Abstract
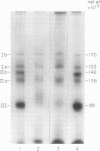
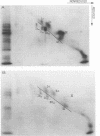
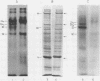
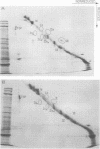
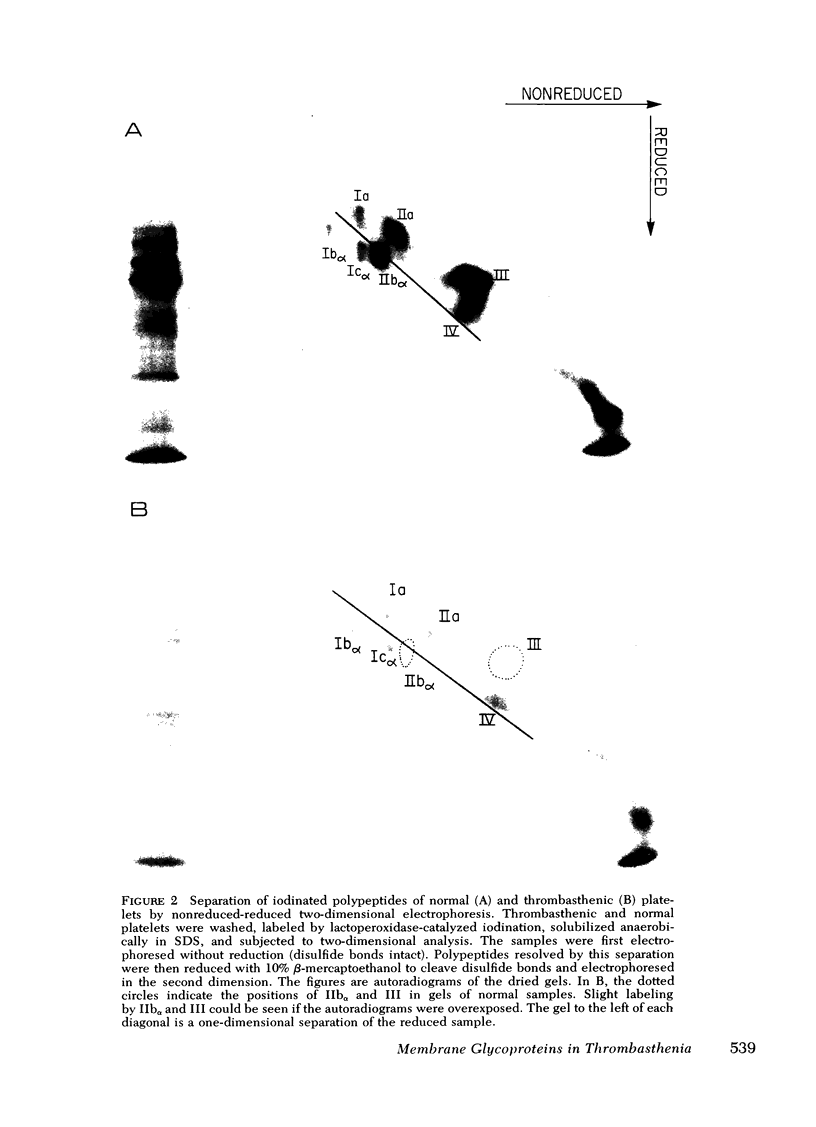
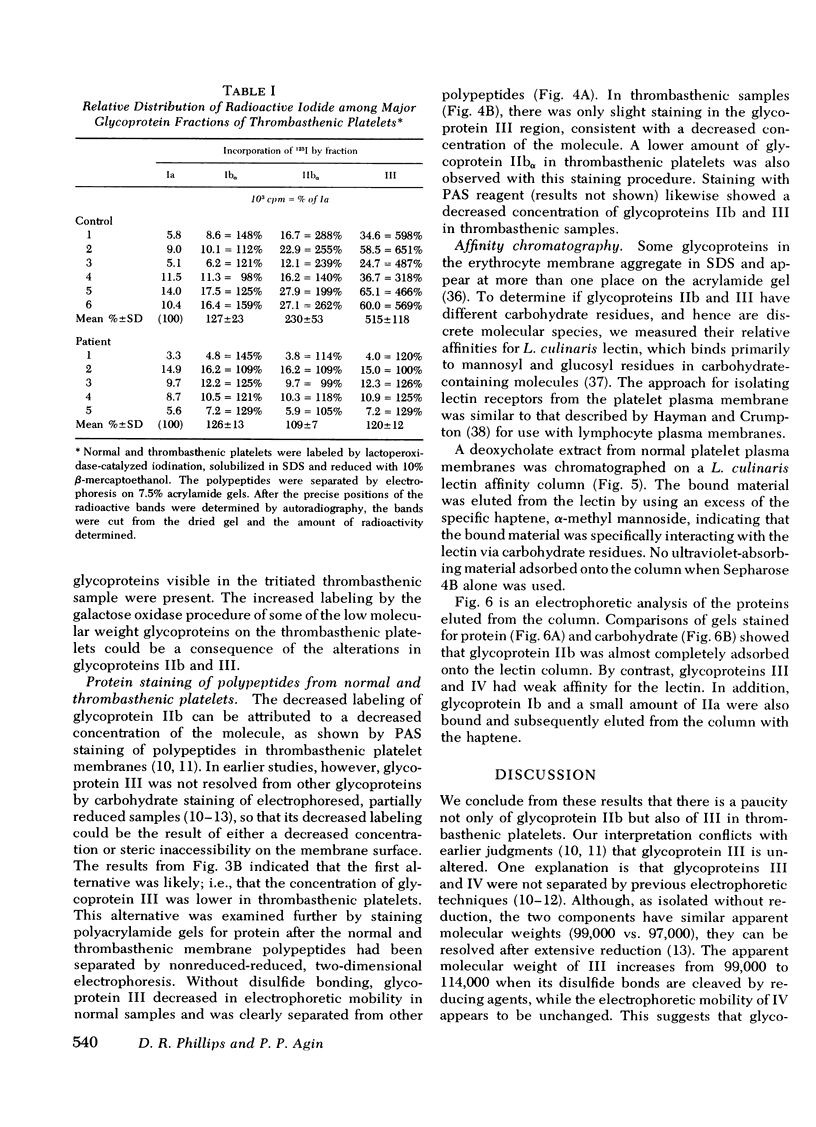
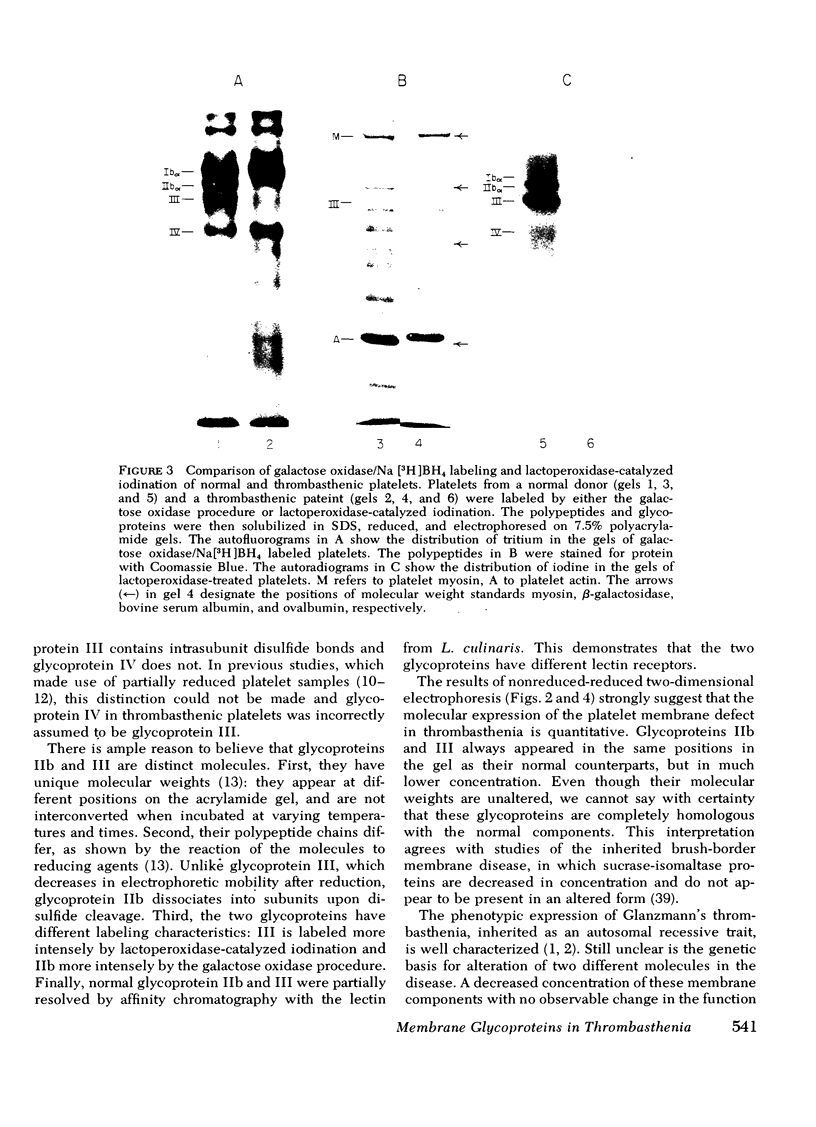
Platelets from patients with Glanzmann's thrombasthenia have a distinct molecular alteration of the plasma membrane surface, namely decreased amounts of a major glycoprotein designated as IIb (apparent mol wt 142,000). To identify other possible surface defects of thrombasthenic platelets, we labeled the membrane polypeptides of normal and thrombasthenic platelets by two different techniques: lactoperoxidase-catalyzed iodination and galactose oxidase oxidation, followed by reduction with tritiated sodium borohydride. Labeling patterns were determined after the polypeptides were separated by two-dimensional polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Before the second dimension was run, platelet samples were incubated with a reducing agent, β-mercapto-ethanol, to cleave the disulfide bonds of certain glycoproteins; the resulting changes in electrophoretic mobility permitted better resolution of individual molecules. Comparison of the labeled polypeptides of normal and thrombasthenic samples after reduction indicated decreased labeling of two major glycoproteins in thrombasthenic platelets: IIb and III (apparent mol wt 114,000). The relative proportions of radioactivity incorporated by these polypeptides were about 60 and 80% less than control values, respectively. With either Coomassie Blue or periodic acid-Schiff's reagent, glycoprotein III stained much less intensely in thrombasthenic compared to normal samples, indicating that the observed labeling deficit was caused by a decreased concentration of the molecule rather than steric inaccessibility on the membrane surface. Analysis of normal plasma membranes by affinity chromatography showed that glycoprotein IIb has receptors for lectin from Lens culinaris, the common lentil, whereas III does not. We conclude that a characteristic feature of Glanzmann's thrombasthenia is a decreased concentration of two discrete glycoproteins in the platelet plasma membrane.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ASTER R. H., JANDL J. H. PLATELET SEQUESTRATION IN MAN. I. METHODS. J Clin Invest. 1964 May;43:843–855. doi: 10.1172/JCI104970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barber A. J., Jamieson G. A. Isolation and characterization of plasma membranes from human blood platelets. J Biol Chem. 1970 Dec 10;245(23):6357–6365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen I., Glaser T., Seligsohn U. Effects of ADP and ATP on bovine fibrinogen- and ristocetin-induced platelet aggregation in Glanzmann's thrombasthenia. Br J Haematol. 1975 Nov;31(3):343–347. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1975.tb00865.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dayton W. R., Goll D. E., Zeece M. G., Robson R. M., Reville W. J. A Ca2+-activated protease possibly involved in myofibrillar protein turnover. Purification from porcine muscle. Biochemistry. 1976 May 18;15(10):2150–2158. doi: 10.1021/bi00655a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbanks G., Steck T. L., Wallach D. F. Electrophoretic analysis of the major polypeptides of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2606–2617. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fish W. W., Reynolds J. A., Tanford C. Gel chromatography of proteins in denaturing solvents. Comparison between sodium dodecyl sulfate and guanidine hydrochloride as denaturants. J Biol Chem. 1970 Oct 10;245(19):5166–5168. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gahmberg C. G., Hakomori S. I. External labeling of cell surface galactose and galactosamine in glycolipid and glycoprotein of human erythrocytes. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jun 25;248(12):4311–4317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerrard J. M., White J. G. The influence of aspirin and indomethacin on the platelet contractile wave. Am J Pathol. 1976 Mar;82(3):513–526. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARDISTY R. M., DORMANDY K. M., HUTTON R. A. THROMBASTHENIA. STUDIES ON THREE CASES. Br J Haematol. 1964 Jul;10:371–387. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1964.tb00714.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatton M. W., Regoeczi E. The proteolytic nature of commercial samples of galactose oxidase. Purification of the enzyme by a simple affinity method. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Jul 8;438(2):339–346. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(76)90251-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayman M. J., Crumpton M. J. Isolation of glycoproteins from pig lymphocyte plasma membrane using Lens culinaris phytohemagglutinin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 May 26;47(4):923–930. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90581-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard I. K., Sage H. J., Stein M. D., Young N. M., Leon M. A., Dyckes D. F. Studies on a phytohemagglutinin from the lentil. II. Multiple forms of Lens culinaris hemagglutinin. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 25;246(6):1590–1595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karpatkin S., Weiss H. J. Deficiency of glutathione peroxidase associated with high levels of reduced glutathione in glanzmann's thrombasthenia. N Engl J Med. 1972 Nov 23;287(21):1062–1066. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197211232872103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORRISON M., HULTQUIST D. E. LACTOPEROXIDASE. II. ISOLATION. J Biol Chem. 1963 Aug;238:2843–2849. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- March S. C., Parikh I., Cuatrecasas P. A simplified method for cyanogen bromide activation of agarose for affinity chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1974 Jul;60(1):149–152. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90139-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massini P., Lüscher E. F. Some effects of ionophores for divalent cations on blood platelets. Comparison with the effects of thrombin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Nov 4;372(1):109–121. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(74)90077-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nurden A. T., Caen J. P. An abnormal platelet glycoprotein pattern in three cases of Glanzmann's thrombasthenia. Br J Haematol. 1974 Oct;28(2):253–260. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1974.tb06660.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nurden A. T., Caen J. P. Specific roles for platelet surface glycoproteins in platelet function. Nature. 1975 Jun 26;255(5511):720–722. doi: 10.1038/255720a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips D. R., Agin P. P. Platelet plasma membrane glycoproteins. Evidence for the presence of nonequivalent disulfide bonds using nonreduced-reduced two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Mar 25;252(6):2121–2126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips D. R., Agin P. P. Platelet plasma membrane glycoproteins. Identification of a proteolytic substrate for thrombin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Apr 25;75(4):940–947. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)91473-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips D. R. Effect of trypsin on the exposed polypeptides and glycoproteins in the human platelet membrane. Biochemistry. 1972 Nov 21;11(24):4582–4588. doi: 10.1021/bi00774a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips D. R., Jenkins C. S., Lüscher E. F., Larrieu M. Molecular differences of exposed surface proteins on thrombasthenic platelet plasma membranes. Nature. 1975 Oct 16;257(5527):599–600. doi: 10.1038/257599a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips D. R., Morrison M. Changes in accessibility of plasma membrane protein as the result of tryptic hydrolysis. Nat New Biol. 1973 Apr 18;242(120):213–215. doi: 10.1038/newbio242213a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips D. R., Morrison M. Exposed protein on the intact human erythrocyte. Biochemistry. 1971 May 11;10(10):1766–1771. doi: 10.1021/bi00786a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollard T. D., Thomas S. M., Niederman R. Human platelet myosin. I. Purification by a rapid method applicable to other nonmuscle cells. Anal Biochem. 1974 Jul;60(1):258–266. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90152-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preiser H., Menard D., Crane R. K., Cerda J. J. Deletion of enzyme protein from the brush border membrane in sucrase-isomaltase deficiency. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Sep 6;363(2):279–282. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(74)90067-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddick R. L., Mason R. G. Freeze-etch observations on the plasma membrane and other structures of normal and abnormal platelets. Am J Pathol. 1973 Mar;70(3):473–488. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichert N., Seligsohn U., Ramot B. Clinical and genetic aspects of Glanzmann's thrombasthenia in Israel: report of 22 cases. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1975 Dec 15;34(3):806–820. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segrest J. P., Jackson R. L., Andrews E. P., Marchesi V. T. Human erythrocyte membrane glycoprotein: a re-evaluation of the molecular weight as determined by SDS polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Jul 16;44(2):390–395. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90612-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharon N., Lis H. Lectins: cell-agglutinating and sugar-specific proteins. Science. 1972 Sep 15;177(4053):949–959. doi: 10.1126/science.177.4053.949. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuart M. J. Inherited defects of platelet function. Semin Hematol. 1975 Jul;12(3):233–253. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuech J. K., Morrison M. Human erythrocyte membrane sialoglycoproteins: a study of interconversion. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Jul 10;59(1):352–360. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(74)80214-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITE J. G., YUNIS E., COLLIANDER M., KRIVIT W. THE CORRECTION OF PROLONGED BLEEDING TIMES IN TWO BROTHERS BY PLATELET TRANSFUSIONS DESPITE NORMAL IN VITRO PLATELET TESTS. Pediatrics. 1964 Apr;33:579–584. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh P. N. Platelet coagulant activities in thrombasthenia. Br J Haematol. 1972 Nov;23(5):553–569. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1972.tb07091.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss H. J., Kochwa S. Studies of platelet function and proteins in 3 patients with Glanzmann's thrombasthenia. J Lab Clin Med. 1968 Jan;71(1):153–165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss H. J. Platelet physiology and abnormalities of platelet function (second of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1975 Sep 18;293(12):580–588. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197509182931204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. G. Effects of cationic polypeptides on thrombasthenic and afibrinogenemic blood platelets. Am J Pathol. 1972 Sep;68(3):447–460. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zucker M. B., Pert J. H., Hilgartner M. W. Platelet function in a patient with thrombasthenia. Blood. 1966 Oct;28(4):524–534. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]