Abstract
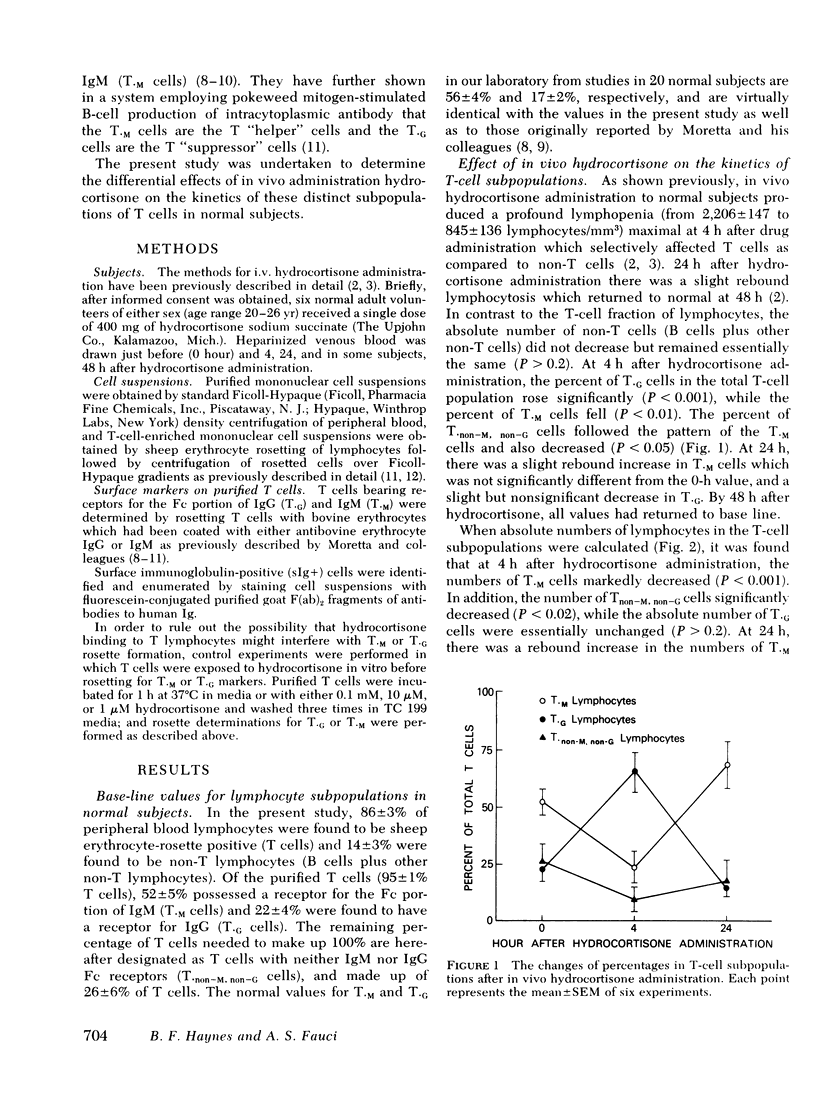
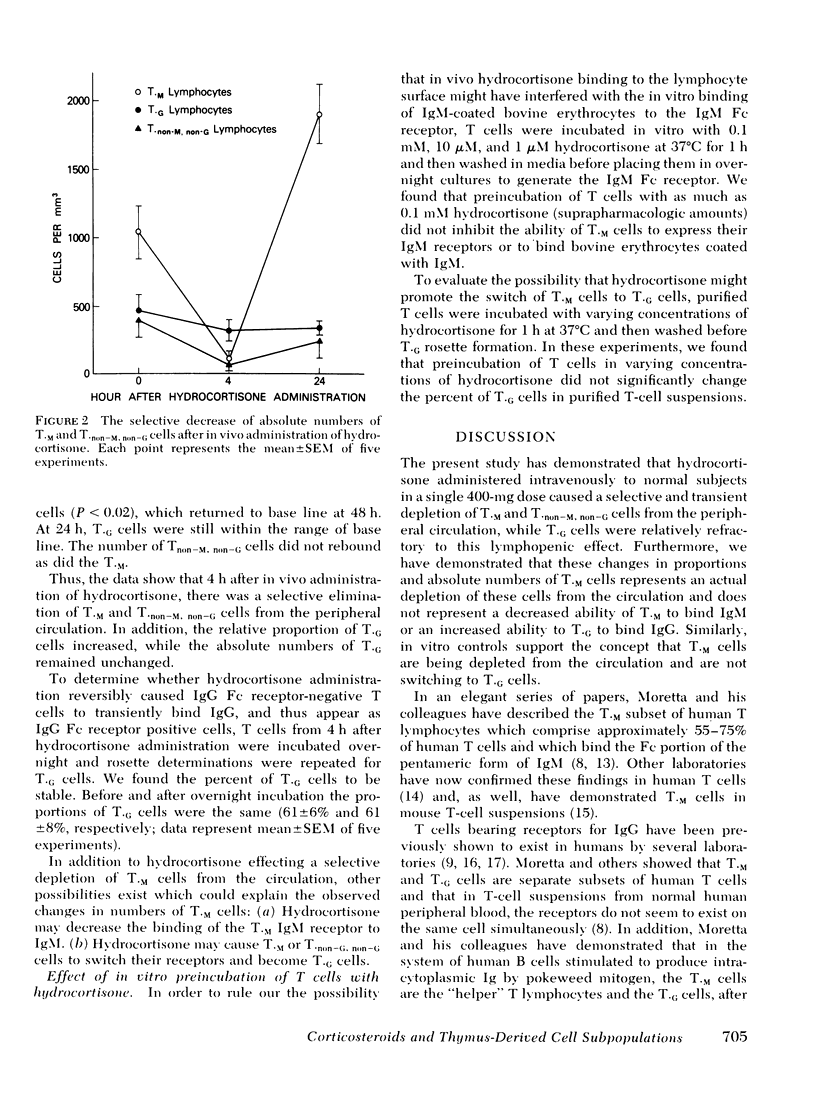
The present study was undertaken to determine the effect of in vivo hydrocortisone on the kinetics of subpopulations of normal human peripheral blood (PB) thymus-derived (T) cells. Normal volunteers received a single i.v. dose of hydrocortisone, and blood was taken just before, as well as 4, 24, and 48 h after hydrocortisone administration. T cells were purified from each specimen, and proportions and absolute numbers of T lymphocytes bearing receptors for the Fc portion of IgG (T·G) and for the Fc portion of IgM (T·M) were enumerated by rosetting T cells with bovine erythrocytes which had been coated with either antibovine erythrocyte IgG or IgM. 4 h after i.v. administration of hydrocortisone, T·M cells decreased from 52 (±5%) to 23 (±6%) of PB T cells (P < 0.01) and the absolute number of T·M cells decreased from 1,028 (±171) per mm3 to 103 (±23) per mm3 (P < 0.001). In contrast, relative proportion of T·G cells increased from 22 (±4%) to 66 (±7%), while the absolute numbers of T·G cells were essentially unchanged (P > 0.2). In vitro studies involving preincubation of T cells with hydrocortisone before rosette determination of T·G or T·M cells demonstrated that the decrease in absolute numbers of T·M cells did not represent hydrocortisone interference with T·M rosette formation, nor did it represent a switch of T·M cells to T·G cells. Thus, administration of hydrocortisone to normal subjects produces a selective depletion from the circulation of T lymphocytes which possess receptors for the Fc portion of IgM (T·M cells) and of T cells which possess no detectable FC receptor (T·non−M, non−G cells). T·G cells are relatively resistant to the lymphopenic effect of hydrocortisone. These data clearly demonstrate that in vivo corticosteroids have a differential effect on the kinetics of identifiable and distinct subsets of cells in the human T-cell class.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abdou N. I., Sagawa A., Pascual E., Hebert J., Sadeghee S. Suppressor T-cell abnormality in idiopathic systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1976 Sep;6(2):192–199. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(76)90110-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown G., Greaves M. F. Cell surface markers for human T and B lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1974 Apr;4(4):302–310. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830040414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickler H. B., Adkinson N. F., Jr, Terry W. D. Evidence for individual human peripheral blood lymphocytes bearing both B and T cell markers. Nature. 1974 Jan 25;247(5438):213–215. doi: 10.1038/247213a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fauci A. S., Dale D. C. Alternate-day prednisone therapy and human lymphocyte subpopulations. J Clin Invest. 1975 Jan;55(1):22–32. doi: 10.1172/JCI107914. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fauci A. S., Dale D. C. The effect of Hydrocortisone on the kinetics of normal human lymphocytes. Blood. 1975 Aug;46(2):235–243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fauci A. S., Dale D. C. The effect of in vivo hydrocortisone on subpopulations of human lymphocytes. J Clin Invest. 1974 Jan;53(1):240–246. doi: 10.1172/JCI107544. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fauci A. S. Mechanisms of corticosteroid action on lymphocyte subpopulations. I. Redistribution of circulating T and b lymphocytes to the bone marrow. Immunology. 1975 Apr;28(4):669–680. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fauci A. S. Mechanisms of corticosteroid action on lymphocyte subpopulations. II. Differential effects of in vivo hydrocortisone, prednisone and dexamethasone on in vitro expression of lymphocyte function. Clin Exp Immunol. 1976 Apr;24(1):54–62. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fauci A. S., Pratt K. R., Whalen G. Activation of human B lymphocytes. II. Cellular interactions in the PFC response of human tonsillar and peripheral blood B lymphocytes to polyclonal activation by pokeweed mitogen. J Immunol. 1976 Dec;117(6):2100–2104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrarini M., Moretta L., Abrile R., Durante M. L. Receptors for IgG molecules on human lymphocytes forming spontaneous rosettes with sheep red cells. Eur J Immunol. 1975 Jan;5(1):70–72. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830050115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrarini M., Moretta L., Mingari M. C., Tonda P., Pernis B. Human T cell receptor for IgM: specificity for the pentameric Fc fragment. Eur J Immunol. 1976 Jul;6(7):520–521. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830060714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gmelig-Meyling F., Van der Ham M., Ballieux R. E. Binding of IgM by human T lymphocytes. Scand J Immunol. 1976;5(5):487–495. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1976.tb00303.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horowitz S., Borcherding W., Moorthy A. V., Chesney R., Schulte-Wisserman H., Hong R. Induction of suppressor T cells in systemic lupus erythematosus by thymosin and cultured thymic epithelium. Science. 1977 Sep 2;197(4307):999–1001. doi: 10.1126/science.302032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jandinski J., Cantor H., Tadakuma T., Peavy D. L., Pierce C. W. Separation of helper T cells from suppressor T cells expressing different Ly components. I. Polyclonal activation: suppressor and helper activities are inherent properties of distinct T-cell subclasses. J Exp Med. 1976 Jun 1;143(6):1382–1390. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.6.1382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamon E. W., Andersson B., Whitten H. D., Hurst M. M., Ghanta V. IgM complex receptors on subpopulations of murine lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1976 May;116(5):1199–1203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moretta L., Ferrarini M., Durante M. L., Mingari M. C. Expression of a receptor for IgM by human T cells in vitro. Eur J Immunol. 1975 Aug;5(8):565–569. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830050812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moretta L., Ferrarini M., Mingari M. C., Moretta A., Webb S. R. Subpopulations of human T cells identified by receptors for immunoglobulins and mitogen responsiveness. J Immunol. 1976 Dec;117(6):2171–2174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moretta L., Webb S. R., Grossi C. E., Lydyard P. M., Cooper M. D. Functional analysis of two human T-cell subpopulations: help and suppression of B-cell responses by T cells bearing receptors for IgM or IgG. J Exp Med. 1977 Jul 1;146(1):184–200. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.1.184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu D. T., Clements P. J., Paulus H. E., Peter J. B., Levy J., Barnett E. V. Human lymphocyte subpopulations. Effect of corticosteroids. J Clin Invest. 1974 Feb;53(2):565–571. doi: 10.1172/JCI107591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


