Abstract
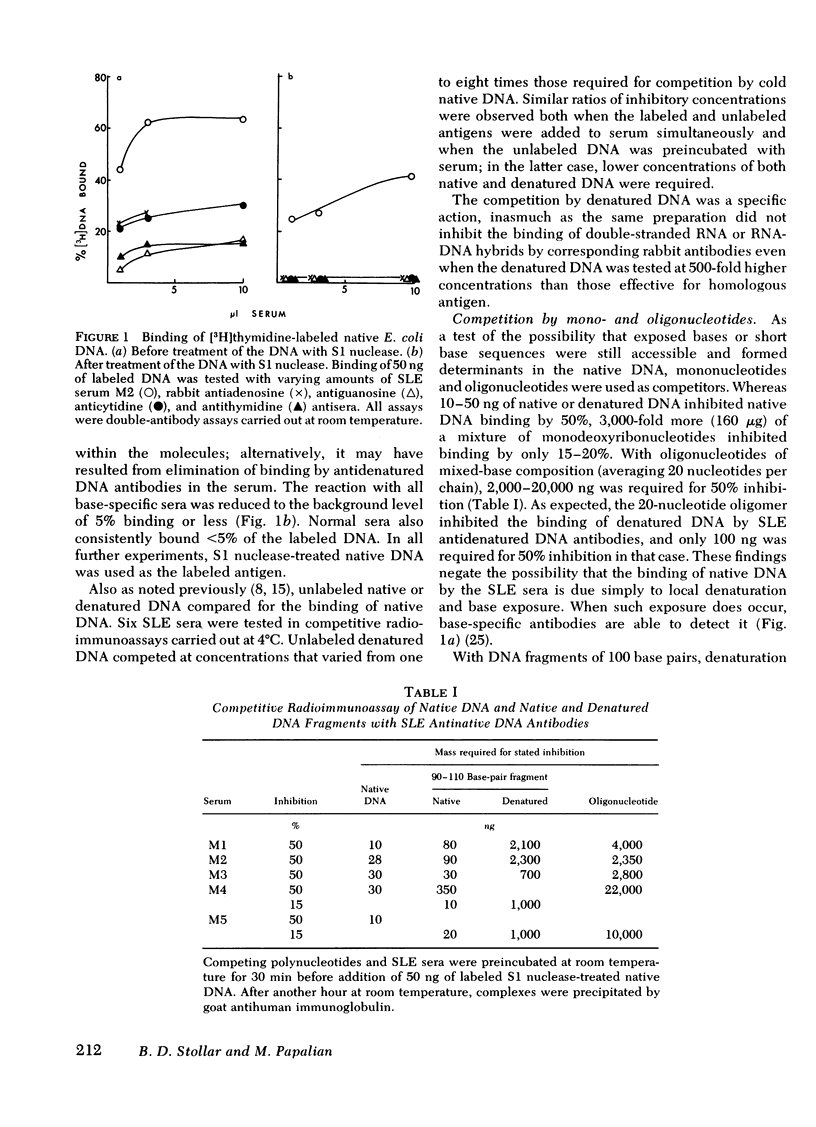
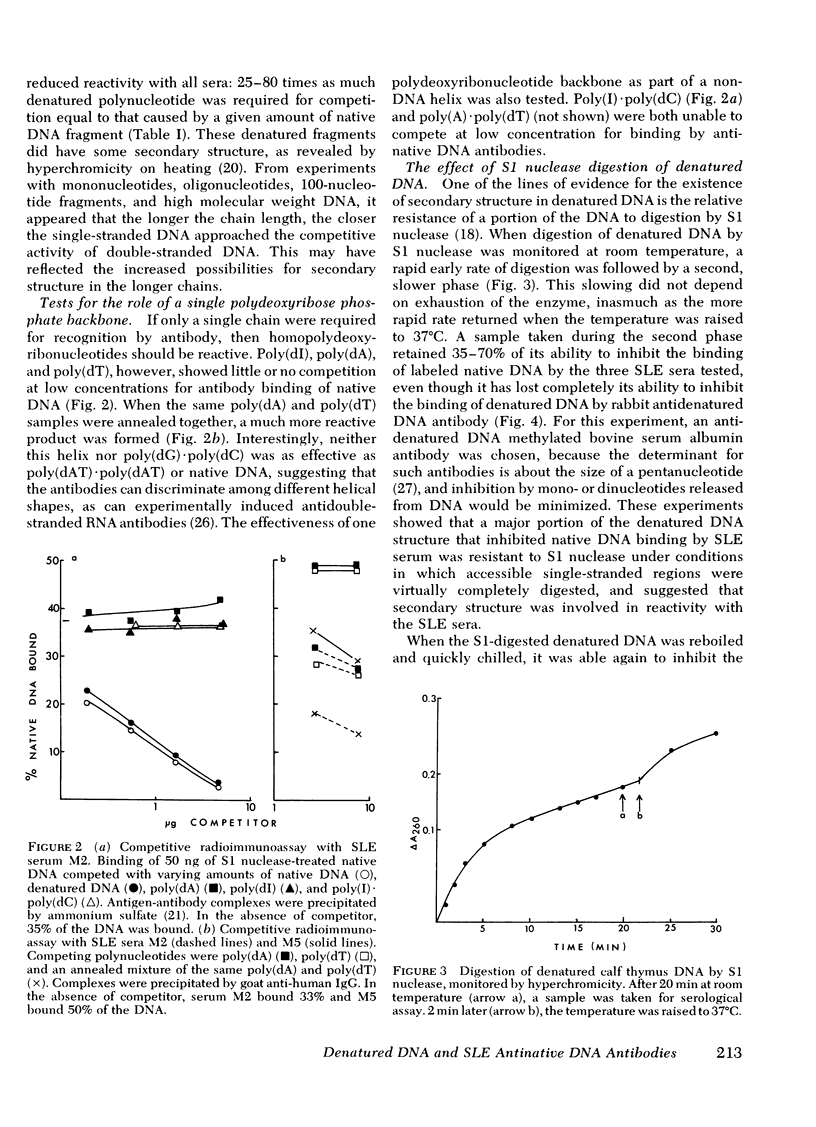
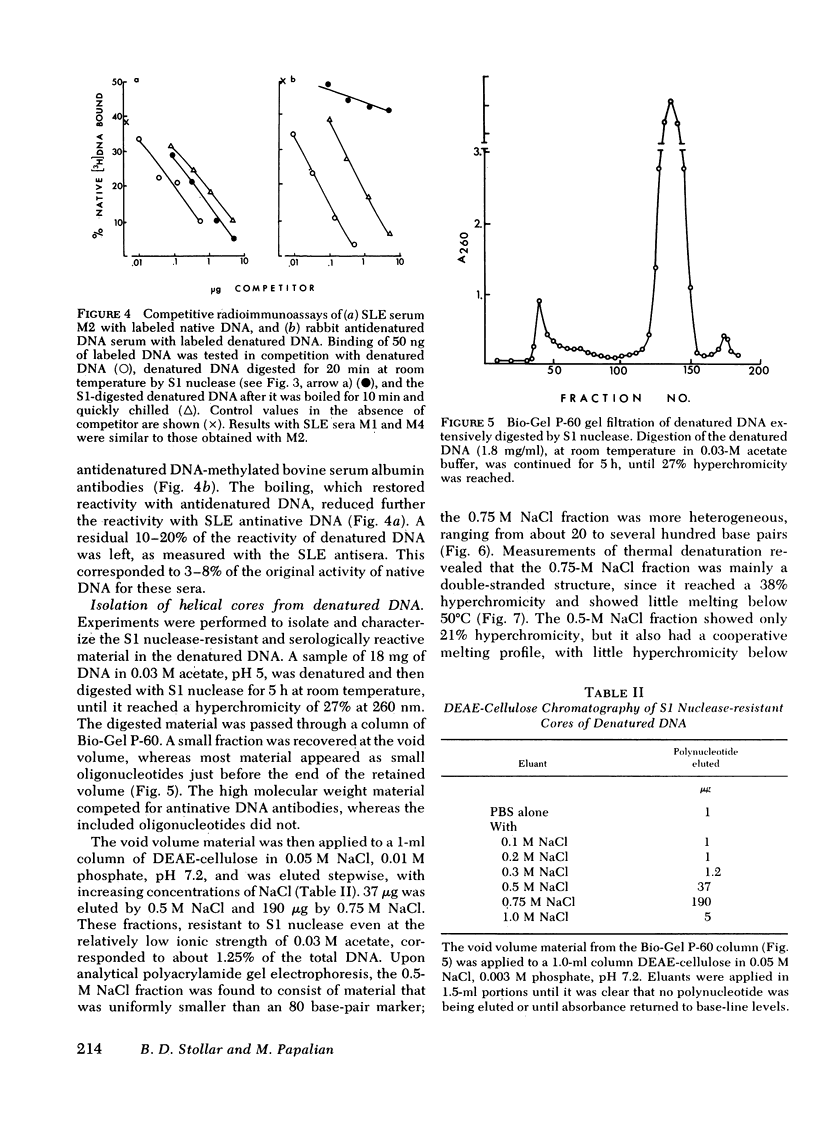
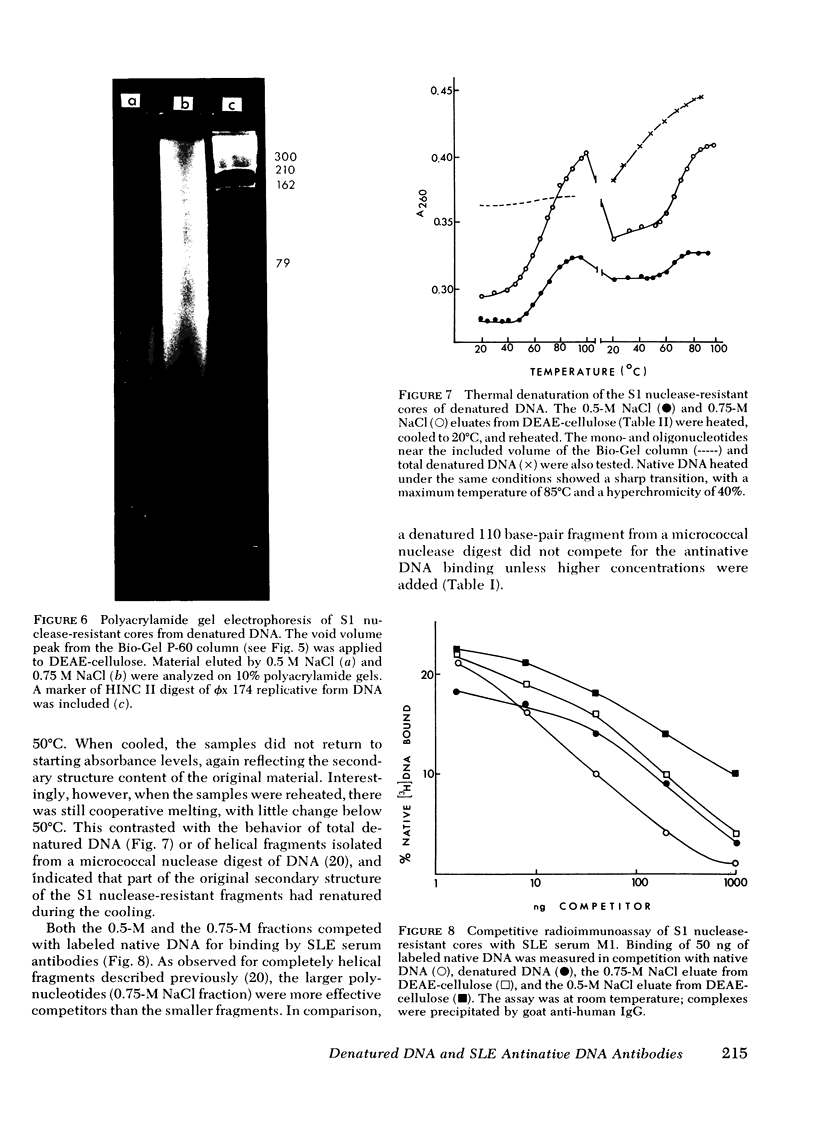
Experiments were designed to determine the basis for the strong competitive reaction of denatured DNA with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) antinative DNA antibodies. Secondary structure in denatured DNA was reflected in hyperchromicity upon heating and in multiphase kinetics of its digestion by S1 nuclease. Partial digestion by S1 nuclease completely eliminated the ability of denatured DNA to react with antidenatured DNA antibodies, but not its ability to react with SLE sera. S1 nuclease-resistant cores were isolated from extensively digested denatured DNA. These cores had secondary structure, including some stable fold-back helical regions. The cores, from 20 to several hundred base pairs in size, competed with native DNA for binding by SLE sera. Other experiments measured reactions of denatured DNA under conditions that affected its secondary structure content. Its competitive activity decreased as temperature was increased from 0° to 37°C, whereas the activity of native DNA was not altered in this temperature range. With DNA pieces of 90-110 base pairs, native fragments were much more effective than the denatured fragments, in which stable helical structure is less likely to occur than in high molecular weight denatured DNA. Competitive assays with mononucleotides, oligonucleotides, homopolymers, and RNA-DNA hybrids also indicated that two strands of polydeoxyribonucleotide were required for optimal reactions with these SLE serum antibodies. The antibodies can measure stable helical regions in denatured DNA; they may also stabilize short helical regions that occur in an equilibrium of conformational forms.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aarden L. A., Lakmaker F., De Groot E. R. Immunology of DNA. IV. Quantitative aspects of the Farr assay. J Immunol Methods. 1976;11(2):153–163. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(76)90143-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aarden L. A., de Groot E. R., Feltkamp T. E. Immunology of DNA. III. Crithidia luciliae, a simple substrate for the determination of anti-dsDNA with the immunofluorescence technique. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1975 Jun 30;254:505–515. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1975.tb29197.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adler M. K., Baumgarten A., Hecht B., Siegel N. J. Prognostic significance of DNA-binding capacity patterns in patients with lupus nephritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1975 Oct;34(5):444–450. doi: 10.1136/ard.34.5.444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ando T. A nuclease specific for heat-denatured DNA in isolated from a product of Aspergillus oryzae. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Jan 18;114(1):158–168. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(66)90263-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arana R., Seligmann M. Antibodies to native and denatured deoxyribonucleic acid in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Invest. 1967 Nov;46(11):1867–1882. doi: 10.1172/JCI105677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagchi B., Misra D. N., Basu S., Das Gupta N. N. Conformation of denatured and renatured DNA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Jun 17;182(2):551–561. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(69)90207-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell C., Talal N., Schur P. H. Antibodies to DNA in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1975 Nov-Dec;18(6):535–540. doi: 10.1002/art.1780180602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blakesley R. W., Dodgson J. B., Nes I. F., Wells R. D. Duplex regions in "single-stranded" phiX174 DNA are cleaved by a restriction endonuclease from Haemophilus aegyptius. J Biol Chem. 1977 Oct 25;252(20):7300–7306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ERLANGER B. F., BEISER S. M. ANTIBODIES SPECIFIC FOR RIBONUCLEOSIDES AND RIBONUCLEOTIDES AND THEIR REACTION WITH DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Jul;52:68–74. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.1.68. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiddes J. C., Barrell B. G., Godson G. N. Nucleotide sequences of the separate origins of synthesis of bacteriophage G4 viral and complementary DNA strands. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1081–1085. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furie B., Schechter A. N., Sachs D. H., Anfinsen C. B. An immunological approach to the conformational equilibrium of staphylococcal nuclease. J Mol Biol. 1975 Mar 15;92(4):497–506. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90305-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasselbacher P., LeRoy E. C. Serum DNA binding activity in healthy subjects and in rheumatic disease. Arthritis Rheum. 1974 Jan-Feb;17(1):63–71. doi: 10.1002/art.1780170110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes G. R., Cohen S. A., Christian C. L. Anti-DNA activity in systemic lupus erythematosus. A diagnostic and therapeutic guide. Ann Rheum Dis. 1971 May;30(3):259–264. doi: 10.1136/ard.30.3.259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izui S., Lambert P. H., Miescher P. A. Determination of anti-DNA antibodies by a modified 125I-labelled DNA-binding test. Elimination of non-specific binding of DNA to non-immunoglobulin basic proteins by using an anionic detergent. Clin Exp Immunol. 1976 Dec;26(3):425–430. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston M. I., Stollar B. D. Antigenic structure of double-stranded RNA analogues having varying activity in interferon induction. Biochemistry. 1978 May 16;17(10):1959–1964. doi: 10.1021/bi00603a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koffler D., Carr R., Agnello V., Thoburn R., Kunkel H. G. Antibodies to polynucleotides in human sera: antigenic specificity and relation to disease. J Exp Med. 1971 Jul 1;134(1):294–312. doi: 10.1084/jem.134.1.294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lightfoot R. W., Jr, Hughes G. R. Significance of persisting serologic abnormalities in SLE. Arthritis Rheum. 1976 Sep-Oct;19(5):837–843. doi: 10.1002/art.1780190501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin H. J., Lee C. L. Isolation of foldback DNA utilizing nuclease S1 digestion in aqueous dioxane. Anal Biochem. 1979 Jul 1;96(1):144–151. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90566-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Locker J. D., Medof M. E., Bennett R. M., Sukhupunyaraksa S. Characterization of DNA used to assay sera for anti-DNA antibodies; determination of the specificities of anti-DNA antibodies in SLE and non-SLE rheumatic disease states. J Immunol. 1977 Feb;118(2):694–701. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niyogi S. K., Mitra S. Isolation and characterization of naturally occurring hairpin structures in single-stranded DNA of coliphage M13. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Dec 21;79(4):1037–1044. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)91109-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PLESCIA O. J., BRAUN W., PALCZUK N. C. PRODUCTION OF ANTIBODIES TO DENATURED DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID (DNA). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Aug;52:279–285. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.2.279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papalian M., Lafer E., Wong R., Stollar B. D. Reaction of systemic lupus erythematosus antinative DNA antibodies with native DNA fragments from 20 to 1,200 base pairs. J Clin Invest. 1980 Feb;65(2):469–477. doi: 10.1172/JCI109690. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picazo J. J., Tan E. M. Specificities of antibodies to native DNA. Scand J Rheumatol Suppl. 1975;11:35–41. doi: 10.3109/03009747509095627. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pincus T., Schur P. H., Rose J. A., Decker J. L., Talal N. Measurement of serum DNA-binding activity in systemic lupus erythematosus. N Engl J Med. 1969 Sep 25;281(13):701–705. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196909252811304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaller H., Voss H., Gucker S. Structure of the DNA of bacteriophage fd. II. Isolation and characterization of a DNA fraction with double strand-like properties. J Mol Biol. 1969 Sep 28;44(3):445–458. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90372-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seaman E., Levine L., Van Vunakis H. Antibodies to the methylene blue sensitized photooxidation product in deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochemistry. 1966 Apr;5(4):1216–1223. doi: 10.1021/bi00868a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shishido K., Ando T. Estimation of the double-helical content in various single-stranded nucleic acids by treatment with a single strand-specific nuclease. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Dec 22;287(3):477–484. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(72)90292-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shishido K., Ikeda Y. Isolation of double-helical regions rich in guanine-cytosine base pairing from bacteriophage fl DNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Feb 5;42(3):482–489. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90396-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinman C. R., Deesomchok U., Spiera H. Detection of anti-DNA antibody using synthetic antigens. Characterization and clinical significance of binding of poly (deoxyadenylate-deoxythymidylate) by serum. J Clin Invest. 1976 May;57(5):1330–1341. doi: 10.1172/JCI108401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stollar B. D. The detections of anti-DNA and DNA/anti-DNA complexes. Scand J Rheumatol Suppl. 1975;11:7–11. doi: 10.3109/03009747509095623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stollar B. D. The specificity and applications of antibodies to helical nucleic acids. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1975 May;3(1):45–69. doi: 10.3109/10409237509102552. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teitelbaum H., Englander S. W. Open states in native polynucleotides. II. Hydrogen-exchange study of cytosine-containing double helices. J Mol Biol. 1975 Feb 15;92(1):79–92. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90092-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakizaka A., Okuhara E. Immunological studies on nucleic acids: an investigation of the antigenic determinants of denatured deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) reactive with rabbit anti-DNA antisera by a radioimmunoassay technique. Immunochemistry. 1975 Oct;12(10):843–845. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(75)90150-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]