Abstract
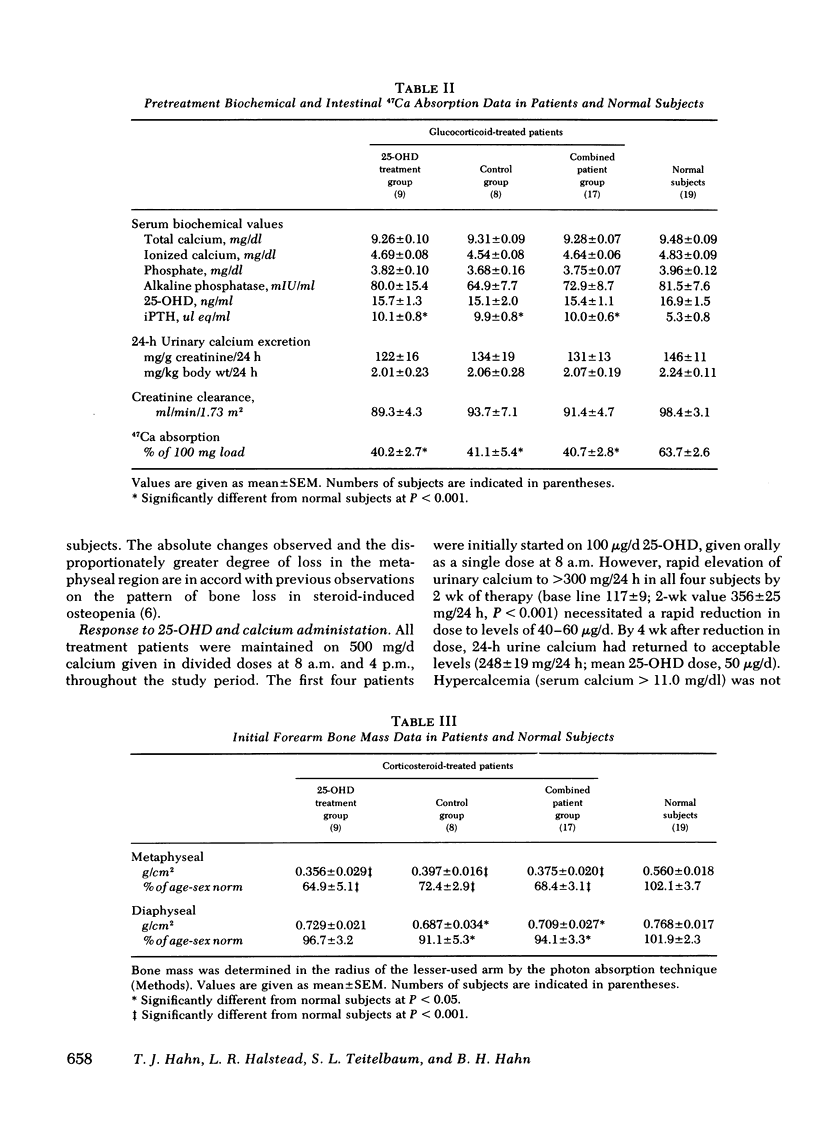
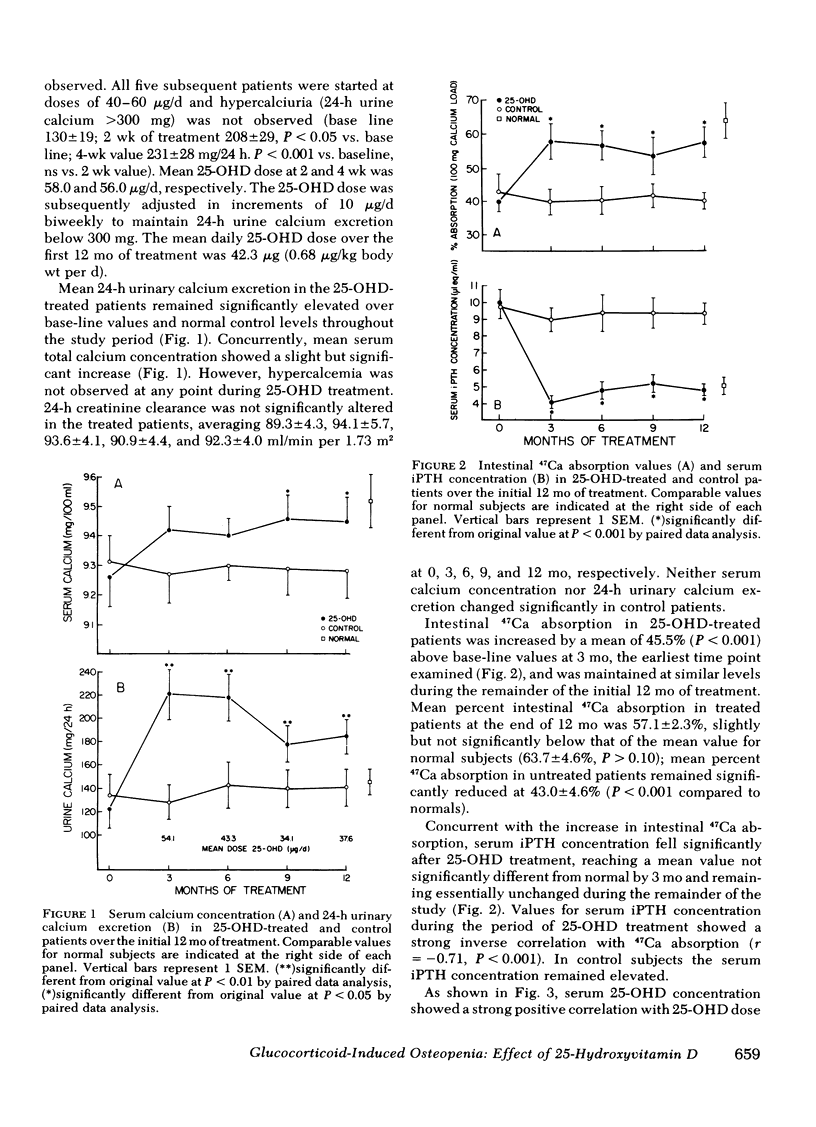
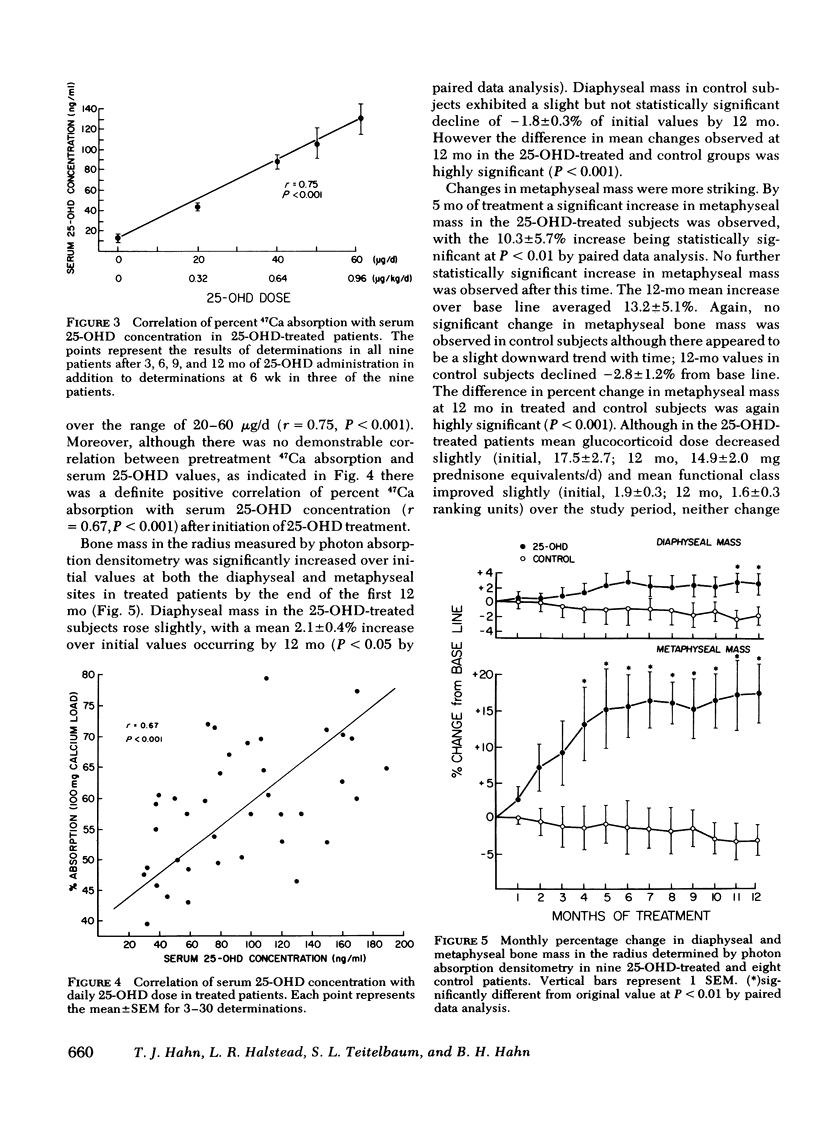
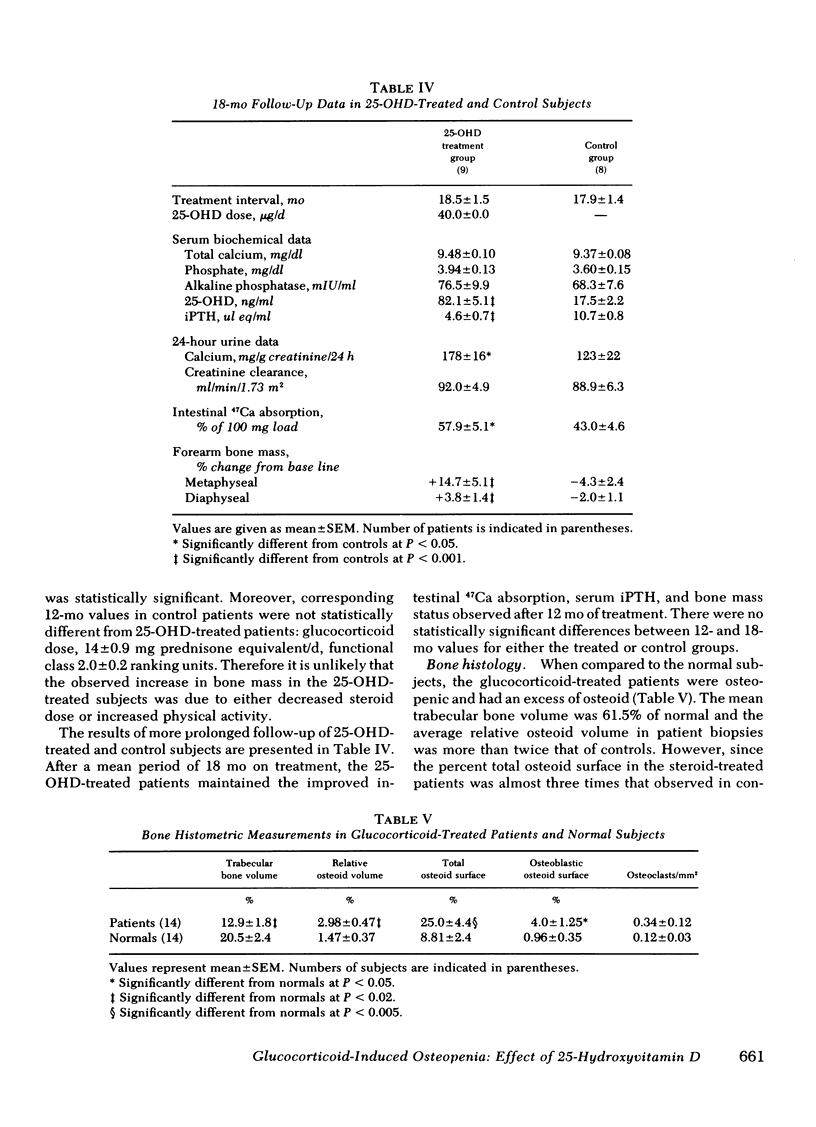
Parameters of mineral and bone metabolism were studied in 17 patients treated chronically with supraphysiologic doses of glucocorticoids. When compared to 15 matched normal subjects, the patient group exhibited similar serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25-OHD) levels, decreased intestinal 47Ca absorption, increased serum immunoreactive parathyroid hormone, and decreased forearm bone mass. Iliac crest bone biopsies revealed a decreased bone formation rate and increased osteoclast number. Treatment with 25-OHD (mean dose 4.03 micrograms/d) and calcium (500 mg/d) in nine patients produced a 46% increase in 47Ca absorption (P less than 0.001) and a 54% decrease in serum immunoreactive parathyroid hormone (P less than 0.001) by 3 mo. In addition, by 12 mo the treatment group exhibited (a) a 13.2 +/- 5.1% increase in metaphyseal (P less than 0.001) and a 2.1 +/- 0.4% increase in diaphyseal (P less than 0.05) forearm bone mass, and (b) significant decreases in cortical and endosteal osteoclast number. Biochemical and bone mass changes persisted through 18 mo. No significant changes in any parameter occurred in eight control patients administered calcium 100 mg/d. It is concluded that treatment with 25-OHD and calcium can significantly improve parameters of mineral and bone metabolism in patients with glucocorticoid-induced osteopenia.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aloia J. F., Roginsky M., Ellis K., Shukla K., Cohn S. Skeletal metabolism and body composition in Cushing's syndrome. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1974 Dec;39(6):981–985. doi: 10.1210/jcem-39-6-981. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avioli L. V., Birge S. J., Lee S. W. Effects of prednisone on vitamin D metabolism in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1968 Sep;28(9):1341–1346. doi: 10.1210/jcem-28-9-1341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BADLEY B. W., ANSELL B. M. Fractures in Still's disease. Ann Rheum Dis. 1960 Jun;19:135–142. doi: 10.1136/ard.19.2.135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baran D. T., Schwartz M. P., Bergfeld M. A., Teitelbaum S. L., Slatopolsky E., Avioli L. V. Lithium inhibition of bone mineralization and osteoid formation. J Clin Invest. 1978 Jun;61(6):1691–1696. doi: 10.1172/JCI109090. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CURTISS P. H., Jr, CLARK W. S., HERNDON C. H. Vertebral fractures resulting from prolonged cortisone and corticotropin therapy. J Am Med Assoc. 1954 Oct 2;156(5):467–469. doi: 10.1001/jama.1954.02950050007002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carré M., Ayigbedé O., Miravet L., Rasmussen H. The effect of Prednisolone upon the metabolism and action of 25-hydroxy-and 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Aug;71(8):2996–3000. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.8.2996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conney A. H. Pharmacological implications of microsomal enzyme induction. Pharmacol Rev. 1967 Sep;19(3):317–366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Luca H. F. Recent advances in our understanding of the vitamin D endocrine system. J Lab Clin Med. 1976 Jan;87(1):7–26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FROST H. M., VILLANUEVA A. R. Human osteoblastic activity. III. The effect of cortisone on lamellar osteoblastic activity. Henry Ford Hosp Med Bull. 1961 Mar;9:97–99. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Favus M. J., Kimberg D. V., Millar G. N., Gershon E. Effects of cortisone administration on the metabolism and localization of 25-hydroxycholecalciferol in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1973 Jun;52(6):1328–1335. doi: 10.1172/JCI107304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frost H. M. Tetracycline-based histological analysis of bone remodeling. Calcif Tissue Res. 1969;3(3):211–237. doi: 10.1007/BF02058664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fucik R. F., Kukreja S. C., Hargis G. K., Bowser E. N., Henderson W. J., Williams G. A. Effect of glucocorticoids on function of the parathyroid glands in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1975 Jan;40(1):152–155. doi: 10.1210/jcem-40-1-152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallagher J. C., Aaron J., Horsman A., Wilkinson R., Nordin B. E. Corticosteroid osteoporosis. Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1973 Jul;2(2):355–368. doi: 10.1016/s0300-595x(73)80048-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOWLAND W. J., Jr, PUGH D. G., SPRAGUE R. G. Roentgenologic changes of the skeletal system in Cushing's syndrome. Radiology. 1958 Jul;71(1):69–78. doi: 10.1148/71.1.69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haddad J. G., Chyu K. J. Competitive protein-binding radioassay for 25-hydroxycholecalciferol. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1971 Dec;33(6):992–995. doi: 10.1210/jcem-33-6-992. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn T. J., Birge S. J., Scharp C. R., Avioli L. V. Phenobarbital-induced alterations in vitamin D metabolism. J Clin Invest. 1972 Apr;51(4):741–748. doi: 10.1172/JCI106868. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn T. J., Boisseau V. C., Avioli L. V. Effect of chronic corticosteroid administration on diaphyseal and metaphyseal bone mass. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1974 Aug;39(2):274–282. doi: 10.1210/jcem-39-2-274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn T. J., Hahn B. H. Osteopenia in patients with rheumatic diseases: principles of diagnosis and therapy. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 1976 Nov;6(2):165–188. doi: 10.1016/0049-0172(76)90020-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn T. J., Halstead L. R., Haddad J. G., Jr Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentrations in patients receiving chronic corticosteroid therapy. J Lab Clin Med. 1977 Aug;90(2):399–404. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn T. J., Hendin B. A., Scharp C. R., Haddad J. G., Jr Effect of chronic anticonvulsant therapy on serum 25-hydroxycalciferol levels in adults. N Engl J Med. 1972 Nov 2;287(18):900–904. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197211022871803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn T. J., Scharp C. R., Halstead L. R., Haddad J. G., Karl D. M., Avioli L. V. Parathyroid hormone status and renal responsiveness in familial hypophosphatemic rickets. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1975 Nov;41(5):926–937. doi: 10.1210/jcem-41-5-926. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris W. H., Heaney R. P. Skeletal renewal and metabolic bone disease. N Engl J Med. 1969 Jan 30;280(5):253–contd. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196901302800507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jee W. S., Park H. Z., Roberts W. E., Kenner G. H. Corticosteroid and bone. Am J Anat. 1970 Dec;129(4):477–479. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001290409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston C. C., Jr, Smith D. M., Yu P. L., Deiss W. P., Jr In vivo measurement of bone mass in the radius. Metabolism. 1968 Dec;17(12):1140–1153. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(68)90094-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jowsey J., Riggs B. L. Bone formation in hypercortisonism. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1970 Jan;63(1):21–28. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0630021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KERMACK K. A., HALDANE J. B. S. Organic correlation and allometry. Biometrika. 1950 Jun;37(1-2):30–41. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimberg D. V., Baerg R. D., Gershon E., Graudusius R. T. Effect of cortisone treatment on the active transport of calcium by the small intestine. J Clin Invest. 1971 Jun;50(6):1309–1321. doi: 10.1172/JCI106610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein R. G., Arnaud S. B., Gallagher J. C., Deluca H. F., Riggs B. L. Intestinal calcium absorption in exogenous hypercortisonism. Role of 25-hydroxyvitamin D and corticosteroid dose. J Clin Invest. 1977 Jul;60(1):253–259. doi: 10.1172/JCI108762. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lukert B. P., Adams J. S. Calcium and phosphorus homeostasis in man. Effect of corticosteroids. Arch Intern Med. 1976 Nov;136(11):1249–1253. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lumb G. A., Stanbury S. W. Parathyroid function in human vitamin D deficiency and vitamin D deficiency in primary hyperparathyroidism. Am J Med. 1974 Jun;56(6):833–839. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(74)90812-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melsen F., Mosekilde L. Morphometric and dynamic studies of bone changes in hyperthyroidism. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand A. 1977 Mar;85A(2):141–150. doi: 10.1089/ten.2005.11.1034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peck W. A., Brandt J., Miller I. Hydrocortisone-induced inhibition of protein synthesis and uridine incorporation in isolated bone cells in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Jun;57(6):1599–1606. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.6.1599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raisz L. G. Physiologic and pharmacologic regulation of bone resorption. N Engl J Med. 1970 Apr 16;282(16):909–916. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197004162821608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saville P. D., Kharmosh O. Osteoporosis of rheumatoid arthritis: influence of age, sex and corticosteroids. Arthritis Rheum. 1967 Oct;10(5):423–430. doi: 10.1002/art.1780100504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slatopolsky E., Caglar S., Pennell J. P., Taggart D. D., Canterbury J. M., Reiss E., Bricker N. S. On the pathogenesis of hyperparathyroidism in chronic experimental renal insufficiency in the dog. J Clin Invest. 1971 Mar;50(3):492–499. doi: 10.1172/JCI106517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern P. H. Inhibition by steroids of parathyroid hormone-induced Ca45 release from embryonic rat bone in vitro. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1969 Aug;168(2):211–217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J. S., Urist M. R. Effects of cortisone on bone metabolism in intact and thyroidectomized rabbits. Calcif Tissue Res. 1973 Oct 23;13(3):197–215. doi: 10.1007/BF02015410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WIDROW S. H., LEVINSKY N. G. The effect of parathyroid extract on renal tubular calcium reabsorption in the dog. J Clin Invest. 1962 Dec;41:2151–2159. doi: 10.1172/JCI104673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wajchenberg B. L., Pereira V. G., Kieffer J., Ursic S. Effect of dexamethasone on calcium metabolism and 47Ca kinetics in normal subjects. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1969 May;61(1):173–192. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0610173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wills M. R., Zisman E., Wortsman J., Evens R. G., Pak C. Y., Bartter F. C. The measurement of intestinal calcium absorption by external radioisotope counting: application to study of nephrolithiasis. Clin Sci. 1970 Jul;39(1):95–106. doi: 10.1042/cs0390095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


