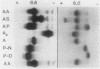
Abstract
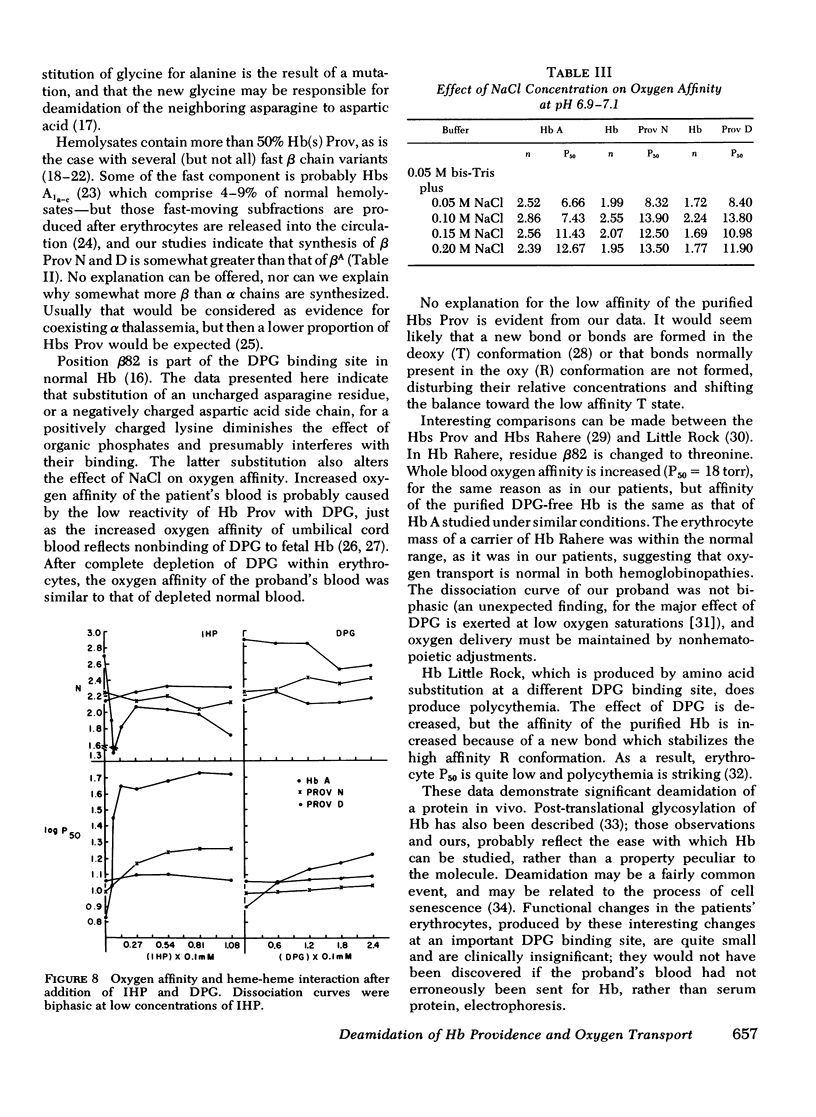
Carriers of hemoglobin Providence have three types of beta chain in their hemolysates. The two abnormal chains have asparagine (Providence N, Prov N) or aspartic acid (Providence D) at position beta 82, instead of lysine. In vitro, only two beta chains are synthesized by reticulocytes of carriers, betaA and betaProv N. In vivo studies showed that the specific activity of Providence N was initially 10-fold higher than that of Providence D; the specific activities of the two labeled hemoglobins were approximately equal 5 wk after injection of isotope. Oxygen affinity of carriers' blood was somewhat increased, but they were not polycythemic. The affinity of the purified hemoglobins Providence was decreased. Addition of 2, 3 diphosphoglycerate had little effect on the affinity of either hemoglobin component, and addition of inositol hexaphosphate produced no change in the affinity of Providence D. These studies demonstrate that Providence N is deamidated to Providence D during the life span of the erythrocyte, and suggest this finding may represent only an easily observed prototype of posttranslational modification of proteins in general. Despite and abnormal P50 of the blood, oxygen transport is probably normal in carriers of the abnormal hemoglobins.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bunn H. F., Jandl J. H. Exchange of heme among hemoglobin molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Sep;56(3):974–978. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.3.974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrell R. W., Kay R. A simple method for the detection of unstable haemoglobins. Br J Haematol. 1972 Nov;23(5):615–619. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1972.tb07096.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charache S., Conley C. L., Doeblin T. D., Bartalos M. Thalassemia in black americans. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1974;232(0):125–134. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1974.tb20577.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charache S., Mondzac A. M., Gessner U. Hemoglobin Hasharon (alpha-2-47 his(CD5)beta-2): a hemoglobin found in low concentration. J Clin Invest. 1969 May;48(5):834–847. doi: 10.1172/JCI106041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clegg J. B., Naughton M. A., Weatherball D. J. Abnormal human haemoglobins. Separation and characterization of the alpha and beta chains by chromatography, and the determination of two new variants, hb Chesapeak and hb J (Bangkok). J Mol Biol. 1966 Aug;19(1):91–108. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80052-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi A., Suzuki T., Shin M. An enzymic reduction system for metmyoglobin and methemoglobin, and its application to functional studies of oxygen carriers. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jun 15;310(2):309–316. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(73)90110-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huisman T. H., Dozy A. M. Studies on the heterogeneity of hemoglobin. IX. The use of Tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethanehcl buffers in the anion-exchange chromatography of hemoglobins. J Chromatogr. 1965 Jul;19(1):160–169. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)99434-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imai K., Morimoto H., Kotani M., Watari H., Hirata W. Studies on the function of abnormal hemoglobins. I. An improved method for automatic measurement of the oxygen equilibrium curve of hemoglobin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Feb 17;200(2):189–196. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(70)90163-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilmartin J. V., Rossi-Bernardi L. Interaction of hemoglobin with hydrogen ions, carbon dioxide, and organic phosphates. Physiol Rev. 1973 Oct;53(4):836–890. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1973.53.4.836. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koenig R. J., Cerami A. Synthesis of hemoglobin AIc in normal and diabetic mice: potential model of basement membrane thickening. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Sep;72(9):3687–3691. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.9.3687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann H., Lang A. Various aspects of alpha-thalassemia. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1974;232(0):152–158. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1974.tb20580.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorkin P. A., Stephens A. D., Beard M. E., Wrigley P. F., Adams L., Lehmann H. Haemoglobin Rahere (beta Lys-Thr): A new high affinity haemoglobin associated with decreased 2, 3-diphosphoglycerate binding and relative polycythaemia. Br Med J. 1975 Oct 25;4(5990):200–202. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5990.200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurer H. S., Behrman R. E., Honig G. R. Dependence of the oxygen affinity of blood on the presence of foetal or adult haemoglobin. Nature. 1970 Jul 25;227(5256):388–390. doi: 10.1038/227388a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moo-Penn W. F., Jue D. L., Bechtel K. C., Johnson M. H., Schmidt R. M. Hemoglobin Providence. A human hemoglobin variant occurring in two forms in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1976 Dec 10;251(23):7557–7562. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perutz M. F. Stereochemical interpretation of high oxygen affinity of haemoglobin Little Rock ( 2 2 143His leads to Gln). Nat New Biol. 1973 Jun 6;243(127):180–180. doi: 10.1038/newbio243180a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perutz M. F. Stereochemistry of cooperative effects in haemoglobin. Nature. 1970 Nov 21;228(5273):726–739. doi: 10.1038/228726a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pootrakul S., Wasi P., Na-Nakorn S. Haemoglobin J-Bangkok: a clinical, haematological and genetical study. Br J Haematol. 1967 May;13(3):303–309. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1967.tb08744.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson A. B., McKerrow J. H., Cary P. Controlled deamidation of peptides and proteins: an experimental hazard and a possible biological timer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Jul;66(3):753–757. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.3.753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson A. B., Rudd C. J. Deamidation of glutaminyl and asparaginyl residues in peptides and proteins. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1974;8(0):247–295. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-152808-9.50013-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz E. Abnormal globin synthesis in thalassemic red cells. Semin Hematol. 1974 Oct;11(4):549–567. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THORUP O. A., ITANO H. A., WHEBY M., LEAVELL B. S. Hemoglobin J. Science. 1956 May 18;123(3203):889–890. doi: 10.1126/science.123.3203.889. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trivelli L. A., Ranney H. M., Lai H. T. Hemoglobin components in patients with diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1971 Feb 18;284(7):353–357. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197102182840703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyuma I., Shimizu K., Imai K. Effect of 2,3-diphosphoglycerate on the cooperativity in oxygen binding of human adult hemoglobin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Apr 16;43(2):423–428. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90770-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Versmold H., Seifert G., Riegel K. P. Blood oxygen affinity in infancy: the interaction of fetal and adult hemoglobin, oxygen capacity, and red cell hydrogen ion and 2,3-diphosphoglycerate concentration. Respir Physiol. 1973 Jun;18(1):14–25. doi: 10.1016/0034-5687(73)90018-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEATHERALL D. J. HEMOGLOBIN J (BALTIMORE) COEXISTING IN A FAMILY WITH HEMOGLOBIN S. Bull Johns Hopkins Hosp. 1964 Jan;114:1–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winslow R. M., Charache S. Hemoglobin Richmond. Subunit dissociation and oxygen equilibrium properties. J Biol Chem. 1975 Sep 10;250(17):6939–6942. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong S. C., Bouver N., Wilson J. B., Huisman T. H. Hb-J-Georgia=Hb-J-Baltimore= 2 2 16 Gly leads to Asp. Clin Chim Acta. 1971 Dec;35(2):521–522. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(71)90235-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]