Abstract
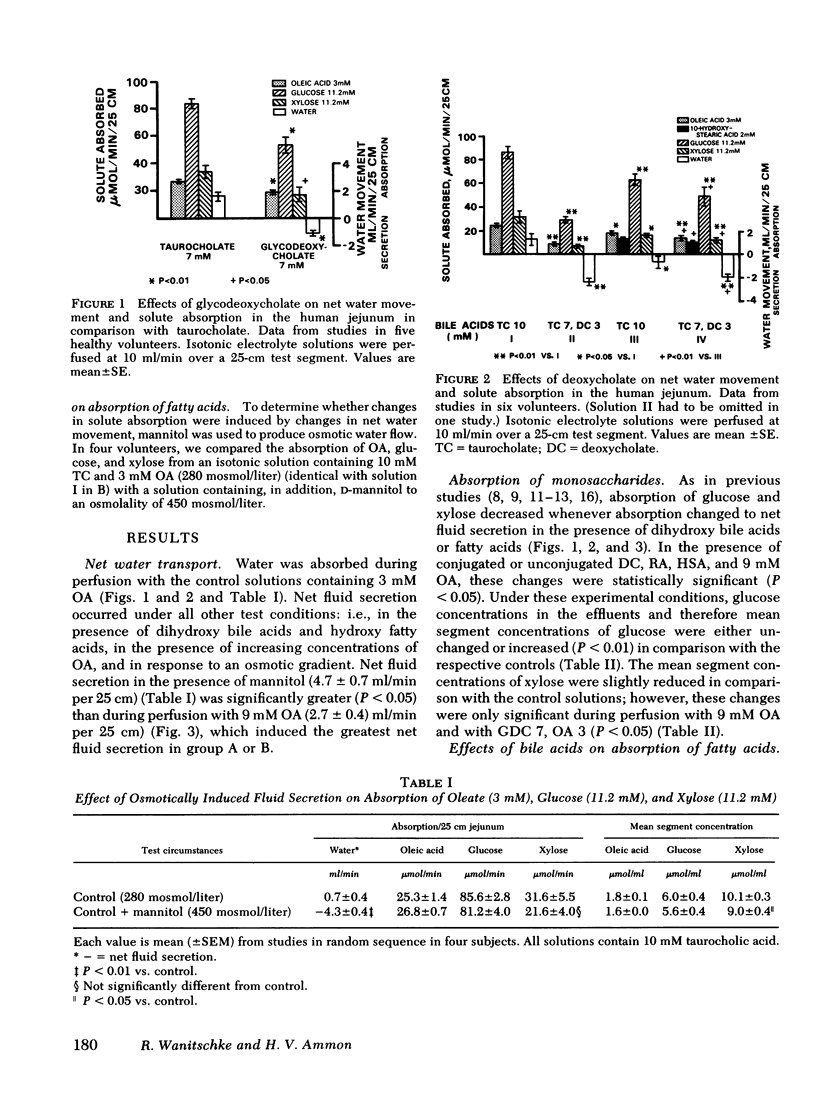
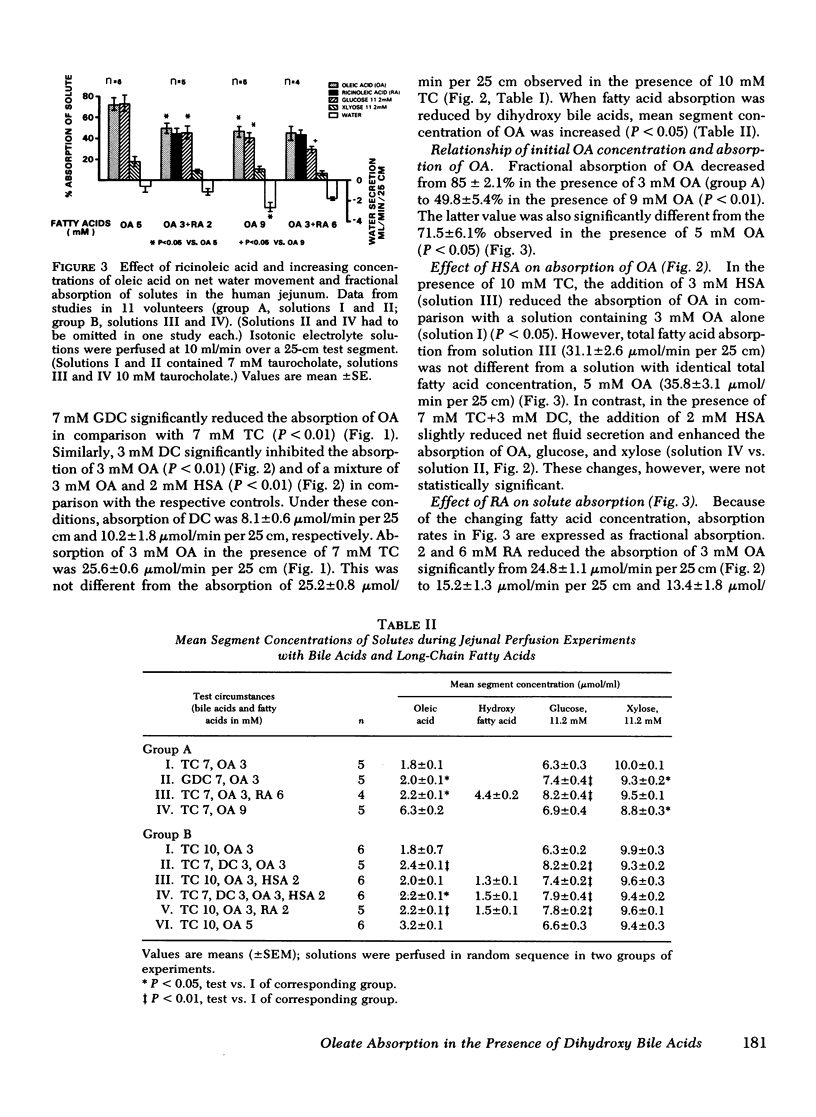
Perfusion studies of the normal human jejunum were performed to test whether dihydroxy bile acids and hydroxy fatty acids inhibit the absorption of oleic acid, since previous reports documented their inhibitory effects on the absorption of several other organic solutes. 3 mM deoxycholate and 7 mM glycodeoxycholate inhibited the absorption of 3 mM oleic acid in isotonic micellar solutions while inducing net fluid secretion. Similarly, fractional absorption of oleic acid decreased in the presence of hydroxy fatty acids. However, only the changes induced by 2 mM ricinoleic acid could be distinguished from changes induced by an increase in total fatty acid concentration. Under all experimental conditions, close linear relationships existed between net water movement and fractional absorption of glucose, xylose, and fatty acids, as well as between the absorption rates of these solutes. In contrast, net fluid secretion induced by hypertonic D-mannitol (450 mosmol/liter) had no effect on solute absorption. Our data and observations in the literature do not allow formulation of a hypothesis which would adequately define all effects of dihydroxy bile acids and fatty acids on intestinal transport processes. The observations help explain the malabsorption of fat and other nutrients in patients with the blind loop syndrome.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ament M. E., Shimoda S. S., Saunders D. R., Rubin C. E. Pathogenesis of steatorrhea in three cases of small intestinal stasis syndrome. Gastroenterology. 1972 Nov;63(5):728–747. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ammon H. V., Phillips S. F. Inhibition of ileal water absorption by intraluminal fatty acids. Influence of chain length, hydroxylation, and conjugation of fatty acids. J Clin Invest. 1974 Jan;53(1):205–210. doi: 10.1172/JCI107539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ammon H. V., Thomas P. J., Phillips S. F. Effects of oleic and ricinoleic acids on net jejunal water and electrolyte movement. Perfusion studies in man. J Clin Invest. 1974 Feb;53(2):374–379. doi: 10.1172/JCI107569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binder H. J., Filburn C., Volpe B. T. Bile salt alteration of colonic electrolyte transport: role of cyclic adenosine monophosphate. Gastroenterology. 1975 Mar;68(3):503–508. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter C. C., Sack R. B., Feeley J. C., Steenberg R. W. Site and characteristics of electrolyte loss and effect of intraluminal glucose in experimental canine cholera. J Clin Invest. 1968 May;47(5):1210–1220. doi: 10.1172/JCI105810. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheney F. E., Burke V., Clark M. L., Senior J. R. Intestinal fatty acid absorption and esterification from luminal micellar solutions containing deoxycholic acid. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1970 Jan;133(1):212–215. doi: 10.3181/00379727-133-34442. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark M. L., Lanz H. C., Senior J. R. Bile salt regulation of fatty acid absorption and esterification in rat everted jejunal sacs in vitro and into thoracic duct lymph in vivo. J Clin Invest. 1969 Sep;48(9):1587–1599. doi: 10.1172/JCI106124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cline W. S., Lorenzsonn V., Benz L., Bass P., Olsen W. A. The effects of sodium ricinoleate on small intestinal function and structure. J Clin Invest. 1976 Aug;58(2):380–390. doi: 10.1172/JCI108482. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen M., Morgan R. G., Hofmann A. F. One-step quantitative extraction of medium-chain and long-chain fatty acids from aqueous samples. J Lipid Res. 1969 Sep;10(5):614–616. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAWSON A. M., ISSELBACHER K. J. Studies on lipid metabolism in the small intestine with observations on the role of bile salts. J Clin Invest. 1960 May;39:730–740. doi: 10.1172/JCI104090. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobbins J. W., Binder H. J. Effect of bile salts and fatty acids on the colonic absorption of oxalate. Gastroenterology. 1976 Jun;70(6):1096–1100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donaldson R. M., Jr Small bowel bacterial overgrowth. Adv Intern Med. 1970;16:191–212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field M. Intestinal secretion. Gastroenterology. 1974 May;66(5):1063–1084. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forth W., Rummel W., Glasner H. Zur resorptionshemmenden Wirkung von Gallensäuren. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmakol Exp Pathol. 1966;254(4):364–380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frizzell R. A., Schultz S. G. Effect of bile salts on transport across brush border of rabbit ileum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Sep 15;211(3):589–592. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(70)90267-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaginella T. S., Chadwick V. S., Debongnie J. C., Lewis J. C., Phillips S. F. Perfusion of rabbit colon with ricinoleic acid: dose-related mucosal injury, fluid secretion, and increased permeability. Gastroenterology. 1977 Jul;73(1):95–101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin J. F. Method for simultaneous direct estimation of glucose and xylose in serum. Clin Chem. 1970 Feb;16(2):85–91. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOFMANN A. F. THE FUNCTION OF BILE SALTS IN FAT ABSORPTION. THE SOLVENT PROPERTIES OF DILUTE MICELLAR SOLUTIONS OF CONJUGATED BILE SALTS. Biochem J. 1963 Oct;89:57–68. doi: 10.1042/bj0890057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hajjar J. J., Khuri R. N., Bikhazi A. B. Effect of bile salts on amino acid transport by rabbit intestine. Am J Physiol. 1975 Aug;229(2):518–523. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1975.229.2.518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman N. E., Simmonds W. J. The intestinal uptake and esterification, in vitro, of fatty acid as a diffusion limited process. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Aug 13;241(2):331–333. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(71)90032-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim Y. S., Spritz N., Blum M., Terz J., Sherlock P. The role of altered bile acid metabolism in the steatorrhea of experimental blind loop. J Clin Invest. 1966 Jun;45(6):956–962. doi: 10.1172/JCI105411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krag E., Phillips S. F. Active and passive bile acid absorption in man. Perfusion studies of the ileum and jejunum. J Clin Invest. 1974 Jun;53(6):1686–1694. doi: 10.1172/JCI107720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krag E., Phillips S. F. Effect of free and conjugated bile acids on net water, electrolyte, and glucose movement in the perfused human ileum. J Lab Clin Med. 1974 Jun;83(6):947–956. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamabadusuriya S. P., Guiraldes E., Harries J. T. Influence of mixtures of taurocholate, fatty acids, and monolein on the toxic effects of deoxycholate in rat jejunum in vivo. Gastroenterology. 1975 Aug;69(2):463–469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore J. D., Zatzman M. L., Overack D. E., Platner W. S. The effects of synthetic surfactants on intestinal permeability to glucose in vitro. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1971 Sep;137(4):1135–1139. doi: 10.3181/00379727-137-35742. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ockner R. K., Manning J. A. Fatty acid-binding protein in small intestine. Identification, isolation, and evidence for its role in cellular fatty acid transport. J Clin Invest. 1974 Aug;54(2):326–338. doi: 10.1172/JCI107768. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips S. F., Summerskill W. H. Occlusion of the jejunum for intestinal perfusion in man. Mayo Clin Proc. 1966 Apr;41(4):224–231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saunders D. R., Sillery J., McDonald G. B. Regional differences in oxalate absorption by rat intestine: evidence for excessive absorption by the colon in steatorrhoea. Gut. 1975 Jul;16(7):543–548. doi: 10.1136/gut.16.7.543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimoda S. S., O'Brien T. K., Saunders D. R. Fat absorption after infusing bile salts into the human small intestine. Gastroenterology. 1974 Jul;67(1):7–18. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sladen G. E., Harries J. T. Studies on the effects of unconjugated dihydroxy bile salts on rat small intestinal function in vivo. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Nov 2;288(2):443–456. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90265-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Small D. M. A classification of biologic lipids based upon their interaction in aqeous systems. J Am Oil Chem Soc. 1968 Mar;45(3):108–119. doi: 10.1007/BF02915334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabaqchali S., Hatzioannou J., Booth C. C. Bile-salt deconjugation and steatorrhoea in patients with the stagnant-loop syndrome. Lancet. 1968 Jul 6;2(7558):12–16. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(68)92888-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. J. Identification of some enteric bacteria which convert oleic acid to hydroxystearic acid in vitro. Gastroenterology. 1972 Mar;62(3):430–435. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westergaard H., Dietschy J. M. The mechanism whereby bile acid micelles increase the rate of fatty acid and cholesterol uptake into the intestinal mucosal cell. J Clin Invest. 1976 Jul;58(1):97–108. doi: 10.1172/JCI108465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wingate D. L., Krag E., Mekhjian H. S., Phillips S. F. Relationships between ion and water movement in the human jejunum, ileum and colon during perfusion with bile acids. Clin Sci Mol Med. 1973 Nov;45(5):593–606. doi: 10.1042/cs0450593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wingate D. L., Phillips S. F., Hofmann A. F. Effect of glycine-conjugated bile acids with and without lecithin on water and glucose absorption in perfused human jejunum. J Clin Invest. 1973 May;52(5):1230–1236. doi: 10.1172/JCI107290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wingate D. L., Sandberg R. J., Phillips S. F. A comparison of stable and 14 C-labelled polyethylene glycol as volume indicators in the human jejunum. Gut. 1972 Oct;13(10):812–815. doi: 10.1136/gut.13.10.812. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu A. L., Clark S. B., Holt P. R. Transmucosal triglyceride transport rates in proximal and distal rat intestine in vivo. J Lipid Res. 1975 Jul;16(4):251–257. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


