Abstract
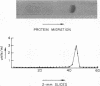
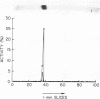
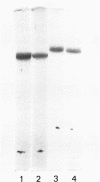
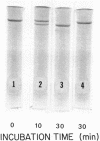
Human Factor IX (Christmas factor) was isolated from the plasma of a patient with mild hemophilia B. The patient's plasma contained 5% Factor IX clotting activity but 100% Factor IX antigenic activity as determined by immunological assays, which included inhibitor neutralization and a radioimmunoassay for Factor IX. This abnormal Factor IX is called Factor IX Chapel Hill (Factor IXCH). Both normal Factor IX and Factor IXCH have tyrosine as the NH2-terminal amino acid. The two proteins have a similar molecular weight, a similar amino acid analysis, the same number of gamma-carboxyglutamic acid residues (10 gamma-carboxyglutamic acid residues), and a similar carbohydrate content. Both exist as a single-chain glycoprotein in plasma. The major difference between normal Factor IX and Factor IXCH is that the latter exhibits delayed activation to Factor IXa in the presence of Factor XIa and Ca2+. Thus, Factor IXCH differs from other previously described abnormal Factor IX molecules.
Full text
PDF


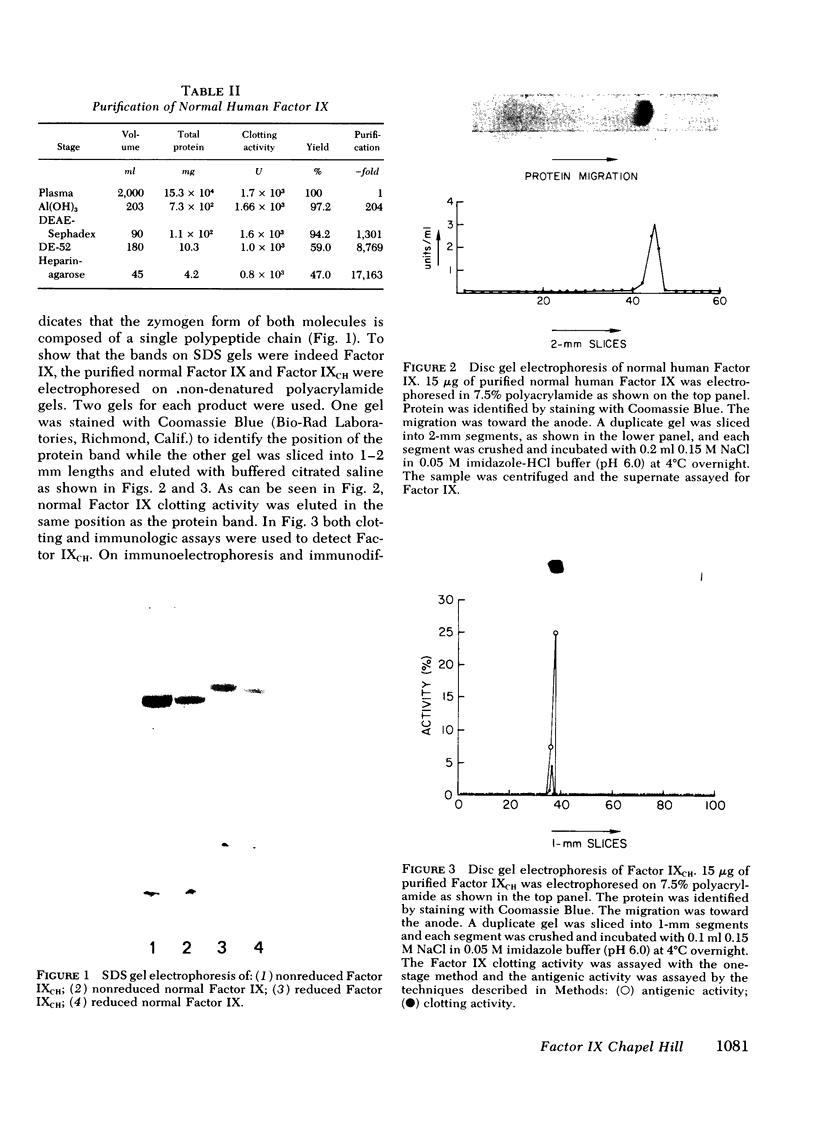
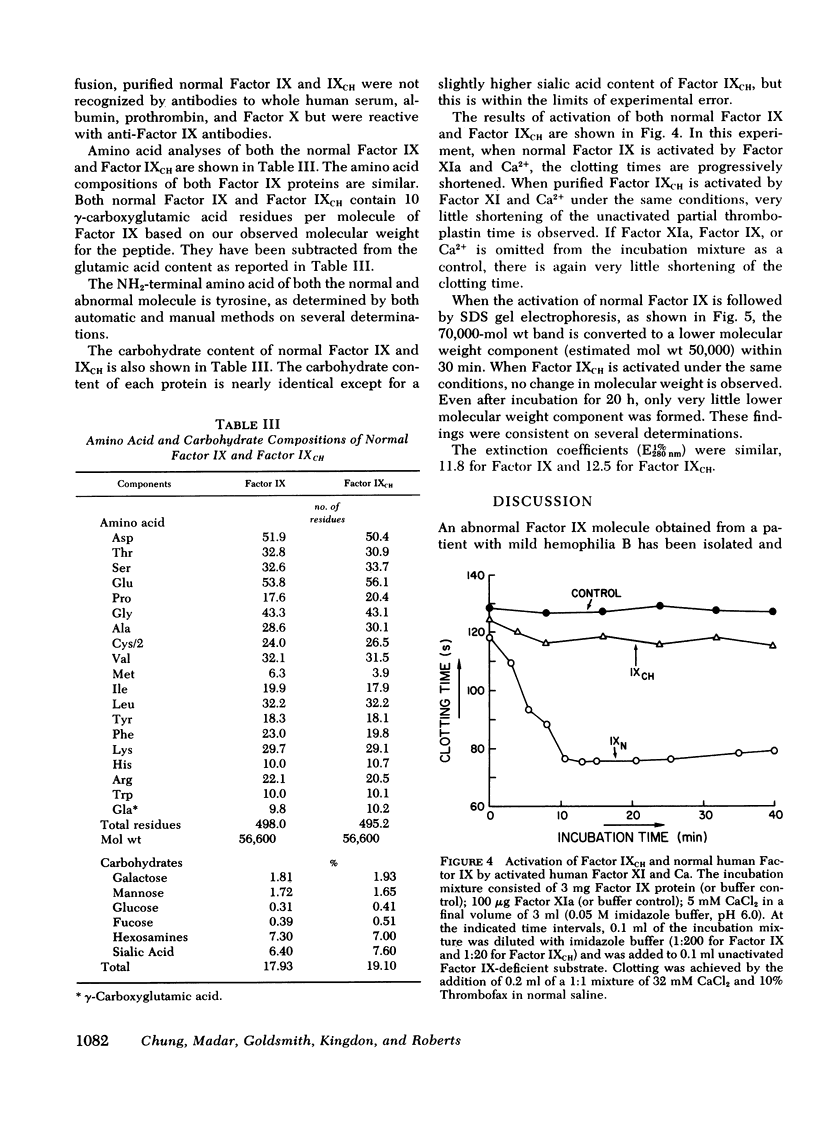



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersson L. O., Borg H., Miller-Andersson M. Purification and characterization of human factor IX. Thromb Res. 1975 Sep;7(3):451–459. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(75)90039-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARROW E. M., BULLOCK W. R., GRAHAM J. B. A study of the carrier state for plasma thromboplastin component (PTC, Christmas factor) deficiency, utilizing a new assay procedure. J Lab Clin Med. 1960 Jun;55:936–945. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown P. E., Hougie C., Roberts H. R. The genetic heterogeneity of hemophilia B. N Engl J Med. 1970 Jul 9;283(2):61–64. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197007092830203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P. Protein purification by affinity chromatography. Derivatizations of agarose and polyacrylamide beads. J Biol Chem. 1970 Jun;245(12):3059–3065. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Scipio R. G., Hermodson M. A., Yates S. G., Davie E. W. A comparison of human prothrombin, factor IX (Christmas factor), factor X (Stuart factor), and protein S. Biochemistry. 1977 Feb 22;16(4):698–706. doi: 10.1021/bi00623a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edman P., Begg G. A protein sequenator. Eur J Biochem. 1967 Mar;1(1):80–91. doi: 10.1007/978-3-662-25813-2_14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elödi S., Puskás E. Variants of haemophilia B. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1972 Dec 31;28(3):489–495. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FANTL P., MARR A. G., SAWERS R. J. Investigation of a haemorrhagic disease due to beta-prothromboplastin deficiency complicated by a specific inhibitor of thromboplastin formation. Australas Ann Med. 1956 Aug;5(3):163–176. doi: 10.1111/imj.1956.5.3.163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujikawa K., Legaz M. E., Kato H., Davie E. W. The mechanism of activation of bovine factor IX (Christmas factor) by bovine factor XIa (activated plasma thromboplastin antecedent). Biochemistry. 1974 Oct 22;13(22):4508–4516. doi: 10.1021/bi00719a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujikawa K., Thompson A. R., Legaz M. E., Meyer R. G., Davie E. W. Isolation and characterization of bovine factor IX (Christmas factor). Biochemistry. 1973 Nov 20;12(24):4938–4945. doi: 10.1021/bi00748a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GARDELL S. Determination of hexosamines. Methods Biochem Anal. 1958;6:289–317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girolami A., Sticchi A., Burul A., Zanon R. D. An immunological investigation of hemophilia B with a tentative classification of the disease into five variants. Vox Sang. 1977;32(4):230–238. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1977.tb00635.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOROWITZ H. I., WILCOX W. P., FUJIMOTO M. M. Assay of plasma thromboplastin antecedent (PTA) with artificially depleted normal plasma. Blood. 1963 Jul;22:35–43. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOUGIE C., BARROW E. M., GRAHAM J. B. Stuart clotting defect. I. Segregation of an hereditary hemorrhagic state from the heterogeneous group heretofore called stable factor (SPCA, proconvertin, factor VII) deficiency. J Clin Invest. 1957 Mar;36(3):485–496. doi: 10.1172/JCI103446. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauschka P. V., Lian J. B., Gallop P. M. Direct identification of the calcium-binding amino acid, gamma-carboxyglutamate, in mineralized tissue. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):3925–3929. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.3925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hougie C., Twomey J. J. Haemophilia Bm: a new type of factor-IX deficiency. Lancet. 1967 Apr 1;1(7492):698–700. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(67)92179-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KINGDON H. S., DAVIE E. W., RATNOFF O. D. THE REACTION BETWEEN ACTIVATED PLASMA THROMBOPLASTIN ANTECEDENT AND DIISOPROPYLPHOSPHOFLUORIDATE. Biochemistry. 1964 Feb;3:166–173. doi: 10.1021/bi00890a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasper C. K., Osterud B., Minami J. Y., Shonick W., Rapaport S. I. Hemophilia B: characterization of genetic variants and detection of carriers. Blood. 1977 Sep;50(3):351–366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANGDELL R. D., WAGNER R. H., BRINKHOUS K. M. Effect of antihemophilic factor on one-stage clotting tests; a presumptive test for hemophilia and a simple one-stage antihemophilic factor assy procedure. J Lab Clin Med. 1953 Apr;41(4):637–647. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laine R., Söderlund H., Renkonen O. Chemical composition of Semliki forest virus. Intervirology. 1973;1(2):110–118. doi: 10.1159/000148837. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindquist P. A., Fujikawa K., Davie E. W. Activation of bovine factor IX (Christmas factor) by factor XIa (activated plasma thromboplastin antecedent) and a protease from Russell's viper venom. J Biol Chem. 1978 Mar 25;253(6):1902–1909. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLester W. D., Roberts H. R., Wagner R. H. Use of an immunosorbent technique in the study of a PTC inhibitor: a new method for the investigation of blood coagulation. J Lab Clin Med. 1965 Oct;66(4):682–687. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer D., Bidwell E., Larrieu M. J. Cross-reacting material in genetic variants of haemophilia B. J Clin Pathol. 1972 May;25(5):433–436. doi: 10.1136/jcp.25.5.433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neal W. R., Tayloe D. T., Jr, Cederbaum A. I., Roberts H. R. Detection of genetic variants of haemophilia B with an immunosorbent technique. Br J Haematol. 1973 Jul;25(1):63–68. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1973.tb01716.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niedermeier W. Gas chromatography of neutral and amino sugars in glycoproteins. Anal Biochem. 1971 Apr;40(2):465–475. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90407-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orstavik K. H., Osterud B., Prydz H., Berg K. Electroimmunoassay of factor IX in hemophilia B. Thromb Res. 1975 Sep;7(3):373–382. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(75)90031-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osterud B., Flengsrud R. Purification and some characteristics of the coagulation factor IX from human plasma. Biochem J. 1975 Mar;145(3):469–474. doi: 10.1042/bj1450469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts H. R., Grizzle J. E., McLester W. D., Penick G. D. Genetic variants of hemophilia B: detection by means of a specific PTC inhibitor. J Clin Invest. 1968 Feb;47(2):360–365. doi: 10.1172/JCI105732. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts H. R., Gross G. P., Webster W. P., Dejanov I. I., Penick G. D. Acquired inhibitors of plasma factor IX. A study of their induction, properties and neutralization. Am J Med Sci. 1966 Jan;251(1):43–50. doi: 10.1097/00000441-196601000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg J. S., McKenna P. W., Rosenberg R. D. Inhibition of human factor IXa by human antithrombin. J Biol Chem. 1975 Dec 10;250(23):8883–8888. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suomela H. Human coagulation factor IX. Isolation and characterization. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Dec;71(1):145–154. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb11100.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson A. R. Factor IX antigen by radioimmunoassay. Abnormal factor IX protein in patients on warfarin therapy and with hemophilia B. J Clin Invest. 1977 May;59(5):900–910. doi: 10.1172/JCI108712. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veltkamp J. J., Meilof J., Remmelts H. G., van der Vlerk D., Loeliger E. A. Another genetic variant of haemophilia B: haemophilia B Leyden. Scand J Haematol. 1970;7(2):82–90. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1970.tb01873.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARREN L. The thiobarbituric acid assay of sialic acids. J Biol Chem. 1959 Aug;234(8):1971–1975. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods K. R., Wang K. T. Separation of dansyl-amino acids by polyamide layer chromatography. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Feb 21;133(2):369–370. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(67)90078-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]