Abstract
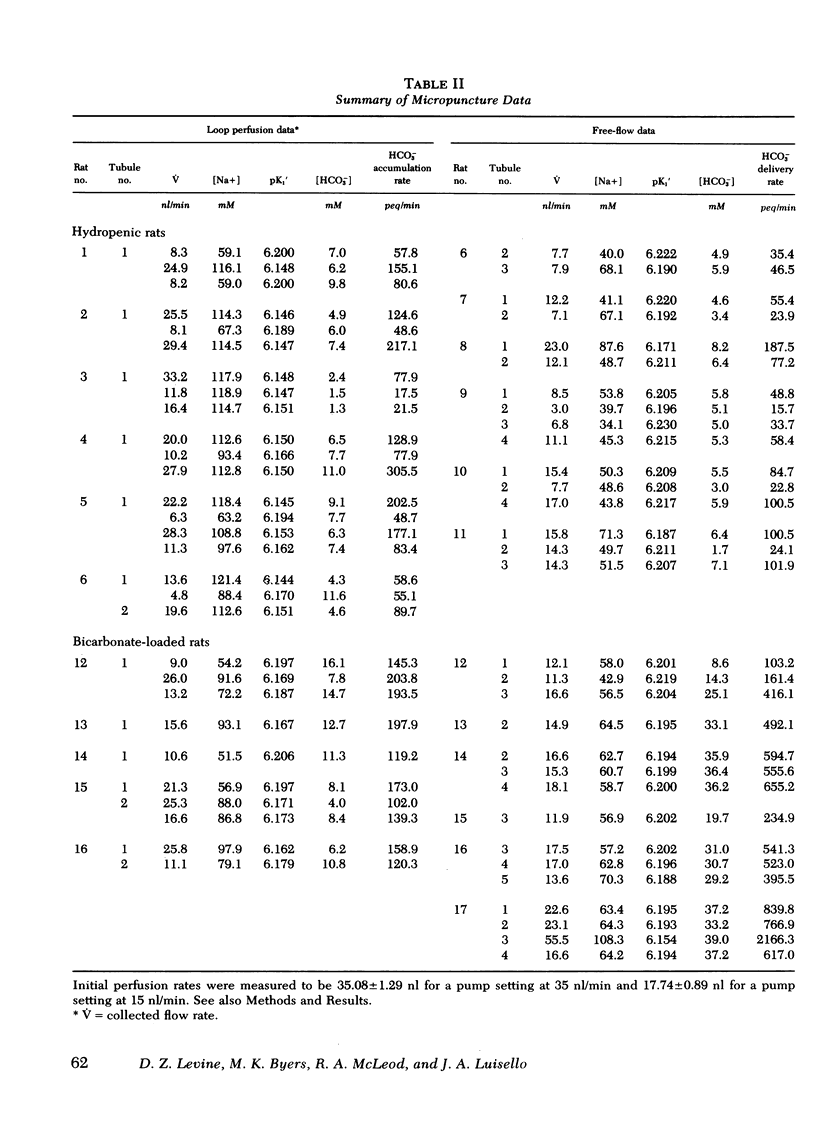
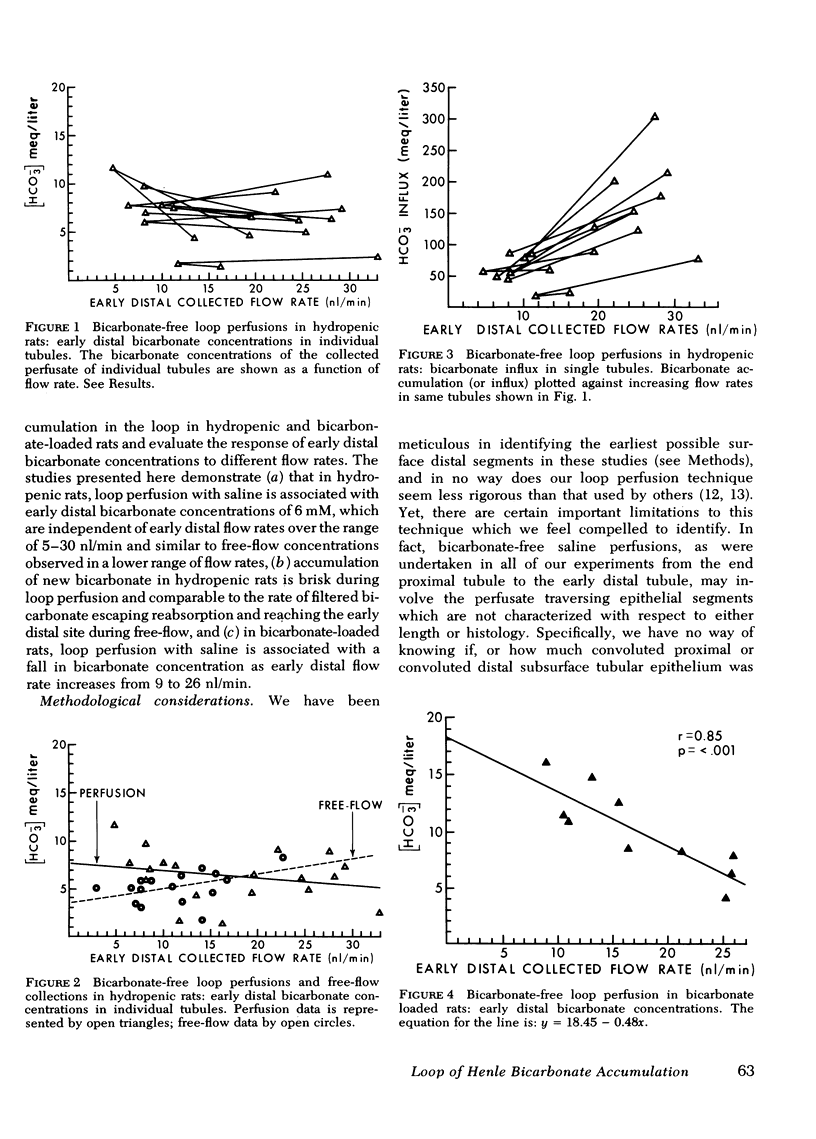
We have carried out perfusion studies on hydropenic and bicarbonate-loaded rats to provide direct in vivo observations on bicarbonate accumulation in the short loops of Henle. Analysis of early distal tubular fluid was made during bicarbonate-free saline perfusion from the end proximal to the early distal site, documenting accumulation of "new" bicarbonate. During perfusion in hydropenic rats, steady-state bicarbonate concentrations were suggested by early distal values of approximately equal to mM, which were independent of perfusion rate and virtually indistinguishable from bicarbonate concentration measured during free flow when filtered bicarbonate was allowed to enter the loop. Thus, loop bicarconate accumulation was apparently sufficient to allow new bicarbonate to enter at a rate comparable to that delivered to the early distal site during free flow, recognizing of course that free-flow delivery rates are the result of complex components of filtration and bidirectional fluxes. In bicarbonate-loaded rats, however, bicarbonate accumulation rates although higher than in hydropenia, were much lower than free-flow delivery rates. Furthermore, early distal bicarbonate concentrations during bicarbonate loading fell as perfusion rate increased, presumably because of a limitation to increasing ionic bicarbonate entry.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bank N., Aynedjian H. S. A microperfusion study of bicarbonate accumulation in the proximal tubule of the rat kidney. J Clin Invest. 1967 Jan;46(1):95–102. doi: 10.1172/JCI105515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulpaep E. L. Permeability changes of the proximal tubule of Necturus during saline loading. Am J Physiol. 1972 Mar;222(3):517–531. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1972.222.3.517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burg M., Green N. Bicarbonate transport by isolated perfused rabbit proximal convoluted tubules. Am J Physiol. 1977 Oct;233(4):F307–F314. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1977.233.4.F307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imai M., Seldin D. W., Kokko J. P. Effect of perfusion rate on the fluxes of water, sodium, chloride and urea across the proximal convoluted tubule. Kidney Int. 1977 Jan;11(1):18–27. doi: 10.1038/ki.1977.3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunau R. T., Jr, Webb H. L., Borman S. C. Characteristics of the relationship between the flow rate of tubular fluid and potassium transport in the distal tubule of the rat. J Clin Invest. 1974 Dec;54(6):1488–1495. doi: 10.1172/JCI107897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine D. Z. Effect of acute hypercapnia on proximal tubular water and bicarbonate reabsorption. Am J Physiol. 1971 Oct;221(4):1164–1170. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.221.4.1164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine D. Z. Measurement of tubular fluid bicarbonate concentration by the cuvette-type glass micro pH electrode. Yale J Biol Med. 1972 Jun-Aug;45(3-4):368–372. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine D. Z., Nash L. A., Chan T., Dubrovskis A. H. Proximal bicarbonate reabsorption during Ringer and albumin infusions in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1976 Jun;57(6):1490–1497. doi: 10.1172/JCI108419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine D. Z., Nash L. A. Effect of chronic NH4Cl acidosis on proximal tubular H2O and HCO3 reabsorption. Am J Physiol. 1973 Aug;225(2):380–384. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1973.225.2.380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine D. Z., Walker T., Nash L. A. Effects of KCl infusions on proximal tubular function in normal and potassium-depleted rats. Kidney Int. 1973 Nov;4(5):318–325. doi: 10.1038/ki.1973.123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malnic G., De Mello Aires M., Giebisch G. Micropuncture study of renal tubular hydrogen ion transport in the rat. Am J Physiol. 1972 Jan;222(1):147–158. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1972.222.1.147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malnic G., Steinmetz P. R. Transport processes in urinary acidification. Kidney Int. 1976 Feb;9(2):172–188. doi: 10.1038/ki.1976.19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malnic G., de Mello-Aires M. Kinetic study of bicarbonate reabsorption in proximal tubule of the rat. Am J Physiol. 1971 Jun;220(6):1759–1767. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.220.6.1759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKinney T. D., Burg M. B. Biocarbonate and fluid absorption by renal proximal straight tubules. Kidney Int. 1977 Jul;12(1):1–8. doi: 10.1038/ki.1977.72. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan T., Berliner R. W. A study by continuous microperfusion of water and electrolyte movements in the loop of Henle and distal tubule of the rat. Nephron. 1969;6(3):388–405. doi: 10.1159/000179741. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raman S., Mousseau G., Levine D. Z. Statistical models for renal micropuncture studies. Am J Physiol. 1977 Oct;233(4):F349–F357. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1977.233.4.F349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnermann J. Microperfusion study of single short loops of Henle in rat kidney. Pflugers Arch Gesamte Physiol Menschen Tiere. 1968;300(4):255–282. doi: 10.1007/BF00364298. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhlich E., Baldamus C. A., Ullrich K. J. Verhalten von CO2-Druck und Bicarbonat im Gegenstromysystem des Nierenmarks. Pflugers Arch. 1968;303(1):31–48. doi: 10.1007/BF00586825. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warnock D. G., Burg M. B. Urinary acidification: CO2 transport by the rabbit proximal straight tubule. Am J Physiol. 1977 Jan;232(1):F20–F25. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1977.232.1.F20. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright F. S. Increasing magnitude of electrical potential along the renal distal tubule. Am J Physiol. 1971 Mar;220(3):624–638. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.220.3.624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright F. S. Sites and mechanisms of potassium transport along the renal tubule. Kidney Int. 1977 Jun;11(6):415–432. doi: 10.1038/ki.1977.60. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


