Abstract
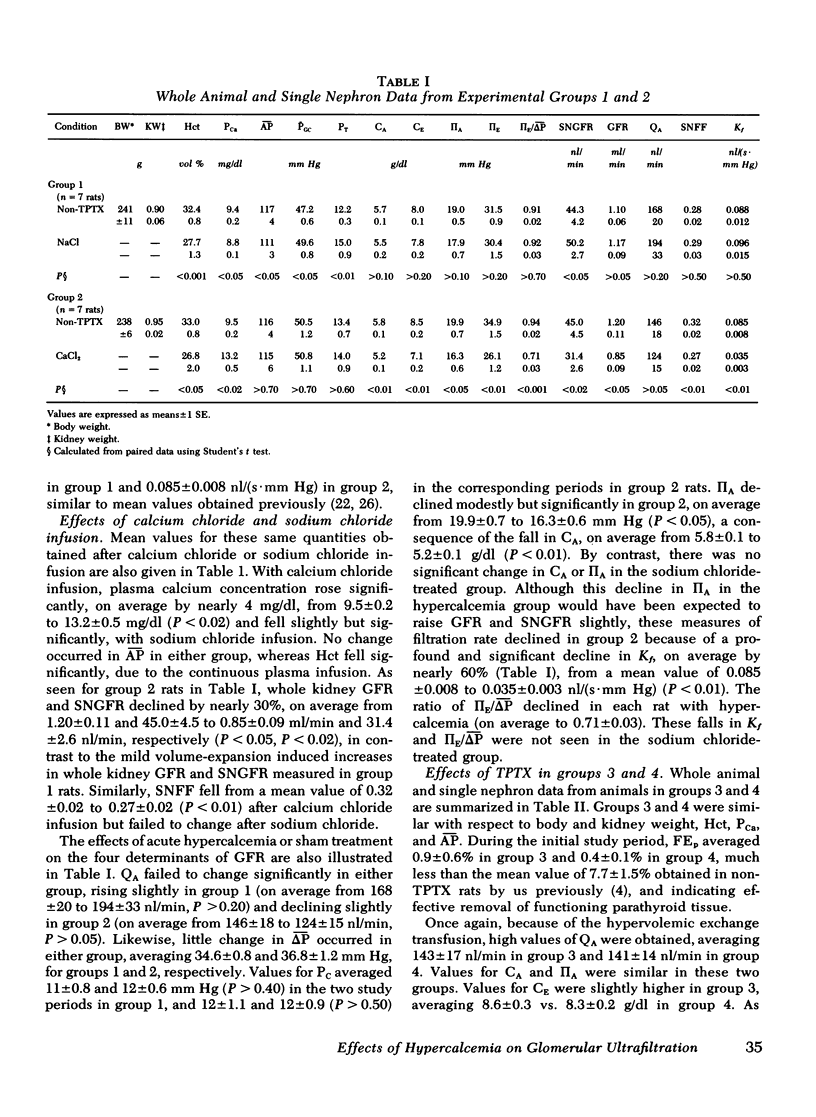
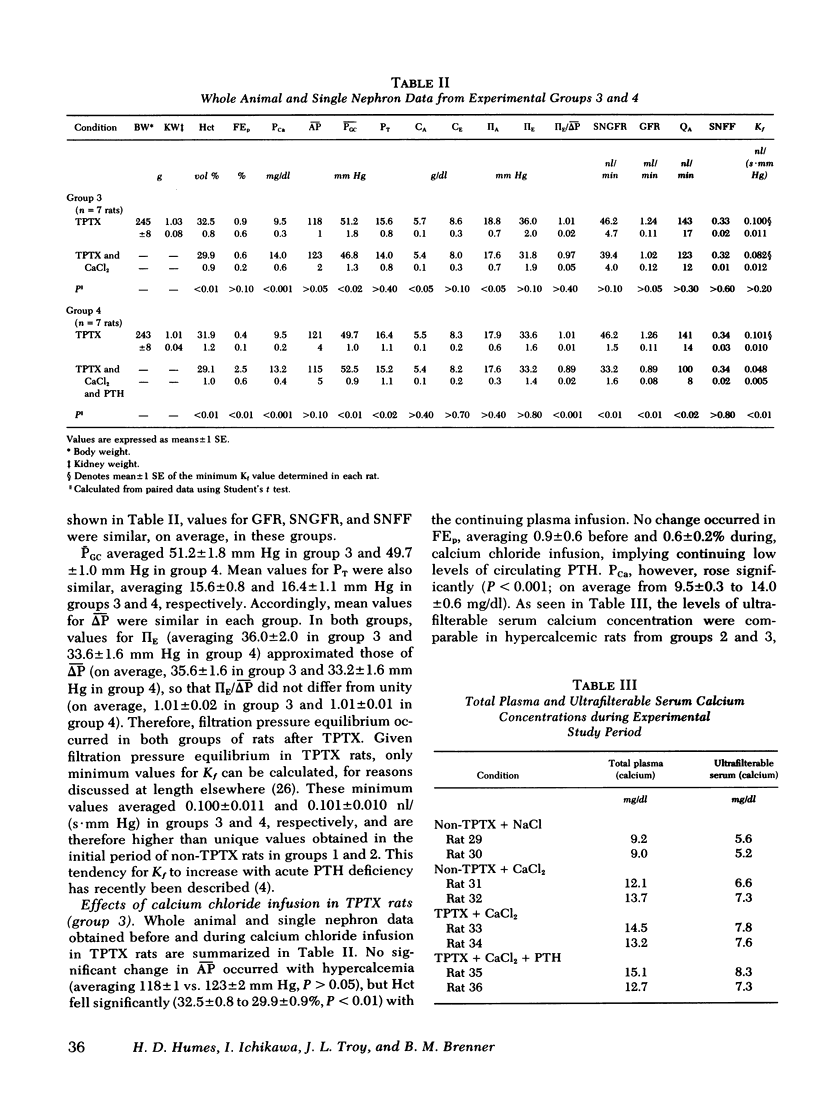
Experiments were performed on 36 plasma-expanded Munich-Wistar rats to examine the effects of acute hypercalcemia on the determinants of glomerular ultrafiltration. Elevation of total plasma calcium concentration to an average value of 13.2 +/- 0.5 mg/dl, by acute infusion of calcium chloride into nonthyroparathyroidectomized (non-TPTX) rats, resulted in significant declines in single nephron and whole kidney glomerular filtration rate. These declines were due primarily to a fall in the glomerular capillary ultrafiltration coefficient (Kf), to a mean value approximately 60% below that determined in the pre-infusion period. These changes were not seen in a separate group of sham-treated non-TPTX rats. It is of interest that these effects of acute hypercalcemia were largely abolished in rats that underwent acute TPTX before hypercalcemia. Infusion of a submaximally phosphaturic dose of parathyroid hormone, together with calcium chloride, into a second group of acute TPTX rats, however, had the effect of reproducing the striking declines in filtration rate and Kf noted in non-TPTX rats given calcium chloride alone. These findings suggest that the decline in filtration rate associated with hypercalcemia is due largely to the reduction in Kf, the latter dependent upon the presence of parathyroid hormone.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baylis C., Deen W. M., Myers B. D., Brenner B. M. Effects of some vasodilator drugs on transcapillary fluid exchange in renal cortex. Am J Physiol. 1976 Apr;230(4):1148–1158. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1976.230.4.1148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baylis C., Ichikawa I., Willis W. T., Wilson C. B., Brenner B. M. Dynamics of glomerular ultrafiltration. IX. Effects of plasma protein concentration. Am J Physiol. 1977 Jan;232(1):F58–F71. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1977.232.1.F58. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett C. M. Urine concentration and dilution in hypokalemic and hypercalcemic dogs. J Clin Invest. 1970 Jul;49(7):1447–1457. doi: 10.1172/JCI106362. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blantz R. C. Effect of mannitol on glomerular ultrafiltration in the hydropenic rat. J Clin Invest. 1974 Nov;54(5):1135–1143. doi: 10.1172/JCI107857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blantz R. C., Konnen K. S., Tucker B. J. Glomerular filtration response to elevated ureteral pressure in both the hydropenic and the plasma-expanded rat. Circ Res. 1975 Dec;37(6):819–829. doi: 10.1161/01.res.37.6.819. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blantz R. C. The mechanism of acute renal failure after uranyl nitrate. J Clin Invest. 1975 Mar;55(3):621–635. doi: 10.1172/JCI107970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borle A. B. Calcium metabolism at the cellular level. Fed Proc. 1973 Sep;32(9):1944–1950. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner B. M., Falchuk K. H., Keimowitz R. I., Berliner R. W. The relationship between peritubular capillary protein concentration and fluid reabsorption by the renal proximal tubule. J Clin Invest. 1969 Aug;48(8):1519–1531. doi: 10.1172/JCI106118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner B. M., Troy J. L., Daugharty T. M., Deen W. M., Robertson C. R. Dynamics of glomerular ultrafiltration in the rat. II. Plasma-flow dependence of GFR. Am J Physiol. 1972 Nov;223(5):1184–1190. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1972.223.5.1184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner B. M., Troy J. L., Daugharty T. M. The dynamics of glomerular ultrafiltration in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1971 Aug;50(8):1776–1780. doi: 10.1172/JCI106667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Criss W. E., Murad F., Kimura H. Properties of guanylate cyclase from rat kidney cortex and transplantable kidney tumors. J Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1976;2(1):11–19. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DELSAL J. L., MANHOURI H. Etude comparative des dosages colorimétriques du phosphore. IV. Dosage de l'orthophosphate en présence d'esters phosphoriques; nouvelles méthodes. Bull Soc Chim Biol (Paris) 1958;40(11):1623–1636. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deen W. M., Robertson C. R., Brenner B. M. A model of glomerular ultrafiltration in the rat. Am J Physiol. 1972 Nov;223(5):1178–1183. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1972.223.5.1178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deen W. M., Troy J. L., Robertson C. R., Brenner B. M. Dynamics of glomerular ultrafiltration in the rat. IV. Determination of the ultrafiltration coefficient. J Clin Invest. 1973 Jun;52(6):1500–1508. doi: 10.1172/JCI107324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dousa T. P., Barnes L. D., Ong S. H., Steiner A. L. Immunohistochemical localization of 3':5'-cyclic AMP and 3':5'-cyclic GMP in rat renal cortex: effect of parathyroid hormone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3569–3573. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards B. R., Sutton R. A., Dirks J. H. Effect of calcium infusion on renal tubular reabsorption in the dog. Am J Physiol. 1974 Jul;227(1):13–18. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1974.227.1.13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein F. H. Calcium and the kidney. Am J Med. 1968 Nov;45(5):700–714. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(68)90206-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLANIGAN W. J., OKEN D. E. RENAL MICROPUNCTURE STUDY OF THE DEVELOPMENT OF ANURIA IN THE RAT WITH MERCURY-INDUCED ACUTE RENAL FAILURE. J Clin Invest. 1965 Mar;44:449–457. doi: 10.1172/JCI105158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FUHR J., KACZMARCZYK J., KRUTTGEN C. D. Eine einfache colorimetrische Methode zur Inulinbestimmung für Nieren-Clearance-Untersuchungen bei Stoffwechselgesunden und Diabetikern. Klin Wochenschr. 1955 Aug 1;33(29-30):729–730. doi: 10.1007/BF01473295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichikawa I., Brenner B. M. Evidence for glomerular actions of ADH and dibutyryl cyclic AMP in the rat. Am J Physiol. 1977 Aug;233(2):F102–F117. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1977.233.2.F102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maddox D. A., Bennett C. M., Deen W. M., Glassock R. J., Knutson D., Daugharty T. M., Brenner B. M. Determinants of glomerular filtration in experimental glomerulonephritis in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1975 Feb;55(2):305–318. doi: 10.1172/JCI107934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagata N., Rasmussen H. Parathyroid hormone, 3'5' AMP, Ca++, and renal gluconeogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Feb;65(2):368–374. doi: 10.1073/pnas.65.2.368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagata N., Rasmussen H. Renal gluconeogenesis: effects of Ca2+ and H+. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Jul 21;215(1):1–16. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(70)90382-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz G., Hardman J. G., Schultz K., Baird C. E., Sutherland E. W. The importance of calcium ions for the regulation of guanosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphage levels. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Dec;70(12):3889–3893. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.12.3889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanherweghem J. L., Ducobu J., d'Hollander A., Toussaint C. Effects of hypercalcemia on water and sodium excretion by the isolated dog kidney. Pflugers Arch. 1976 May 6;363(1):75–80. doi: 10.1007/BF00587405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


