Abstract
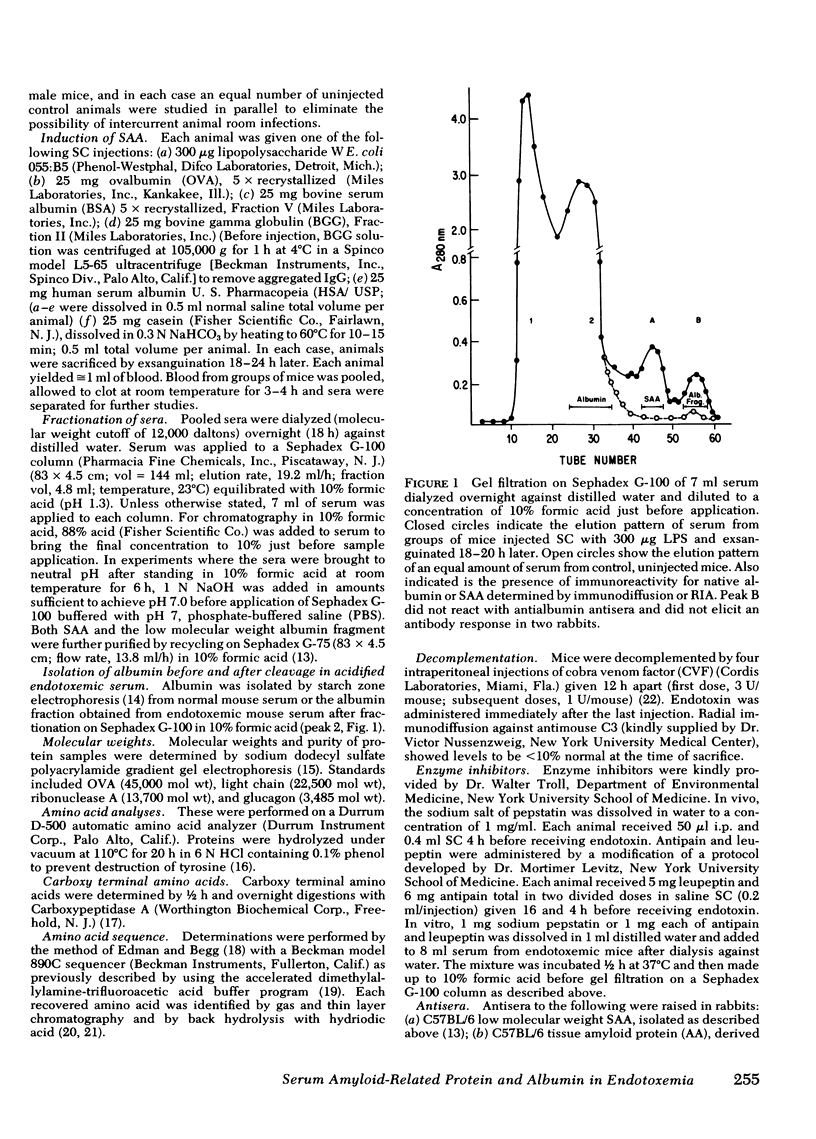
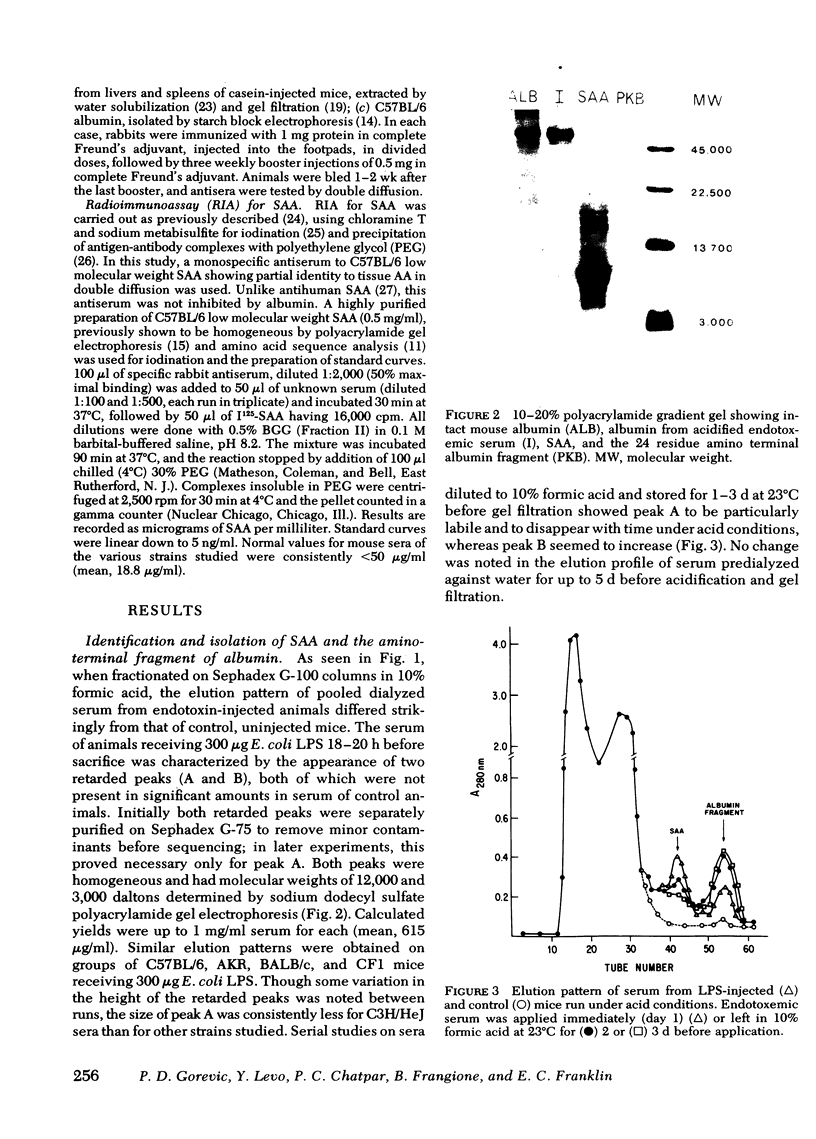
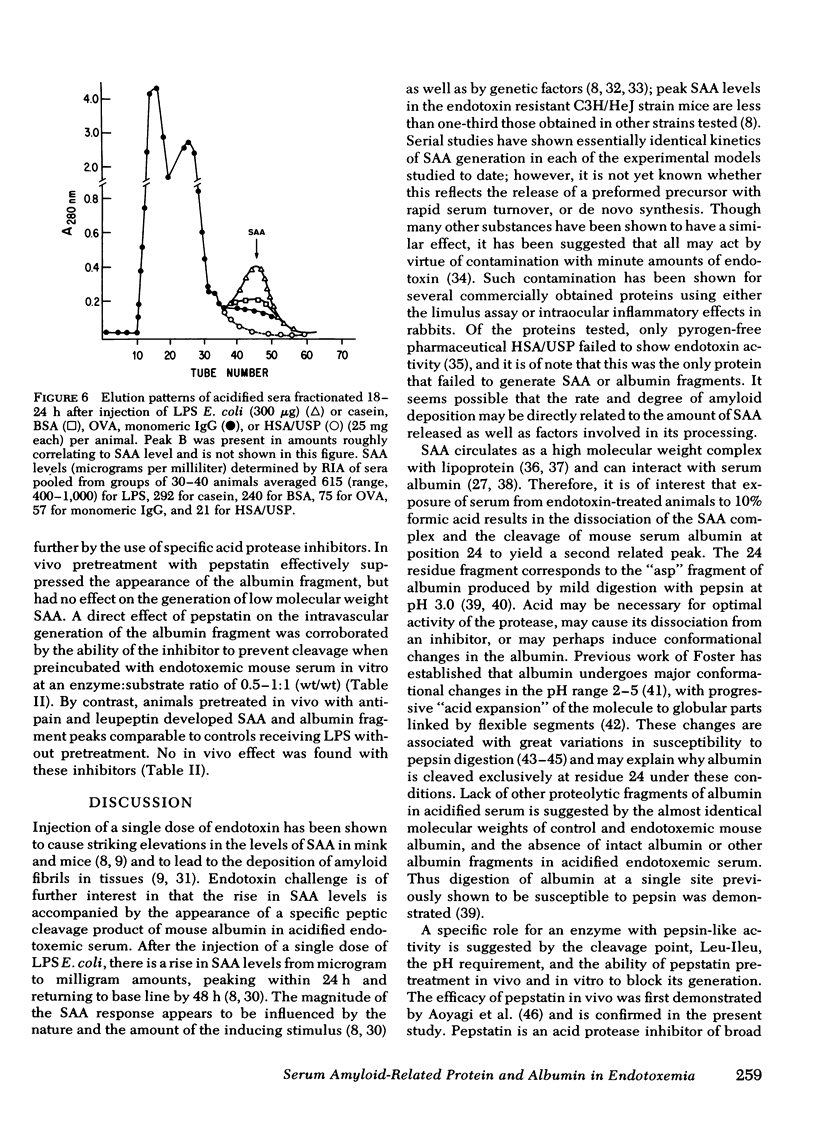
Endotoxin has been shown to induce amyloidosis in mice and to result in the appearance in serum of large amounts of amyloidrelated protein (SAA). After injection of 300 μg lipopolysaccharide Escherichia coli, SAA behaves as an acute phase reactant with levels reaching a peak of >600 μg/ml at 18-22 h and returning to base line (<50 μg/ml) by 48 h in each of four strains tested; only the endotoxin-resistant C3H/HeJ strain showed a smaller response. Lesser, though significant, elevations were also found after subcutaneous injection of 25 mg of casein, bovine serum albumin, ovalbumin, or monomeric immunoglobulin G, whereas pyrogen-free human serum albumin/U. S. Pharmacopeia failed to raise SAA levels. SAA generation may thus be a result of endotoxin contamination of these protein preparations.
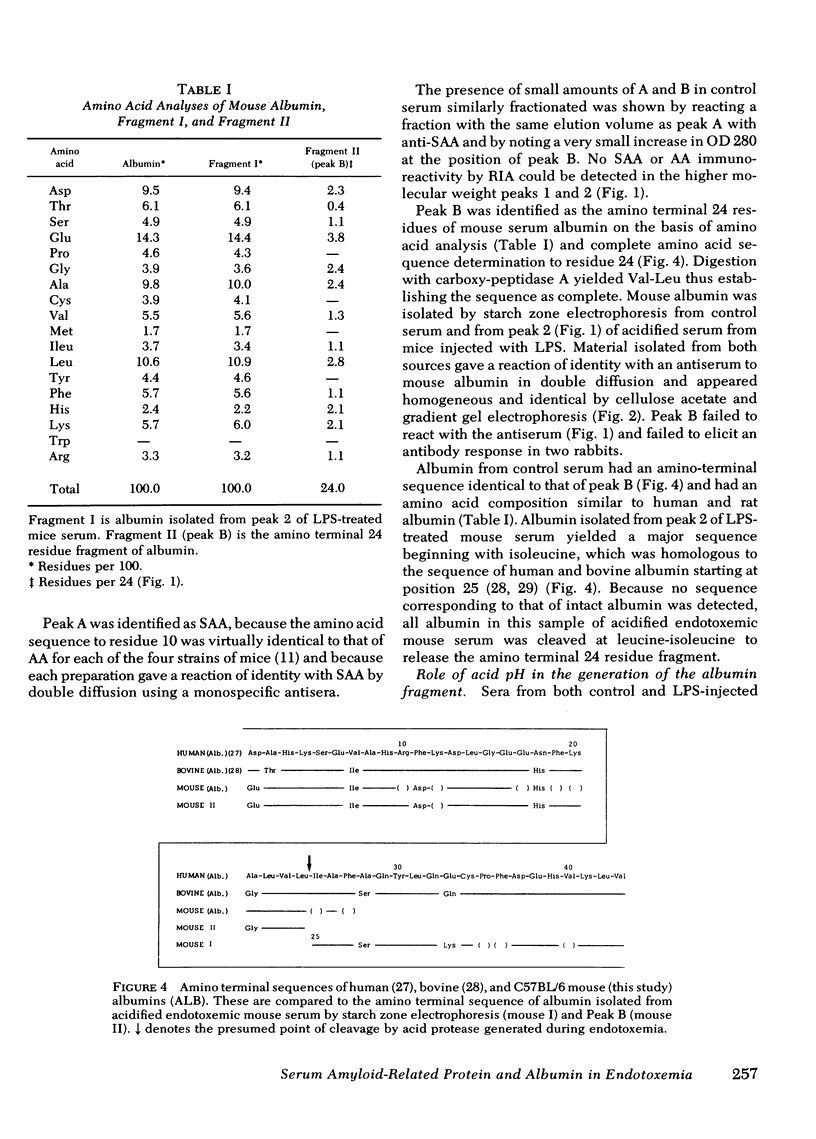
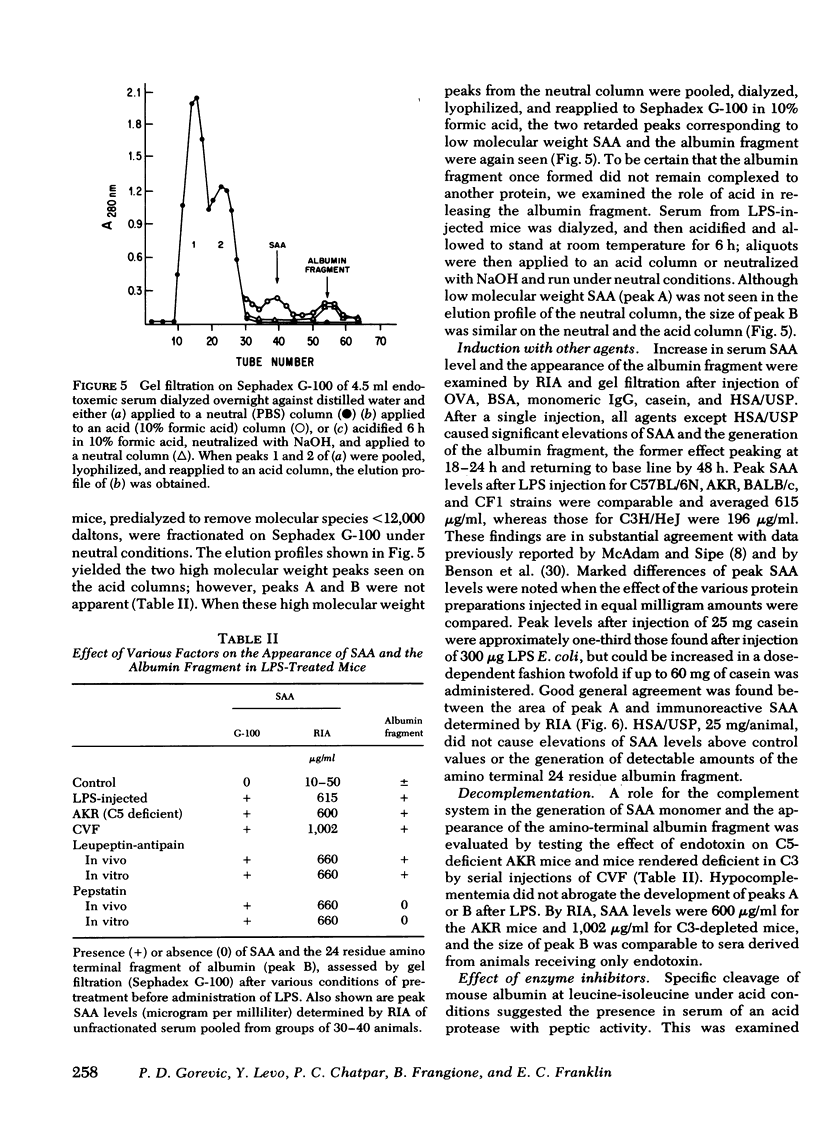
Also present in equivalent amounts in acidified serum from endotoxin-treated mice, but barely detectable in control sera, was a 3,000-dalton molecule whose amino acid sequence is identical to the amino terminal 24 residues of mouse albumin. The appearance of SAA and the amino terminal albumin fragment after endotoxin were unaffected by pretreatment with cobra venom factor, and equivalent levels were found in C5-deficient mice. Pretreatment with pepstatin in vivo, or before acidification in vitro, prevented the appearance of the albumin fragment but had no effect on the appearance of SAA, whereas leupeptin and antipain did not affect the appearance of either SAA or the albumin fragment. These studies suggest that the generation of SAA after endotoxin administration does not involve complement activation or intravascular proteolytic activity, whereas the liberation of a specific peptic-like cleavage product of albumin appears to be the consequence of an acid protease.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anders R. F., Nordstoga K., Natvig J. B., Husby G. Amyloid-related serum protein SAA in endotoxin-induced amyloidosis of the mink. J Exp Med. 1976 Mar 1;143(3):678–683. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.3.678. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aoyagi T., Kunimoto S., Morishima H., Takeuchi T., Umezawa H. Effect of pepstatin on acid proteases. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1971 Oct;24(10):687–694. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.24.687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barth W. F., Willerson J. T., Asofsky R., Sheagren J. N., Wolff S. M. Experimental murine amyloid. 3. Amyloidosis induced with endotoxins. Arthritis Rheum. 1969 Dec;12(6):615–626. doi: 10.1002/art.1780120609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benditt E. P., Eriksen N. Amyloid protein SAA is associated with high density lipoprotein from human serum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):4025–4028. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.4025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benson M. D., Scheinberg M. A., Shirahama T., Cathcart E. S., Skinner M. Kinetics of serum amyloid protein A in casein-induced murine amyloidosis. J Clin Invest. 1977 Mar;59(3):412–417. doi: 10.1172/JCI108654. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bito L. Z. Inflammatory effects of endotoxin-like contaminants in commonly used protein preparations. Science. 1977 Apr 1;196(4285):83–85. doi: 10.1126/science.557238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. R. Structural origins of mammalian albumin. Fed Proc. 1976 Aug;35(10):2141–2144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cline M. J., Melmon K. L., Davis W. C., Williams H. E. Mechanism of endotoxin interaction with human leucocytes. Br J Haematol. 1968 Dec;15(6):539–547. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1968.tb01576.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochrane C. G., Müller-Eberhard H. J., Aikin B. S. Depletion of plasma complement in vivo by a protein of cobra venom: its effect on various immunologic reactions. J Immunol. 1970 Jul;105(1):55–69. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desbuquois B., Aurbach G. D. Use of polyethylene glycol to separate free and antibody-bound peptide hormones in radioimmunoassays. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1971 Nov;33(5):732–738. doi: 10.1210/jcem-33-5-732. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edman P., Begg G. A protein sequenator. Eur J Biochem. 1967 Mar;1(1):80–91. doi: 10.1007/978-3-662-25813-2_14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elin R. J., Wolff S. M. Biology of endotoxin. Annu Rev Med. 1976;27:127–141. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.27.020176.001015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank M. M., May J. E., Kane M. A. Contributions of the classical and alternate complement pathways to the biological effects of endotoxin. J Infect Dis. 1973 Jul;128(Suppl):176–181. doi: 10.1093/infdis/128.supplement_1.s176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franklin E. C. Some properties of antisera to serum amyloid A protein (SAA): inhibition of precipitation by complexing of SAA to albumin. J Exp Med. 1976 Dec 1;144(6):1679–1682. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.6.1679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENWOOD F. C., HUNTER W. M., GLOVER J. S. THE PREPARATION OF I-131-LABELLED HUMAN GROWTH HORMONE OF HIGH SPECIFIC RADIOACTIVITY. Biochem J. 1963 Oct;89:114–123. doi: 10.1042/bj0890114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenner G. G., Ein D., Eanes E. D., Bladen H. A., Terry W., Page D. L. Creation of "amyloid" fibrils from Bence Jones proteins in vitro. Science. 1971 Nov 12;174(4010):712–714. doi: 10.1126/science.174.4010.712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorevic P. D., Levo Y., Frangione B., Franklin E. C. Polymorphism of tissue and serum amyloid A (AA and SAA) proteins in the mouse. J Immunol. 1978 Jul;121(1):138–140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilak M. C., Harmsen B. J., Braam W. G., Joordens J. J., Van Os G. A. Conformational studies on large fragments of bovine serum albumin in relation to the structure of the molecule. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1974;6(2):95–101. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1974.tb02366.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JANOFF A., WEISSMANN G., ZWEIOFACH B. W., THOMAS L. Pathogenesis of experimental shock. IV. Studies on lysosomes in normal and tolerant animals subjected to lethal trauma and endotoxemia. J Exp Med. 1962 Oct 1;116:451–466. doi: 10.1084/jem.116.4.451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King T. P. Limited pepsin digestion of bovine plasma albumin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1973 Jun;156(2):509–520. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(73)90300-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavie G., Zucker-Franklin D., Franklin E. C. Degradation of serum amyloid A protein by surface-associated enzymes of human blood monocytes. J Exp Med. 1978 Oct 1;148(4):1020–1031. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.4.1020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin M., Franklin E. C., Frangione B., Pras M. The amino acid sequence of a major nonimmunoglobulin component of some amyloid fibrils. J Clin Invest. 1972 Oct;51(10):2773–2776. doi: 10.1172/JCI107098. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linke R. P., Zucker-Franklin D., Franklin E. D. Morphologic, chemical, and immunologic studies of amyloid-like fibrils formed from Bence Jones Proteins by proteolysis. J Immunol. 1973 Jul;111(1):10–23. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis J., Kenrick K. G. Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis in a continuous molecular sieve gradient. Anal Biochem. 1968 Oct 24;25(1):347–362. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(68)90109-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAdam K. P., Elin R. J., Sipe J. D., Wolff S. M. Changes in human serum amyloid A and C-reactive protein after etiocholanolone-induced inflammation. J Clin Invest. 1978 Feb;61(2):390–394. doi: 10.1172/JCI108949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAdam K. P., Ryan J. L. C57BL/10/CR mice: nonresponders to activation by the lipid a moiety of bacterial lipopolysaccharide. J Immunol. 1978 Jan;120(1):249–253. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAdam K. P., Sipe J. D. Murine model for human secondary amyloidosis: genetic variability of the acute-phase serum protein SAA response to endotoxins and casein. J Exp Med. 1976 Oct 1;144(4):1121–1127. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.4.1121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters T., Jr, Blumenstock F. A. Copper-binding properties of bovine serum albumin and its amino-terminal peptide fragment. J Biol Chem. 1967 Apr 10;242(7):1574–1578. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters T., Jr, Hawn C. Isolation of two large peptide fragments from the amino- and carboxyl-terminal positions of bovine serum albumin. J Biol Chem. 1967 Apr 10;242(7):1566–1573. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pisano J. J., Bronzert T. J. Analysis of amino acid phenylthiohydantoins by gas chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1969 Oct 25;244(20):5597–5607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pras M., Schubert M., Zucker-Franklin D., Rimon A., Franklin E. C. The characterization of soluble amyloid prepared in water. J Clin Invest. 1968 Apr;47(4):924–933. doi: 10.1172/JCI105784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal C. J., Franklin E. C., Frangione B., Greenspan J. Isolation and partial characterization of SAA-an amyloid-related protein from human serum. J Immunol. 1976 May;116(5):1415–1418. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal C. J., Franklin E. C. Serum amyloid A (SAA) protein-interaction with itself and serum albumin. J Immunol. 1977 Aug;119(2):630–634. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal C. J., Franklin E. C. Variation with age and disease of an amyloid A protein-related serum component. J Clin Invest. 1975 Apr;55(4):746–753. doi: 10.1172/JCI107985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SANGER F., THOMPSON E. O. Halogenation of tyrosine during acid hydrolysis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 May 14;71:468–471. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)91108-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skogen B., Natvig J. B., Michaelsen T. E., Anders R. F. A high molecular weight serum protein is the carrier for amyloid-related protein SAA. Scand J Immunol. 1977;6(12):1363–1368. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1977.tb00379.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slayter E. M. An electron microscope study of the conformational change in bovine serum albumin at low pH. J Mol Biol. 1965 Dec;14(2):443–452. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80194-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sleeman H. K., Lamborn P. B., Diggs J. W., Emery C. E. Effects of endotoxin and histamine on serum enzyme activity. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1971 Nov;138(2):536–541. doi: 10.3181/00379727-138-35934. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers M. R., Smythers G. W., Oroszlan S. Thin-layer chromatography of sub-nanomole amounts of phenylthiohydantoin (PTH) amino acids on polyamide sheets. Anal Biochem. 1973 Jun;53(2):624–628. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90114-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan M., Epstein W. Polymer formation during the degradation of human light chain and Bence-Jones proteins by an extrct of the lysosomal fraction of normal human kidney. Immunochemistry. 1972 Jan;9(1):9–16. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(72)90278-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umezawa H. Structures and activities of protease inhibitors of microbial origin. Methods Enzymol. 1976;45:678–695. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(76)45058-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEBER G., YOUNG L. B. FRAGMENTATION OF BOVINE SERUM ALBUMIN BY PEPSIN. I. THE ORIGIN OF THE ACID EXPANSION OF THE ALBUMIN MOLECULE. J Biol Chem. 1964 May;239:1415–1423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEISSMANN G., THOMAS L. Studies on lysosomes. I. The effects of endotoxin, endotoxin tolerance, and cortisone on the release of acid hydrolases from a granular fraction of rabbit liver. J Exp Med. 1962 Oct 1;116:433–450. doi: 10.1084/jem.116.4.433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson J., Largen M., McAdam K. P. Genetic control of endotoxic responses in mice. J Exp Med. 1978 Jan 1;147(1):39–49. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.1.39. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]