Abstract
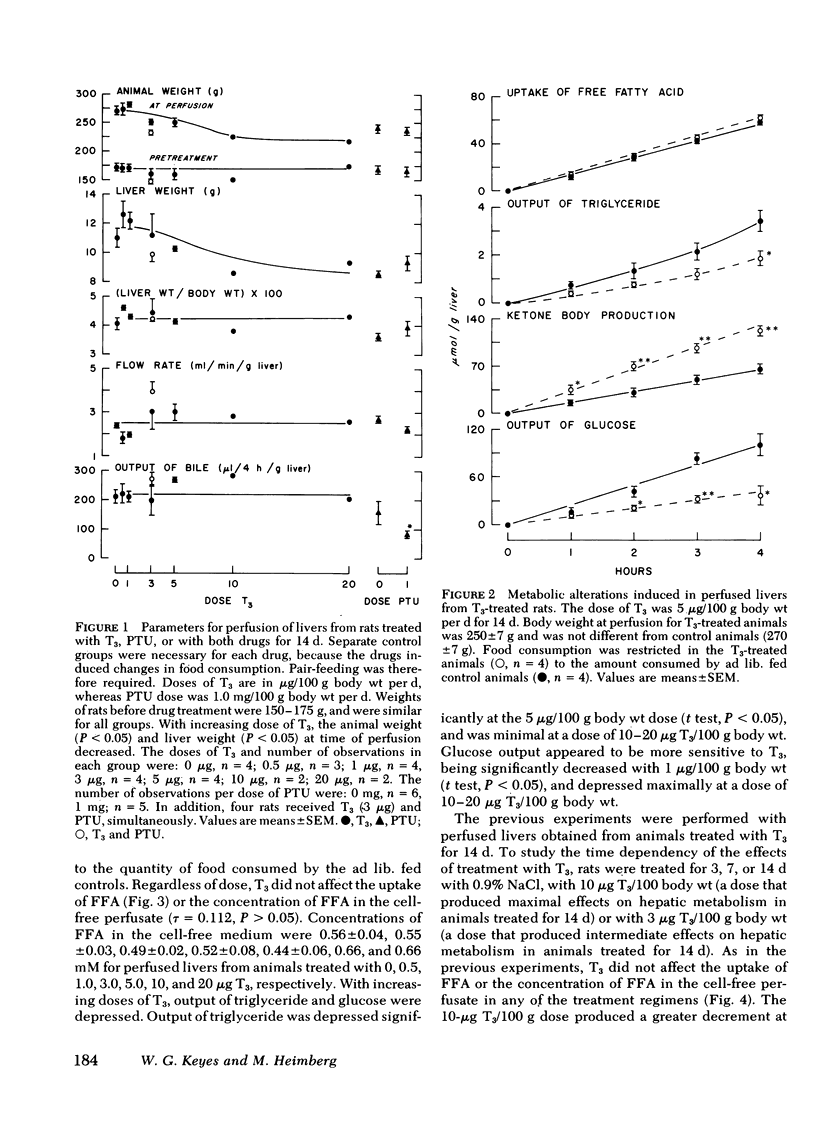
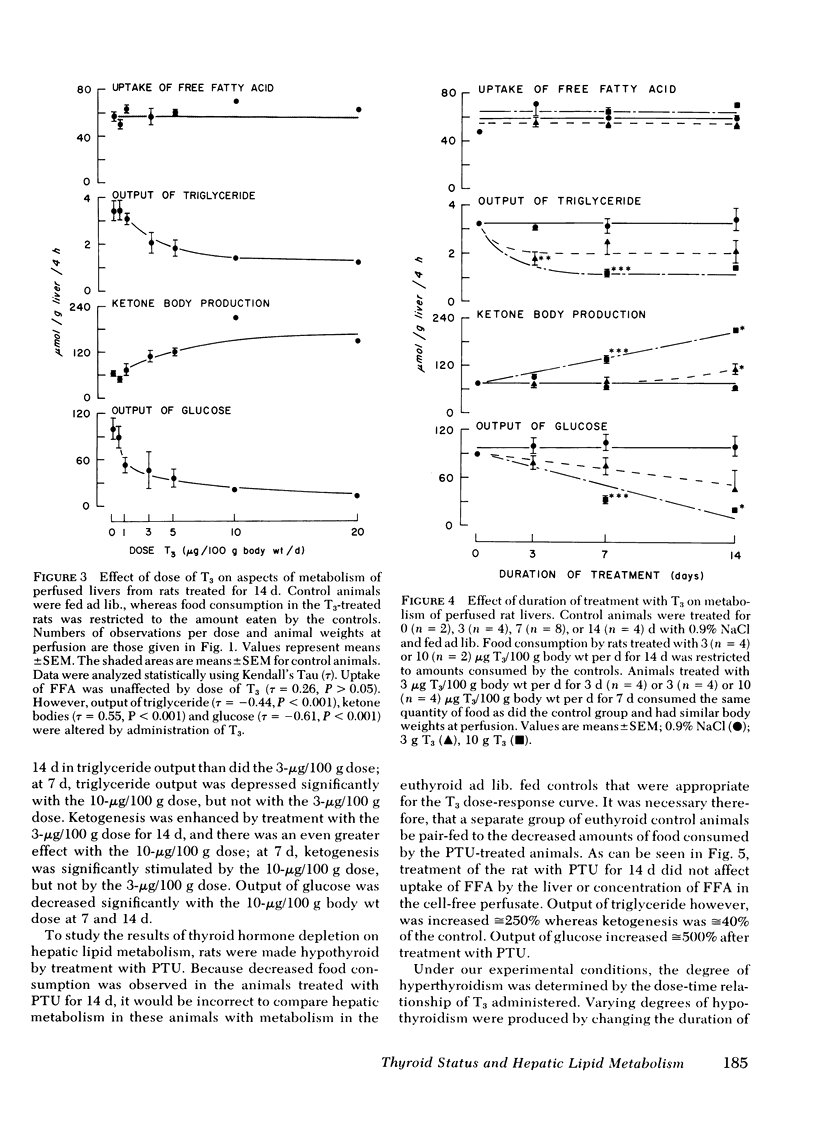
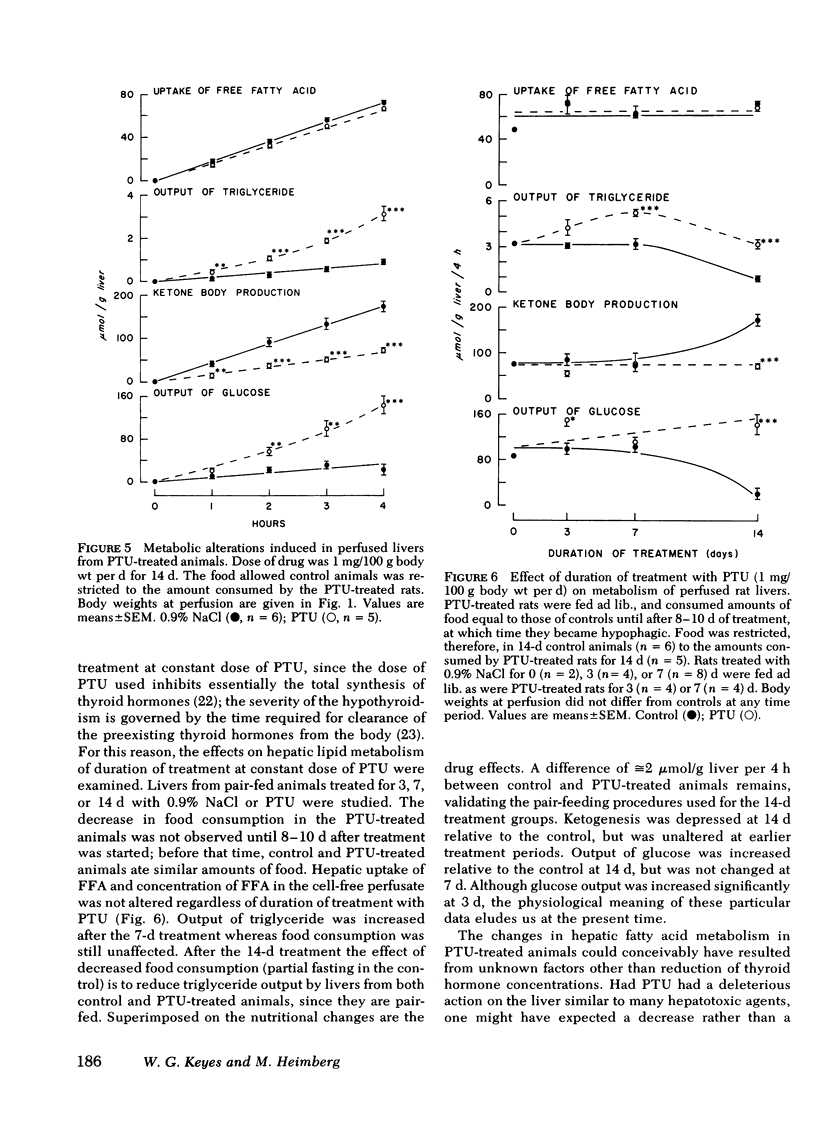
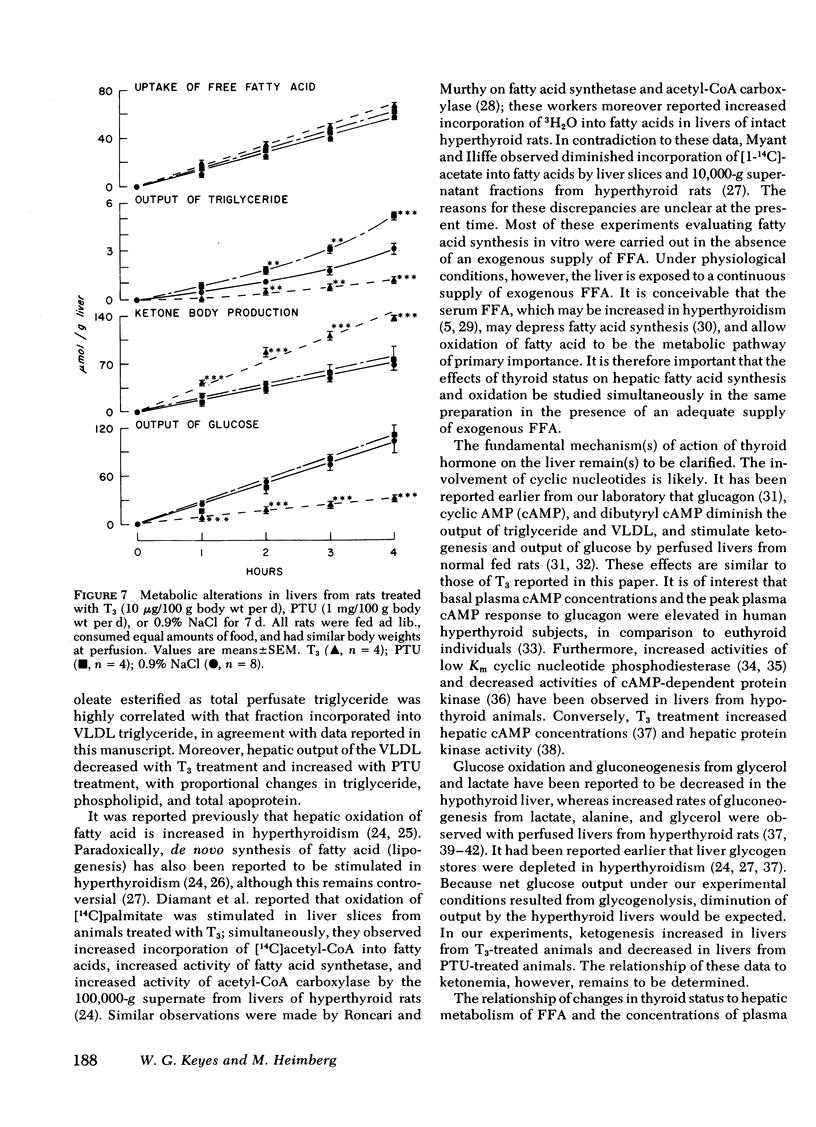
Thyroid disease is often accompanied by changes in the concentrations of serum lipids and lipoproteins. To evaluate the hepatic contribution to the serum abnormalities in thyroid disease, we examined fatty acid metabolism in perfused livers from pair-fed rats made hypothyroid with propylthiouracil (PTU) or made hyperthyroid by treatment with triiodothyronine (T3). The animals treated with T3 became hyperphagic, depending on dose of drug and duration of hyperthyroidism. It was necessary, therefore, for appropriate controls, that food intake of T3-treated rats be restricted to quantities consumed by euthyroid rats. Animals treated with PTU for 2 wk became hypophagic, and therefore, food consumption of controls was restricted to that eaten by rats receiving PTU. Dependent on dose of T3 and duration of treatment, the output of triglyceride and glucose was diminished, whereas output of ketone bodies was increased by livers from hyperthyroid animals. In contrast, livers from PTU-treated animals secreted increased amounts of triglyceride and glucose, whereas ketogenesis was diminished. The best models for study proved to be animals treated with either 10 μg T3/100 g body wt per d or 1 mg PTU/100 g body wt per d for 7 d. Under these conditions, all animals consumed the same quantity of food as did the euthyroid rats, but continued to display the metabolic alterations outlined above. The effects of PTU on hepatic metabolism were readily reversible by simultaneous administration of T3. It is clear from these data that the thyroid status of the rat regulates hepatic triglyceride formation and secretion, and ketogenesis.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BAKKE J. L., LAWRENCE N. INFLUENCE OF PROPYLTHIOURACIL AND THYROXINE ON SYNTHESIS AND SECRETION OF THYROID-STIMULATING HORMONE IN THE HYPOTHYROID RAT. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1964 May;46:111–123. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0460111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOYD G. S., OLIVER M. F. Thyroid hormones and plasma lipids. Br Med Bull. 1960 May;16:138–142. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a069813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baquer N. Z., Cascales M., McLean P., Greenbaum A. L. Effects of thyroid hormone deficiency on the distribution of hepatic metabolites and control of pathways of carbohydrate metabolism in liver and adipose tissue of the rat. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Sep 15;68(2):403–413. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10827.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Correze C., Auclair R., Nunez J. Cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases, insulin and thyroid hormones. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1976 Jun-Jul;5(1-2):67–79. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(76)90071-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Correze C., Pinell P., Nunez J. Effects of thyroid hormones on phosphorylation of liver ribosomal proteins and on protein phosphokinase activity. FEBS Lett. 1972 Jun 1;23(1):87–91. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80291-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamant S., Gorin E., Shafrir E. Enzyme activities related to fatty-acid synthesis in liver and adipose tissue of rats treated with triiodothyronine. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Apr 24;26(4):553–559. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01798.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doar J. W., Stamp T. C., Wynn V., Audhya T. K. Effects of oral and intravenous glucose loading in thyrotoxicosis. Studies of plasma glucose, free fatty acid, plasma insulin and blood pyruvate levels. Diabetes. 1969 Sep;18(9):633–639. doi: 10.2337/diab.18.9.633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Exton J. H., Corbin J. G., Park C. R. Control of gluconeogenesis in liver. IV. Differential effects of fatty acids and glucagon on ketogenesis and gluconeogenesis in the perfused rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 10;244(15):4095–4102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLCH J., LEES M., SLOANE STANLEY G. H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J Biol Chem. 1957 May;226(1):497–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FURMAN R. H., HOWARD R. P., LAKSHMI K., NORCIA L. N. The serum lipids and lipoproteins in normal and hyperlipidemic subjects as determined by preparative ultracentrifugation. Effects of dietary and therapeutic measures. Changes induced by in vitro exposure of serum to sonic forces. Am J Clin Nutr. 1961 Jan-Feb;9:73–102. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/9.1.73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gumaa K. A., Hothersall J. S., Greenbaum A. L., McLean P. Thyroid hormone control of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases and the regulation of the sensitivity of the liver to hormones. FEBS Lett. 1977 Aug 1;80(1):45–48. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80403-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guttler R. B., Croxson M. S., DeQuattro V. L., Warren D. W., Otis C. L., Nicoloff J. T. Effects of thyroid hormone on plasma adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate production in man. Metabolism. 1977 Oct;26(10):1155–1162. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(77)90043-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heimberg M., Weinstein I., Kohout M. The effects of glucagon, dibutyryl cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate, and concentration of free fatty acid on hepatic lipid metabolism. J Biol Chem. 1969 Oct 10;244(19):5131–5139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- IINO S., YAMADA T., GREER M. A. Effect of graded doses of propylthiouracil on biosynthesis of thyroid hormones. Endocrinology. 1961 Apr;68:582–588. doi: 10.1210/endo-68-4-582. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobsen B. B. Blood lipids during treatment of hyperthyroidism. A statistical evaluation of the relationship between lipids and thyroid variables. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1973 Mar;72(3):443–452. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirkeby K. Post heparin plasma lipoprotein lipase activity in thyroid disease. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1968 Dec;59(4):555–563. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0590555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klausner H. J., Soler-Argilaga C., Heimberg M. Effects of dibutyryl adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate on hepatic metabolism of free fatty acids. Metabolism. 1978 Jan;27(1):13–25. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(78)90119-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohout M., Kohoutova B., Heimberg M. The regulation of hepatic triglyceride metabolism by free fatty acids. J Biol Chem. 1971 Aug 25;246(16):5067–5074. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kutty K. M., Bryant D. G., Farid N. R. Serum lipids in hypothyroidism--a re-evaluation. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1978 Jan;46(1):55–56. doi: 10.1210/jcem-46-1-55. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MALMROS H., SWAHN B. Lipid metabolism in myxedema. Acta Med Scand. 1953;145(5):361–369. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1953.tb07030.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menahan L. A., Wieland O. The role of thyroid function in the metabolism of perfused rat liver with particular reference to gluconeogenesis. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Aug;10(1):188–194. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00672.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miettinen T. A. Mechanism of serum cholesterol reduction by thyroid hormones in hypothyroidism. J Lab Clin Med. 1968 Apr;71(4):537–547. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mishkel M. A., Crowther S. M. Hypothyroidism, an important cause of reversible hyperlipidemia. Clin Chim Acta. 1977 Jan 17;74(2):139–151. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(77)90215-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myant N. B., Iliffe J. The influence of thyroid hormone upon the synthesis of fatty acids in the liver. Biochem Soc Symp. 1963;24:145–154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikkilä E. A., Kekki M. Plasma triglyceride metabolism in thyroid disease. J Clin Invest. 1972 Aug;51(8):2103–2114. doi: 10.1172/JCI107017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hara D. D., Porte D., Jr, Williams R. H. The effect of diet and thyroxin on plasma lipids in myxedema. Metabolism. 1966 Feb;15(2):123–134. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(66)90033-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PETERS J. P., MAN E. B. The significance of serum cholesterol in thyroid disease. J Clin Invest. 1950 Jan;29(1):1–11. doi: 10.1172/JCI102224. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porte D., Jr, O'Hara D. D., Williams R. H. The relation between postheparin lipolytic activity and plasma triglyceride in myxedema. Metabolism. 1966 Feb;15(2):107–113. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(66)90031-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roncari D. A., Murthy V. K. Effects of thyroid hormones on enzymes involved in fatty acid and glycerolipid synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jun 10;250(11):4134–4138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roques M., Tirard A., DeGroot L. J. Liver protein kinase activity and triiodothyronine. Endocrinology. 1977 Apr;100(4):967–973. doi: 10.1210/endo-100-4-967. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPIRTES M. A., MEDES G., WEINHOUSE S. A study of acetate metabolism and fatty acid synthesis in liver slices of hyperthyroid rats. J Biol Chem. 1953 Oct;204(2):705–713. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandhofer F., Sailer S., Braunsteiner H. Plasmalipide bei Störungen der Schilddrüsenfunktion des Menschen. Klin Wochenschr. 1966 Apr 15;44(8):433–436. doi: 10.1007/BF01727456. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sestoft L., Bartels P. D., Fleron P., Folke M., Gammeltoft S., Kristensen L. O. Influence of thyroid state on the effects of glycerol on gluconeogenesis and energy metabolism in perfused rat liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Aug 25;499(1):119–130. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(77)90234-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh S. P., Snyder A. K. Effect of thyrotoxicosis on gluconeogenesis from alanine in the perfused rat liver. Endocrinology. 1978 Jan;102(1):182–187. doi: 10.1210/endo-102-1-182. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soler-Argilaga C., Heimberg M. Comparison of metabolism of free fatty acid by isolated perfused livers from male and female rats. J Lipid Res. 1976 Nov;17(6):605–615. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tulloch B. R., Lewis B., Fraser T. R. Triglyceride metabolism in thyroid disease. Lancet. 1973 Feb 24;1(7800):391–394. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)90250-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahlqvist M. L., Fidge N. H., Lomas F. Lipoprotein composition in hypothyroidism. Clin Chim Acta. 1977 Jun 15;77(3):269–274. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(77)90229-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walton K. W., Campbell D. A., Tonks E. L. The significance of alterations in serum lipids in thyroid dysfunction. I. The relation between serum lipoproteins, carotenoids and vitamin A in hypothyroidism and thyrotoxicosis. Clin Sci. 1965 Oct;29(2):199–215. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walton K. W., Scott P. J., Dykes P. W., Davies J. W. The significance of alterations in serum lipids in thyroid dysfunction. II. Alterations of the metabolism and turnover of 131-I-low-density lipoproteins in hypothyroidism and thyrotoxicosis. Clin Sci. 1965 Oct;29(2):217–238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilcow H. G., Dunn G. D., Heimberg M. Effects of several common long chain fatty acids on the properties and lipid composition of the very low density lipoprotein secreted by the perfused rat liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Jul 22;398(1):39–54. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(75)90168-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodside W. F., Heimberg M. The metabolism of oleic acid by the perfused rat liver in experimental diabetes induced by antiinsulin serum. Metabolism. 1978 Dec;27(12):1763–1777. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(78)90262-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


