Abstract
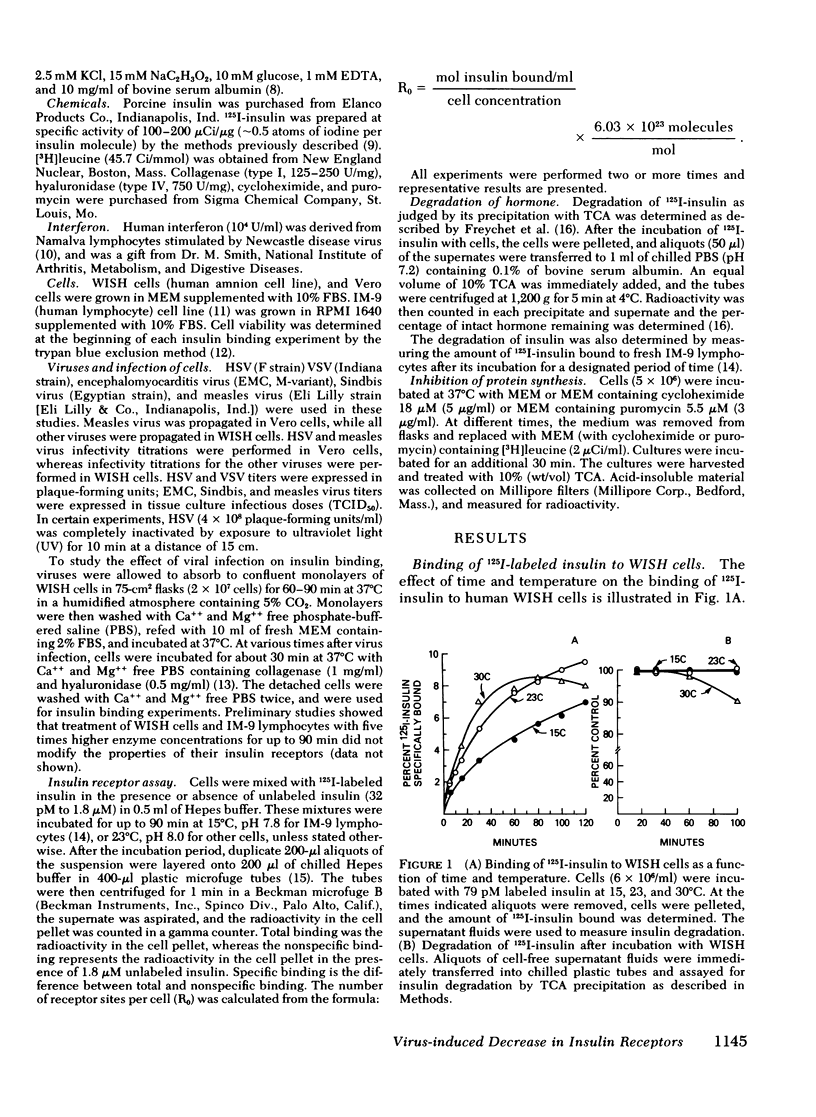
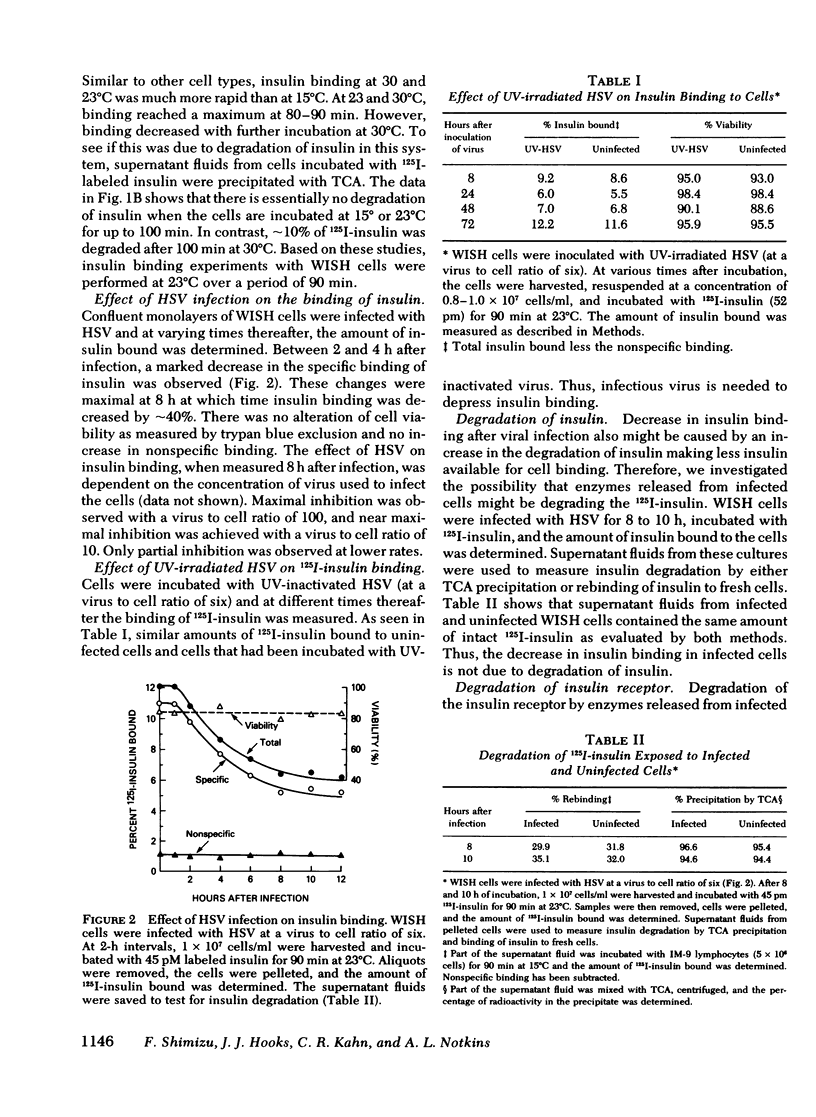
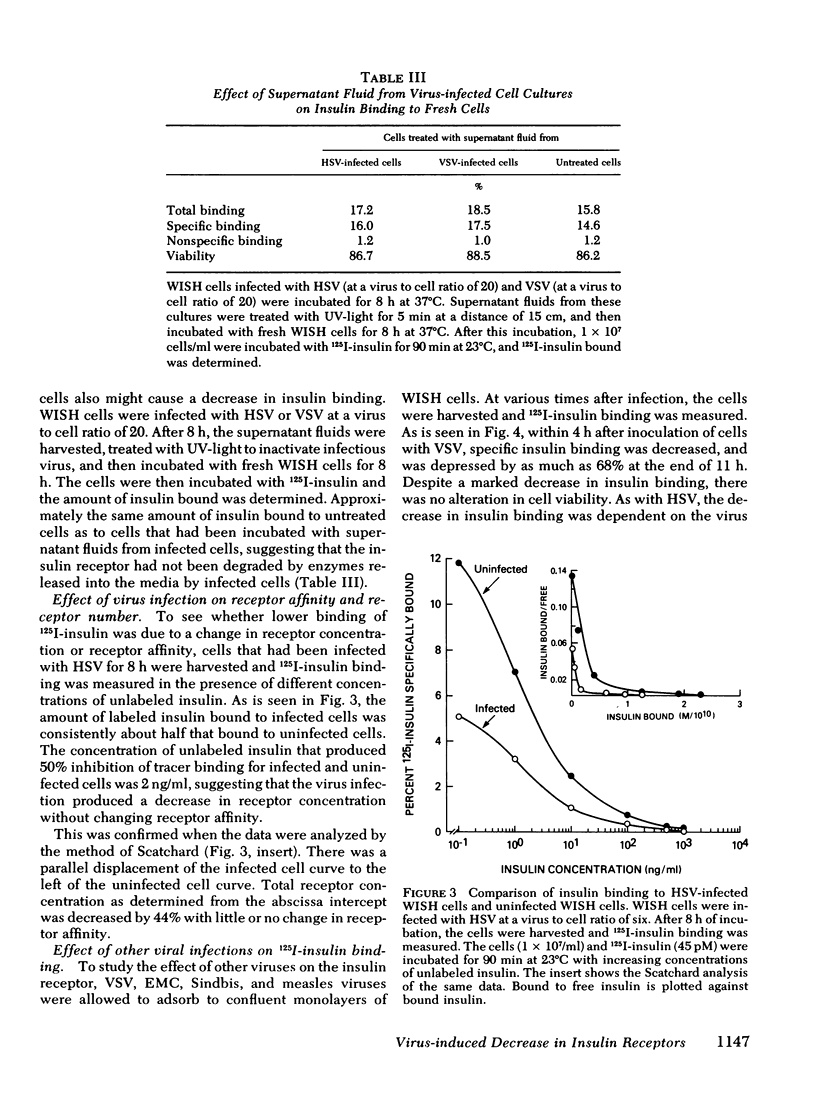
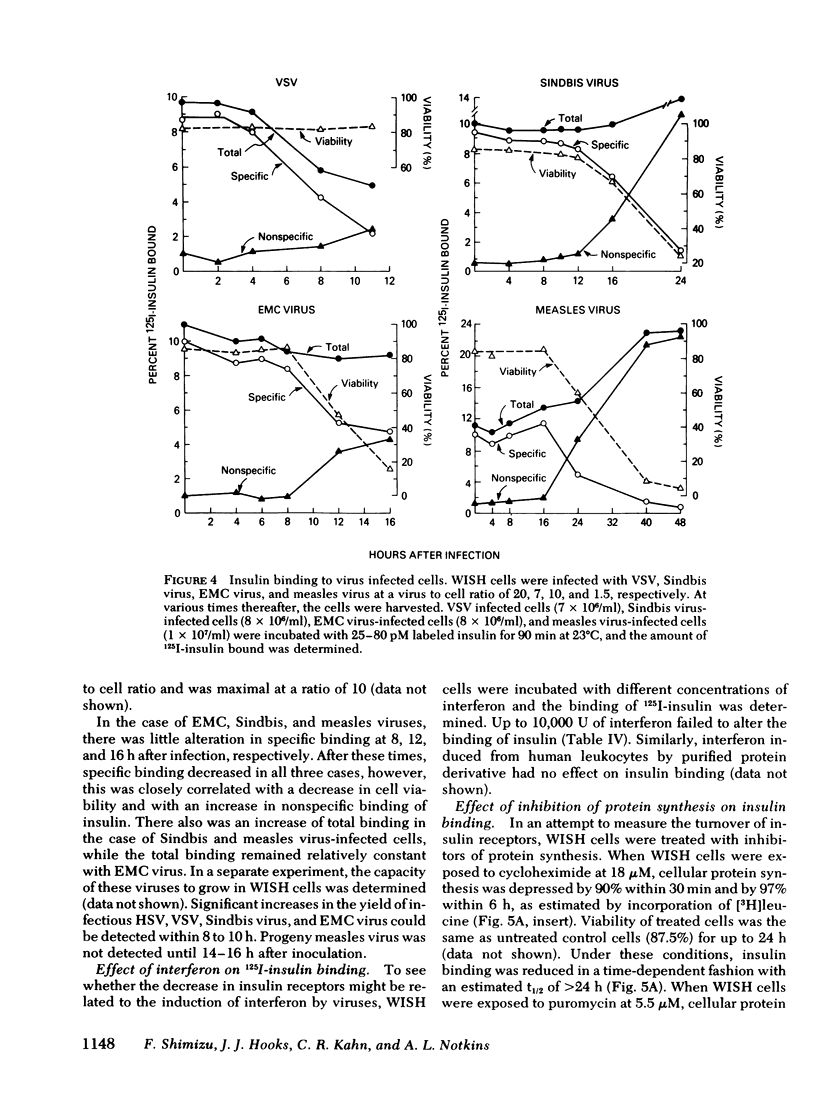
Viral infections may produce abnormalities in carbohydrate metabolism in normal subjects and profound changes in glucose homeostasis in insulin-dependent diabetics. Using an in vitro radio-receptor assay with 125I-labeled insulin and human-amnion (WISH) cells, the effect of viral infections on insulin receptors was examined. Both herpes simplex virus and vesicular stomatitis virus produced a 50% decrease in insulin binding. There was no evidence that this decrease was due to degradation of insulin. On quantitative analysis, this decrease in binding was found to be the result of a decrease in receptor concentration with no change in receptor affinity. The decrease in receptors occurred between 4 and 12 h, at the time viral antigens were being inserted into the plasma membrane of infected cells. Because the t 1/2 of insulin receptors in uninfected cells was between 14 and 24 h, the decrease in insulin receptors cannot be explained solely by virus-induced shut-off of macromolecular synthesis. Moreover, viruses such as encephalomyocarditis that do not insert new antigens into the plasma membrane, did not cause changes in the number of insulin receptors. The most likely explanation is that virus-induced changes in the plasma membrane altered or displaced insulin receptors. It is concluded that the insulin receptor assay is a sensitive and quantitative method for studying the effect of viral infections on cell membranes. These data also suggest that abnormalities in glucose metabolism associated with some viral infections may be due, in part, to changes in the concentration of insulin receptors.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allison A. C. The role of membranes in the replication of animal viruses. Int Rev Exp Pathol. 1971;10:181–242. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Attallah A. M., Strong D. M. Differential effects of interferon on the MHC expression of human lymphocytes. Enhanced expression of HLA without effect on Ia. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1979;60(1):101–105. doi: 10.1159/000232328. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bar R. S., Harrison L. C., Muggeo M., Gorden P., Kahn C. R., Roth J. Regulation of insulin receptors in normal and abnormal physiology in humans. Adv Intern Med. 1979;24:23–52. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birdwell C. R., Strauss J. H. Agglutination of Sindbis virus and of cells infected with Sindbis virus by plant lectins. J Virol. 1973 Apr;11(4):502–507. doi: 10.1128/jvi.11.4.502-507.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Detrick-Hooks B., Smith H. G., Bast R. C., Jr, Dunkel V. C., Borsos T. Naturally soluble tumor antigens from guinea pig hepatomas: isolation and partial characterization. J Immunol. 1976 May;116(5):1324–1331. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fahey J. L., Buell D. N., Sox H. C. Proliferation and differentiation of lymphoid cells: studies with human lymphoid cell lines and immunoglobulin synthesis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1971 Dec 31;190:221–234. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1971.tb13537.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freychet P., Kahn R., Roth J., Neville D. M., Jr Insulin interactions with liver plasma membranes. Independence of binding of the hormone and its degradation. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jun 25;247(12):3953–3961. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gavin J. R., 3rd, Gorden P., Roth J., Archer J. A., Buell D. N. Characteristics of the human lymphocyte insulin receptor. J Biol Chem. 1973 Mar 25;248(6):2202–2207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gavin J. R., 3rd, Roth J., Jen P., Freychet P. Insulin receptors in human circulating cells and fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Mar;69(3):747–751. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.3.747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glorioso J. C., Smith J. W. Immune interactions with cells infected with herpes simplex virus: antibodies to radioiodinated surface antigens. J Immunol. 1977 Jan;118(1):114–121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haspel M. V., Pellegrino M. A., Lampert P. W., Oldstone M. B. Human histocompatibility determinants and virus antigens: effect of measles virus infection on HLA expression. J Exp Med. 1977 Jul 1;146(1):146–156. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.1.146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi K., Niwa A., Rosenthal J., Notkins A. L. Detection of virus-induced membrane and cytoplasmic antigens: comparison of the 125I-labeled antiviral antibody binding technique with immunofluorescence. Intervirology. 1974;2(1):48–51. doi: 10.1159/000149404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hecht T. T., Summers D. F. Effect of vesicular stomatitis virus infection on the histocompatibility antigen of L cells. J Virol. 1972 Oct;10(4):578–585. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.4.578-585.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hecht T. T., Summers D. F. Interactions of vesicular stomatitis virus with murine cell surface antigens. J Virol. 1976 Sep;19(3):833–845. doi: 10.1128/jvi.19.3.833-845.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hecht T. T., Summers D. F. Newcastle disease virus infection of L cells. J Virol. 1974 Jul;14(1):162–169. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.1.162-169.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huet C., Gresser I., Bandu M. T., Lindahl P. Increased binding of concanavalin A to interferon-treated murine leukemia L 1210 cells. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1974 Oct;147(1):52–57. doi: 10.3181/00379727-147-38279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn C. R., Goldfine I. D., Neville D. M., Jr, De Meyts P. Alterations in insulin binding induced by changes in vivo in the levels of glucocorticoids and growth hormone. Endocrinology. 1978 Oct;103(4):1054–1066. doi: 10.1210/endo-103-4-1054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlsson F. A., Grunfeld C., Kahn C. R., Roth J. Regulation of insulin receptors and insulin responsiveness in 3T3-L1 fatty fibroblasts. Endocrinology. 1979 May;104(5):1383–1392. doi: 10.1210/endo-104-5-1383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohn L. D., Friedman R. M., Holmes J. M., Lee G. Use of thyrotropin and cholera toxin to probe the mechanism by which interferon initiates its antiviral activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Oct;73(10):3695–3699. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.10.3695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koszinowski U., Ertl H. Altered serological and cellular reactivity to H-2 antigens after target cell infection with vaccinia virus. Nature. 1975 Oct 16;257(5527):596–597. doi: 10.1038/257596a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence C., Thach R. E. Encephalomyocarditis virus infection of mouse plasmacytoma cells. I. Inhibition of cellular protein synthesis. J Virol. 1974 Sep;14(3):598–610. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.3.598-610.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl P., Gresser I., Leary P., Tovey M. Interferon treatment of mice: enhanced expression of histocompatibility antigens on lymphoid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Apr;73(4):1284–1287. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.4.1284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore G. E., Ito E., Ulrich K., Sandberg A. A. Culture of human leukemia cells. Cancer. 1966 May;19(5):713–723. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(196605)19:5<713::aid-cncr2820190518>3.0.co;2-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Notkins A. L. The causes of diabetes. Sci Am. 1979 Nov;241(5):62–73. doi: 10.1038/scientificamerican1179-62. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pellegrino M. A., Pellegrino A., Ferrone S., Kahan B. D., Reisfeld R. A. Extraction and purification of soluble HL-A antigens from exhausted media of human lymphoid cell lines. J Immunol. 1973 Sep;111(3):783–788. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penhoet E., Olsen C., Carlson S., Lacorbiere M., Nicolson G. L. Quantitative interaction of Ricinus communis agglutinin and concanavalin A with influenza and vesicular stomatitis viruses and virus-infected normal and polyoma-transformed cells. Biochemistry. 1974 Aug 13;13(17):3561–3566. doi: 10.1021/bi00714a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poste G., Reeve P. Increased mobility and redistribution of concanavalin A receptors on cells infected with Newcastle disease virus. Nature. 1974 Feb 15;247(5441):469–471. doi: 10.1038/247469a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rayfield E. J., Curnow R. T., George D. T., Beisel W. R. Impaired carbohydrate metabolism during a mild viral illness. N Engl J Med. 1973 Sep 20;289(12):618–621. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197309202891207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rayfield E. J., Curnow R. T., Reinhard D., Kochicheril N. M. Effects of acute endotoxemia on glucoregulation in normal and diabetic subjects. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1977 Sep;45(3):513–521. doi: 10.1210/jcem-45-3-513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen O. M., Chia G. H., Fung C., Rubin C. S. Tunicamycin-mediated depletion of insulin receptors in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. J Cell Physiol. 1979 Apr;99(1):37–42. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040990106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth J. Assay of peptide hormones using cell receptors: application to insulin and to human growth hormone. Methods Enzymol. 1975;37:66–82. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(75)37006-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shambaugh G. E., 3rd, Beisel W. R. Insulin response during tularemia in man. Diabetes. 1967 Jun;16(6):369–376. doi: 10.2337/diab.16.6.369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tevethia S. S., Lowry S., Rawls W. E., Melnick J. L., McMillan V. Detection of early cell surface changes in herpes simplex virus infected cells by agglutination with concanavalin A. J Gen Virol. 1972 Apr;15(1):93–97. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-15-1-93. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomopoulos P., Roth J., Lovelace E., Pastan I. Insulin receptors in normal and transformed fibroblasts: relationship to growth and transformation. Cell. 1976 Jul;8(3):417–423. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90154-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Obberghen E., De Meyts P., Roth J. Cell surface receptors for insulin and human growth hormone. Effect of microtubule and microfilament modifiers. J Biol Chem. 1976 Nov 10;251(21):6844–6851. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner R. R., Heine J. W., Goldstein G., Schnaitman C. A. Use of antiviral-antiferritin hybrid antibody for localization of viral antigen in plasma membrane. J Virol. 1971 Feb;7(2):274–277. doi: 10.1128/jvi.7.2.274-277.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamanouchi K., Kobune F., Fukuda A., Hayami M., Shishido A. Comparative immunofluorescent studies on measles, canine distemper, and rinderpest viruses. Immunofluorescence of measles, distemper, and rinderpest viruses. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1970;29(1):90–100. doi: 10.1007/BF01253884. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zarling J. M., Tevethia S. S. Expression of concanavalin A binding sites in rabbit kidney cells infected with vaccinia virus. Virology. 1971 Jul;45(1):313–316. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90140-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoon K. C., Buckler C. E., Bridgen P. J., Gurari-Rotman D. Production of human lymphoblastoid interferon by Namalva cells. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Jan;7(1):44–51. doi: 10.1128/jcm.7.1.44-51.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


