Abstract
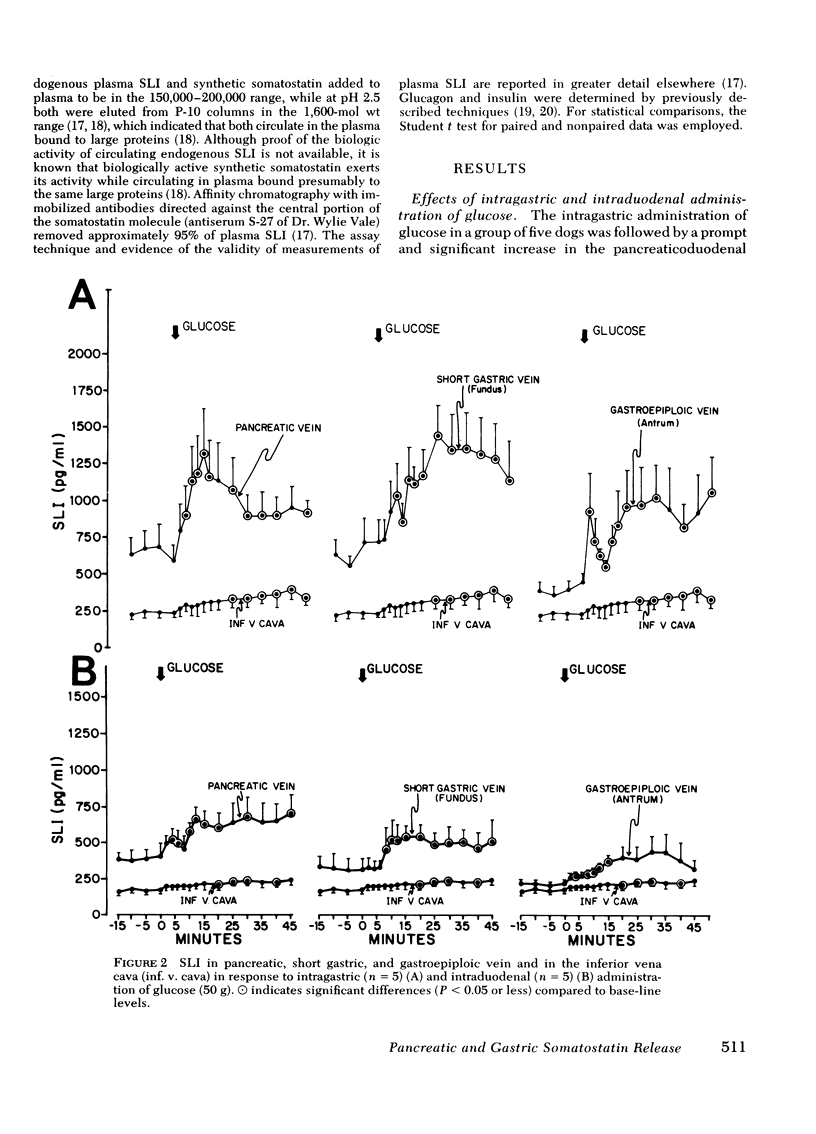
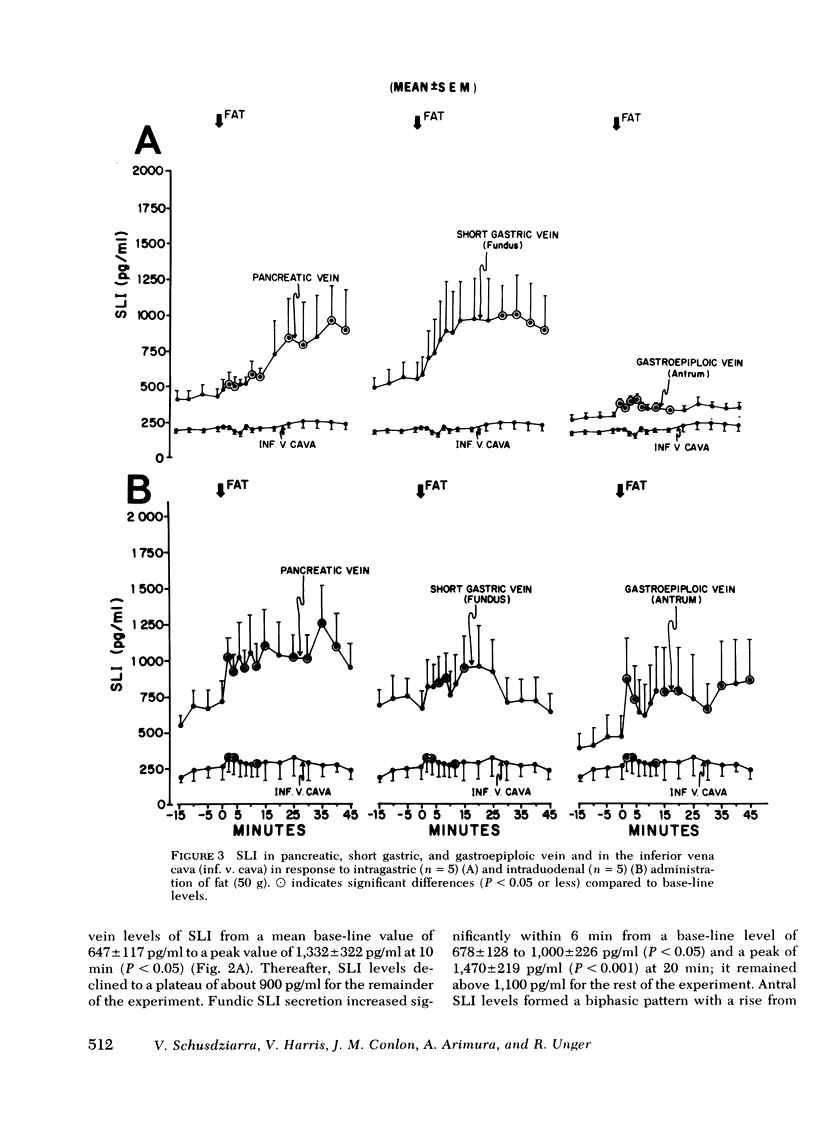
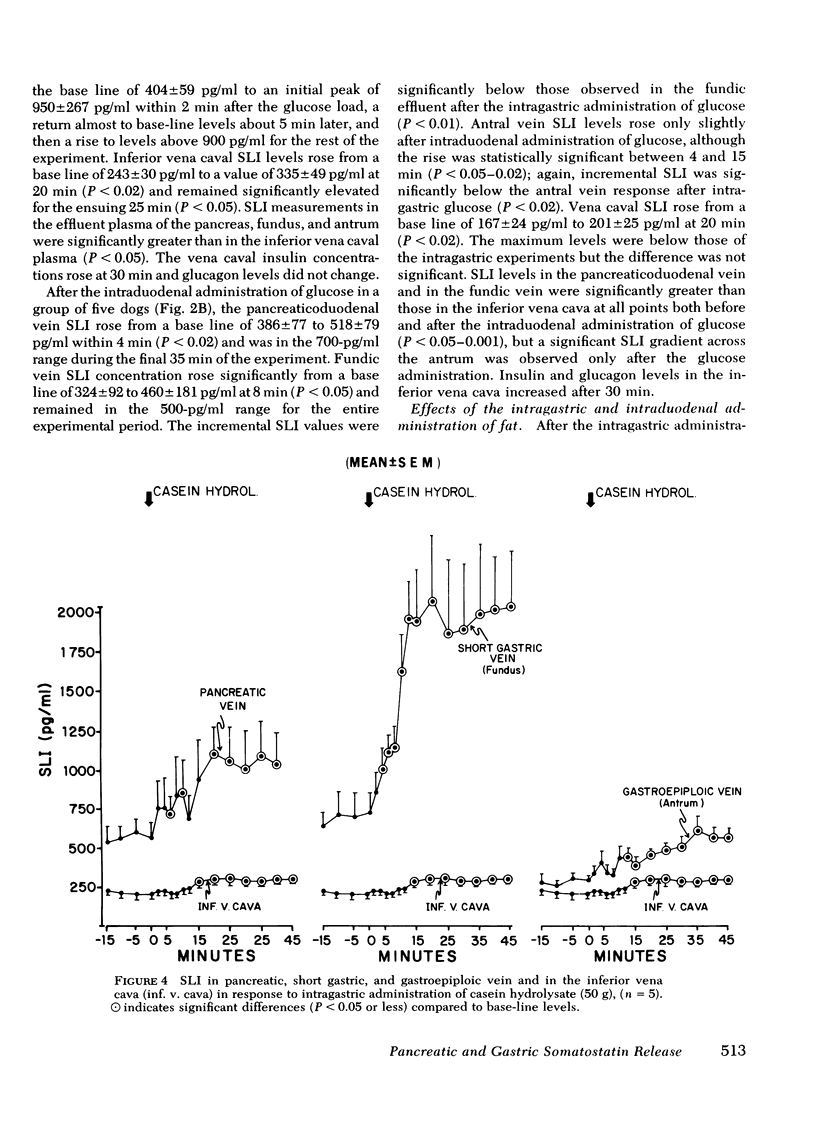
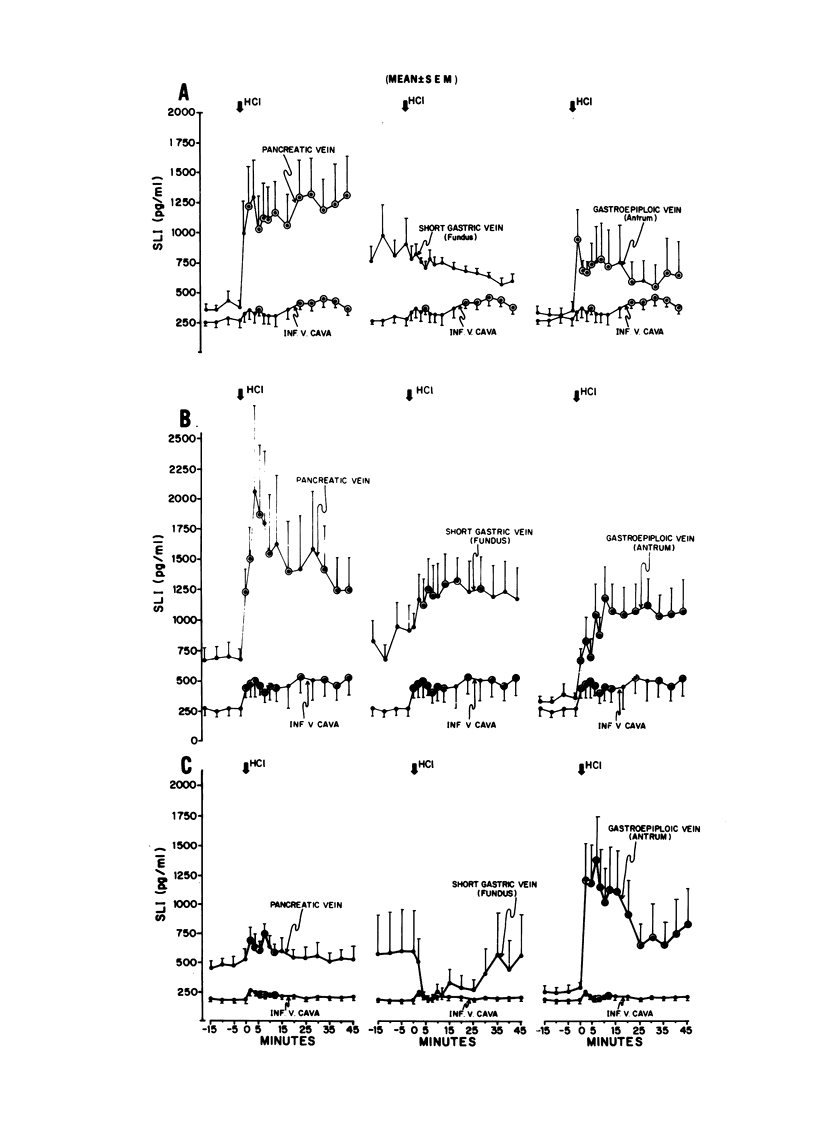
The effects of the instillation of glucose, fat, casein hydrolysate, and HCl into the gastrointestinal tract upon plasma levels of somatostatin-like immunoreactivity (SLI) in the venous effluent of the pancreas, fundus and antrum of the stomach, and in the inferior vena cava (IVC) were determined in normal laparotomized dogs. Fasting SLI levels in the effluent plasma from these sites were significantly greater than IVC levels. The intragastric administration of glucose elicited a prompt and significant rise in SLI levels in pancreatic, fundic and antral venous plasma, and in IVC plasma; intraduodenal glucose elicited smaller increments. After intragastric fat, a smaller, more gradual increase in the pancreatic and fundic effluents was observed, whereas the rise in antral SLI was minute, and IVC SLI did not rise significantly. Intraduodenal fat elicited a prompt increase in the pancreatic and antral vein SLI levels, and a small but significant increase in fundic and IVC plasma which suggests faster release of enteric factors that influence SLI secretion in the pancreas and antrum. Intragastric casein hydrolysate elicited a prompt increase in SLI in both the pancreatic and fundic veins, the latter being marked, but the antral SLI response was small; IVC SLI rose significantly within 15 min. Intragastric HCl provoked a prompt and marked rise in pancreaticoduodenal and antral vein SLI but no increase in fundic vein SLI; IVC SLI levels rose significantly within 20 min. Intraduodenal HCl elicited an even more prompt and marked pancreatic SLI response, and SLI rose significantly in both the fundic and antral venous effluents; IVC SLI also rose more promptly. In dogs with a gastric fistula that prevented intraduodenal entry of HCl, intragastric HCl elicited only a very small and transient rise in pancreaticoduodenal vein SLI, markedly stimulated the antral SLI response, but completely suppressed fundic venous SLI levels.
The results indicate that all three nutrients stimulate SLI release from the pancreas and stomach. The greater SLI response to intragastric, as opposed to intraduodenal, glucose suggests that unidentified local factors are of importance. The responses to the intraduodenal instillation of HCl and fat suggest a role of enteric hormones in the release of SLI from the pancreas and fundus and antrum of the stomach. Additionally, there is evidence of direct effects of HCl upon gastric SLI release.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alberti K. G., Christensen N. J., Christensen S. E., Hansen A. P., Iversen J., Lundbaek K., Seyer-Hansen K., Orskov H. Inhibition of insulin secretion by somatostatin. Lancet. 1973 Dec 8;2(7841):1299–1301. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)92873-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arimura A., Sato H., Coy D. H., Schally A. V. Radioimmunoassay for GH-release inhibiting hormone. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1975 Mar;148(3):784–789. doi: 10.3181/00379727-148-38631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arimura A., Sato H., Dupont A., Nishi N., Schally A. V. Somatostatin: abundance of immunoreactive hormone in rat stomach and pancreas. Science. 1975 Sep 19;189(4207):1007–1009. doi: 10.1126/science.56779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom S. R., Mortimer C. H., Thorner M. O., Besser G. M., Hall R., Gomez-Pan A., Roy V. M., Russell R. C., Coy D. H., Kastin A. J. Inhibition of gastrin and gastric-acid secretion by growth-hormone release-inhibiting hormone. Lancet. 1974 Nov 9;2(7889):1106–1109. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)90869-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom S. R., Ralphs D. N., Besser G. M., Hall R., Coy D. H., Kastin A. J., Schally A. V. Proceedings: Effect of somatostatin on motilin levels and gastric emptying. Gut. 1975 Oct;16(10):834–834. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boden G., Essa N., Owen O. E., Reichle F. A. Effects of intraduodenal administration of HCl and glucose on circulating immunoreactive secretin and insulin concentrations. J Clin Invest. 1974 Apr;53(4):1185–1193. doi: 10.1172/JCI107657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen S. E., Hansen A. P., Iversen J., Lundbaek K., Orskov H., Seyer-Hansen K. Somatostatin as a tool in studies of basal carbohydrate and lipid metabolism in man: modifications of glucagon and insulin release. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1974 Dec;34(4):321–325. doi: 10.3109/00365517409049887. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeVane G. W., Siler T. M., Yen S. S. Acute suppression of insulin and glucose levels by synthetic somatostatin in normal human subjects. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1974 May;38(5):913–915. doi: 10.1210/jcem-38-5-913. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubois M. P. Immunoreactive somatostatin is present in discrete cells of the endocrine pancreas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Apr;72(4):1340–1343. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.4.1340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fahrenkrug J., Schaffalitzky de Muckadell O. B. Plasma secretin concentration in man: effect of intraduodenal glucose, fat, amino acids, ethanol, HCl, or ingestion of a meal. Eur J Clin Invest. 1977 Jun;7(3):201–203. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1977.tb01598.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerich J. E., Lorenzi M., Schneider V., Forsham P. H. Effect of somatostatin on plasma glucose and insulin responses to glucagon and tolbutamide in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1974 Dec;39(6):1057–1060. doi: 10.1210/jcem-39-6-1057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerich J. E., Lorenzi M., Schneider V., Kwan C. W., Karam J. H., Guillemin R., Forsham P. H. Inhibition of pancreatic glucagon responses to arginine by somatostatin in normal man and in insulin-dependent diabetics. Diabetes. 1974 Nov;23(11):876–880. doi: 10.2337/diab.23.11.876. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomez-Pan A., Reed J. D., Albinus M., Shaw B., Hall R. Direct inhibition of gastric acid and pepsin secretion by growth-hormone release-inhibiting hormone in cats. Lancet. 1975 Apr 19;1(7912):888–890. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)91686-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hökfelt T., Efendić S., Hellerström C., Johansson O., Luft R., Arimura A. Cellular localization of somatostatin in endocrine-like cells and neurons of the rat with special references to the A1-cells of the pancreatic islets and to the hypothalamus. Acta Endocrinol Suppl (Copenh) 1975;200:5–41. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ipp E., Dobbs R. E., Arimura A., Vale W., Harris V., Unger R. H. Release of immunoreactive somatostatin from the pancreas in response to glucose, amino acids, pancreozymin-cholecystokinin, and tolbutamide. J Clin Invest. 1977 Sep;60(3):760–765. doi: 10.1172/JCI108829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ipp E., Dobbs R. E., Harris V., Arimura A., Vale W., Unger R. H. The effects of gastrin, gastric inhibitory polypeptide, secretin, and the octapeptide of cholecystokinin upon immunoreactive somatostatin release by the perfused canine pancreas. J Clin Invest. 1977 Nov;60(5):1216–1219. doi: 10.1172/JCI108875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koerker D. J., Ruch W., Chideckel E., Palmer J., Goodner C. J., Ensinck J., Gale C. C. Somatostatin: hypothalamic inhibitor of the endocrine pancreas. Science. 1974 Apr 26;184(4135):482–484. doi: 10.1126/science.184.4135.482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronheim S., Berelowitz M., Pimstone B. L. A radioimmunoassay for growth hormone release-inhibiting hormone: method and quantitative tissue distribution. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 1976 Nov;5(6):619–630. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.1976.tb03865.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luft R., Efendic S., Hökfelt T., Johansson O., Arimura A. Immunohistochemical evidence for the localization of somatostatin--like immunoreactivity in a cell population of the pancreatic islets. Med Biol. 1974 Dec;52(6):428–430. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mortimer C. H., Tunbridge W. M., Carr D., Yeomans L., Lind T., Coy D. H., Bloom S. R., Kastin A., Mallinson C. N., Besser G. M. Effects of growth-hormone release-inhibiting hormone on circulating glucagon, insulin, and growth hormone in normal, diabetic, acromegalic, and hypopituitary patients. Lancet. 1974 Apr 20;1(7860):697–701. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)92903-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orci L., Baetens D., Dubois M. P., Rufener C. Evidence for the D-cell of the pancreas secreting somatostatin. Horm Metab Res. 1975 Sep;7(5):400–402. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1093736. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orci L., Unger R. H. Functional subdivision of islets of Langerhans and possible role of D cells. Lancet. 1975 Dec 20;2(7947):1243–1244. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)92078-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearse A. G., Polak J. M., Bloom S. R. The newer gut hormones. Cellular sources, physiology, pathology, and clinical aspects. Gastroenterology. 1977 Apr;72(4 Pt 1):746–761. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pederson R. A., Schubert H. E., Brown J. C. Gastric inhibitory polypeptide. Its physiologic release and insulinotropic action in the dog. Diabetes. 1975 Dec;24(12):1050–1056. doi: 10.2337/diab.24.12.1050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelletier G., Leclerc R., Arimura A., Schally A. V. Letter: Immunohistochemical localization of somatostatin in the rat pancreas. J Histochem Cytochem. 1975 Sep;23(9):699–702. doi: 10.1177/23.9.1100709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polak J. M., Pearse A. G., Grimelius L., Bloom S. R. Growth-hormone release-inhibiting hormone in gastrointestinal and pancreatic D cells. Lancet. 1975 May 31;1(7918):1220–1222. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)92198-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeder D. D., Becker H. D., Smith N. J., Rayford P. L., Thompson J. C. Measurement of endogenous release of cholecystokinin by radioimmunoassay. Ann Surg. 1973 Sep;178(3):304–310. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197309000-00010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacks H., Waligora K., Matthews J., Pimstone B. Inhibition by somatostatin of glucagon-induced glucose release from the isolated perfused rat liver. Endocrinology. 1977 Dec;101(6):1751–1759. doi: 10.1210/endo-101-6-1751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schusdziarra V., Dobbs R. E., Harris V., Unger R. H. Immunoreactive somatostatin levels in plasma of normal and alloxan diabetic dogs. FEBS Lett. 1977 Sep 1;81(1):69–72. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80930-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unger R. H., Ipp E., Schusdziarra V., Orci L. Hypothesis: physiologic role of pancreatic somatostatin and the contribution of D-cell disorders to diabetes mellitus. Life Sci. 1977 Jun 15;20(12):2081–2085. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(77)90188-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YALOW R. S., BERSON S. A. Immunoassay of endogenous plasma insulin in man. J Clin Invest. 1960 Jul;39:1157–1175. doi: 10.1172/JCI104130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


