Abstract
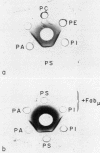
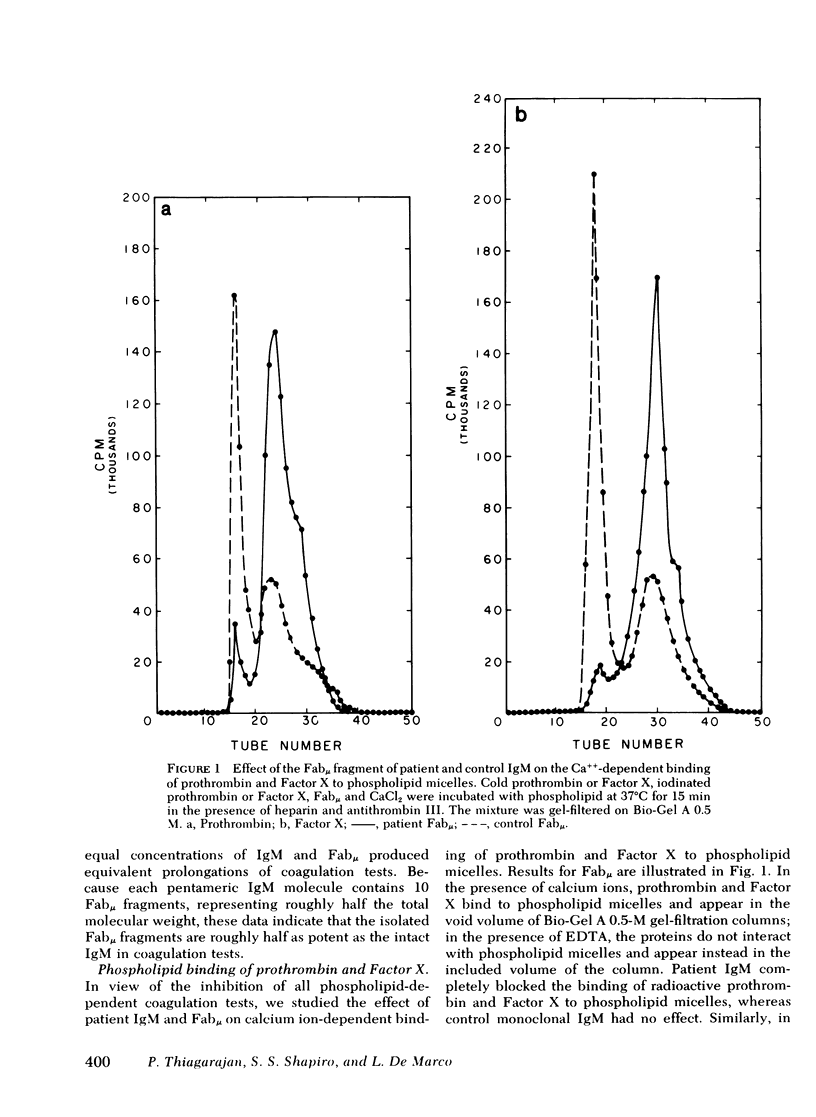
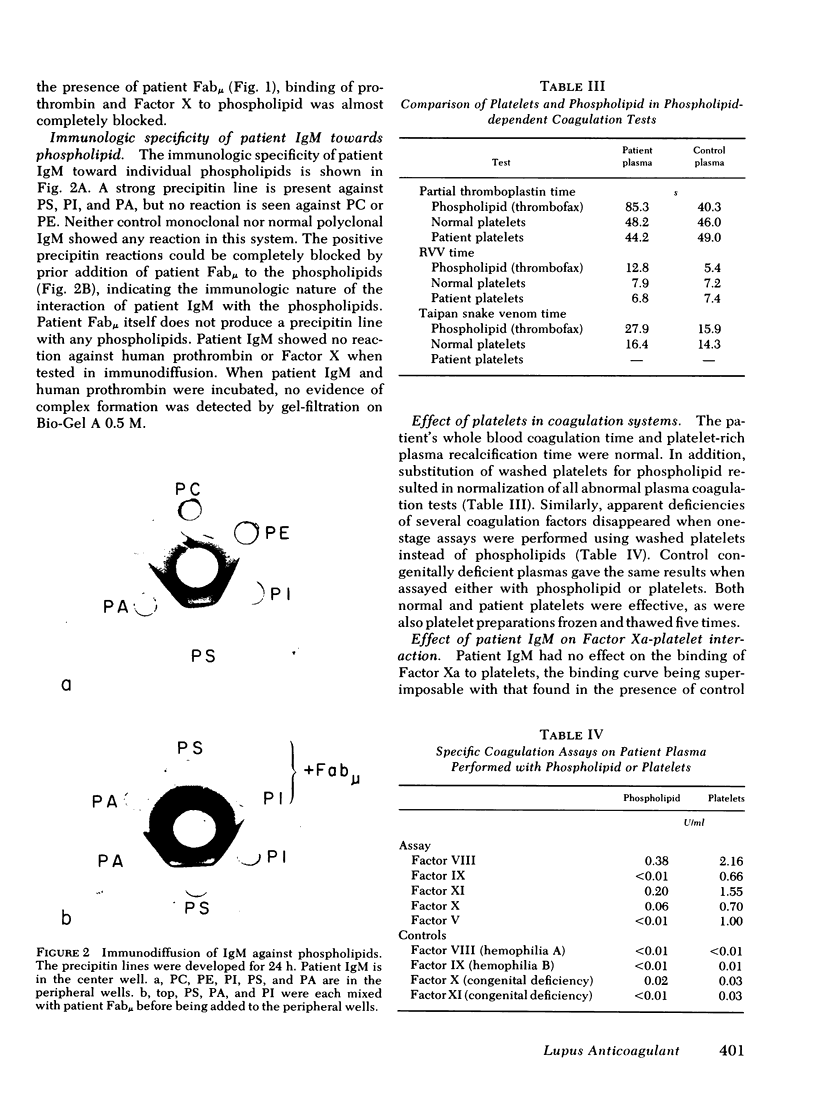
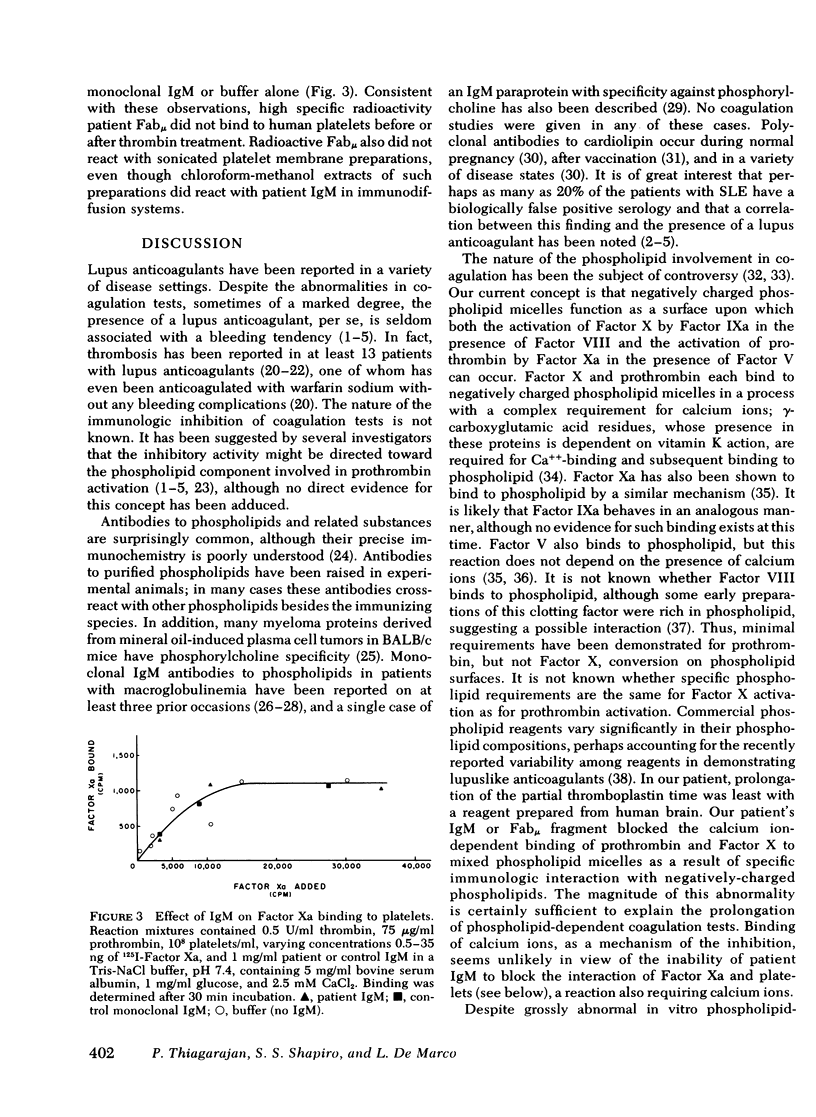
Prolongation of all phospholipid-dependent coagulation tests was found in a patient with macroglobulinemia, despite absence of bleeding manifestations. The purified monoclonal IgM lambda protein and its Fabmu tryptic fragment induced similar changes in normal plasma. Patient IgM and Fabmu completely inhibited Ca++-dependent binding of radiolabeled prothrombin and Factor X to mixed phospholipid micelles. The patient's IgM lambda paraprotein reacted with phosphatidylserine and, to a lesser extent, with phosphatidylinositol and phosphatidic acid, but not with phosphatidylcholine or phosphatidylethanolamine. Prior incubation of phospholipid with patient Fabmu blocked the positive reactions. Substitution of washed platelets for phospholipid led to normalization of patient coagulation tests and corrected all abnormalities produced in normal plasma by patient IgM. Furthermore, binding of 125I-Factor Xa to thrombin-treated platelets was entirely normal in the presence of patient IgM. These studies support the concept that platelets, rather than phospholipid micelles, are the primary locus of prothrombin and Factor X activation in normal hemostasis.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BELL W. N., ALTON H. G. A brain extract as a substitute for platelet suspensions in the thromboplastin generation test. Nature. 1954 Nov 6;174(4436):880–881. doi: 10.1038/174880a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOWIE E. J., THOMPSON J. H., Jr, PASCUZZI C. A., OWEN C. A., Jr THROMBOSIS IN SYSTEMIC LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS DESPITE CIRCULATING ANTICOAGULANTS. J Lab Clin Med. 1963 Sep;62:416–430. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom J. W., Nesheim M. E., Mann K. G. Phospholipid-binding properties of bovine factor V and factor Va. Biochemistry. 1979 Oct 2;18(20):4419–4425. doi: 10.1021/bi00587a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper M. R., Cohen H. J., Huntley C. C., Waite B. M., Spees L., Spurr C. L. A monoclonal IgM with antibodylike specificity for phospholipids in a patient with lymphoma. Blood. 1974 Apr;43(4):493–504. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drusin L. M., Litwin S. D., Armstrong D., Webster B. P. Waldenström's macroglobulinemia in a patient with a chronic biologic false-positive serologic test for syphilis. Am J Med. 1974 Mar;56(3):429–432. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(74)90626-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esmon C. T., Owen W. G., Duiguid D. L., Jackson C. M. The action of thrombin on blood clotting factor V: conversion of factor V to a prothrombin-binding protein. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 May 17;310(1):289–294. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(73)90034-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinstein D. I., Rapaport S. I. Acquired inhibitors of blood coagulation. Prog Hemost Thromb. 1972;1:75–95. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franza B. R., Jr, Aronson D. L. Detection and measurement of low levels of prothrombin. Use of a procoagulant from Echis carinatus venom. Thromb Res. 1976 Mar;8(3):329–336. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(76)90026-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franza B. R., Jr, Aronson D. L., Finlayson J. S. Activation of human prothrombin by a procoagulant fraction from the venom of Echis carinatus. Identification of a high molecular weight intermediate with thrombin activity. J Biol Chem. 1975 Sep 10;250(17):7057–7068. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gisler R., Pillot J. Activite anticardiolipide liée à un complexe macroglobuline de Waldenström-IgG cryoprécipitant. Immunochemistry. 1968 Nov;5(6):543–555. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(68)90090-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gitel S. N., Owen W. G., Esmon C. T., Jackson C. M. A polypeptide region of bovine prothrombin specific for binding to phospholipids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 May;70(5):1344–1348. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.5.1344. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordesky S. E., Marinetti G. V. The asymetric arrangement of phospholipids in the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Feb 20;50(4):1027–1031. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)91509-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg A. J., Trevor A. J., Johnson D. A., Loh H. H. Immunochemical studies of phospholipids: production of antibodies to triphosphoinositide. Mol Immunol. 1979 Mar;16(3):193–196. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(79)90145-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kane W. H., Lindhout M. J., Jackson C. M., Majerus P. W. Factor Va-dependent binding of factor Xa to human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1980 Feb 10;255(3):1170–1174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lechner K. Acquired inhibitors in nonhemophilic patients. Haemostasis. 1974;3(2):65–93. doi: 10.1159/000214043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARGOLIUS A., Jr, JACKSON D. P., RATNOFF O. D. Circulating anticoagulants: a study of 40 cases and a review of the literature. Medicine (Baltimore) 1961 May;40:145–202. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mannucci P. M., Canciani M. T., Mari D., Meucci P. The varied sensitivity of partial thromboplastin and prothrombin time reagents in the demonstration of the lupus-like anticoagulant. Scand J Haematol. 1979 May;22(5):423–432. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1979.tb00440.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manoharan A., Gibson L., Rush B., Feery B. J. Recurrent venous thrombosis with a "lupus" coagulation inhibitor in the absence of systemic lupus. Aust N Z J Med. 1977 Aug;7(4):422–426. doi: 10.1111/j.1445-5994.1977.tb04410.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus A. J. The role of lipids in blood coagulation. Adv Lipid Res. 1966;4:1–37. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus A. J., Zucker-Franklin D., Safier L. B., Ullman H. L. Studies on human platelet granules and membranes. J Clin Invest. 1966 Jan;45(1):14–28. doi: 10.1172/JCI105318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miletich J. P., Jackson C. M., Majerus P. W. Interaction of coagulation factor Xa with human platelets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):4033–4036. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.4033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miletich J. P., Jackson C. M., Majerus P. W. Properties of the factor Xa binding site on human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1978 Oct 10;253(19):6908–6916. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miletich J. P., Kane W. H., Hofmann S. L., Stanford N., Majerus P. W. Deficiency of factor Xa-factor Va binding sites on the platelets of a patient with a bleeding disorder. Blood. 1979 Nov;54(5):1015–1022. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miletich J. P., Majerus D. W., Majerus P. W. Patients with congenital factor V deficiency have decreased factor Xa binding sites on their platelets. J Clin Invest. 1978 Oct;62(4):824–831. doi: 10.1172/JCI109194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueh J. R., Herbst K. D., Rapaport S. I. Thrombosis in patients with the lupus anticoagulant. Ann Intern Med. 1980 Feb;92(2 Pt 1):156–159. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-92-2-156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nesheim M. E., Taswell J. B., Mann K. G. The contribution of bovine Factor V and Factor Va to the activity of prothrombinase. J Biol Chem. 1979 Nov 10;254(21):10952–10962. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Op den Kamp J. A. Lipid asymmetry in membranes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:47–71. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.000403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepper D. S., Prowse C. Chromatography of human prothrombin complex or dextran sulphate agarose. Thromb Res. 1977 Nov;11(5):687–692. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(77)90026-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plaut A. G., Tomasi T. B., Jr Immunoglobulin M: pentameric Fcmu fragments released by trypsin at higher temperatures. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Feb;65(2):318–322. doi: 10.1073/pnas.65.2.318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter M. Immunoglobulin-producing tumors and myeloma proteins of mice. Physiol Rev. 1972 Jul;52(3):631–719. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1972.52.3.631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riesen W., Rudikoff S., Oriol R., Potter M. An IgM Waldenström with specificity against phosphorylcholine. Biochemistry. 1975 Mar 11;14(5):1052–1057. doi: 10.1021/bi00676a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg J. S., McKenna P. W., Rosenberg R. D. Inhibition of human factor IXa by human antithrombin. J Biol Chem. 1975 Dec 10;250(23):8883–8888. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPAET T. H., CINTRON J. STUDIES ON PLATELET FACTOR-3 AVAILABILITY. Br J Haematol. 1965 May;11:269–275. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1965.tb06587.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schick P. K., Kurica K. B., Chacko G. K. Location of phosphatidylethanolamine and phosphatidylserine in the human platelet plasma membrane. J Clin Invest. 1976 May;57(5):1221–1226. doi: 10.1172/JCI108390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schleider M. A., Nachman R. L., Jaffe E. A., Coleman M. A clinical study of the lupus anticoagulant. Blood. 1976 Oct;48(4):499–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro S. S., Martinez J. Human prothrombin metabolism in normal man and in hypocoagulable subjects. J Clin Invest. 1969 Jul;48(7):1292–1298. doi: 10.1172/JCI106095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro S. S., Waugh D. F. The purification of human prothrombin. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1966 Dec 1;16(3):468–490. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw J. M., Moore N. F., Patzer E. J., Correa-Freire M. C., Wagner R. R., Thompsom T. E. Compositional asymmetry and transmembrane movement of phosphatidylcholine in vesicular stomatitis virus membranes. Biochemistry. 1979 Feb 6;18(3):538–543. doi: 10.1021/bi00570a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenflo J. Vitamin K, prothrombin, and gamma-carboxyglutamic acid. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1978;46:1–31. doi: 10.1002/9780470122914.ch1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subbaiah P. V., Bajwa S. S., Smith C. M., Hanahan D. J. Interactions of the components of the prothrombinase complex. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Aug 24;444(1):131–146. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(76)90230-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tollefsen D. M., Jackson C. M., Majerus P. W. Binding of the products of prothrombin activation to human platelets. J Clin Invest. 1975 Jul;56(1):241–245. doi: 10.1172/JCI108075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracy P. B., Peterson J. M., Nesheim M. E., McDuffie F. C., Mann K. G. Interaction of coagulation factor V and factor Va with platelets. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 25;254(20):10354–10361. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veltkamp J. J., Kerkhoven P., Loeliger E. A. Circulating anticoagulant in disseminated lupus erythematosus. Proposed mode of action. Haemostasis. 1973;2(6):253–259. doi: 10.1159/000214029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zwaal R. F. Membrane and lipid involvement in blood coagulation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Jul 31;515(2):163–205. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(78)90003-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]