Abstract
Acanthocytic red cells in patients with abetalipoproteinemia are morphologically similar to the red cells in spur cell anemia. Fluidity of membrane lipids is decreased in spur cells due to their excess cholesterol content. Acanthocyte membranes have an increased content of sphingomyelin and a decreased content of lecithin. To assess the effect of this abnormality of acanthocyte membrane lipid composition on membrane fluidity, we studied red cells from five patients with abetalipoproteinemia and four obligate heterozygote family members.
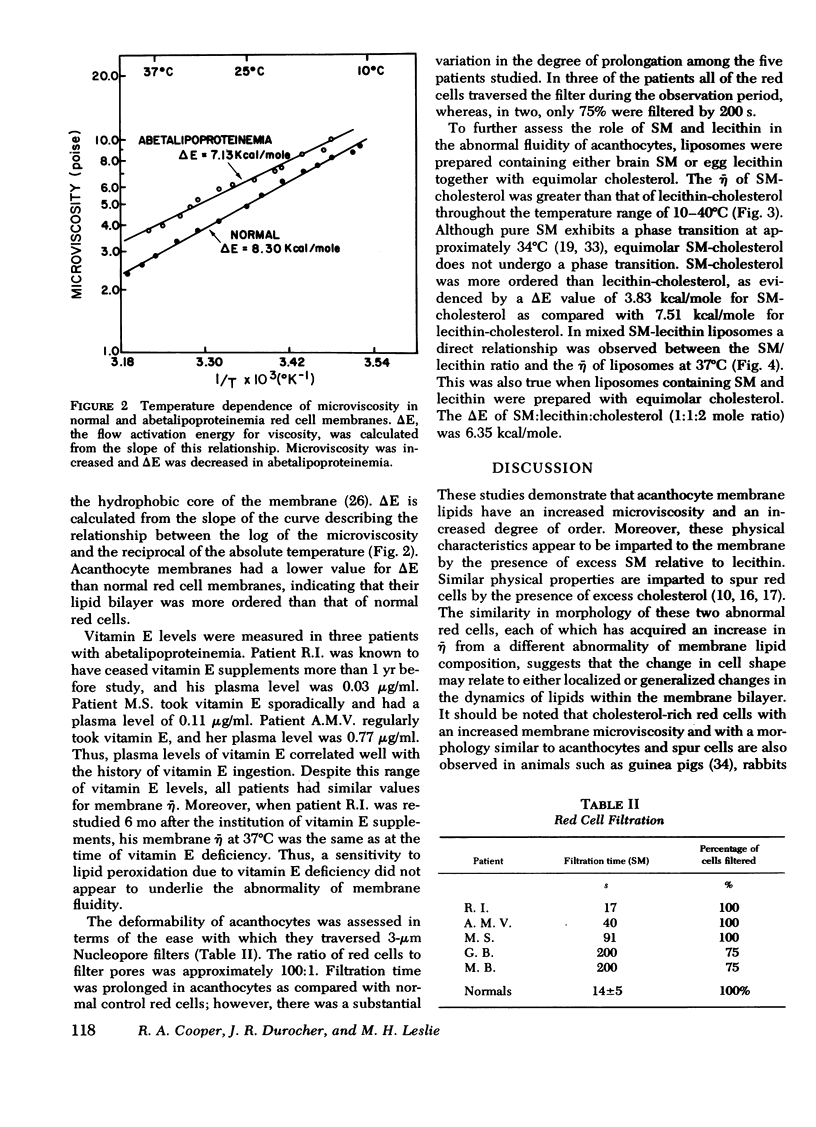
Membrane fluidity was measured in terms of microviscosity (¯η) at 37°C, assessed by means of the fluorescence polarization of 1,6-diphenyl-1,3,5-hexatriene. It was increased from 3.2±0.1 poise in normals to 4.01-4.14 poise in acanthocytes. This was associated with an increase in the sphingomyelin/lecithin ratio from 0.84±0.08 in normals in 1.45-1.61 in acanthocytes. The ¯η of acanthocyte membranes was not influenced by the degree of vitamin E deficiency. Similar changes in ¯η were observed in liposomes prepared from red cell lipids. Heterozygotes had normal sphingomyelin/lecithin ratios and normal values for ¯η. The flow activation energy for viscosity, a measure of the degree of order in the hydrophobic portion of the membrane, was decreased from 8.3 kcal/mole in normal red cells to 7.2 kcal/mole in acanthocytes, indicating that acanthocyte membrane lipids are more ordered. Variations in the sphingomyelin/lecithin mole ratio of liposomes prepared from brain sphingomyelin and egg lecithin with equimolar cholesterol caused similar changes in both ¯η and activation energy. The deformability of acanthocytes, assessed by means of filtration through 3-μm filters, was decreased.
These studies indicate that the increased sphingomyelin/lecithin ratio of acanthocytes is responsible for their decreased membrane fluidity. As in spur cells and in red cells enriched with cholesterol in vitro, this decrease in membrane fluidity occurs coincidentally with an abnormality in cell contour and an impairment in cell deformability.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARTLETT G. R. Phosphorus assay in column chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1959 Mar;234(3):466–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BASSEN F. A., KORNZWEIG A. L. Malformation of the erythrocytes in a case of atypical retinitis pigmentosa. Blood. 1950 Apr;5(4):381–387. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barańska J., Wlodawer P. Influence of temperature on the composition of fatty acids and on lipogenesis in frog tissues. Comp Biochem Physiol. 1969 Feb;28(2):553–570. doi: 10.1016/0010-406x(69)92089-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloj B., Zilversmit D. B. Asymmetry and transposition rates of phosphatidylcholine in rat erythrocyte ghosts. Biochemistry. 1976 Mar 23;15(6):1277–1283. doi: 10.1021/bi00651a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bretscher M. S. Asymmetrical lipid bilayer structure for biological membranes. Nat New Biol. 1972 Mar 1;236(61):11–12. doi: 10.1038/newbio236011a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cogan U., Shinitzky M., Weber G., Nishida T. Microviscosity and order in the hydrocarbon region of phospholipid and phospholipid-cholesterol dispersions determined with fluorescent probes. Biochemistry. 1973 Jan 30;12(3):521–528. doi: 10.1021/bi00727a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper R. A. Anemia with spur cells: a red cell defect acquired in serum and modified in the circulation. J Clin Invest. 1969 Oct;48(10):1820–1831. doi: 10.1172/JCI106148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper R. A., Arner E. C., Wiley J. S., Shattil S. J. Modification of red cell membrane structure by cholesterol-rich lipid dispersions. A model for the primary spur cell defect. J Clin Invest. 1975 Jan;55(1):115–126. doi: 10.1172/JCI107901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper R. A., Diloy Puray M., Lando P., Greenverg M. S. An analysis of lipoproteins, bile acids, and red cell membranes associated with target cells and spur cells in patients with liver disease. J Clin Invest. 1972 Dec;51(12):3182–3192. doi: 10.1172/JCI107145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper R. A., Gulbrandsen C. L. The relationship between serum lipoproteins and red cell membranes in abetalipoproteinemia: deficiency of lecithin:cholesterol acyltransferase. J Lab Clin Med. 1971 Sep;78(3):323–335. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper R. A., Kimball D. B., Durocher J. R. Role of the spleen in membrane conditioning and hemolysis of spur cells in liver disease. N Engl J Med. 1974 Jun 6;290(23):1279–1284. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197406062902303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodge J. T., Cohen G., Kayden H. J., Phillips G. B. Peroxidative hemolysis of red blood cells from patients with abetalipoproteinemia (acanthocytosis). J Clin Invest. 1967 Mar;46(3):357–368. doi: 10.1172/JCI105537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans E. A., Hochmuth R. M. Membrane viscoplastic flow. Biophys J. 1976 Jan;16(1):13–26. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(76)85659-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans E. A., La Celle P. L. Intrinsic material properties of the erythrocyte membrane indicated by mechanical analysis of deformation. Blood. 1975 Jan;45(1):29–43. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FREZAL J., REY J., POLONOVSKI J., LEVY G., LAMY M. [Congenital absence of beta-lipoproteins: study of fat absorption after exsanguinotransfusion measuring the half-life of injected beta-lipoproteins]. Rev Fr Etud Clin Biol. 1961 Aug-Sep;6:677–683. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farkas T., Herodek S. The effect of environmental temperature on the fatty acid composition of crustacean plankton. J Lipid Res. 1964 Jul;5(3):369–373. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman S. S. Cold resistance of the brain during hibernation. III. Evidence of a lipid adaptation. Am J Physiol. 1975 Mar;228(3):834–838. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1975.228.3.834. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbell W. L., McConnell H. M. Molecular motion in spin-labeled phospholipids and membranes. J Am Chem Soc. 1971 Jan 27;93(2):314–326. doi: 10.1021/ja00731a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ISSELBACHER K. J., SCHEIG R., PLOTKIN G. R., CAULFIELD J. B. CONGENITAL BETA-LIPOPROTEIN DEFICIENCY: AN HEREDITARY DISORDER INVOLVING A DEFECT IN THE ABSORPTION AND TRANSPORT OF LIPIDS. Medicine (Baltimore) 1964 May;43:347–361. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keith A. D., Aloia R. C., Lyons J., Snipes W., Pengelley E. T. Spin label evidence for the role of lysoglycerophosphatides in cellular membranes of hibernating mammals. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Jun 25;394(2):204–210. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(75)90258-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knipprath W. G., Mead J. F. Influence of temperature on the fatty acid pattern of mosquitofish (Gambusia affinis) and guppies (Lebistes reticulatus). Lipids. 1966 Mar;1(2):113–117. doi: 10.1007/BF02533001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroes J., Ostwald R., Keith A. Erythrocyte membranes--compression of lipid phases by increased cholesterol content. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jul 3;274(1):71–74. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90281-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ladbrooke B. D., Williams R. M., Chapman D. Studies on lecithin-cholesterol-water interactions by differential scanning calorimetry and X-ray diffraction. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Apr 29;150(3):333–340. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(68)90132-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARKS P. A., GELLHORN A., KIDSON C. Lipid synthesis in human leukocytes, platelets, and erythrocytes. J Biol Chem. 1960 Sep;235:2579–2583. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBride J. A., Jacob H. S. Abnormal kinetics of red cell membrane cholesterol in acanthocytes: studies in genetic and experimental abetalipoproteinaemia and in spur cell anaemia. Br J Haematol. 1970 Apr;18(4):383–397. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1970.tb01452.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostwald R., Shannon A. Composition of tissue lipids and anaemia of guinea pigs in response to dietary cholesterol. Biochem J. 1964 Apr;91(1):146–154. doi: 10.1042/bj0910146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PHILLIPS G. B. Quantitative chromatographic analysis of plasma and red blood cell lipids in patients with acanthocytosis. J Lab Clin Med. 1962 Mar;59:357–363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSE H. G., OKLANDER M. IMPROVED PROCEDURE FOR THE EXTRACTION OF LIPIDS FROM HUMAN ERYTHROCYTES. J Lipid Res. 1965 Jul;6:428–431. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed C. F. Phospholipid exchange between plasma and erythrocytes in man and the dog. J Clin Invest. 1968 Apr;47(4):749–760. doi: 10.1172/JCI105770. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SIMON E. R., WAYS P. INCUBATION HEMOLYSIS AND RED CELL METABOLISM IN ACANTHOCYTOSIS. J Clin Invest. 1964 Jul;43:1311–1321. doi: 10.1172/JCI105006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH J. A., LONERGAN E. T., STERLING K. SPUR-CELL ANEMIA: HEMOLYTIC ANEMIA WITH RED CELLS RESEMBLING ACANTHOCYTES IN ALCOHOLIC CIRRHOSIS. N Engl J Med. 1964 Aug 20;271:396–398. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196408202710804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinitzky M., Barenholz Y. Dynamics of the hydrocarbon layer in liposomes of lecithin and sphingomyelin containing dicetylphosphate. J Biol Chem. 1974 Apr 25;249(8):2652–2657. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinitzky M., Inbar M. Difference in microviscosity induced by different cholesterol levels in the surface membrane lipid layer of normal lymphocytes and malignant lymphoma cells. J Mol Biol. 1974 Jan 5;85(4):603–615. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90318-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinitzky M., Inbar M. Microviscosity parameters and protein mobility in biological membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Apr 16;433(1):133–149. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90183-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shipley G. G., Avecilla L. S., Small D. M. Phase behavior and structure of aqueous dispersions of sphingomyelin. J Lipid Res. 1974 Mar;15(2):124–131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silber R., Winter R., Kayden H. J. Tocopherol transport in the rat erythrocyte. J Clin Invest. 1969 Nov;48(11):2089–2095. doi: 10.1172/JCI106175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skipski V. P., Peterson R. F., Barclay M. Quantitative analysis of phospholipids by thin-layer chromatography. Biochem J. 1964 Feb;90(2):374–378. doi: 10.1042/bj0900374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanderkooi J., Fischkoff S., Chance B., Cooper R. A. Fluorescent probe analysis of the lipid architecture of natural and experimental cholesterol-rich membranes. Biochemistry. 1974 Apr 9;13(8):1589–1595. doi: 10.1021/bi00705a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WAYS P., REED C. F., HANAHAN D. J. RED-CELL AND PLASMA LIPIDS IN ACANTHOCYTOSIS. J Clin Invest. 1963 Aug;42:1248–1260. doi: 10.1172/JCI104810. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEBER G. Rotational Brownian motion and polarization of the fluorescence of solutions. Adv Protein Chem. 1953;8:415–459. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60096-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waku K., Lands W. E. Control of lecithin biosynthesis in erythrocyte membranes. J Lipid Res. 1968 Jan;9(1):12–18. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westerman M. P., Wiggans G., 3rd, Mao R. Anemia and hypercholesterolemia in cholesterol-fed rabbits. J Lab Clin Med. 1970 Jun;75(6):893–902. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZLATKIS A., ZAK B., BOYLE A. J. A new method for the direct determination of serum cholesterol. J Lab Clin Med. 1953 Mar;41(3):486–492. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


