Abstract
Collagen synthesis was measured in liver slices obtained from mice with hepatosplenic schistosomiasis. Enlarged fibrotic livers from these mice contained 20 times more collagen than normal. This model of hepatic fibrosis results from an inflammatory granulomatous host response to Schistosoma mansoni ova in portal tracts, rather than from direct lover cell injury as with carbon tetrachloride-induced liver fibrosis. Collagen synthesis, as measured by the formation of labeled protein-bound hydroxyproline, occurred in granulomas isolated from fibrotic livers. Labeled collagen that cochromatographed with type I collagen was extracted with neutral salt solution from liver slices incubated with labeled proline. The free proline pool of the liver was doubled in infected mice; coordinately, liver slices from these animals showed maximal collagen production when the concentration of free proline in the medium was raised to 0.4 mM, the same level measured in the fibrotic livers. Under such conditions, collagen synthesis was at a rate equivalent to the formation of 5.4 nmol of protein-bound hydroxyproline per g liver in 6 h. In comparative incubations in medium containing 0.2 mM proline, fibrotic liver slices produced 16-fold more collagen than normal slices. The proline analogue, L-azetidine 2-carboxylic acid, effectively inhibited synthesis of labeled collagen by fibrotic liver slices. These studies show the synthesis of collagen in a reproducible animal model of the most prevalent form of human liver fibrosis. Difinitition of the controlling factors in this system is of interest for the general problem of fibrosis produced by immunological responses.
Full text
PDF
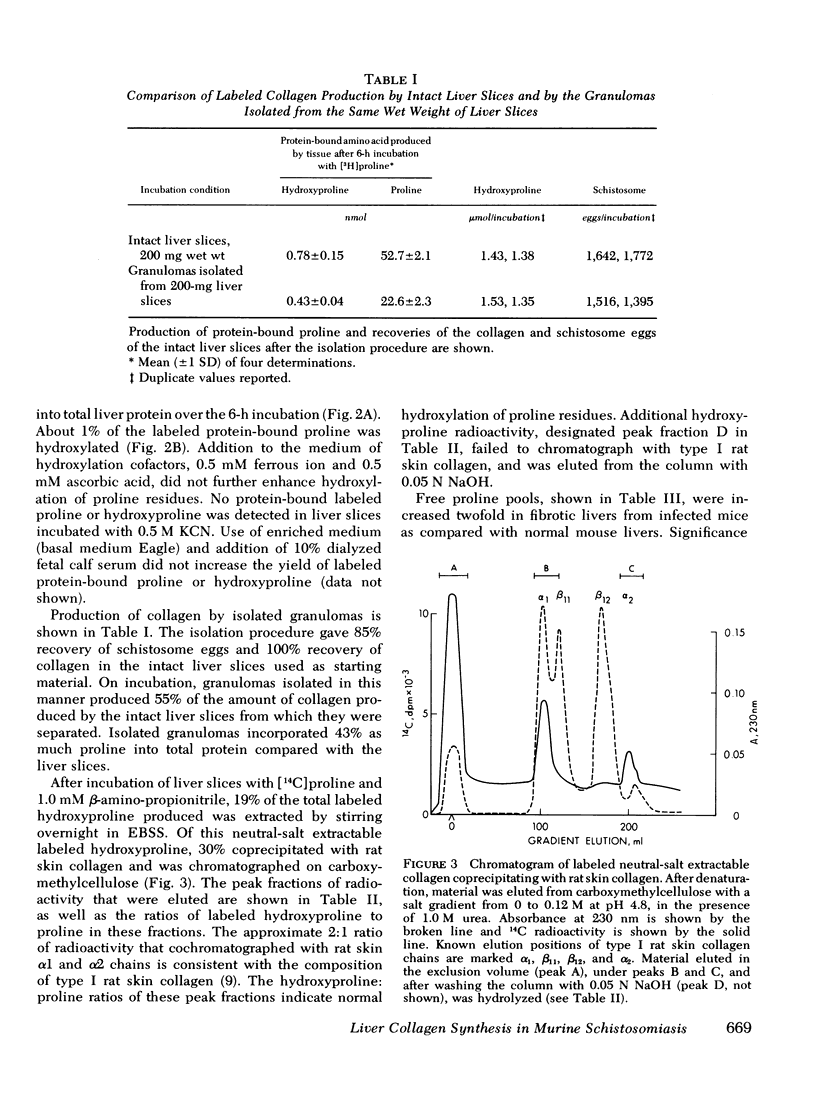
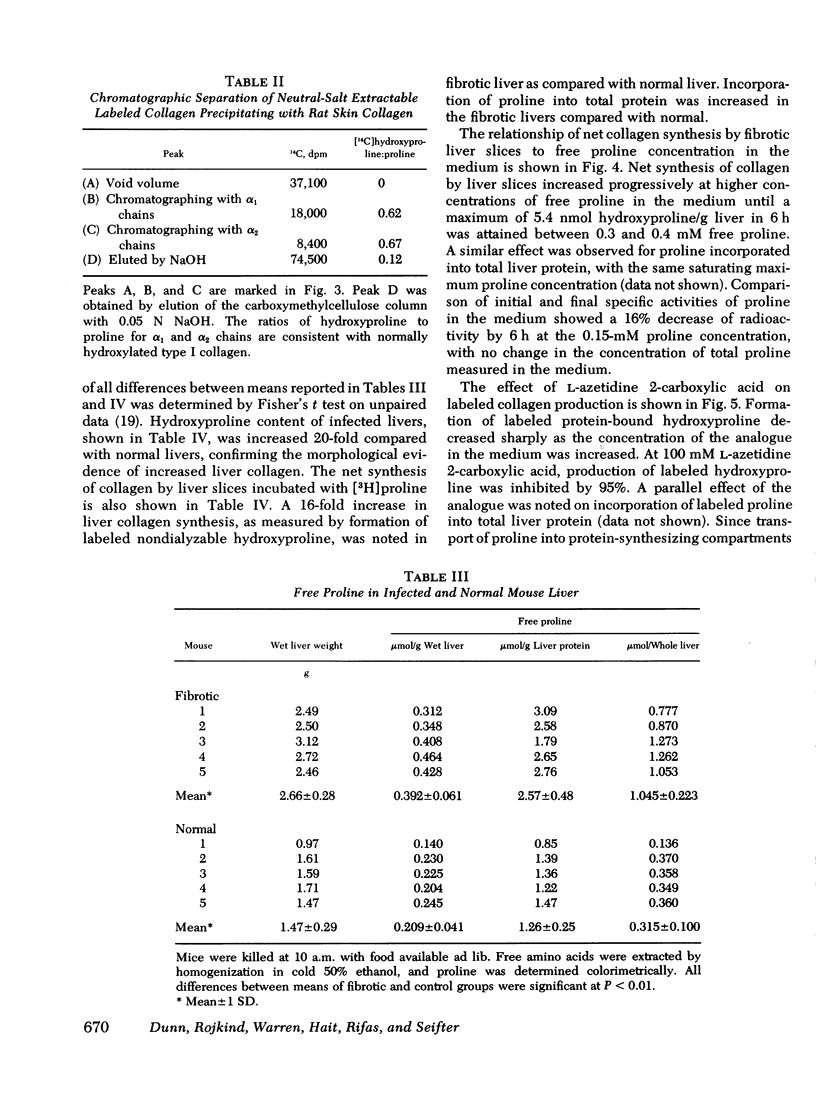
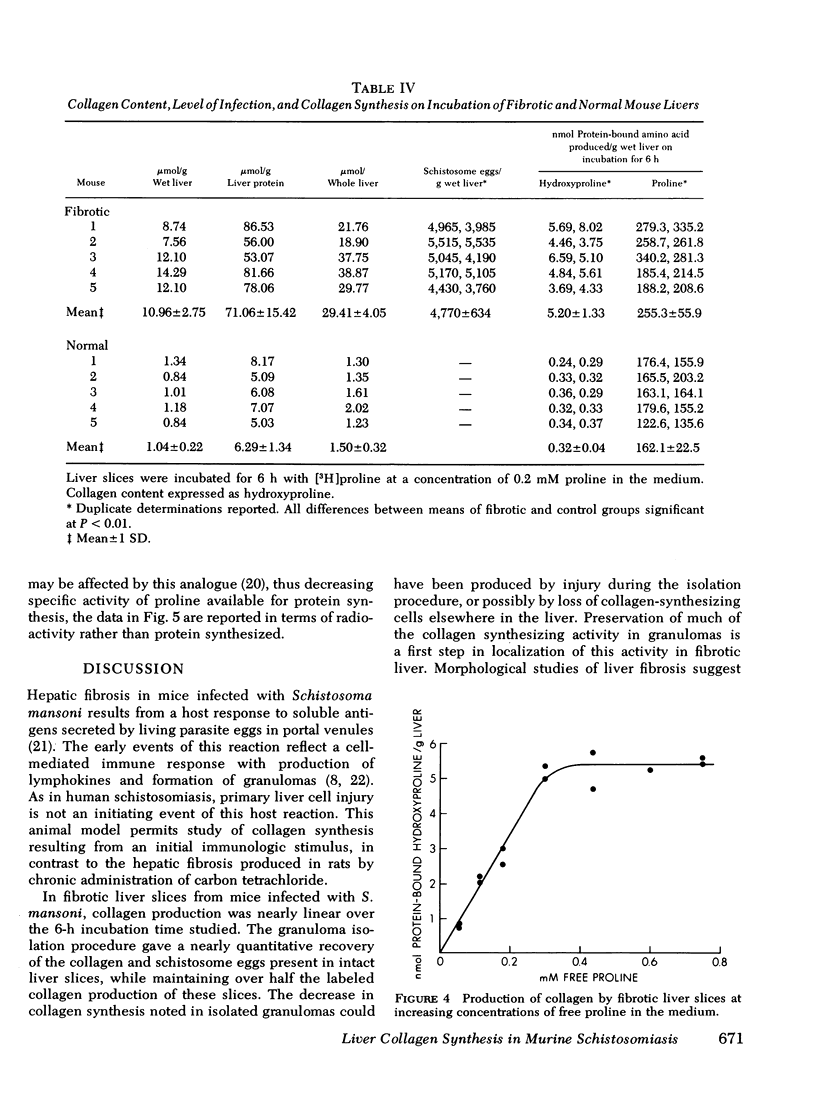
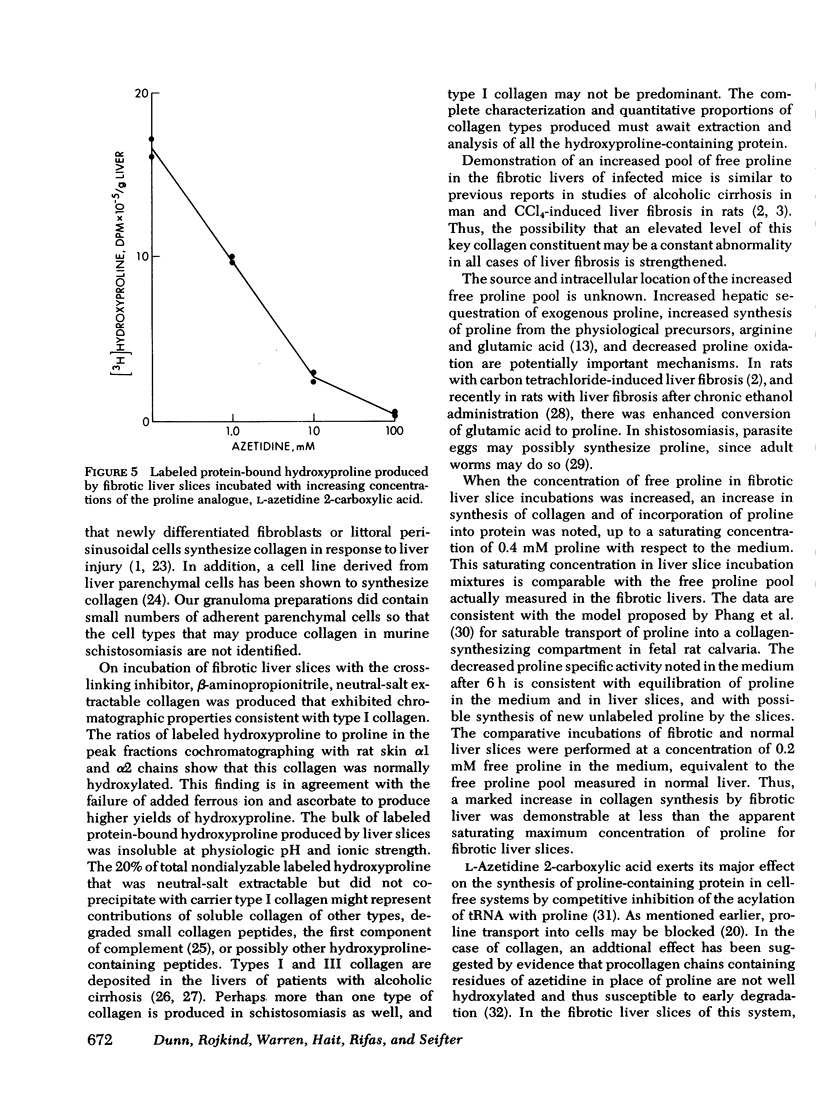


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boros D. L., Warren K. S. Delayed hypersensitivity-type granuloma formation and dermal reaction induced and elicited by a soluble factor isolated from Schistosoma mansoni eggs. J Exp Med. 1970 Sep 1;132(3):488–507. doi: 10.1084/jem.132.3.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boros D. L., Warren K. S., Pelley R. P. The secretion of migration inhibitory factor by intact schistosome egg granulomas maintained in vitro. Nature. 1973 Nov 23;246(5430):224–226. doi: 10.1038/246224a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAMERON G. R., GANGULY N. C. AN EXPERIMENTAL STUDY OF THE PATHOGENESIS AND REVERSIBILITY OF SCHISTOSOMAL HEPATIC FIBROSIS. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1964 Apr;87:217–237. doi: 10.1002/path.1700870202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheever A. W. Conditions affecting the accuracy of potassium hydroxide digestion techniques for counting Schistosoma mansoni eggs in tissues. Bull World Health Organ. 1968;39(2):328–331. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finerman G. A., Downing S., Rosenberg L. E. Amino acid transport in bone. II. Regulation of collagen synthesis by perturbation of proline transport. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967;135(5):1008–1015. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(67)90071-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gay S., Fietzek P. P., Remberger K., Eder M., Kühn K. Liver cirrhosis: immunofluorescence and biochemical studies demonstrate two types of collagen. Klin Wochenschr. 1975 Mar 1;53(5):205–208. doi: 10.1007/BF01468808. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hkkinen H. M., Kulonen E. Effect of ethanol on the metabolsim of alanine glutamic acid, and proline in rat liver. Biochem Pharmacol. 1975 Jan 15;24(2):199–204. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(75)90277-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. L., Ziff M. Lymphokine stimulation of collagen accumulation. J Clin Invest. 1976 Jul;58(1):240–252. doi: 10.1172/JCI108455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kershenobich D., Fierro F. J., Rojkind M. The relationship between the free pool of proline and collagen content in human liver cirrhosis. J Clin Invest. 1970 Dec;49(12):2246–2249. doi: 10.1172/JCI106443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGee J. O., Patrick R. S. The role of perisinusoidal cells in hepatic fibrogenesis. An electron microscopic study of acute carbon tetrachloride liver injury. Lab Invest. 1972 Apr;26(4):429–440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller E. J. Isolation and characterization of a collagen from chick cartilage containing three identical alpha chains. Biochemistry. 1971 Apr 27;10(9):1652–1659. doi: 10.1021/bi00785a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PIEZ K. A., MORRIS L. A modified procedure for the automatic analysis of amino acids. Anal Biochem. 1960 Nov;1:187–201. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(60)90045-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PROCKOP D. J., UDENFRIEND S. A specific method for the analysis of hydroxyproline in tissues and urine. Anal Biochem. 1960 Nov;1:228–239. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(60)90050-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phang J. M., Finerman G. A., Singh B., Rosenberg L. E., Berman M. Compartmental analysis of collagen synthesis in fetal rat calvaria. I. Perturbations of proline transport. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Jan 26;230(1):146–159. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(71)90062-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popper H., Uenfriend S. Hepatic fibrosis. Correlation of biochemical and morphologic investigations. Am J Med. 1970 Nov;49:707–721. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9343(70)80135-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid K. B., Lowe D. M., Porter R. R. Isolation and characterization of C1q, a subcomponent of the first component of complement, from human and rabbit sera. Biochem J. 1972 Dec;130(3):749–763. doi: 10.1042/bj1300749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rojkind M., Diaz de León L. Collagen biosynthesis in cirrhotic rat liver slices a regulatory mechanism. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Oct 15;217(2):512–522. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(70)90548-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rojkind M., González E. An improved method for determining specific radioactivities of proline-14C and hydroxyproline-14C in collagen and in noncollagenous proteins. Anal Biochem. 1974 Jan;57(1):1–7. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90043-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rojkind M. Inhibition of liver fibrosis by 1-azetidine-2-carboxylic acid in rats treated with carbon tetrachloride. J Clin Invest. 1973 Oct;52(10):2451–2456. doi: 10.1172/JCI107436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rojkind M., Martinez-Palomo A. Increase in type I and type III collagens in human alcoholic liver cirrhosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Feb;73(2):539–543. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.2.539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SENFT A. W. OBSERVATIONS ON AMINO ACID METABOLISM OF SCHISTOSOMA MANSONI IN A CHEMICALLY DEFINED MEDIUM. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1963 Dec 30;113:272–288. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1963.tb40670.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakakibapa K., Saito M., Umeda M., Enaka K., Tsukada Y. Native collagen formation by liver parenchymal cells in culture. Nature. 1976 Jul 22;262(5566):316–318. doi: 10.1038/262316a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen T. F., Strecker H. J. Synthesis of proline and hydroxyproline in human lung (WI-38) fibroblasts. Biochem J. 1975 Sep;150(3):453–461. doi: 10.1042/bj1500453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeuchi T., Prockop D. J. Biosynthesis of abnormal collagens with amino acid analogues. I. Incorporation of L-azetidine-2-carboxylic acid and cis-4-fluoro-L-proline into protocollagen and collagen. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Feb 4;175(1):142–155. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(69)90153-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren K. S., Domingo E. O., Cowan R. B. Granuloma formation around schistosome eggs as a manifestation of delayed hypersensitivity. Am J Pathol. 1967 Nov;51(5):735–756. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren K. S. Regulation of the prevalence and intensity of schistosomiasis in man: immunology or ecology? J Infect Dis. 1973 May;127(5):595–609. doi: 10.1093/infdis/127.5.595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren K. S. The pathogenesis of "clay-pipe stem cirrhosis" in mice with chronic schistosomiasis mansoni, with a note on the longevity of the schistosomes. Am J Pathol. 1966 Sep;49(3):477–489. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]