Abstract
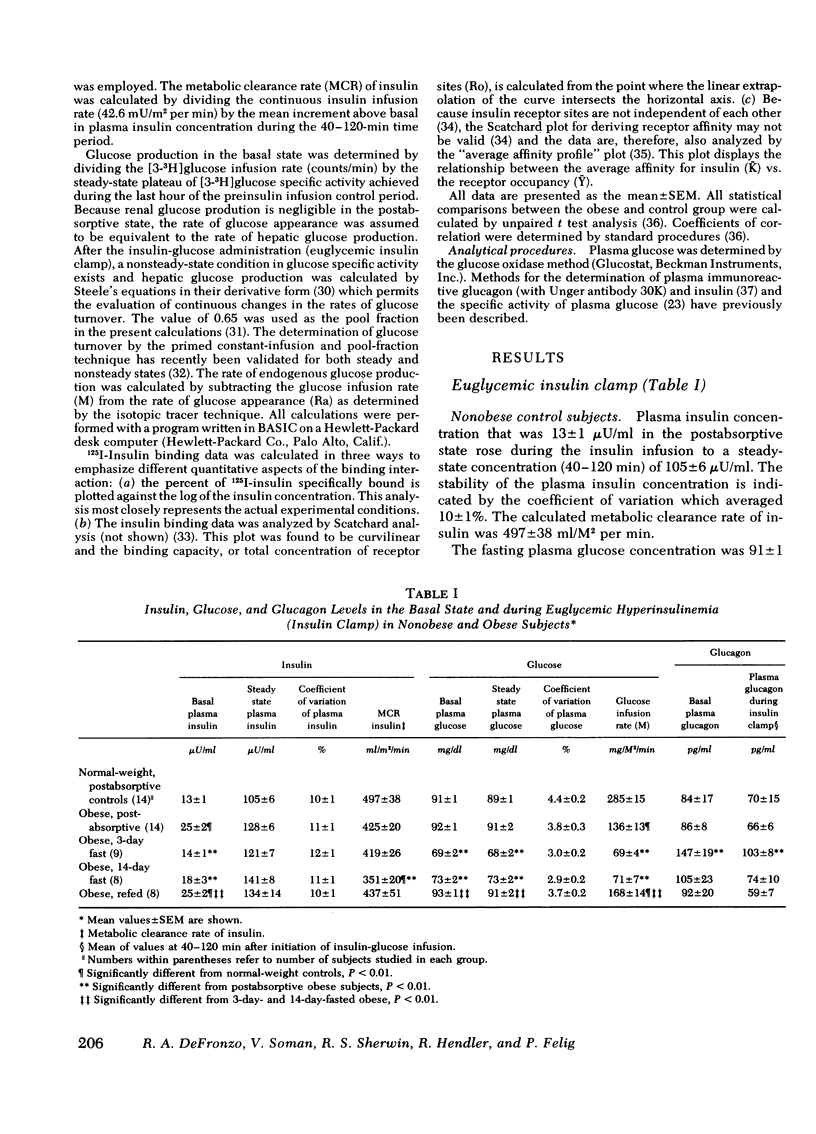
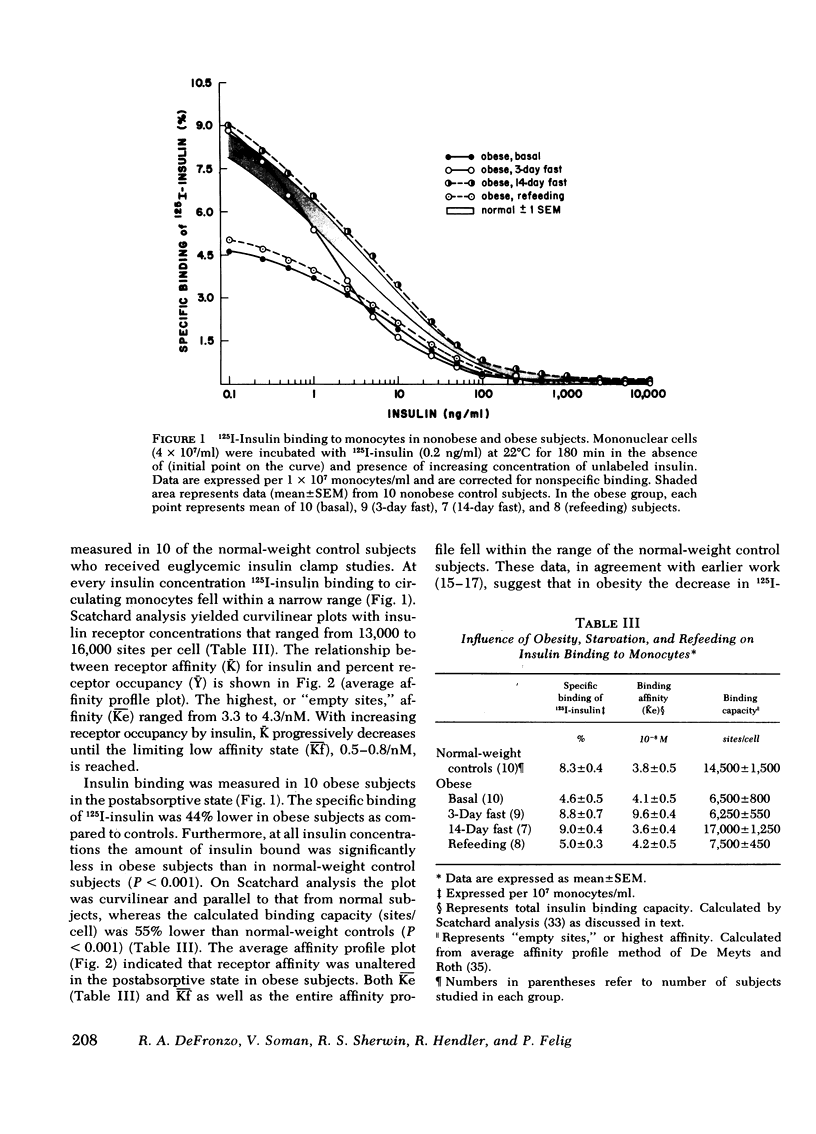
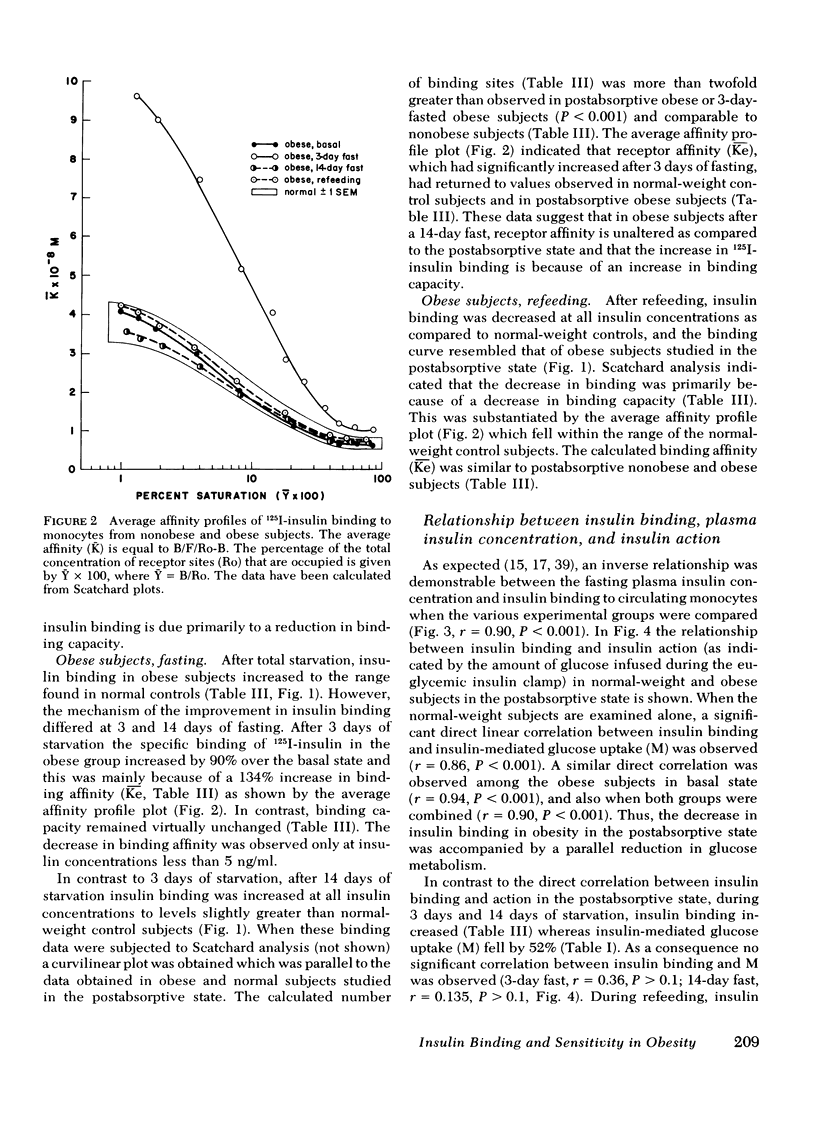
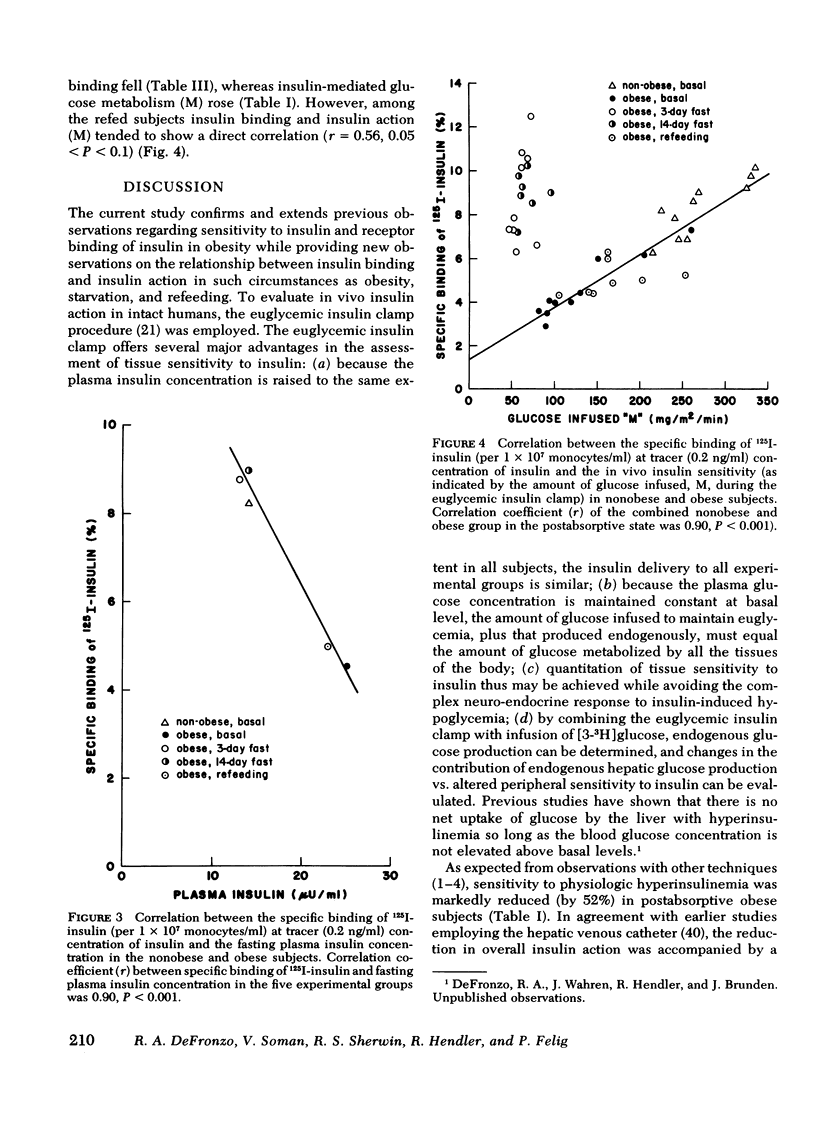
Insulin binding to monocytes and insulin action in vivo was examined in 14 obese subjects during the postabsorptive state and after starvation and refeeding. Tissue sensitivity to insulin was evaluated with the euglycemic insulin clamp technique. The plasma insulin concentration is acutely raised and maintained 100 μU/ml above the fasting level, and plasma glucose is held constant by a variable glucose infusion. The amount of glucose infused is a measure of tissue sensitivity to insulin and averaged 285±15 mg/m2 per min in controls compared to 136±13 mg/m2 per min in obese subjects (P <0.001). 125I-Insulin binding to monocytes averaged 8.3±0.4% in controls vs. 4.6±0.5% in obese subjects (P < 0.001). Insulin binding and insulin action were highly correlated in both control (r = 0.86, P < 0.001) and obese (r = 0.94, P < 0.001) groups. Studies employing tritiated glucose to measure glucose production indicated hepatic as well as extrahepatic resistance to insulin in obesity.
After 3 and 14 days of starvation, insulin sensitivity in obese subjects decreased to 69±4 and 71±7 mg/m2 per min, respectively, whereas 125I-insulin binding increased to 8.8±0.7 and 9.0±0.4%. In contrast to the basal state, there was no correlation between insulin binding and insulin action. After refeeding, tissue sensitivity increased to 168±14 mg/m2 per min (P < 0.001) whereas insulin binding fell to 5.0±0.3%.
We conclude that (a) in the postabsorptive state insulin binding to monocytes provides an index of in vivo insulin action in nonobese and obese subjects and, (b) during starvation and refeeding, insulin binding and insulin action changes in opposite directions suggesting that postreceptor events determine in vivo insulin sensitivity.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Archer J. A., Gorden P., Gavin J. R., 3rd, Lesniak M. A., Roth J. Insulin receptors in human circulating lymphocytes: application to the study of insulin resistance in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1973 Apr;36(4):627–633. doi: 10.1210/jcem-36-4-627. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Archer J. A., Gorden P., Roth J. Defect in insulin binding to receptors in obese man. Amelioration with calorie restriction. J Clin Invest. 1975 Jan;55(1):166–174. doi: 10.1172/JCI107907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagdade J. D., Bierman E. L., Porte D., Jr The significance of basal insulin levels in the evaluation of the insulin response to glucose in diabetic and nondiabetic subjects. J Clin Invest. 1967 Oct;46(10):1549–1557. doi: 10.1172/JCI105646. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bar R. S., Gorden P., Roth J., Kahn C. R., De Meyts P. Fluctuations in the affinity and concentration of insulin receptors on circulating monocytes of obese patients: effects of starvation, refeeding, and dieting. J Clin Invest. 1976 Nov;58(5):1123–1135. doi: 10.1172/JCI108565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxter D., Lazarus N. R. The control of insulin receptors in the New Zealand obese mouse. Diabetologia. 1975 Aug;11(4):261–267. doi: 10.1007/BF00422389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cahill G. F., Jr, Herrera M. G., Morgan A. P., Soeldner J. S., Steinke J., Levy P. L., Reichard G. A., Jr, Kipnis D. M. Hormone-fuel interrelationships during fasting. J Clin Invest. 1966 Nov;45(11):1751–1769. doi: 10.1172/JCI105481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cline M. J., Lehrer R. I. Phagocytosis by human monocytes. Blood. 1968 Sep;32(3):423–435. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowan J. S., Hetenyi G., Jr Glucoregulatory responses in normal and diabetic dogs recorded by a new tracer method. Metabolism. 1971 Apr;20(4):360–372. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(71)90098-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czech M. P. Cellular basis of insulin insensitivity in large rat adipocytes. J Clin Invest. 1976 Jun;57(6):1523–1532. doi: 10.1172/JCI108422. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Meyts P., Roth J. Cooperativity in ligand binding: a new graphic analysis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Oct 27;66(4):1118–1126. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90473-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felig P., Wahren J., Hendler R., Brundin T. Splanchnic glucose and amino acid metabolism in obesity. J Clin Invest. 1974 Feb;53(2):582–590. doi: 10.1172/JCI107593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher M., Sherwin R. S., Hendler R., Felig P. Kinetics of glucagon in man: effects of starvation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 May;73(5):1735–1739. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.5.1735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forgue M. E., Freychet P. Insulin receptors in the heart muscle. Demonstration of specific binding sites and impairment of insulin binding in the plasma membrane of the obese hyperglycemic mouse. Diabetes. 1975 Aug;24(8):715–723. doi: 10.2337/diab.24.8.715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freychet P., Laudat M. H., Laudat P., Rosselin G., Kahn C. R., Gorden P., Roth J. Impairment of insulin binding to the fat cell plasma membrane in the obese hyperglycemic mouse. FEBS Lett. 1972 Sep 15;25(2):339–342. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80519-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freychet P., Roth J., Neville D. M., Jr Monoiodoinsulin: demonstration of its biological activity and binding to fat cells and liver membranes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Apr 16;43(2):400–408. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90767-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garber A. J., Cryer P. E., Santiago J. V., Haymond M. W., Pagliara A. S., Kipnis D. M. The role of adrenergic mechanisms in the substrate and hormonal response to insulin-induced hypoglycemia in man. J Clin Invest. 1976 Jul;58(1):7–15. doi: 10.1172/JCI108460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gavin J. R., 3rd, Gorden P., Roth J., Archer J. A., Buell D. N. Characteristics of the human lymphocyte insulin receptor. J Biol Chem. 1973 Mar 25;248(6):2202–2207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gavin J. R., 3rd, Roth J., Neville D. M., Jr, de Meyts P., Buell D. N. Insulin-dependent regulation of insulin receptor concentrations: a direct demonstration in cell culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jan;71(1):84–88. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.1.84. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNTER W. M., GREENWOOD F. C. Preparation of iodine-131 labelled human growth hormone of high specific activity. Nature. 1962 May 5;194:495–496. doi: 10.1038/194495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison L. C., Martin F. I., Melick R. A. Correlation between insulin receptor binding in isolated fat cells and insulin sensitivity in obese human subjects. J Clin Invest. 1976 Dec;58(6):1435–1441. doi: 10.1172/JCI108599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klotz I. M., Hunston D. L. Protein interactions with small molecules. Relationships between stoichiometric binding constants, site binding constants, and empirical binding parameters. J Biol Chem. 1975 Apr 25;250(8):3001–3009. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreisberg R. A., Boshell B. R., DiPlacido J., Roddam R. F. Insulin secretion in obesity. N Engl J Med. 1967 Feb 9;276(6):314–319. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196702092760603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li C. Y., Lam K. W., Yam L. T. Esterases in human leukocytes. J Histochem Cytochem. 1973 Jan;21(1):1–12. doi: 10.1177/21.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGuire E. A., Helderman J. H., Tobin J. D., Andres R., Berman M. Effects of arterial versus venous sampling on analysis of glucose kinetics in man. J Appl Physiol. 1976 Oct;41(4):565–573. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1976.41.4.565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mogensen C. E. The glomerular permeability determined by dextran clearance using Sephadex gel filtration. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1968;21(1):77–82. doi: 10.3109/00365516809076979. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olefsky J. M. Decreased insulin binding to adipocytes and circulating monocytes from obese subjects. J Clin Invest. 1976 May;57(5):1165–1172. doi: 10.1172/JCI108384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olefsky J. M., Jen P., Reaven G. M., Alto P. Insulin binding to isolated human adipocytes. Diabetes. 1974 Jul;23(7):565–571. doi: 10.2337/diab.23.7.565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olefsky J., Bacon V. C., Baur S. Insulin receptors of skeletal muscle: specific insulin binding sites and demonstration of decreased numbers of sites in obese rats. Metabolism. 1976 Feb;25(2):179–191. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(76)90048-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olefsky J., Reaven G. M., Farquhar J. W. Effects of weight reduction on obesity. Studies of lipid and carbohydrate metabolism in normal and hyperlipoproteinemic subjects. J Clin Invest. 1974 Jan;53(1):64–76. doi: 10.1172/JCI107560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RABINOWITZ D., ZIERLER K. L. Forearm metabolism in obesity and its response to intra-arterial insulin. Characterization of insulin resistance and evidence for adaptive hyperinsulinism. J Clin Invest. 1962 Dec;41:2173–2181. doi: 10.1172/JCI104676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radziuk J., Norwich K. H., Vranic M. Measurement and validation of nonsteady turnover rates with applications to the inulin and glucose systems. Fed Proc. 1974 Jul;33(7):1855–1864. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth J. Peptide hormone binding to receptors: a review of direct studies in vitro. Metabolism. 1973 Aug;22(8):1059–1073. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(73)90225-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEELE R. Influences of glucose loading and of injected insulin on hepatic glucose output. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1959 Sep 25;82:420–430. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1959.tb44923.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherwin R. S., Hendler R., DeFronzo R., Wahren J., Felic P. Glucose homeostasis during prolonged suppression of glucagon and insulin secretion by somatostatin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jan;74(1):348–352. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.1.348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherwin R. S., Kramer K. J., Tobin J. D., Insel P. A., Liljenquist J. E., Berman M., Andres R. A model of the kinetics of insulin in man. J Clin Invest. 1974 May;53(5):1481–1492. doi: 10.1172/JCI107697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soli A. H., Kahn C. R., Neville D. M., Jr, Roth J. Insulin receptor deficiency in genetic and acquired obesity. J Clin Invest. 1975 Oct;56(4):769–780. doi: 10.1172/JCI108155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soll A. H., Goldfine I. D., Roth J., Kahn C. R. Thymic lymphocytes in obese (ob-ob) mice. A mirror of the insulin receptor defect in liver and fat. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jul 10;249(13):4127–4131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soll A. H., Kahn C. R., Neville D. M., Jr Insulin binding to liver plasm membranes in the obese hyperglycemic (ob/ob) mouse. Demonstration of a decreased number of functionally normal receptors. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jun 25;250(12):4702–4707. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise J. K., Hendler R., Felig P. Influence of glucocorticoids on glucagon secretion and plasma amino acid concentrations in man. J Clin Invest. 1973 Nov;52(11):2774–2782. doi: 10.1172/JCI107473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


