Abstract
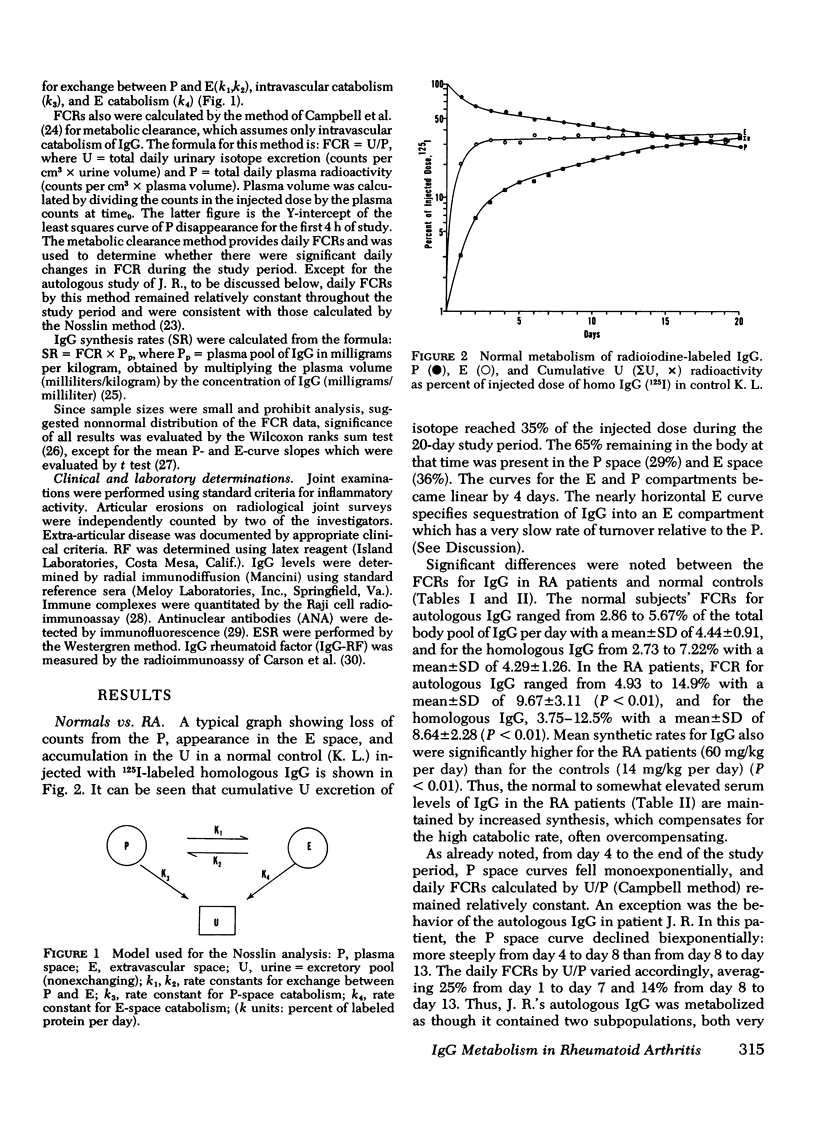
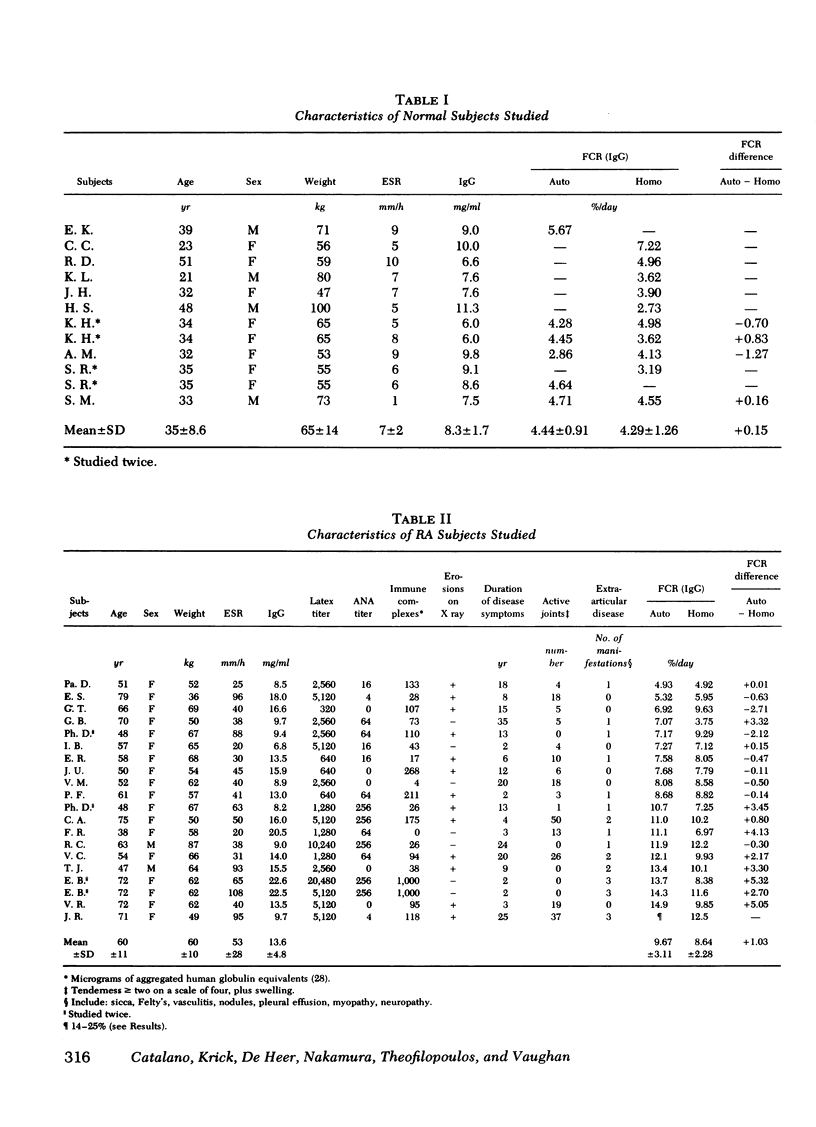
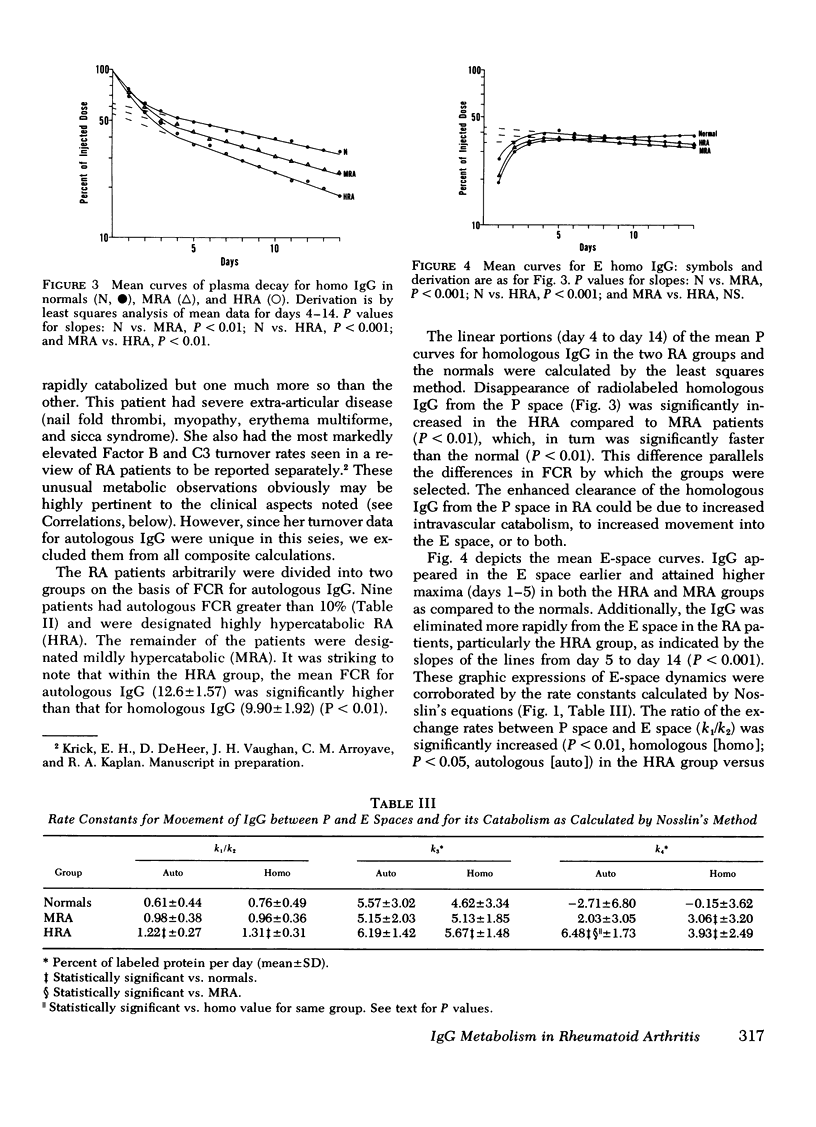
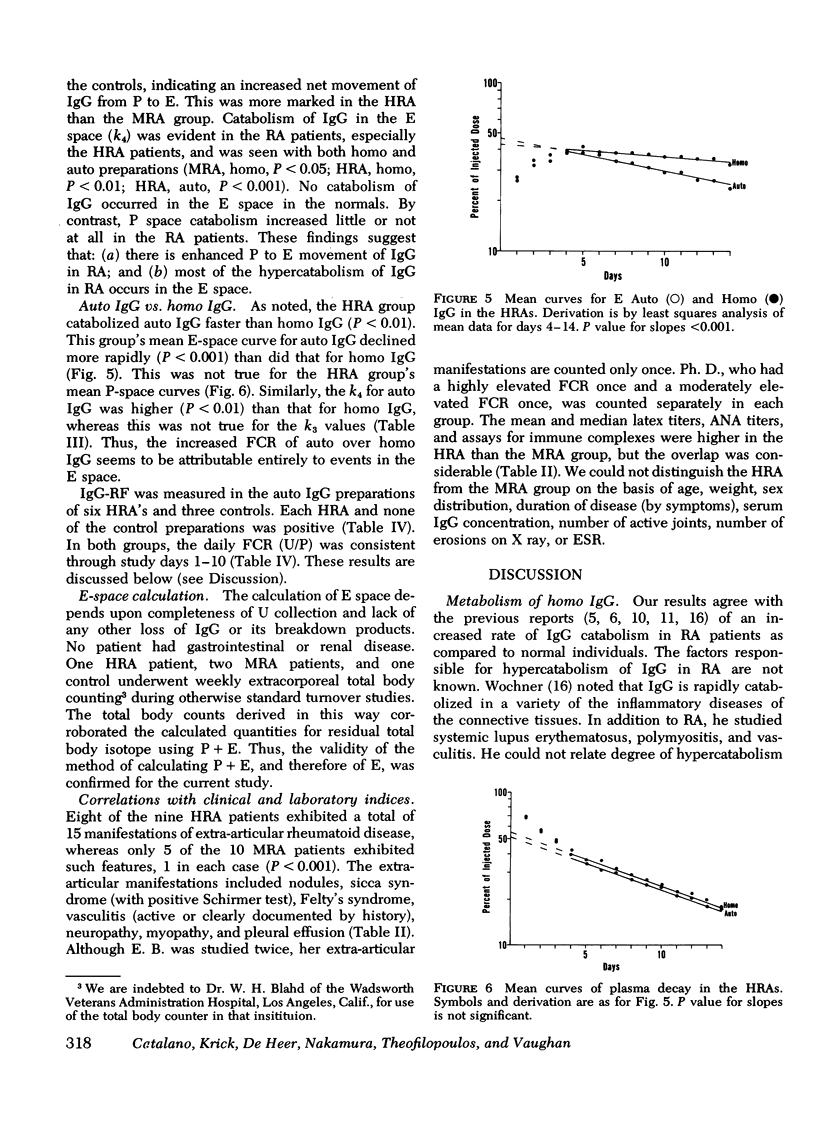
The metabolism of radioiodinated IgG was studied in 20 patients with rheumatoid arthritis and 11 normal controls using autologous IgG and homologous IgG pooled from normal donors. Fractional catabolic rates in the controls were 4.44% of the autologous- and 4.29% of the homologous-labeled protein per day. The corresponding rates in the rheumatoid patients were 9.67% of the autologous- and 8.64% of the homologous-labeled protein per day. Extravascular catabolism occurred only in the rheumatoid group and accounted essentially for the entire increased catabolism of IgG observed in these patients. 10 patients were especially hypercatabolic, with fractional catabolic rates for autologous IgG greater than 10%. Moreover, they catabolized their autologous IgG significantly faster than the homologous IgG (12.6 vs. 9.9%). The increment of catabolism of autologous over homologous IgG also occurred in the extravascular compartment. These highly hypercatabolic patients had a significantly increased number of manifestations of extra-articular disease.
The hypercatabolism of IgG could not be correlated with age, weight, sex, duration of disease, joint erosions, corticosteroid therapy, erythrocyte sedimentation rate, rheumatoid factor titer, serum IgG concentration, or circulating immune complexes as measured by the Raji cell radioimmunoassay.
Conceivable sites of extravascular catabolism and possible causes of faster catabolism of autologous (rheumatoid) than of homologous (normal) IgG are discussed.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALPER C. A., FREEMAN T., WALDENSTROEM J. THE METABOLISM OF GAMMA GLOBULINS IN MYELOMA AND ALLIED CONDITIONS. J Clin Invest. 1963 Dec;42:1858–1868. doi: 10.1172/JCI104870. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bandilla K. K., McDuffie F. C. Reactivity of rheumatoid factor with autologous IgG antibodies. Arthritis Rheum. 1969 Apr;12(2):74–81. doi: 10.1002/art.1780120203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brambell F. W. The transmission of immunity from mother to young and the catabolism of immunoglobulins. Lancet. 1966 Nov 19;2(7473):1087–1093. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(66)92190-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAMPBELL R. M., CUTHBERTSON D. P., MATTHEWS C. M., MCFARLANE A. S. Behaviour of 14C- and 131I-labelled plasma proteins in the rat. Int J Appl Radiat Isot. 1956 Jul;1(1-2):66–84. doi: 10.1016/0020-708x(56)90020-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CARTWRIGHT G. E., ATHENS J. W., WINTROBE M. M. THE KINETICS OF GRANULOPOIESIS IN NORMAL MAN. Blood. 1964 Dec;24:780–803. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIXON F. J., TALMAGE D. W., MAURER P. H., DEICHMILLER M. The half-life on homologous gamma globulin (antibody) in several species. J Exp Med. 1952 May;95(5):313–318. doi: 10.1084/jem.96.4.313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DONOHUE D. M., REIFF R. H., HANSON M. L., BETSON Y., FINCH C. A. Quantitative measurement of the erythrocytic and granulocytic cells of the marrow and blood. J Clin Invest. 1958 Nov;37(11):1571–1576. doi: 10.1172/JCI103750. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griggs R. C., Condemi J. J., Vaughan J. H. Effect of therapeutic dosages of prednisone on human immunoglobulin G metabolism. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1972 May;49(5):267–273. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(72)90094-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HELMKAMP R. W., GOODLAND R. L., BALE W. F., SPAR I. L., MUTSCHLER L. E. High specific activity iodination of gamma-globulin with iodine-131 monochloride. Cancer Res. 1960 Nov;20:1495–1500. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. M., Watkins J., Scopes P. M., Tracey B. M. Differences in serum IgG structure in health and rheumatoid disease. Circular dichroism studies. Ann Rheum Dis. 1974 Jul;33(4):366–370. doi: 10.1136/ard.33.4.366. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. M., Watkins J., Wolborow E. J. Antiglobulin production to altered IgG in rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 1975 Mar 15;1(7907):611–614. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)91888-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence D. A., Weigle W. O., Spiegelberg H. L. Immunoglobulins cytophilic for human lymphocytes, monocytes, and neutrophils. J Clin Invest. 1975 Feb;55(2):368–376. doi: 10.1172/JCI107940. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy J., Barnett E. V., MacDonald N. S., Klinenberg J. R. Altered immunoglobulin metabolism in systemic lupus erythematosus and heumatoid arthritis. J Clin Invest. 1970 Apr;49(4):708–715. doi: 10.1172/JCI106283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy J., Barnett E. V., MacDonald N. S., Klinenberg J. R., Pearson C. M. The effect of azathioprine on gammaglobulin synthesis in man. J Clin Invest. 1972 Sep;51(9):2233–2238. doi: 10.1172/JCI107031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MATTHEWS C. M. The theory of tracer experiments with 131I-labelled plasma proteins. Phys Med Biol. 1957 Jul;2(1):36–53. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/2/1/305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILLS J. A., CALKINS E., COHEN A. S. The plasma disappearance time and catabolic half-life of I-131-labeled normal human gamma globulin in amyloidosis and inrheumatoid arthritis. J Clin Invest. 1961 Oct;40:1926–1934. doi: 10.1172/JCI104418. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMillan R., Longmire R. L., Yelenosky R., Lang J. E., Heath V., Craddock C. G. Immunoglobulin synthesis by human lymphoid tissues: normal bone marrow as a major site of IgG production. J Immunol. 1972 Dec;109(6):1386–1394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meuret G., Hoffmann G. Monocyte kinetic studies in normal and disease states. Br J Haematol. 1973 Mar;24(3):275–285. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1973.tb01652.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morell A., Terry W. D., Waldmann T. A. Metabolic properties of IgG subclasses in man. J Clin Invest. 1970 Apr;49(4):673–680. doi: 10.1172/JCI106279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mouridsen H. T., Baerentsen O., Rossing N., Jensen K. B. Lack of effect of gold therapy on abnormal IgG and IgM metabolism in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1974 Jul-Aug;17(4):391–396. doi: 10.1002/art.1780170408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Natvig J. B., Gaarder P. I., Turner M. W. IgG antigens of the C gamma 2 and C gamma 3 homology regions interacting with rheumatoid factors. Clin Exp Immunol. 1972 Oct;12(2):177–184. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OLHAGEN B., BIRKE G., PLANTIN L. O., AHLINDER S. ISOTOPE STUDIES OF GAMMAGLOBULIN CATABOLISM IN COLLAGEN DISORDERS. Acta Rheumatol Scand. 1963;9:88–93. doi: 10.3109/rhe1.1963.9.issue-1-4.13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PEKIN T. J., Jr, ZVAIFLER N. J. HEMOLYTIC COMPLEMENT IN SYNOVIAL FLUID. J Clin Invest. 1964 Jul;43:1372–1382. doi: 10.1172/JCI105013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panush R. S., Bianco N. E., Schur P. H. Serum and synovial fluid IgG, IgA and IgM antigammaglobulins in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1971 Nov-Dec;14(6):737–747. doi: 10.1002/art.1780140609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RESTIFO R. A., LUSSIER A. J., RAWSON A. J., ROCKEY J. H., HOLLANDER J. L. STUDIES ON THE PATHOGENESIS OF RHEUMATOID JOINT INFLAMMATION. 3. THE EXPERIMENTAL PRODUCTION OF ARTHRITIS BY THE INTRA-ARTICULAR INJECTION OF PURIFIED 7S GAMMA GLOBULIN. Ann Intern Med. 1965 Feb;62:285–291. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-62-2-285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossing N., Mouridsen H. T., Baerentsen O., Jensen K. B. Immunoglobulin (IgG and IgM) metabolism in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1973 Aug;32(1):15–20. doi: 10.3109/00365517309082446. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SOLOMON A., WALDMANN T. A., FAHEY J. L. Clinical and experimental metabolism of normal 6.6s gamma-globulin in normal subjects and in patients with macroglobulinemia and multiple myeloma. J Lab Clin Med. 1963 Jul;62:1–17. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiegelberg H. L., Fishkin B. G., Grey H. M. Catabolism of human gammaG-immunoglobulins of different heavy chain subclasses. I. Catabolism of gammaG-myeloma proteins in man. J Clin Invest. 1968 Oct;47(10):2323–2330. doi: 10.1172/JCI105917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan E. M. Relationship of nuclear staining patterns with precipitating antibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Lab Clin Med. 1967 Nov;70(5):800–812. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theofilopoulos A. N., Wilson C. B., Dixon F. J. The Raji cell radioimmune assay for detecting immune complexes in human sera. J Clin Invest. 1976 Jan;57(1):169–182. doi: 10.1172/JCI108257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VAUGHAN J. H., ARMATO A., GOLDTHWAIT J. C., BRACHMAN P., FAVOUR C. B., BAYLES T. B. A study of gamma globulin in rheumatoid arthritis. J Clin Invest. 1955 Jan;34(1):75–85. doi: 10.1172/JCI103065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaughan J. H., Barnett E. V., Leddy J. P. Autosensitivity diseases (concluded). Immunologic and pathogenetic concepts in lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis and hemolytic anemia. N Engl J Med. 1966 Dec 29;275(26):1486–concl. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196612292752607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaughan J. H., Chihara T., Moore T. L., Robbins D. L., Tanimoto K., Johnson J. S., McMillan R. Rheumatoid factor-producing cells detected by direct hemolytic plaque assay. J Clin Invest. 1976 Oct;58(4):933–941. doi: 10.1172/JCI108546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldmann T. A., Strober W. Metabolism of immunoglobulins. Prog Allergy. 1969;13:1–110. doi: 10.1159/000385919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins J., Swannell A. J. Catabolism of human serum IgG in health, rheumatoid arthritis, and active tuberculous disease. Possible influence of IgG structure. Ann Rheum Dis. 1973 May;32(3):247–250. doi: 10.1136/ard.32.3.247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins J., Tee D. E. Catabolism of gamma G-globulin and myeloma proteins of the subclasses gamma G1 and gamma G2 in a healthy volunteer. Immunology. 1970 Apr;18(4):537–543. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wochner R. D. Hypercatabolism of normal IgG; an unexplained immunoglobulin abnormality in the connective tissue diseases. J Clin Invest. 1970 Mar;49(3):454–464. doi: 10.1172/JCI106254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zvaifler N. J. Rheumatoid synovitis. An extravascular immune complex disease. Arthritis Rheum. 1974 May-Jun;17(3):297–305. doi: 10.1002/art.1780170315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



