Abstract
The method of producing experimental glucagon deficiency by administration of glucagon antiserum was evaluated in rats. A pool of antisera was prepared, the affinity of which exceeded that of the glucagon receptors of liver cell membranes, whereas the binding capacity of the volume used amounted to more than one-third of the total glucagon content in the rat pancreas. That rapid, extensive, and lasting neutralization of glucagon had taken place after antiserum treatment was indicated by the following findings: When examined more than 1 h after the injection and after 60 min of exercise-stimulated glucagon production, all rats had excess free antibodies in plasma. The concentration of free glucagon was lowered to one-third of the concentration in control rats; at 37°C plasma samples could bind 25% of additional 300 pmol/liter of glucagon in 10 s, and 69% in 120 s; the glycemic response to exogenous glucagon was abolished. Antiserum treatment, however, had no effect on blood glucose in rats fasted for 3 and 10 h, in chemically sympathectomized and adrenomedullectomized rats, and in 48-h-fasted, acutely adrenalectomized rats. The antiserum was found to contain 460 nmol/liter of antibody-bound glucagon, originating in the rabbit in which the antiserum was raised. However, antibody preparations from which the bound glucagon had been effectively removed were equally ineffective in lowering the basal blood glucose in rats, although in three-fourths of the rats the concentration of free glucagon was lowered beyond detection limit.
The data indicate that the absolute concentration of glucagon in plasma is of minor importance for the maintenance of basal blood glucose in the rat.
Full text
PDF
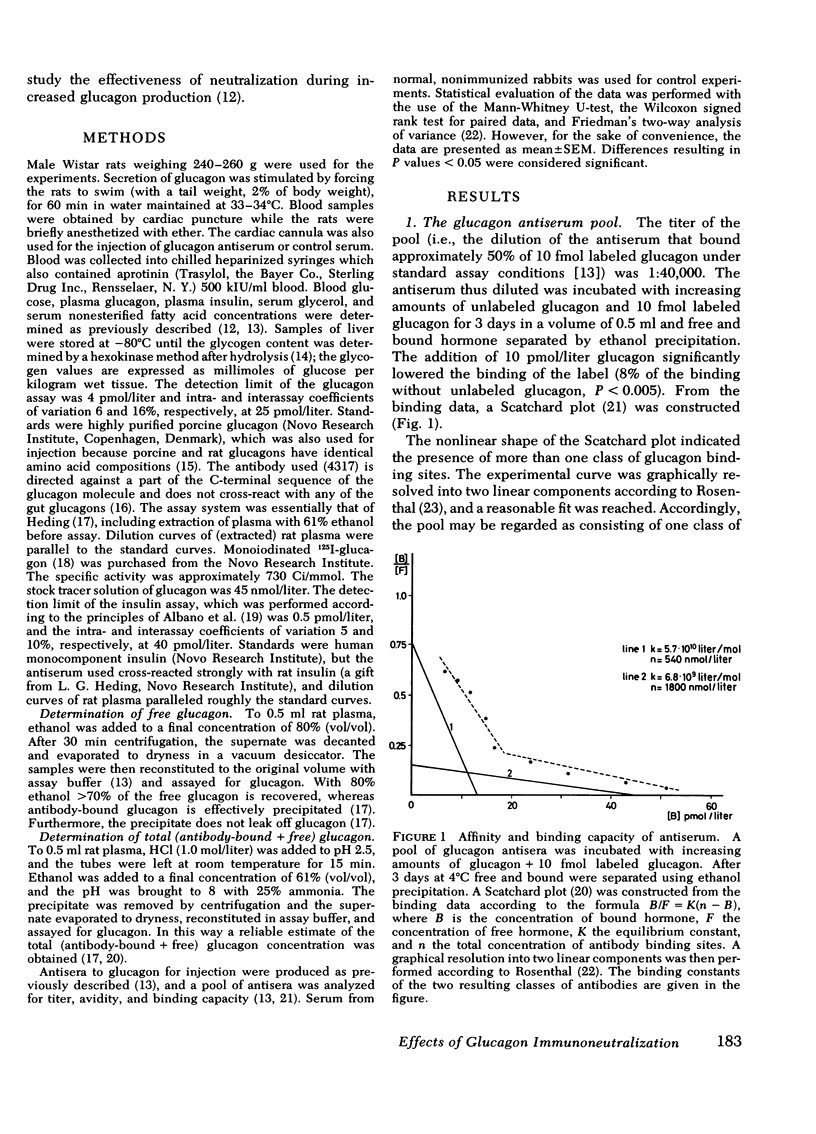
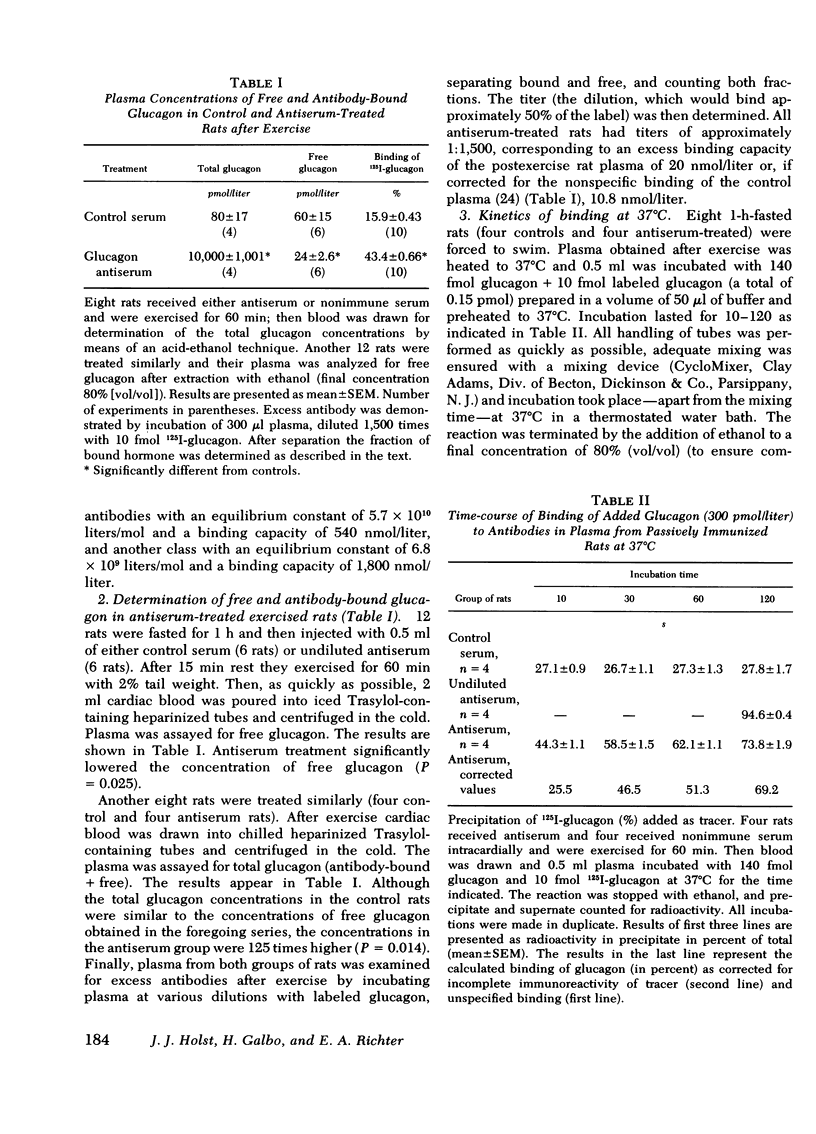
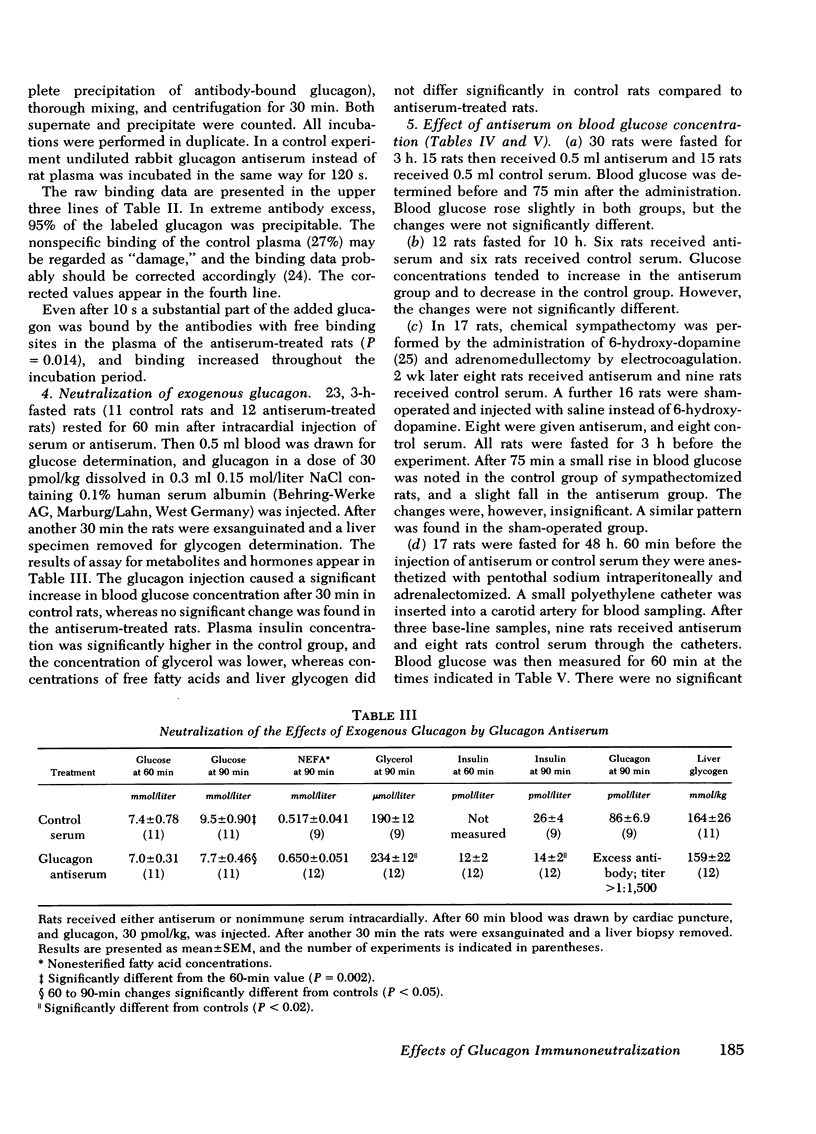
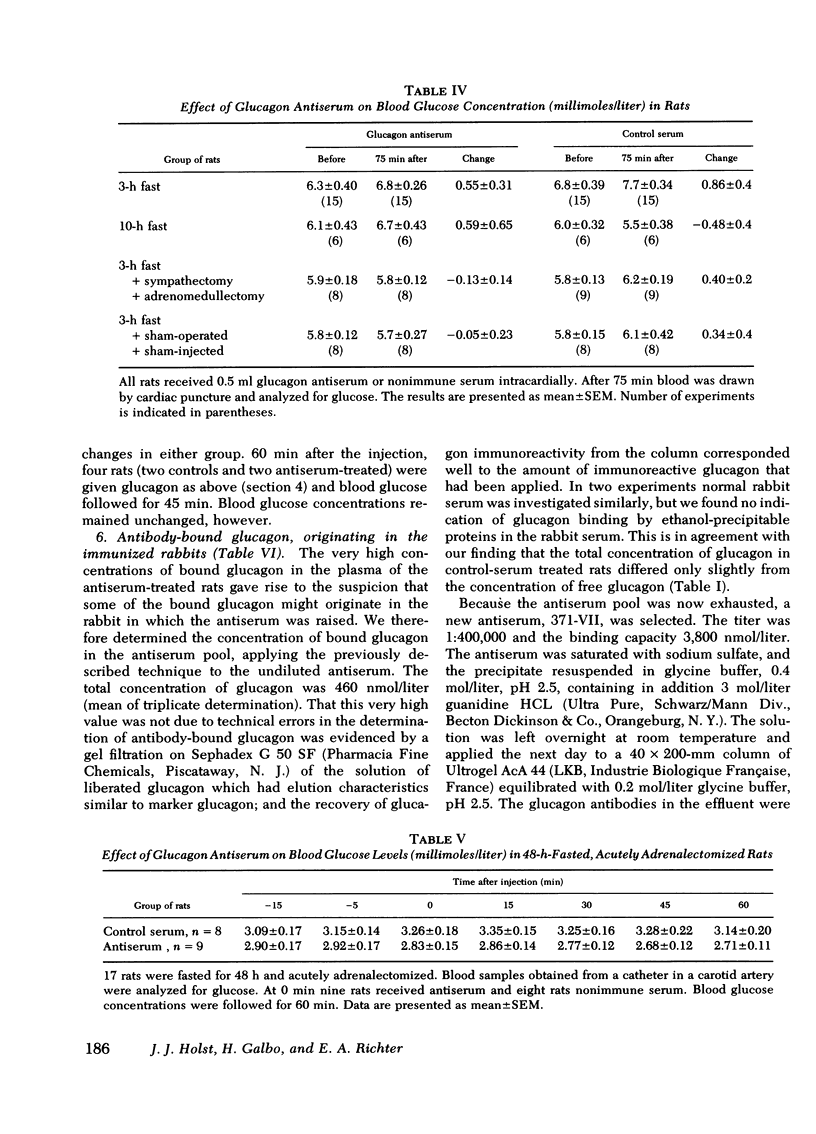



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albano J. D., Ekins R. P., Maritz G., Turner R. C. A sensitive, precise radioimmunoassay of serum insulin relying on charcoal separation of bound and free hormone moieties. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1972 Jul;70(3):487–509. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0700487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alford F. P., Bloom S. R., Nabarro J. D., Hall R., Besser G. M., Coy D. H., Kastin A. J., Schally A. V. Glucagon control of fasting glucose in man. Lancet. 1974 Oct 26;2(7887):974–977. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)92071-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barling P., Beloff-Chain A. Studies on the administration of glucagon and insulin antibodies to rats. Horm Metab Res. 1973 May;5(3):154–159. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1093962. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherrington A. D., Chiasson J. L., Liljenquist J. E., Jennings A. S., Keller U., Lacy W. W. The role of insulin and glucagon in the regulation of basal glucose production in the postabsorptive dog. J Clin Invest. 1976 Dec;58(6):1407–1418. doi: 10.1172/JCI108596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeVane G. W., Siler T. M., Yen S. S. Acute suppression of insulin and glucose levels by synthetic somatostatin in normal human subjects. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1974 May;38(5):913–915. doi: 10.1210/jcem-38-5-913. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobbs R., Sakurai H., Sasaki H., Faloona G., Valverde I., Baetens D., Orci L., Unger R. Glucagon: role in the hyperglycemia of diabetes mellitus. Science. 1975 Feb 14;187(4176):544–547. doi: 10.1126/science.1089999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards A. V., Silver M. Comparison of the hyperglycaemic and glycogenolytic responses to catecholamines with those to stimulation of the hepatic sympathetic innervation in the dog. J Physiol. 1972 Jun;223(2):571–593. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards A. V. The hyperglycaemic response to stimulation of the hepatic sympathetic innervation in adrenalectomized cats and dogs. J Physiol. 1972 Feb;220(3):697–710. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009730. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epand R. M., Douglas R. J. The effect of glucagon antibodies on plasma glucose and insulin levels. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Oct 5;320(3):741–744. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(73)90156-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felig P., Wahren J., Sherwin R., Hendler R. Insulin, glucagon, and somatostatin in normal physiology and diabetes mellitus. Diabetes. 1976 Dec;25(12):1091–1099. doi: 10.2337/diab.25.12.1091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frohman L. A., Reichlin M., Sokal J. E. Immunologic and biologic properties of antibodies to a glucagon-serum albumin polymer. Endocrinology. 1970 Nov;87(5):1055–1061. doi: 10.1210/endo-87-5-1055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galbo H., Holst J. J. The influence of glucagon on hepatic glycogen mobilization in exercising rats. Pflugers Arch. 1976 May 6;363(1):49–53. doi: 10.1007/BF00587401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerich J. E., Lorenzi M., Schneider V., Forsham P. H. Effect of somatostatin on plasma glucose and insulin responses to glucagon and tolbutamide in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1974 Dec;39(6):1057–1060. doi: 10.1210/jcem-39-6-1057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grey N., McGuigan J. E., Kipnis D. M. Neutralization of endogenous glucagon by high titer glucagon antiserum. Endocrinology. 1970 Jun;86(6):1383–1388. doi: 10.1210/endo-86-6-1383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heding L. G. Determination of total serum insulin (IRI) in insulin-treated diabetic patients. Diabetologia. 1972 Aug;8(4):260–266. doi: 10.1007/BF01225569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heding L. G. Radioimmunological determination of pancreatic and gut glucagon in plasma. Diabetologia. 1971 Feb;7(1):10–19. doi: 10.1007/BF02346248. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holst J. J., Aasted B. Production and evaluation of glucagon antibodies for radioimmunoassay. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1974 Dec;77(4):715–726. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0770715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen K. H., Larsen U. D. Purification of 125 I-glucagon by anion exchange chromatography. Horm Metab Res. 1972 May;4(3):223–224. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1097092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlsson J., Diamant B., Saltin B. Muscle metabolites during submaximal and maximal exercise in man. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1970 Dec;26(4):385–394. doi: 10.3109/00365517009046250. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOLONEY P. J., COVAL M. Antigenicity of insulin: diabetes induced by specific antibodies. Biochem J. 1955 Feb;59(2):179–185. doi: 10.1042/bj0590179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orskov H., Seyer-Hansen K. Measurement of and correction for incubation damage in radioimmunoassay. Eur J Clin Invest. 1974 Jun;4(3):207–211. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1974.tb00394.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodbell M., Krans H. M., Pohl S. L., Birnbaumer L. The glucagon-sensitive adenyl cyclase system in plasma membranes of rat liver. 3. Binding of glucagon: method of assay and specificity. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 25;246(6):1861–1871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal H. E. A graphic method for the determination and presentation of binding parameters in a complex system. Anal Biochem. 1967 Sep;20(3):525–532. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(67)90297-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundby F., Markussen J. Isolation, crystallization and amino acid composition of rat glucagon. Horm Metab Res. 1971 May;3(3):184–187. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1094153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thoenen H., Tranzer J. P. The pharmacology of 6-hydroxydopamine. Annu Rev Pharmacol. 1973;13:169–180. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.13.040173.001125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WRIGHT P. H. The production of experimental diabetes by means of insulin antibodies. Am J Med. 1961 Dec;31:892–900. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(61)90031-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


