Abstract
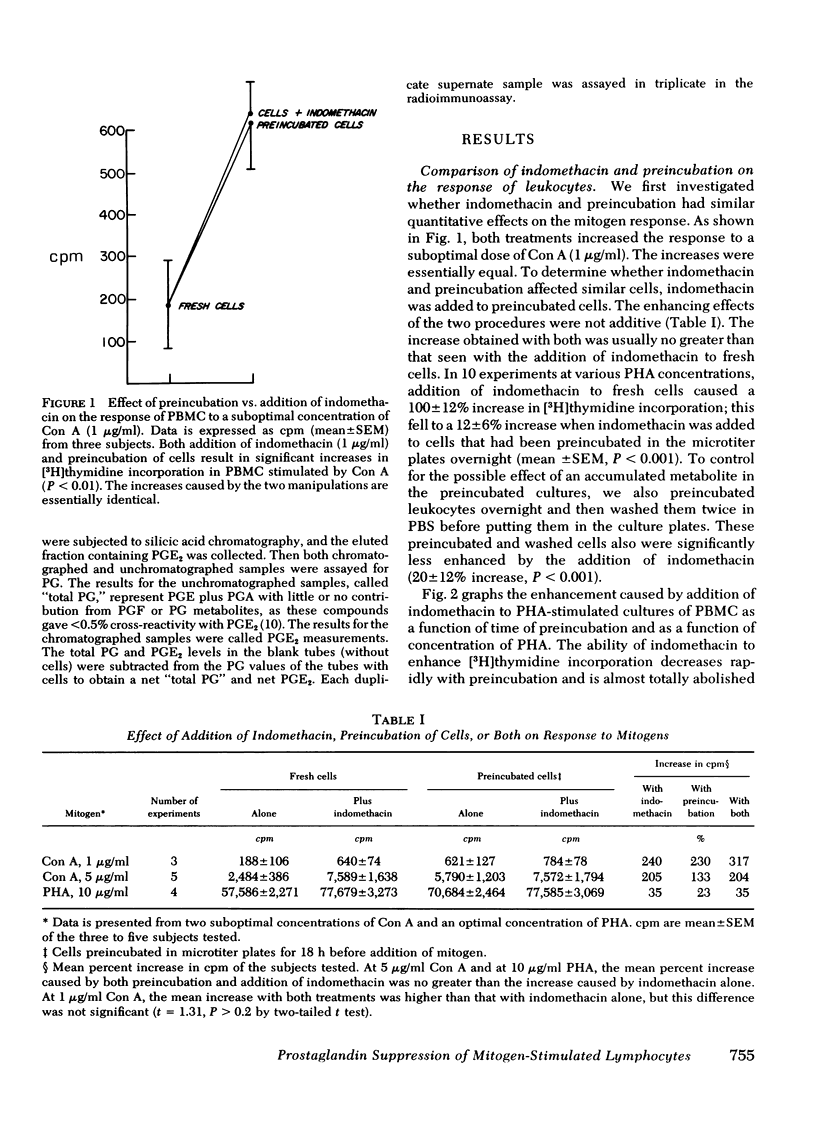
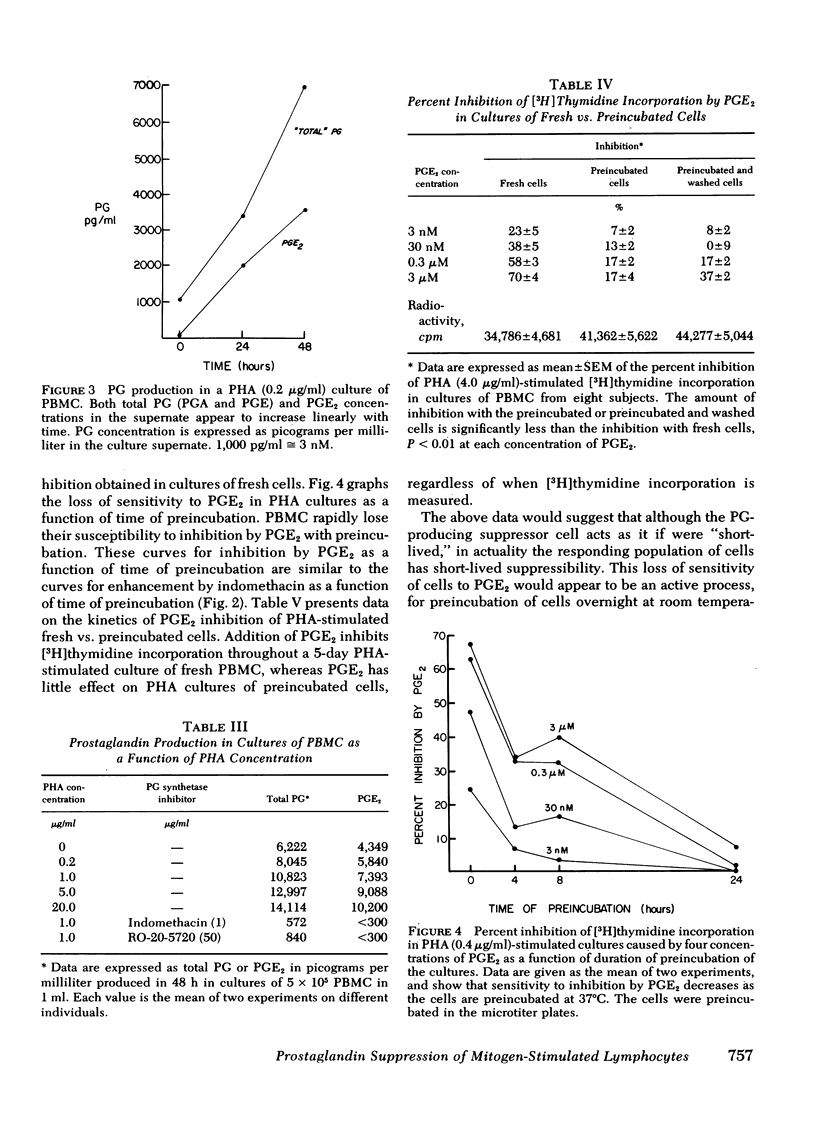
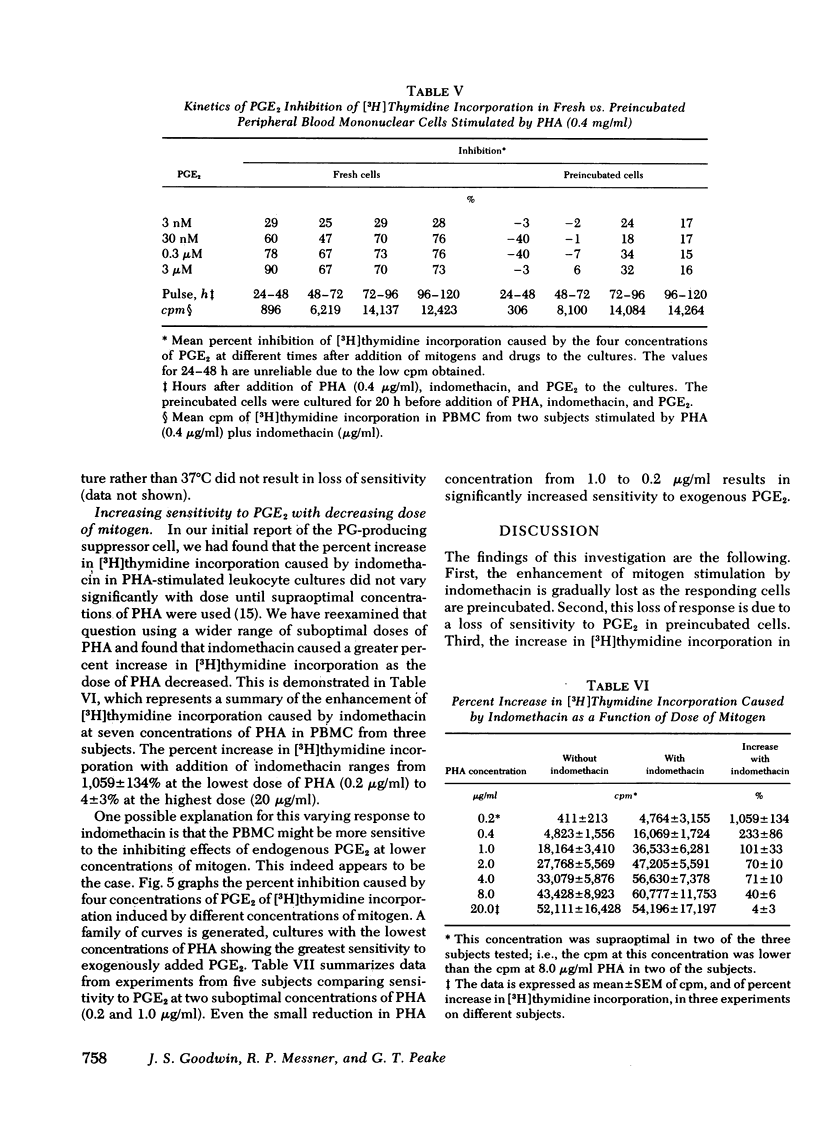
In this study we further characterize the properties of the prostaglandin-producing suppressor cell. Overnight preincubation of peripheral blood mononuclear cells results in an increased response of the cells to phytohemagglutinin or Concanavalin A compared to the response of fresh cells. This increase in mitogen response with preincubation was similar in magnitude to the increase in mitogen response of fresh cells after the addition of indomethacin. The two manipulations were not additive; that is, after preincubation, indomethacin caused much less enhancement of mitogen stimulation of peripheral blood mononuclear cells (100 ± 12% increase before preincubation vs. 12 ± 6% after preincubation; mean±SEM, P < 0.001). Preincubated cells also lose sensitivity to inhibition by exogenous prostaglandin E2. It requires the addition of 100- to > 1,000-fold more exogenous PGE2 to produce comparable inhibition of phytohemagglutinin-stimulated preincubated cells than is required for inhibition of phytohemagglutinin-stimulated fresh cells.
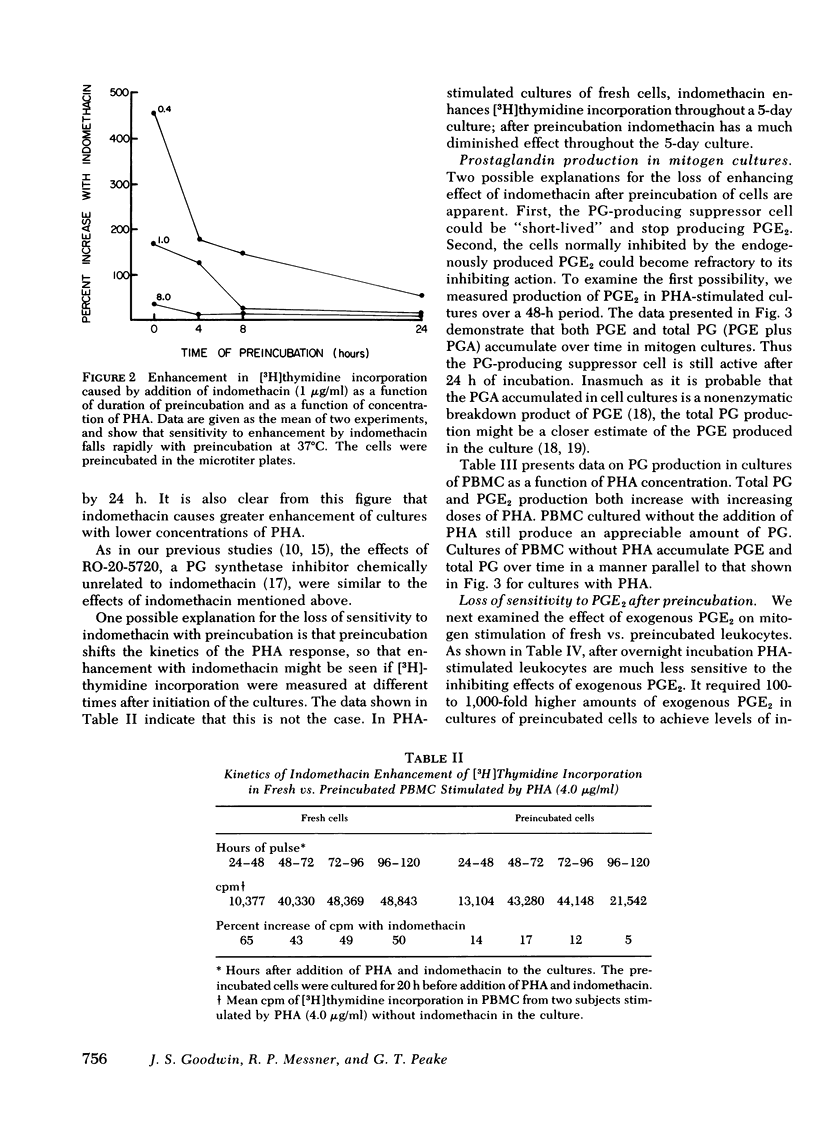
The enhancing effect of indomethacin increases with decreasing doses of phytohemagglutinin. Indomethacin causes a 1,059±134% increase in [3H]thymidine incorporation at the lowest dose of phytohemagglutinin (0.2 μg/ml), and a 4±3% increase at the highest dose (20 μg/ml). This increase in response to indomethacin with a lower dose of phytohemagglutinin is due to increased sensitivity to inhibition by PGE2 at lower mitogen doses.
The prostaglandin-producing suppressor cell assay and the short-lived suppressor cell assay measure over-lapping phenomena. The increased suppressive effect of the prostaglandin-producing suppressor at suboptimal mitogen dose must be taken into account in the interpretation of any study where the response to a range of mitogen doses is studied.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baird L. G., Kaplan A. M. Macrophage regulation of mitogen-induced blastogenesis. I. Demonstration of inhibitory cells in the spleens and peritoneal exudates of mice. Cell Immunol. 1977 Jan;28(1):22–35. doi: 10.1016/s0008-8749(77)80003-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baird L. G., Kaplan A. M. Macrophage regulation of mitogen-induced blastogenesis. II. Mechanism of inhibition. Cell Immunol. 1977 Jan;28(1):36–50. doi: 10.1016/s0008-8749(77)80004-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bresnihan B., Jasin H. E. Suppressor function of peripheral blood mononuclear cells in normal individuals and in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Invest. 1977 Jan;59(1):106–116. doi: 10.1172/JCI108607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broder S., Humphrey R., Durm M., Blackman M., Meade B., Goldman C., Strober W., Waldmann T. Impaired synthesis of polyclonal (non-paraprotein) immunoglobulins by circulating lymphocytes from patients with multiple myeloma Role of suppressor cells. N Engl J Med. 1975 Oct 30;293(18):887–892. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197510302931801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delespesse G., Gausset P., Cauchie C., Govaerts A. Cellular aspects of selective IgA deficiency. Clin Exp Immunol. 1976 May;24(2):273–279. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferraris V. A., DeRubertis F. R. Release of prostaglandin by mitogen- and antigen-stimulated leukocytes in culture. J Clin Invest. 1974 Aug;54(2):378–386. doi: 10.1172/JCI107773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaut Z. N., Baruth H., Randall L. O., Ashley C., Paulsrud J. R. Stereoisomeric relationships among anti-inflammatory activity, inhibition of platelet aggregation, and inhibition of prostaglandin synthetase. Prostaglandins. 1975 Jul;10(1):59–66. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(75)90093-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin J. S., Bankhurst A. D., Messner R. P. Suppression of human T-cell mitogenesis by prostaglandin. Existence of a prostaglandin-producing suppressor cell. J Exp Med. 1977 Dec 1;146(6):1719–1734. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.6.1719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin J. S., Messner R. P., Bankhurst A. D., Peake G. T., Saiki J. H., Williams R. C., Jr Prostaglandin-producing suppressor cells in Hodgkin's disease. N Engl J Med. 1977 Nov 3;297(18):963–968. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197711032971802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubert C., Delespesse G., Govaerts A. Concanavalin A-activated suppressor cells in normal human peripheral blood lymphocytes. Clin Exp Immunol. 1976 Oct;26(1):95–98. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz S. I., Parker D., Turk J. L. B-cell suppression of delayed hypersensitivity reactions. Nature. 1974 Oct 11;251(5475):550–551. doi: 10.1038/251550a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller R. Major changes in lymphocyte proliferation evoked by activated macrophages. Cell Immunol. 1975 Jun;17(2):542–551. doi: 10.1016/s0008-8749(75)80058-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Namba Y., Jegasothy B. V., Waksman B. H. Regulatory substances produced by lymphocytes. V. Production of inhibitor of DNA synthesis (IDS) by proliferating T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1977 Apr;118(4):1379–1384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olding L. B., Murgita R. A., Wigzell H. Mitogen-stimulated lymphoid cells from human newborns suppress the proliferation of maternal lymphocytes actoss a cell-impermeable membrane. J Immunol. 1977 Sep;119(3):1109–1114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigler G. L., Peake G. T., Ratner A. Effects of follicle-stimulating hormone and luteinizing hormone on ovarian cyclic AMP and prostaglandin E in vivo in rats treated with indomethacin. J Endocrinol. 1976 Aug;70(2):285–291. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0700285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritzi E. M., Stylos W. A. Prostaglandin production in cultures of BALB/3T3 and SV3T3 mouse fibroblasts. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1976 Mar;56(3):529–533. doi: 10.1093/jnci/56.3.529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritzi E. M., Stylos W. A. The simultaneous use of two prostaglandin radioimmunoassays employing two antisera of differing specificity. II. Relative stability of prostaglandins E1, E2 and F1alpha in cell cultures of BALB/c 3T3 and SV3T3 mouse fibroblasts. Prostaglandins. 1976 Nov;12(5):871–880. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(76)90060-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shou L., Schwartz S. A., Good R. A. Suppressor cell activity after concanavalin A treatment of lymphocytes from normal donors. J Exp Med. 1976 May 1;143(5):1100–1110. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.5.1100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sibbitt W. L., Jr, Bankhurst A. D., Williams R. C., Jr Studies of cell subpopulations mediating mitogen hyporesponsiveness in patients with Hodgkin's disease. J Clin Invest. 1978 Jan;61(1):55–63. doi: 10.1172/JCI108925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. W., Steiner A. L., Parker C. W. Human lymphocytic metabolism. Effects of cyclic and noncyclic nucleotides on stimulation by phytohemagglutinin. J Clin Invest. 1971 Feb;50(2):442–448. doi: 10.1172/JCI106511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stobo J. D. Immunosuppression in man: suppression by macrophages can be mediated by interactions with regulatory T cells. J Immunol. 1977 Sep;119(3):918–924. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stobo J. D., Paul S., Van Scoy R. E., Hermans P. E. Suppressor thymus-derived lymphocytes in fungal infection. J Clin Invest. 1976 Feb;57(2):319–328. doi: 10.1172/JCI108283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tadakuma T., Pierce C. W. Site of action of a soluble immune response suppressor (SIRS) produced by concanavalin A-activated spleen cells. J Immunol. 1976 Sep;117(3):967–972. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twomey J. J., Laughter A. H., Farrow S., Douglass C. C. Hodgkin's disease. An immunodepleting and immunosuppressive disorder. J Clin Invest. 1975 Aug;56(2):467–475. doi: 10.1172/JCI108113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldmann T. A., Durm M., Broder S., Blackman M., Blaese R. M., Strober W. Role of suppressor T cells in pathogenesis of common variable hypogammaglobulinaemia. Lancet. 1974 Sep 14;2(7881):609–613. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)91940-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


