalian distal nephron and gains access to urine from this site. Its activity is regulated, in part, by aldosterone. These facts led us to study the effects of amiloride, a drug known to inhibit sodium reabsorption and potassium secretion at this site, on kallikrein activity. Amiloride inhibited the esterolytic activity of purified rat or human urinary kallikrein or of rat renal cortical cells upon a synthetic substrate (ID50 = 0.12-0.23 mM). Kinetic analyses showed that the enzyme inhibition was noncompetitive and reversible in nature. The kinin-generating activity of kallikrein acting upon kininogen substrates was also inhibited by amiloride, as measured by bioassay in the rat uterus of guinea pig ileum or by radioimmunoassay of liberated kinins (ID50 = 85 microM). No other diuretic drug tested inhibited kallikrein activity, except triamterene, which did so, weakly. In addition, kallikrein-like enzyme activity was discovered in the urinary bladder or skin of Bufo marinus toads and this activity was also inhibited by amiloride. The localization of the enzyme and its inhibition by this drug suggest that further study of relationships amongst the glandular kallikrein-kinen system and renal ion and water transport is warranted.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beaven V. H., Pierce J. V., Pisano J. J. A sensitive isotopic procedure for the assay of esterase activity: measurement of human urinary kallikrein. Clin Chim Acta. 1971 Mar;32(1):67–73. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(71)90465-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bentley P. J. Amiloride: a potent inhibitor of sodium transport across the toad bladder. J Physiol. 1968 Mar;195(2):317–330. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chao J., Margolius H. S. Isozymes of rat urinary kallikrein. Biochem Pharmacol. 1979 Jul 1;28(13):2071–2079. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(79)90226-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chao J., Margolius H. S. Studies on rat renal cortical cell kallikrein. II. Identification of kallikrein as an ecto-enzyme. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Oct 11;570(2):330–340. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(79)90153-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crocker A. D., Willavoys S. P. Effect of bradykinin on transepithelial transfer of sodium and water in vitro. J Physiol. 1975 Dec;253(2):401–410. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuthbert A. W. An upper limit to the number of sodium channels in frog skin epithelium. J Physiol. 1973 Feb;228(3):681–692. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duarte C. G., Chomety F., Giebisch G. Effect of amiloride, ouabain, and furosemide on distal tubular function in the rat. Am J Physiol. 1971 Aug;221(2):632–640. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.221.2.632. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eigler J., Kelter J., Renner E. Wirkungscharakteristika eines neuen Acylguanidins--Amiloride-HCL (MK 870)--an der isolierten Haut von Amphibien. Klin Wochenschr. 1967 Jul 15;45(14):737–738. doi: 10.1007/BF01746103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geller R. G., Margolius H. S., Pisano J. J., Keiser H. R. Effects of mineralocorticoids, altered sodium intake, and adrenalectomy on urinary kallikrein in rats. Circ Res. 1972 Dec;31(6):857–861. doi: 10.1161/01.res.31.6.857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green G. D., Shaw E. Thiobenzyl benzyloxycarbonyl-L-lysinate, substrate for a sensitive colorimetric assay for trypsin-like enzymes. Anal Biochem. 1979 Mar;93(2):223–226. doi: 10.1016/s0003-2697(79)80141-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOSKINS J. M., MEYNELL G. G., SANDERS F. K. A comparison of methods for estimating the viable count of a suspension of tumour cells. Exp Cell Res. 1956 Aug;11(2):297–305. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(56)90105-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halushka P. V., Wohltmann H., Privitera P. J., Hurwitz G., Margolius H. S. Bartter's syndrome: urinary prostaglandin E-like material and kallikrein; indomethacin effects. Ann Intern Med. 1977 Sep;87(3):281–286. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-87-3-281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz D., Margolius H. S., Keiser H. R. Effects of dietary potassium and race on urinary excretion of kallikrein and aldosterone in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1978 Aug;47(2):296–299. doi: 10.1210/jcem-47-2-296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaizu T., Margolius H. S. Studies on rat renal cortical cell kallikrein. I. Separation and measurement. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Dec 5;411(2):305–315. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(75)90310-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lechi A., Covi G., Lechi C., Mantero F., Scuro L. A. Urinary kallikrein excretion in Bartter's syndrome. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1976 Nov;43(5):1175–1178. doi: 10.1210/jcem-43-5-1175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolius H. S., Horwitz D., Geller R. G., Alexander R. W., Gill J. R., Jr, Pisano J. J., Keiser H. R. Urinary kallikrein excretion in normal man. Relationships to sodium intake and sodium-retaining steroids. Circ Res. 1974 Dec;35(6):812–819. doi: 10.1161/01.res.35.6.812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolius H. S., Horwitz D., Pisano J. J., Keiser H. R. Urinary kallikrein excretion in hypertensive man. Relationships to sodium intake and sodium-retaining steroids. Circ Res. 1974 Dec;35(6):820–825. doi: 10.1161/01.res.35.6.820. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mimran A., Baudin G., Casellas D., Soulas D. Urinary kallikrein and changes in endogenous aldosterone in the rat. Eur J Clin Invest. 1977 Dec;7(6):497–502. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1977.tb01642.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasjletti A., McGiff J. C., Colina-Chourio J. Interrelations of the renal kallikrein-kinin system and renal prostaglandins in the conscious rat. Influence of mineralocorticoids. Circ Res. 1978 Nov;43(5):799–807. doi: 10.1161/01.res.43.5.799. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nustad K. The relationship between kidney and urinary kininogenase. Br J Pharmacol. 1970 May;39(1):73–86. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1970.tb09557.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orstabik T. B., Nustad K., Brandtzaeg P., Pierce J. V. Cellular origin of urinary kallikreins. J Histochem Cytochem. 1976 Sep;24(9):1037–1039. doi: 10.1177/24.9.965714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scicli A. G., Carretero O. A., Hampton A., Cortes P., Oza N. B. Site of kininogenase secretion in the dog nephron. Am J Physiol. 1976 Feb;230(2):533–536. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1976.230.2.533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimamoto K., Ando T., Nakao T., Tanaka S., Sakuma M., Miyahara M. A sensitive radioimmunoassay method for urinary kinins in man. J Lab Clin Med. 1978 May;91(5):721–728. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimamoto K., Tanaka S., Nakao T., Ando T., Nakahashi Y., Sakuma M., Miyahara M. Measurement of urinary kallikrein acitvity by kinin radioimmunoassay. Jpn Circ J. 1979 Mar;43(3):147–152. doi: 10.1253/jcj.43.147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simson J. A., Spicer S. S., Chao J., Grimm L., Margolius H. S. Kallikrein localization in rodent salivary glands and kidney with the immunoglobulin-enzyme bridge technique. J Histochem Cytochem. 1979 Dec;27(12):1567–1576. doi: 10.1177/27.12.391993. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tidwell R. R., Fox L. L., Geratz J. D. Aromatic Tris-amidines. A new class of highly active inhibitors of trypsin-like proteases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Oct 11;445(3):729–738. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(76)90123-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vinci J. M., Gill J. R., Jr, Bowden R. E., Pisano J. J., Izzo J. L., Jr, Radfar N., Taylor A. A., Zusman R. M., Bartter F. C., Keiser H. R. The kallikrein-kinin system in Bartter's syndrome and its response to prostaglandin synthetase inhibition. J Clin Invest. 1978 Jun;61(6):1671–1682. doi: 10.1172/JCI109088. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vinci J. M., Zusman R. M., Izzo J. L., Jr, Bowden R. E., Horwitz D., Pisano J. J., Keiser H. R. Human urinary and plasma kinins: relationship to sodium-retaining steroids and plasma renin activity. Circ Res. 1979 Feb;44(2):228–237. doi: 10.1161/01.res.44.2.228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward P. E., Gedney C. D., Dowben R. M., Erdös E. G. Isolation of membrane-bound renal kallikrein and kininase. Biochem J. 1975 Dec;151(3):755–758. doi: 10.1042/bj1510755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


