Abstract
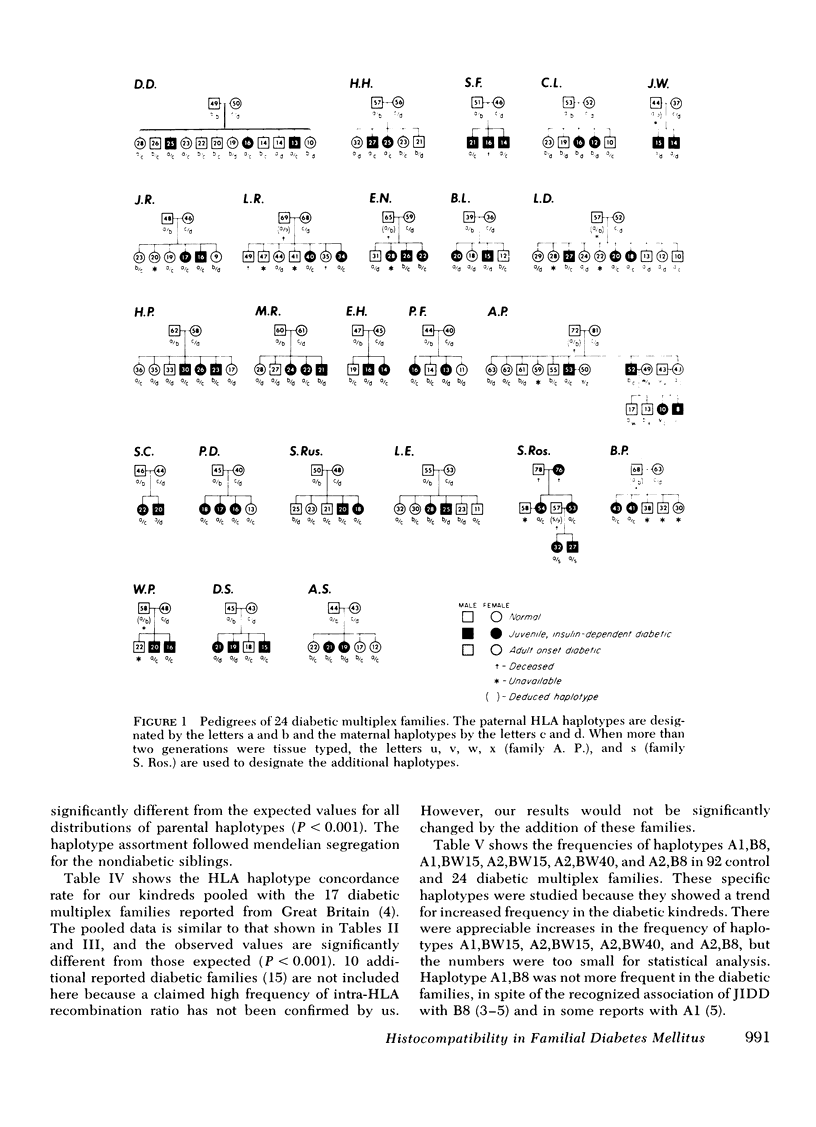
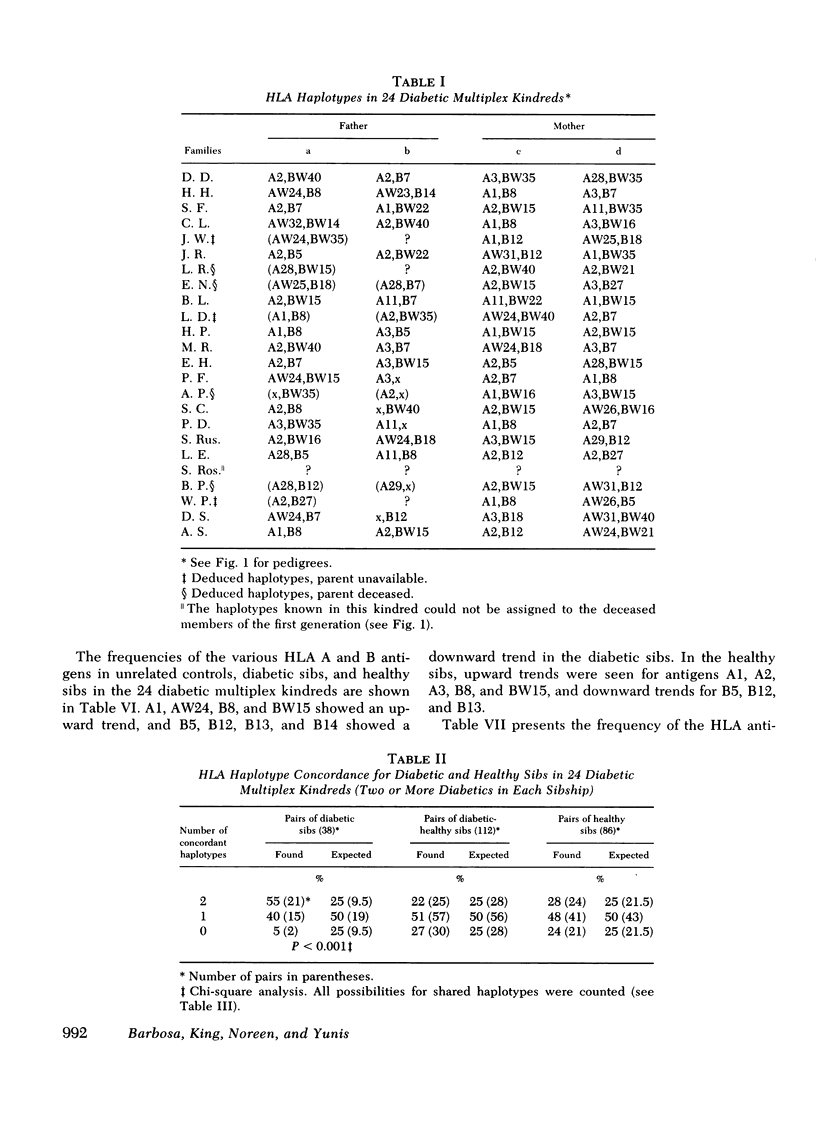
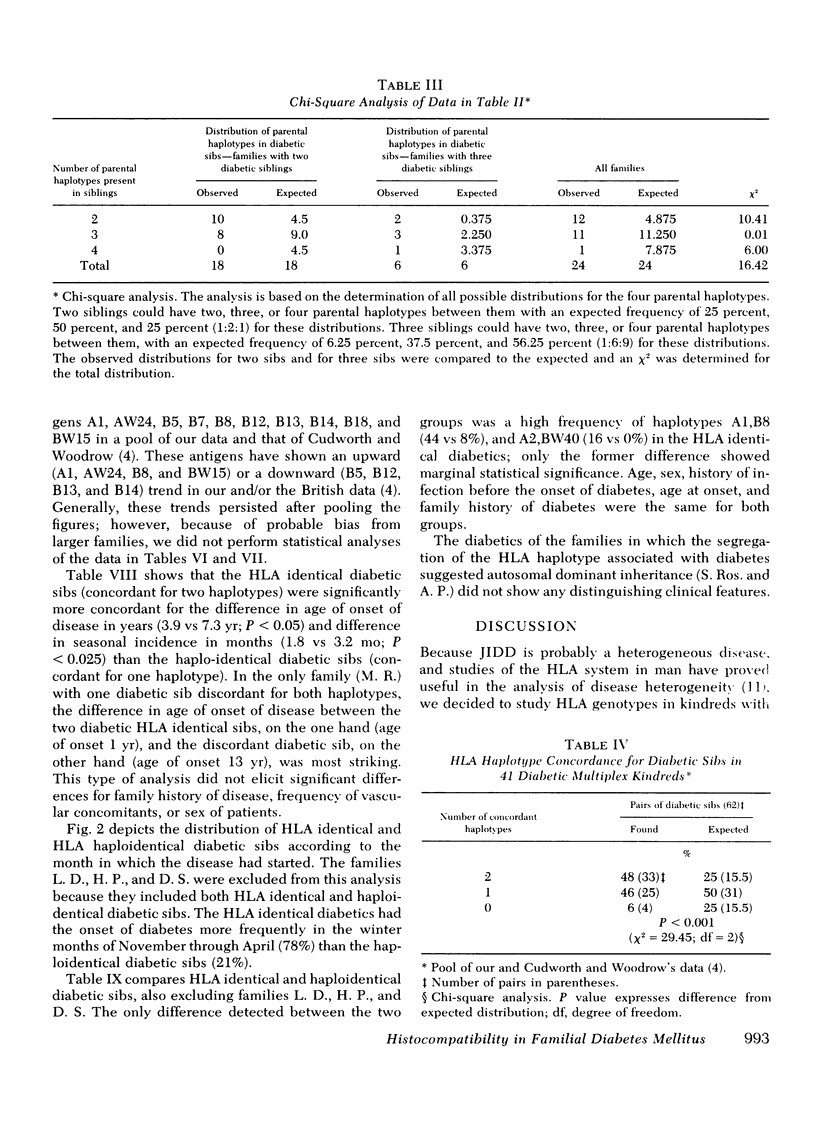
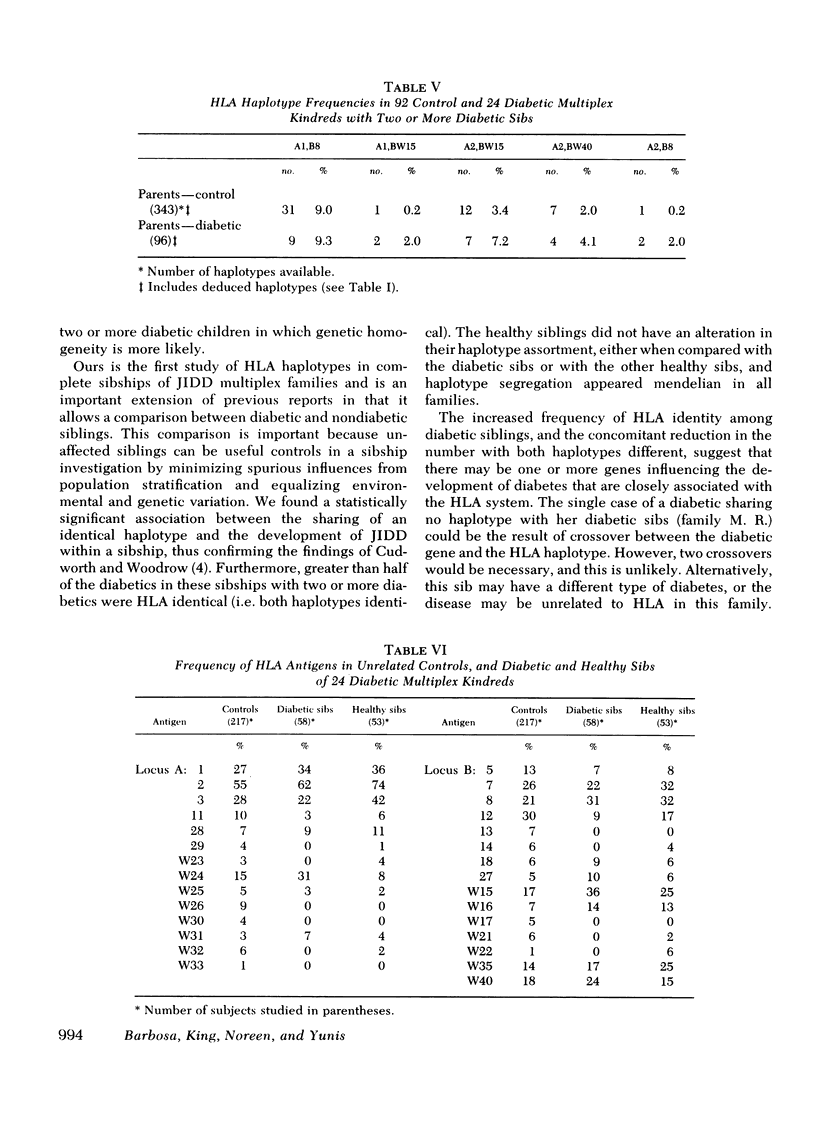
We have histocompatibility (HLA) genotyped 24 families with two or more juvenile, insulin-dependent, ketosis-prone diabetic siblings. This criterion for family selection was used to obtain a homogeneous form of diabetes within a sibship, because diabetes appears to be a genetically heterogeneous disease. 58 diabetic and 53 nondiabetic sibs and 40 parents were studied. 55% of the diabetic pairs were concordant for both HLA haplotypes (expected 25%), 40% were concordant for one haplotype (expected 50%), and 5% were discordant for both haplotypes (expected 25%). These values are significantly different from the expected values (P < 0.001). On the other hand, the inheritance of haplotypes among the nondiabetic sibs in these families was not significantly different from the expected mendelian segregation.
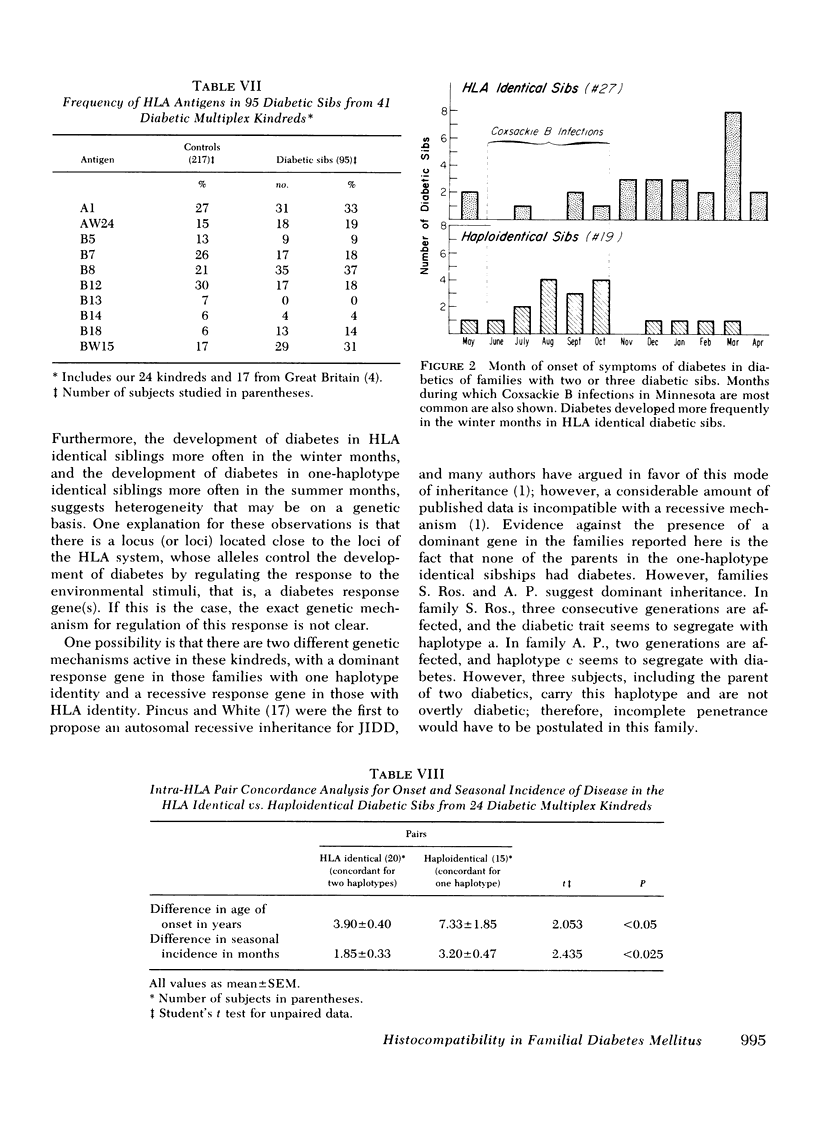
When comparing 20 pairs of HLA identical (sharing two haplotypes) with 15 pairs of haploidential (sharing one haplotype) diabetic sibs for the intrapair difference in age of onset of disease, we found that the HLA identical sibs were significantly more concordant for age of onset (3.9 yr difference) than the haploidential (7.3 yr difference) (P < 0.05). The same type of analysis for the difference in seasonal incidence in months revealed that the HLA indentical sibs were more concordant (1.8 mo difference) than the haploidentical sibs (3.2 mo difference) (P < 0.025). Furthermore, the HLA identical diabetic sibs were more likely to develop diabetes in the winter months (78%) than the haploidentical diabetic sibs (21%).
No particular HLA haplotype or antigen seemed to be associated with any particular clinical feature.
These data are compatible with the theory of genetic heterogeneity of juvenile, insulin-dependent diabetes. It is suggested that there are one or more diabetes response genes in the HLA region playing an important role in the pathogenesis of juvenile, insulin-dependent diabetes in the families studied here. It is, however, possible that other genes, not associated with the HLA complex, may play an etiologic role in some cases of juvenile, insulin-dependent diabetes, resulting in lack of association between HLA and some forms of diabetes.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amos D. B., Bashir H., Boyle W., MacQueen M., Tiilikainen A. A simple micro cytotoxicity test. Transplantation. 1969 Mar;7(3):220–223. doi: 10.1097/00007890-196903000-00023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbosa J., Noreen H., Goetz F., Simmons R., Najarian J., Yunis E. J. Letter: Juvenile diabetes and viruses. Lancet. 1976 Feb 14;1(7955):371–371. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)90136-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom A., Hayes T. M., Gamble D. R. Register of newly diagnosed diabetic children. Br Med J. 1975 Sep 6;3(5983):580–583. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5983.580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buschard K., Rygaard J., Lung E. The inability of a diabetogenic virus to induce diabetes mellitus in athymic (nude) mice. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand C. 1976 Aug;84(4):299–303. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1976.tb00033.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craighead J. E., Higgins D. A. Genetic influences affecting the occurrence of a diabetes mellitus-like disease in mice infected with the encephalomyocarditis virus. J Exp Med. 1974 Feb 1;139(2):414–426. doi: 10.1084/jem.139.2.414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cudworth A. G., Woodrow J. C. Evidence for HL-A-linked genes in "juvenile" diabetes mellitus. Br Med J. 1975 Jul 19;3(5976):133–135. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5976.133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gamble D. R., Taylor K. W., Cumming H. Coxsackie viruses and diabetes mellitus. Br Med J. 1973 Nov 3;4(5887):260–262. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5887.260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludvigsson J., Heding L. G. C-peptide in children with juvenile diabetes. A preliminary report. Diabetologia. 1976 Dec;12(6):627–630. doi: 10.1007/BF01220642. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludvigsson J., Säfwenberg J., Heding L. G. HLA-types, C-peptide and insulin antibodies in juvenile diabetes. Diabetologia. 1977 Jan;13(1):13–17. doi: 10.1007/BF00996321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludwig H., Schernthaner G., Mayr W. R. Letter: Is HLA-B7 a marker associated with a protective gene in juvenile-onset diabetes mellitus? N Engl J Med. 1976 May 6;294(19):1066–1066. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197605062941916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris P. J., Irvine W. J., Gray R. S., Duncan L. J., Vaughan H., McCallum F. J., Campbell C. J., Farquhar J. W. HLA and pancreatic islet cell antibodies in diabetes. Lancet. 1976 Sep 25;2(7987):652–653. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)92464-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson P. G., Pyke D. A., Cudworth A. G., Woodrow J. C., Batchelor J. R. Histocompatibility antigens in diabetic identical twins. Lancet. 1975 Aug 2;2(7927):193–194. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)90668-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson P. G., Pyke D. A. Genetic diabetes not linked to the HLA locus. Br Med J. 1976 Jan 24;1(6003):196–197. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6003.196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nerup J., Platz P., Andersen O. O., Christy M., Lyngsoe J., Poulsen J. E., Ryder L. P., Nielsen L. S., Thomsen M., Svejgaard A. HL-A antigens and diabetes mellitus. Lancet. 1974 Oct 12;2(7885):864–866. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)91201-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rimoin D. L. Inheritance in diabetes mellitus. Med Clin North Am. 1971 Jul;55(4):807–819. doi: 10.1016/s0025-7125(16)32477-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rolles C. J., Rayner P. H., Mackintosh P. Letter: Aetiology of juvenile diabetes. Lancet. 1975 Aug 2;2(7927):230–230. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)90698-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubinstein P., Suciu-Foca N., Nicholson J. F., Fotino M., Molinaro A., Harisiadis L., Hardy M. A., Reemtsma K., Allen F. H., Jr The HLA system in the families of patients with juvenile diabetes mellitus. J Exp Med. 1976 May 1;143(5):1277–1282. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.5.1277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schernthaner G., Mayr W. R., Pacher M., Ludwig H., Erd W., Eibl M. HL-A8, W15 and T3 in juvenile onset diabetes mellitus. Horm Metab Res. 1975 Nov;7(6):521–522. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1095680. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singal D. P., Blajchman M. A. Histocompatibility (HL-A) antigens, lymphocytotoxic antibodies and tissue antibodies in patients with diabetes mellitus. Diabetes. 1973 Jun;22(6):429–432. doi: 10.2337/diab.22.6.429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinke J., Taylor K. W. Viruses and the etiology of diabetes. Diabetes. 1974 Jul;23(7):631–633. doi: 10.2337/diab.23.7.631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svejgaard A., Platz P., Ryder L. P., Nielsen L. S., Thomsen M. HL-A and disease associations--a survey. Transplant Rev. 1975;22:3–43. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1975.tb01550.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tattersal R. B., Fajans S. S. Prevalence of diabetes and glucose intolerance in 199 offspring of thirty-seven conjugal diabetic parents. Diabetes. 1975 May;24(5):452–462. doi: 10.2337/diab.24.5.452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomsen M., Platz P., Andersen O. O., Christy M., Lyngsøoe, Nerup J., Rasmussen K., Ryder L. P., Nielsen L. S., Svejgaard A. MLC typing in juvenile diabetes mellitus and idiopathic Addison's disease. Transplant Rev. 1975;22:125–147. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1975.tb01555.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van de Putte I., Vermylen C., Decraene P., Vlietinck R., van de Berghe H. Letter: Segregation of HLA B7 in juvenile-onset diabetes mellitus. Lancet. 1976 Jul 31;2(7979):251–251. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)91043-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb S. R., Loria R. M., Madge G. E., Kibrick S. Susceptibility of mice to group B coxsackie virus is influenced by the diabetic gene. J Exp Med. 1976 May 1;143(5):1239–1248. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.5.1239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


