Abstract
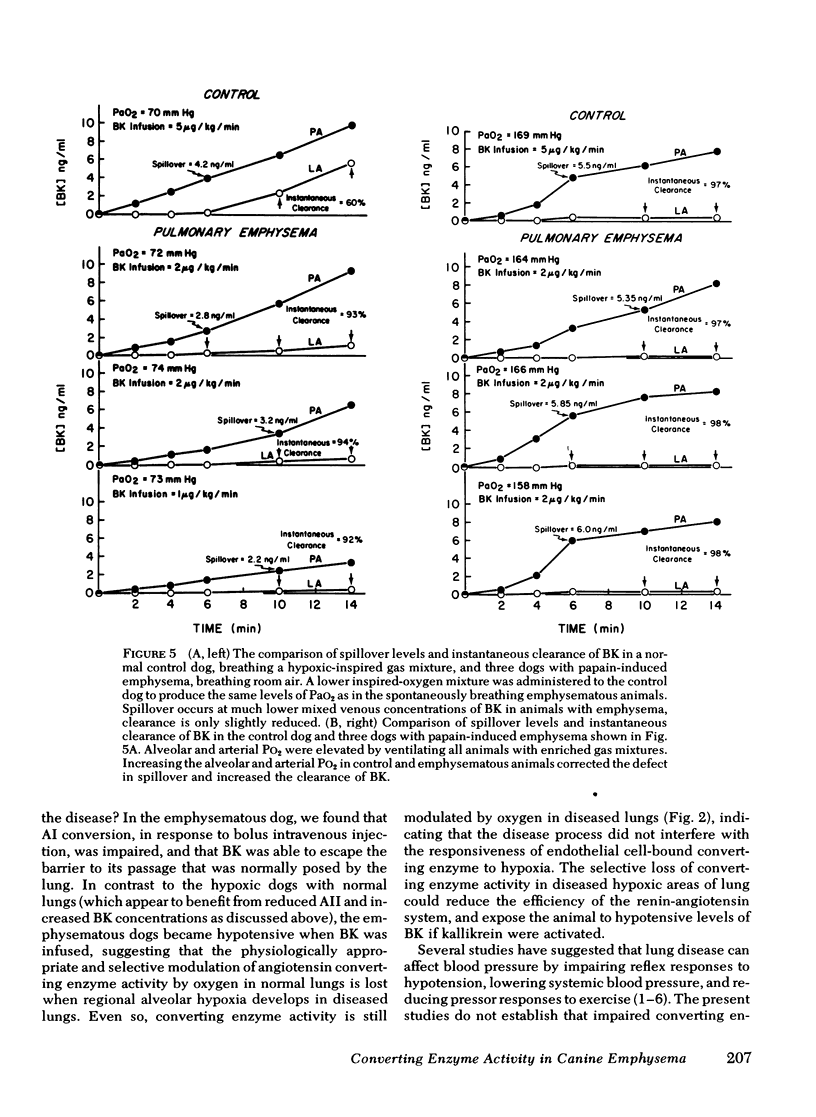
Chronic hypoxic lung diseases are associated with abnormal blood pressure regulation. Because the lung is the principal site of angiotensin conversion and because hypoxia decreases converting enzyme activity, we examined whether angiotensin converting enzyme activity was impaired in lung disease. 12 dogs received a 6 wk course of aerosolized and intratracheal papain that produced moderate panlobular emphysema. These dogs and 24 control dogs were anesthetized and sampling catheters were placed under fluoroscopic control. Angiotensin conversion was measured by a blood pressure response bioassay. Pulmonary converting enzyme activity was also assessed by infusing bradykinin (BK) and using radioimmunoassay to measure the instantaneous clearance of BK and the concentration of BK in the pulmonary artery which first produced spillover of BK into left atrial blood. Angiotensin conversion was reduced in the emphysematous dogs to 81.1% (13.2 SD) from 92% (6 SD) in the control dogs (P < 0.01). Instantaneous clearance of BK in the emphysematous dogs was only slightly reduced (93%), despite reduction in their Pao2 to 75 mm Hg, indicating that the greatest proportion of the perfused vascular bed was exposed to alveolar Po2 of >90 mm Hg. However, the barrier to BK passage provided by the lung, and measured by the spillover level, was reduced ¼ to ½ that observed in control animals. That the defect was promptly corrected by supplemental oxygen indicates that regional pulmonary vascular converting enzyme activity had been impaired by regional alveolar hypoxia, which permitted some peptide to pass through the lungs unmetabolized. Determination of peptide metabolism in the lungs may provide a useful measure of regional alveolar hypoxia and may lead to new ways of assessing lung injury.
Full text
PDF

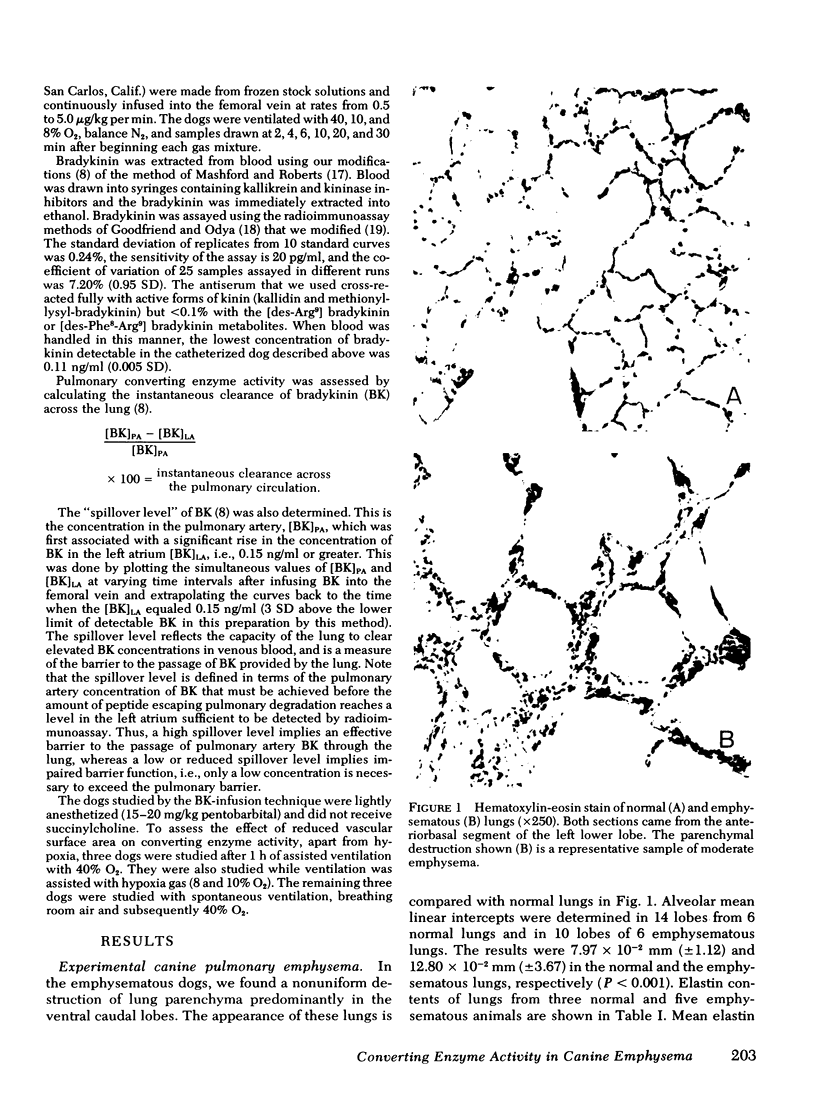
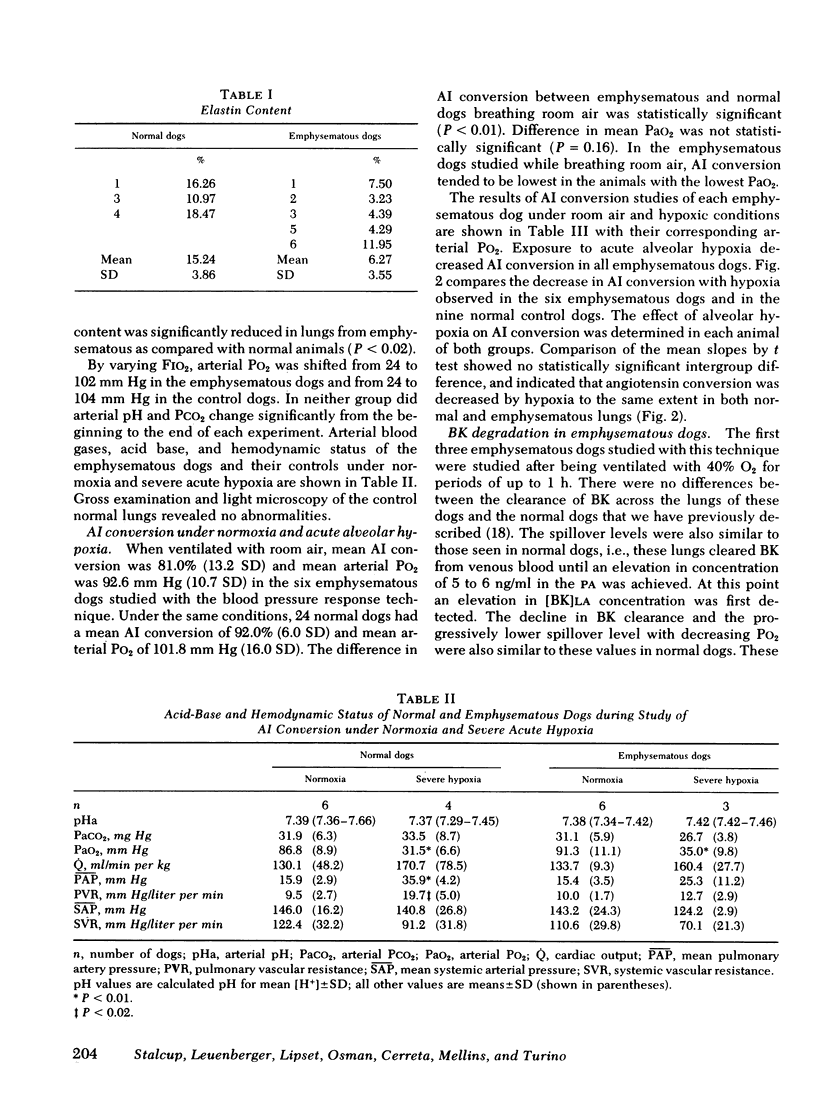
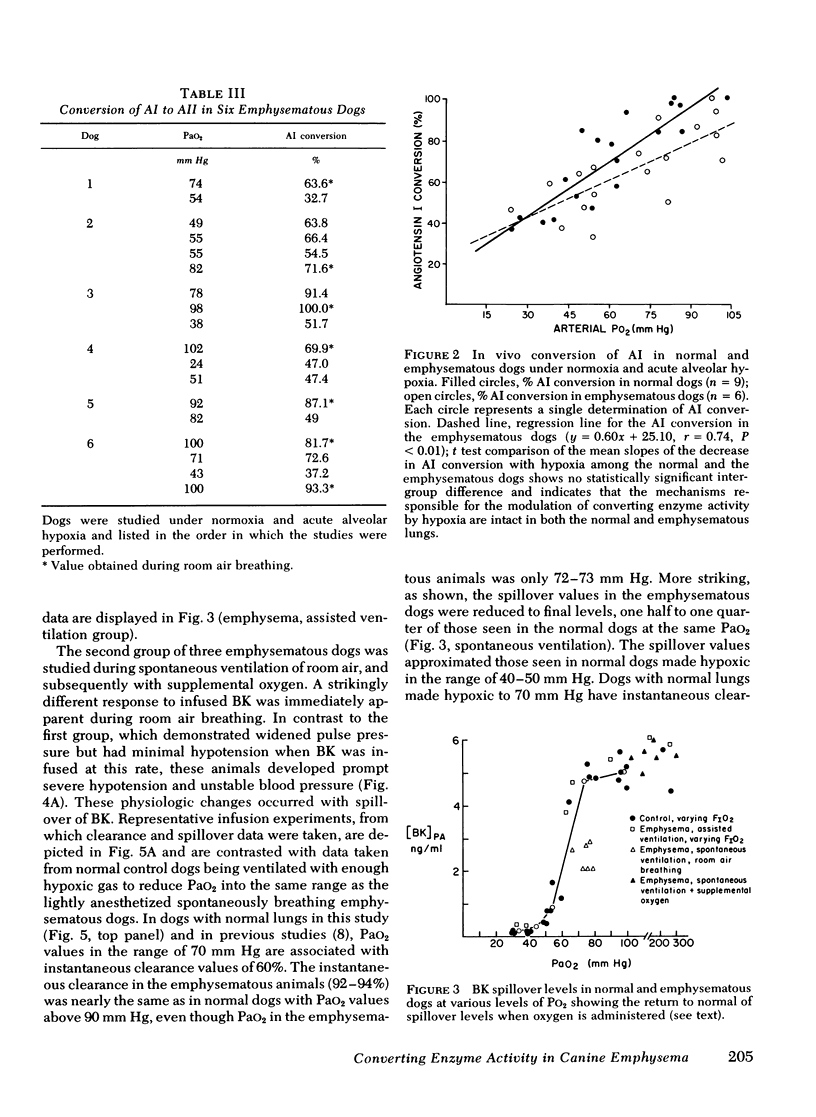



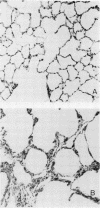
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson A. E., Jr, Bedrossian C. W., Foraker A. G. Systemic blood pressure in subjects with and without emphysema. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1971 Apr;103(4):576–578. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1971.103.4.576. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biron P., Meyer P., Panisset J. C. Removal of angiotensins from the systemic circulation. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1968 Mar;46(2):175–178. doi: 10.1139/y68-029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohn J. N., Luria M. H. Studies in clinical shock and hypotension. IV. Variations in reflex vasoconstriction and cardiac stimulation. Circulation. 1966 Nov;34(5):823–832. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.34.5.823. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedli B., Kent G., Olley P. M. Inactivation of bradykinin in the pulmonary vascular bed of newborn and fetal lambs. Circ Res. 1973 Oct;33(4):421–427. doi: 10.1161/01.res.33.4.421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg N. D., Haddox M. K., Nicol S. E., Glass D. B., Sanford C. H., Kuehl F. A., Jr, Estensen R. Biologic regulation through opposing influences of cyclic GMP and cyclic AMP: the Yin Yang hypothesis. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1975;5:307–330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammill S. C., Wagner W. W., Jr, Latham L. P., Frost W. W., Weil J. V. Autonomic cardiovascular control during hypoxia in the dog. Circ Res. 1979 Apr;44(4):569–575. doi: 10.1161/01.res.44.4.569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heistad D. D., Abboud F. M., Mark A. L., Schmid P. G. Impaired reflex vasoconstriction in chronically hypoxemic patients. J Clin Invest. 1972 Feb;51(2):331–337. doi: 10.1172/JCI106818. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heistad D. D., Wheeler R. C., Aoki V. S. Reflex cardiovascular responses after 36 hr of hypoxia. Am J Physiol. 1971 Jun;220(6):1673–1676. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.220.6.1673. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heistad D. D., Wheeler R. C. Effect of acute hypoxia on vascular responsiveness in man. I. Responsiveness to lower body negative pressure and ice on the forehead. II. Responses to norepinephrine and angiotensin. 3. Effect of hypoxia and hypocapnia. J Clin Invest. 1970 Jun;49(6):1252–1265. doi: 10.1172/JCI106338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leuenberger P. J., Stalcup S. A., Greenbaum L. M., Mellins R. B., Turino G. M. Angiotensin I conversion and vascular reactivity in pathophysiological states in dogs. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1980 Feb;48(2):308–312. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1980.48.2.308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leuenberger P. J., Stalcup S. A., Mellins R. B., Greenbaum L. M., Turino G. M. Decrease in angiotensin I conversion by acute hypoxia in dogs. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1978 Sep;158(4):586–589. doi: 10.3181/00379727-158-40252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieberman J., Rodbard S. Low blood pressure in young adults with cystic fibrosis: an effect of chronic salt loss in sweat? Ann Intern Med. 1975 Jun;82(6):806–808. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-82-6-806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marco V., Meranze D. R., Yoshida M., Kimbel P. Papain-induced experimental emphysema in the dog. J Appl Physiol. 1972 Sep;33(3):293–299. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1972.33.3.293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mashford M. L., Roberts M. L. Determination of blood kinin levels by radioimmunoassay. Biochem Pharmacol. 1972 Oct 15;21(20):2727–2735. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(72)90021-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messina E. J., Weiner R., Kaley G. Prostaglandins and local circulatory control. Fed Proc. 1976 Oct;35(12):2367–2375. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pushpakom R., Hogg J. C., Woolcock A. J., Angus A. E., Macklem P. T., Thurlbeck W. M. Experimental papain-induced emphysema in dogs. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1970 Nov;102(5):778–789. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1970.102.5.778. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothschild A. M., Gomes J. C., Castania A. Adrenergic and cholinergic control of the activation of the kalli-krein-kinin system in the rat blood. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1976;70(00):197–200. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-3267-1_24. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan J. W., Ryan U. S. Pulmonary endothelial cells. Fed Proc. 1977 Dec;36(13):2683–2691. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stalcup S. A., Lipset J. S., Legant P. M., Leuenberger P. J., Mellins R. B. Inhibition of converting enzyme activity by acute hypoxia in dogs. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1979 Feb;46(2):227–234. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1979.46.2.227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stalcup S. A., Lipset J. S., Woan J. M., Leuenberger P., Mellins R. B. Inhibition of angiotensin converting enzyme activity in cultured endothelial cells by hypoxia. J Clin Invest. 1979 May;63(5):966–976. doi: 10.1172/JCI109397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar] [Retracted]
- Stalcup S. A., Pang L. M., Lipset J. S., Odya C. E., Goodfriend T. L., Mellins R. B. Gestational changes in pulmonary converting enzyme activity in the fetal rabbit. Circ Res. 1978 Nov;43(5):705–711. doi: 10.1161/01.res.43.5.705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sylvester J. T., Scharf S. M., Gilbert R. D., Fitzgerald R. S., Traystman R. J. Hypoxic and CO hypoxia in dogs: hemodynamics, carotid reflexes, and catecholamines. Am J Physiol. 1979 Jan;236(1):H22–H28. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1979.236.1.H22. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thurlbeck W. M. Measurement of pulmonary emphysema. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1967 May;95(5):752–764. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1967.95.5.752. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueda H., Yasuda H., Takabatake Y., Iizuka M., Iizuka T. Observations on the mechanism of renin release by catecholamines. Circ Res. 1970 Oct;27(Suppl):195+–195+. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zakheim R. M., Molteni A., Mattioli L., Park M. Plasma angiotensin II levels in hypoxic and hypovolemic stress in unanesthetized rabbits. J Appl Physiol. 1976 Oct;41(4):462–465. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1976.41.4.462. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]