Abstract
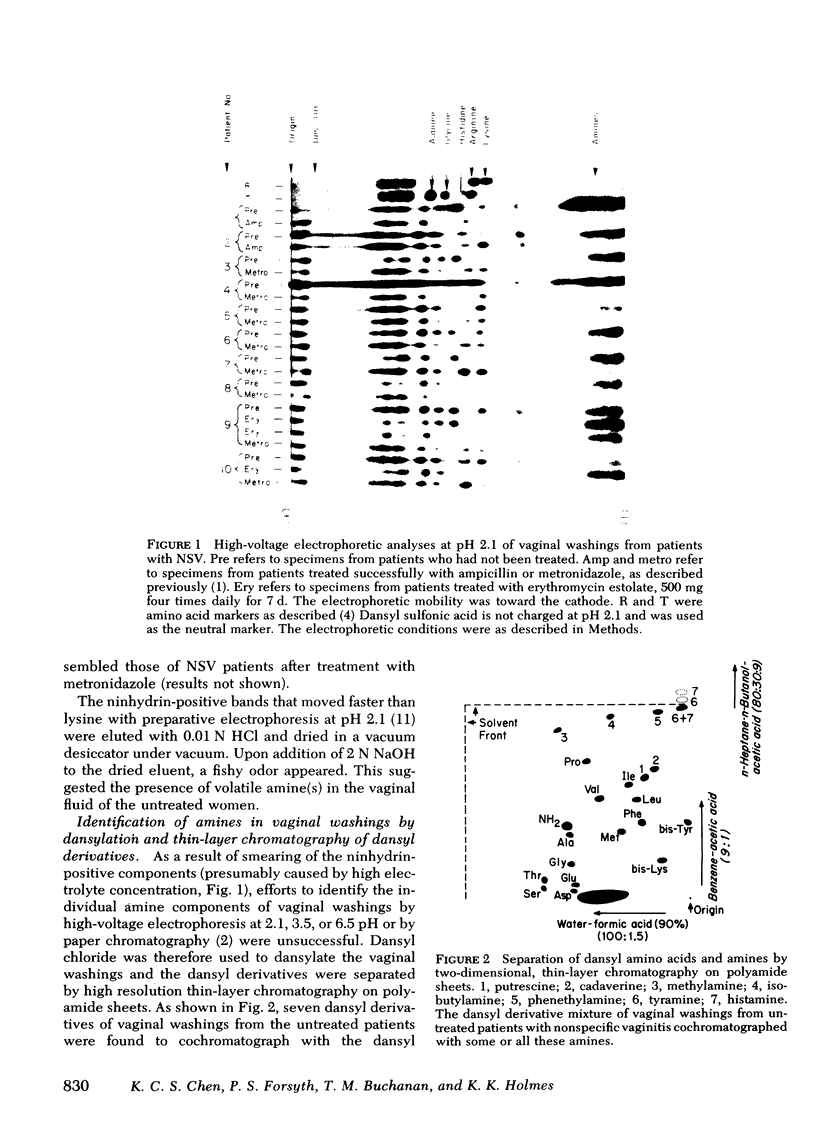
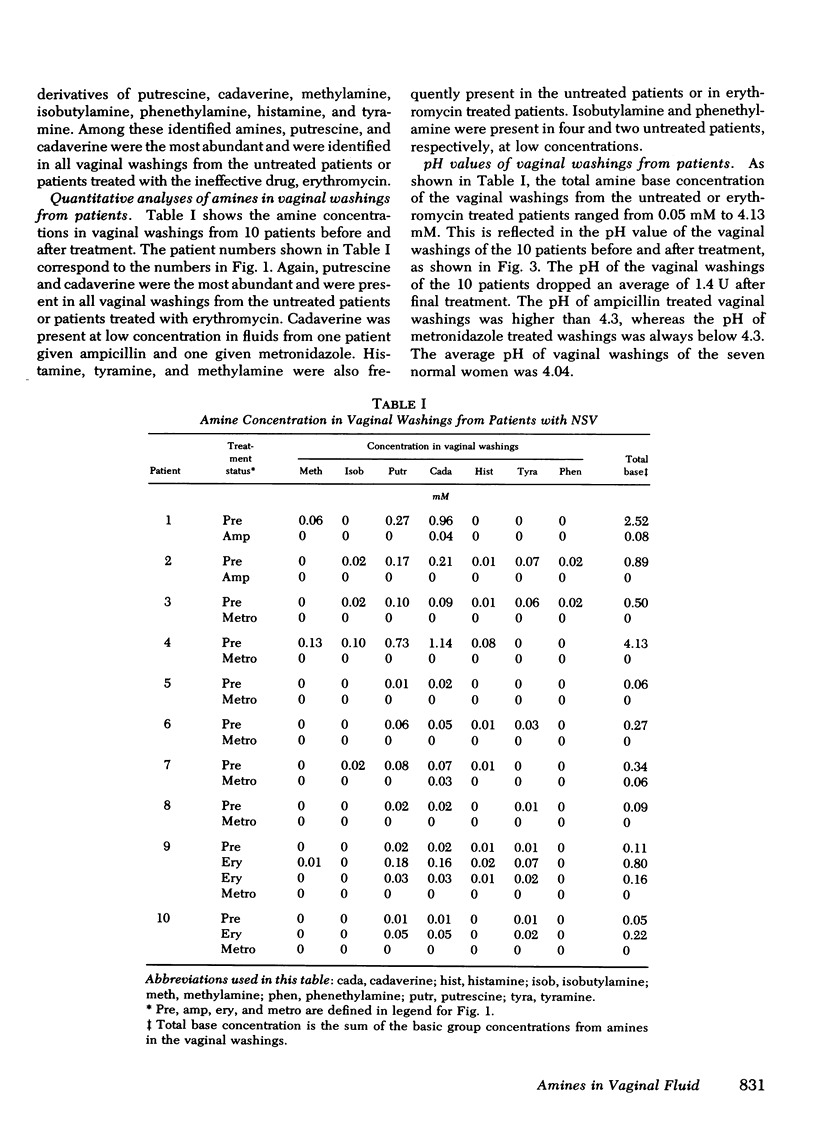
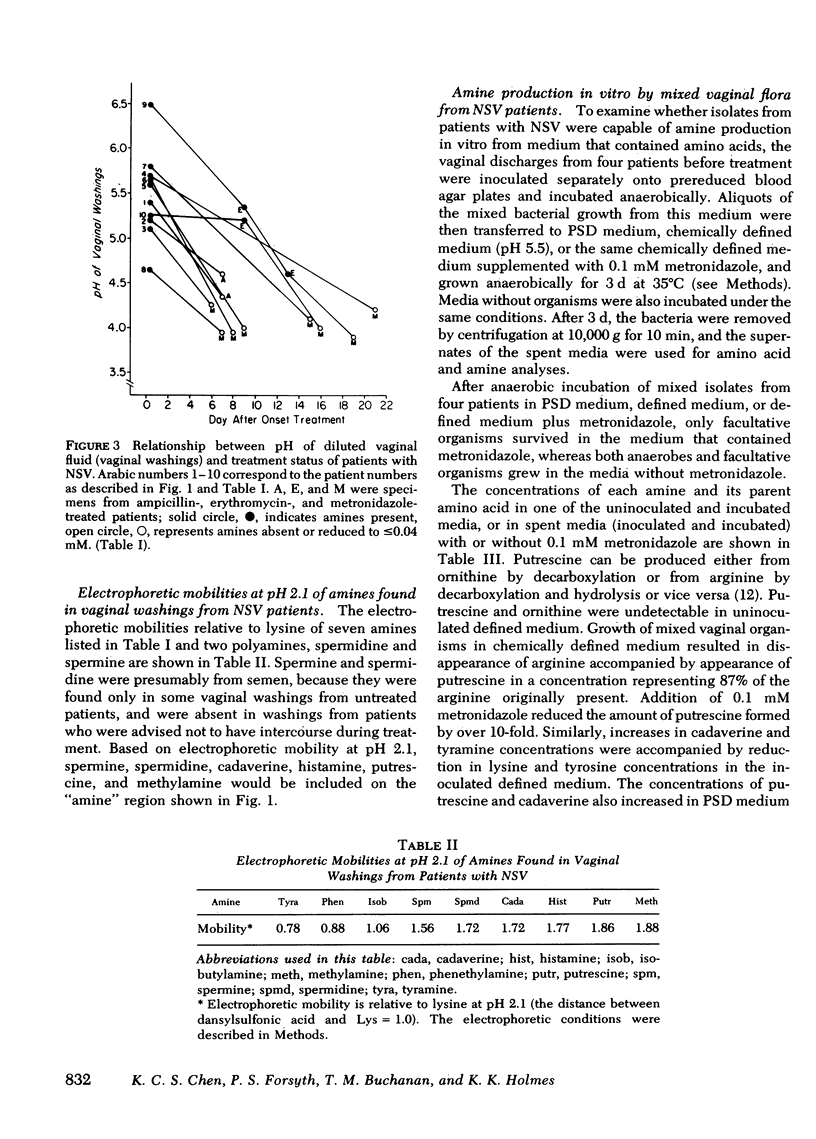
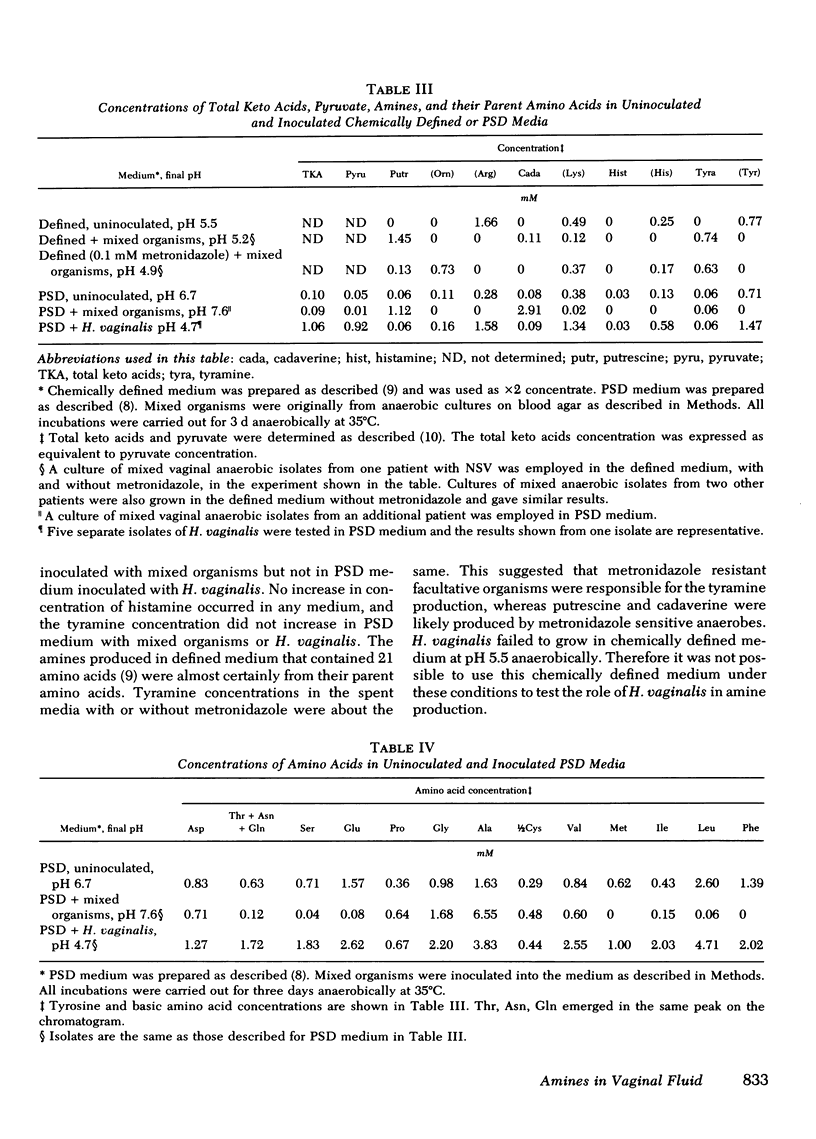
We examined the vaginal washings from patients with nonspecific vaginitis (NSV) to seek biochemical markers and possible explanations for the signs and symptoms of this syndrome. Seven amines were identified including methylamine, isobutylamine, putrescine, cadaverine, histamine, tyramine, and phenethylamine. These amines may contribute to the symptoms of NSV and may contribute to the elevated pH of the vaginal discharge. They may also be partly responsible for the "fishy" odor that is characteristic of vaginal discharges from these patients. Among the seven amines, putrescine and cadaverine were the most abundant and were present in all vaginal discharges from each of ten patients before treatment. These amines are produced in vitro during growth of mixed vaginal bacteria in chemically defined medium, presumably by decarboxylation of the corresponding amino acids. We hypothesize the anaerobic vaginal organisms, previously shown to be quantitatively increased in NSV, are responsible for the amine production, because metronidazole inhibited the production of amines by vaginal bacteria in vitro, and Haemophilus vaginalis did not produce amines. H. vaginalis did release high concentrations of pyruvic acid and of amino acids during growth in peptone-starch-dextrose medium, whereas, other vaginal flora consumed both pyruvic acid and amino acids in the same medium during growth. These findings suggest that a symbiotic relationship may exist between H. vaginalis and other vaginal flora in patients with NSV.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akerlund M., Mårdh P. A. Isolation and identification of Corynebacterium vaginale (Haemophilus vaginalis) in women with infections of the lower genital tract. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 1974;53(1):85–90. doi: 10.3109/00016347409156894. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catlin B. W. Nutritional profiles of Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Neisseria meningitidis, and Neisseria lactamica in chemically defined media and the use of growth requirements for gonococcal typing. J Infect Dis. 1973 Aug;128(2):178–194. doi: 10.1093/infdis/128.2.178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen K. C., Kindt T. J., Krause R. M. Primary structure of the L chain from a rabbit homogeneous antibody to streptococcal carbohydrate. I. Purification of antibody and sequence determination of peptides from alpha-chymo-tryptic and thermolytic digests. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 10;250(9):3280–3288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen K. C., Krause R. M. A peptide mapping technique--a three map system. Anal Biochem. 1975 Nov;69(1):180–186. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90579-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunkelberg W. E. Corynebacterium vaginale. Sex Transm Dis. 1977 Apr-Jun;4(2):69–75. doi: 10.1097/00007435-197704000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunkelberg W. E., Jr, Skaggs R., Kellogg D. S., Jr Method for isolation and identification of Corynebacterium vaginale (Haemophilus vaginalis). Appl Microbiol. 1970 Jan;19(1):47–52. doi: 10.1128/am.19.1.47-52.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eschenbach D. A., Buchanan T. M., Pollock H. M., Forsyth P. S., Alexander E. R., Lin J. S., Wang S. P., Wentworth B. B., MacCormack W. M., Holmes K. K. Polymicrobial etiology of acute pelvic inflammatory disease. N Engl J Med. 1975 Jul 24;293(4):166–171. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197507242930403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GARDNER H. L., DUKES C. D. Haemophilus vaginalis vaginitis: a newly defined specific infection previously classified non-specific vaginitis. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1955 May;69(5):962–976. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEILMANN J., BARROLLIER J., WATZKE E. Beitrag zur Aminosäurebestimmung auf Papierchromatogrammen. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1957;309(4-6):219–220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTIN W. H., Jr, PELCZAR M. J., Jr, HANSEN P. A. Putrescine as a growth requirement for Neisseria. Science. 1952 Oct 31;116(3018):483–484. doi: 10.1126/science.116.3018.483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss C. W., Dunkelberg W. E., Jr Volatile and cellular fatty acids of Haemophilus vaginalis. J Bacteriol. 1969 Oct;100(1):544–546. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.1.544-546.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pheifer T. A., Forsyth P. S., Durfee M. A., Pollock H. M., Holmes K. K. Nonspecific vaginitis: role of Haemophilus vaginalis and treatment with metronidazole. N Engl J Med. 1978 Jun 29;298(26):1429–1434. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197806292982601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROGOSA M., BISHOP F. S. THE GENUS VEILLONELLA . II. NUTRITIONAL STUDIES. J Bacteriol. 1964 Mar;87:574–580. doi: 10.1128/jb.87.3.574-580.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson K. J. Use of visual dye markers on high-voltage paper ionophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1971 Mar;40(1):29–34. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90080-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods K. R., Wang K. T. Separation of dansyl-amino acids by polyamide layer chromatography. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Feb 21;133(2):369–370. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(67)90078-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]