Abstract
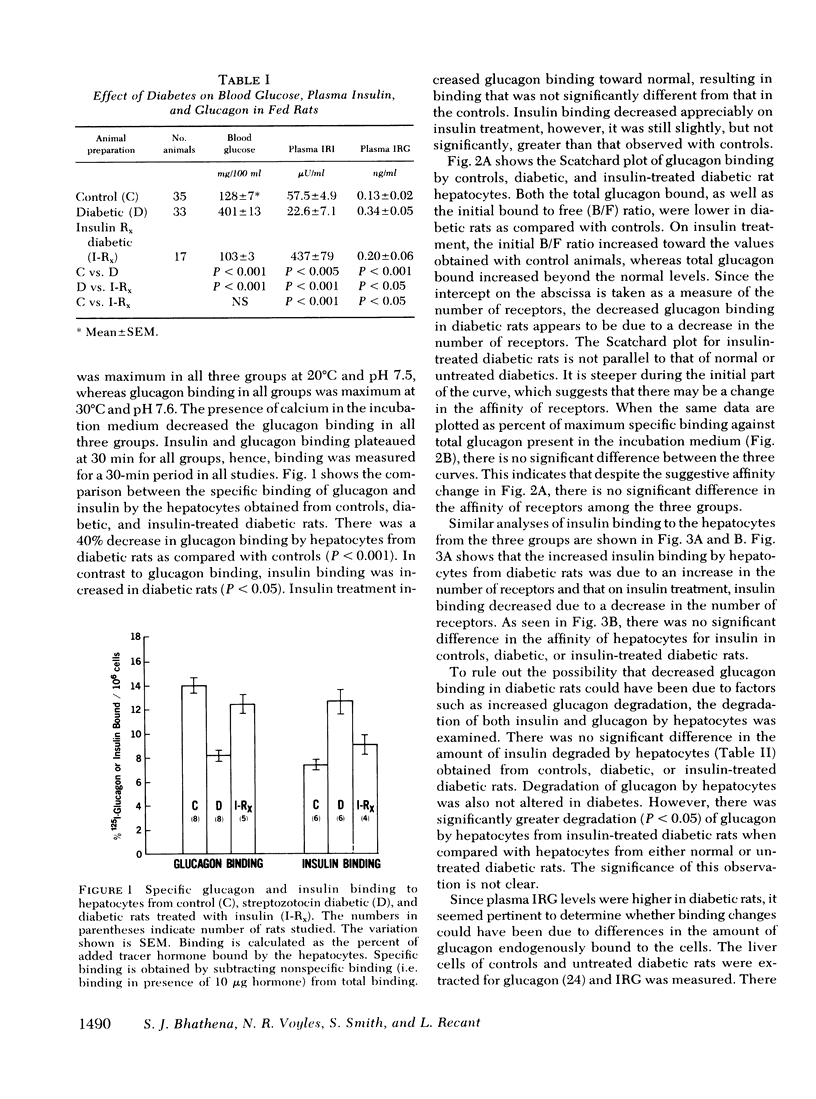
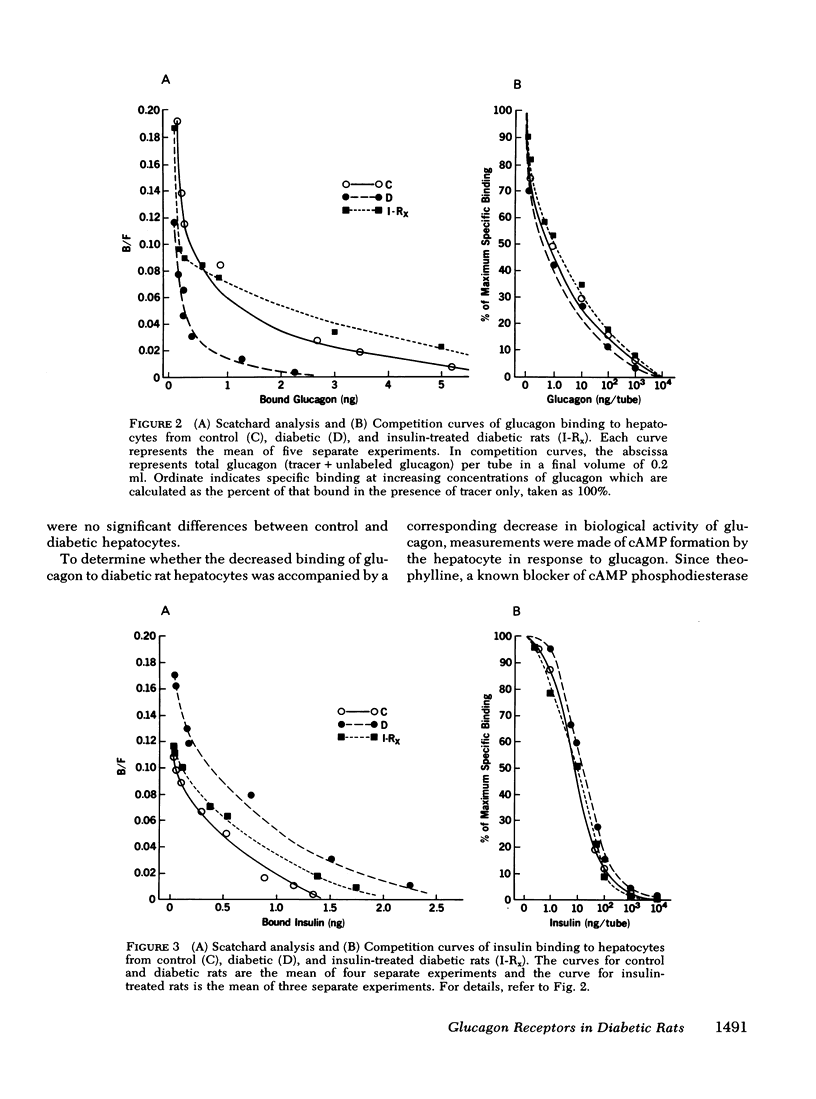
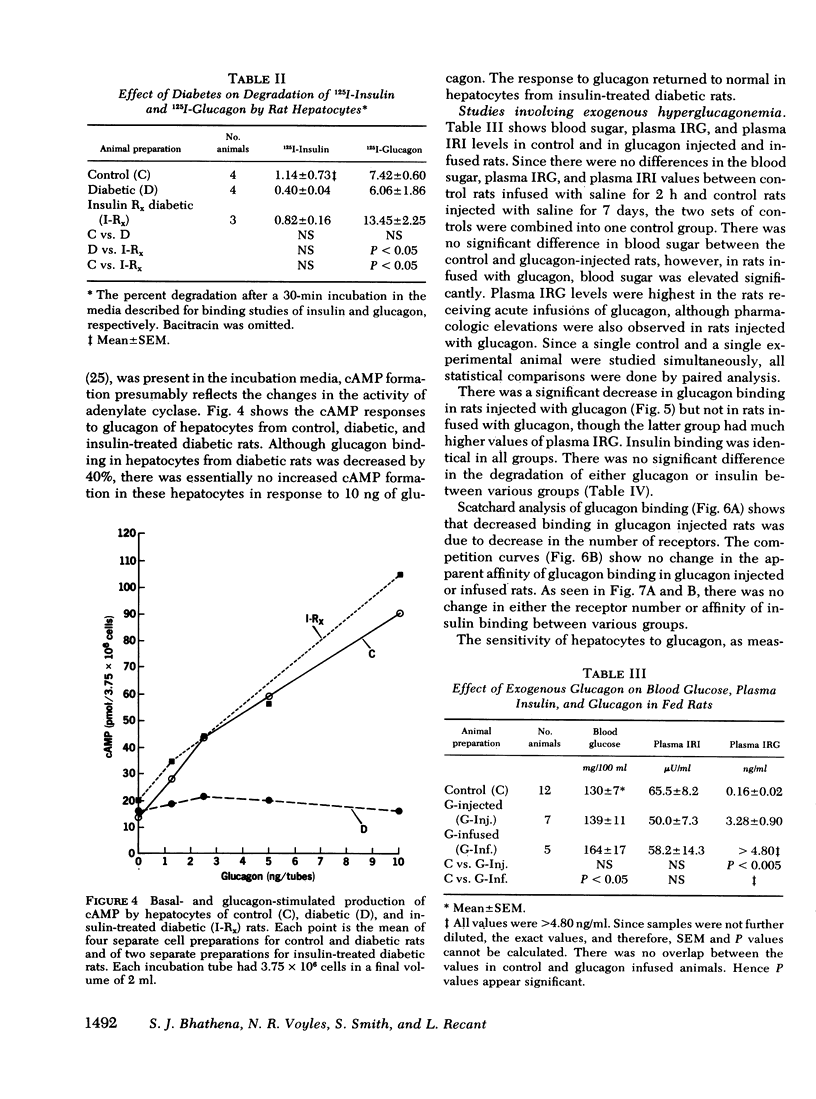
The effects of endogenous and exogenous hyperglucagonemia on the specific binding of glucagon to hepatocyte receptors was studied, as was the response of cAMP to glucagon. In streptozotocin diabetic rats, blood glucose and plasma glucagon increased and plasma insulin decreased as compared with controls. Insulin treatment in diabetic rats restored blood glucose and plasma glucagon toward normal and elevated plasma insulin. Specific binding of 125I-glucagon to isolated hepatocytes (106 cells) decreased in diabetic rats (8.17±0.38%) compared to controls (14.05±0.87%) and was restored by insulin treatment (12.25±0.93%). Specific binding of 125I-insulin in controls was 7.30±10.16%; it increased in diabetic rats to 12.50±0.86%, and decreased in diabetic rats after insulin treatment (9.08±0.87%). Scatchard analysis and the competition plots of the data indicate that decreased glucagon binding and increased insulin binding in diabetes were due to change in the number of receptors rather than a change in their affinity. Hepatocyte cAMP response to glucagon (0.25-5.0 ng/ml) was almost abolished in diabetic rats and was restored with insulin treatment.
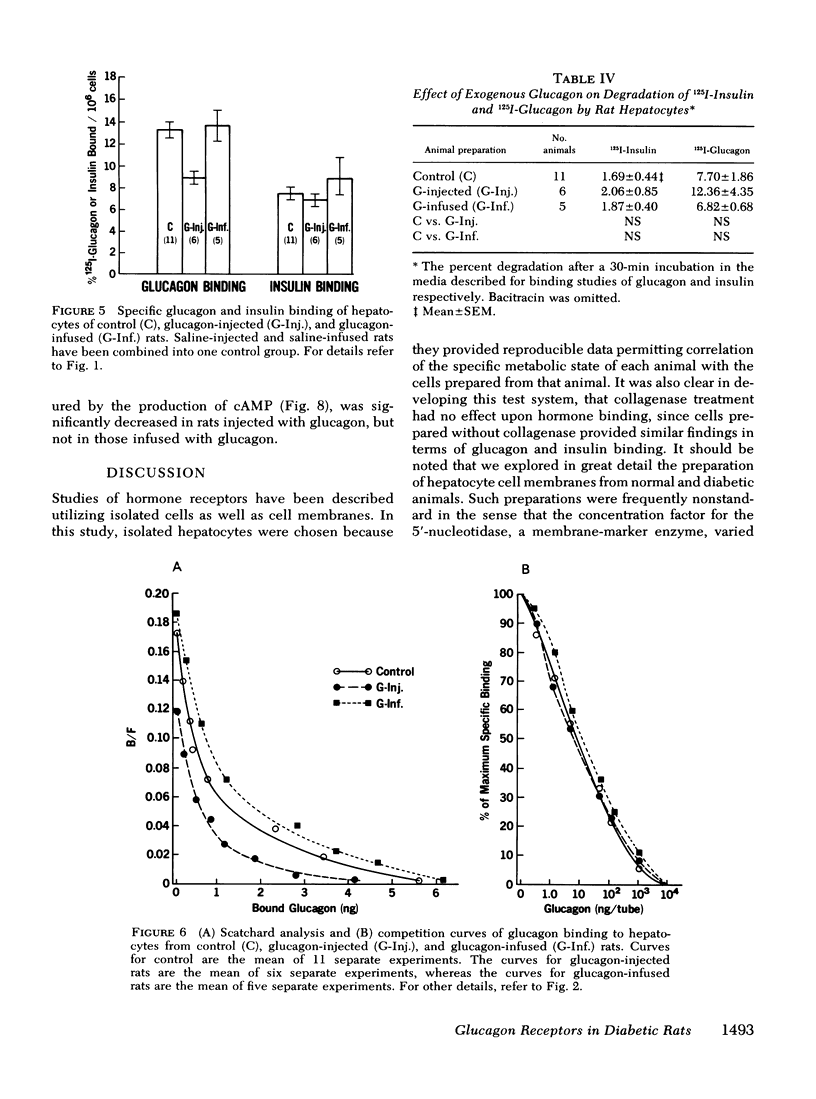
Specific glucagon binding by hepatocytes from chronically hyperglucagonemic (glucagon injected) rats was decreased (P < 0.005) to 8.76±0.61% compared with controls (13.20±0.74%) and acutely hyperglucagonemic animals (13.53±1.33%). The decreased binding was associated with a 70% decrease in hepatocyte cAMP response to glucagon compared with a normal response in acutely hyperglucagonemic rats.
These data appear to support the concept of receptor regulation by ambient hormone level. In both endogenous and exogenous hyperglucagonemia, however, there was a disproportionately large decrease in cAMP response to glucagon compared to the decrease in glucagon binding.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BUTCHER R. W., SUTHERLAND E. W. Adenosine 3',5'-phosphate in biological materials. I. Purification and properties of cyclic 3',5'-nucleotide phosphodiesterase and use of this enzyme to characterize adenosine 3',5'-phosphate in human urine. J Biol Chem. 1962 Apr;237:1244–1250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhathena S. J., Smith S. S., Voyles N. R., Penhos J. C., Recant L. Studies on submaxillary gland immunoreactive glucagon. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Feb 21;74(4):1574–1581. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)90622-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braaten J. T., Faloona G. R., Unger R. H. The effect of insulin on the alpha-cell response to hyperglycemia in long-standing alloxan diabetes. J Clin Invest. 1974 Apr;53(4):1017–1021. doi: 10.1172/JCI107638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crane L. J., Miller D. L. Synthesis and secretion of fibrinogen and albumin by isolated rat hepatocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Oct 23;60(4):1269–1277. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90335-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P., Desbuquois B., Krug F. Insulin-receptor interactions in liver cell membranes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Jul 16;44(2):333–339. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90604-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P. Properties of the insulin receptor of isolated fat cell membranes. J Biol Chem. 1971 Dec 10;246(23):7265–7274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVOREN P. R. The isolation of insulin from a single cat pancreas. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Sep 10;63:150–153. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90347-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson M. B., Kaplan S. A. Increased insulin binding by hepatic plasma membranes from diabetic rats: normalization by insulin therapy. J Clin Invest. 1977 Jan;59(1):22–30. doi: 10.1172/JCI108618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeMeyts P., Bainco A. R., Roth J. Site-site interactions among insulin receptors. Characterization of the negative cooperativity. J Biol Chem. 1976 Apr 10;251(7):1877–1888. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Exton J. H., Robison G. A., Sutherland E. W., Park C. R. Studies on the role of adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate in the hepatic actions of glucagon and catecholamines. J Biol Chem. 1971 Oct 25;246(20):6166–6177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flier J. S., Kahn C. R., Roth J., Bar R. S. Antibodies that impair insulin receptor binding in an unusual diabetic syndrome with severe insulin resistance. Science. 1975 Oct 3;190(4209):63–65. doi: 10.1126/science.170678. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fouchereau-Peron M., Rançon F., Freychet P., Rosselin G. Effect of feeding and fasting on the early steps of glucagon action in isolated rat liver cells. Endocrinology. 1976 Mar;98(3):755–760. doi: 10.1210/endo-98-3-755. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freychet P. Interactions polypeptide hormones with cell membrane specific receptors: studies with insulin and glucagon. Diabetologia. 1976 May;12(2):83–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00428972. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freychet P., Roth J., Neville D. M., Jr Monoiodoinsulin: demonstration of its biological activity and binding to fat cells and liver membranes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Apr 16;43(2):400–408. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90767-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrison J. C., Haynes R. C., Jr Hormonal control of glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis in isolated rat liver cells. J Biol Chem. 1973 Aug 10;248(15):5333–5343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gavin J. R., 3rd, Roth J., Neville D. M., Jr, de Meyts P., Buell D. N. Insulin-dependent regulation of insulin receptor concentrations: a direct demonstration in cell culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jan;71(1):84–88. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.1.84. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsberg B. H., Kahn C. R., Roth J., De Meyts P. Insulin-induced dissociation of its receptor into subunits: possible molecular concomitant of negative cooperativity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Dec 20;73(4):1068–1074. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90232-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giorgio N. A., Johnson C. B., Blecher M. Hormone receptors. 3. Properties of glucagon-binding proteins isolated from liver plasma membranes. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jan 25;249(2):428–437. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg N. D., Dietz S. B., O'Toole A. G. Cyclic guanosine 3',5'-monophosphate in mammalian tissues and urine. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4458–4466. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein S., Blecher M., Binder R., Perrino P. V., Recant L. Hormone receptors, 5. Binding of glucagon and insulin to human circulating mononuclear cells in diabetes mellitus. Endocr Res Commun. 1975;2(4-5):367–376. doi: 10.1080/07435807509089009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNTER W. M., GREENWOOD F. C. Preparation of iodine-131 labelled human growth hormone of high specific activity. Nature. 1962 May 5;194:495–496. doi: 10.1038/194495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hepp K. D., Langley J., Funcke HJ Von, Renner R., Kemmler W. Increased insulin binding capacity of liver membranes from diabetic Chinese hamsters. Nature. 1975 Nov 13;258(5531):154–154. doi: 10.1038/258154a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jefferson L. S., Exton J. H., Butcher R. W., Sutherland E. W., Park C. R. Role of adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate in the effects of insulin and anti-insulin serum on liver metabolism. J Biol Chem. 1968 Mar 10;243(5):1031–1038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn C. R., Freychet P., Roth J., Neville D. M., Jr Quantitative aspects of the insulin-receptor interaction in liver plasma membranes. J Biol Chem. 1974 Apr 10;249(7):2249–2257. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn C. R., Neville D. M., Jr, Roth J. Insulin-receptor interaction in the obese-hyperglycemic mouse. A model of insulin resistance. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jan 10;248(1):244–250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuku S. F., Zeidler A., Emmanouel D. S., Katz A. I., Rubenstein A. H. Heterogeneity of plasma glucagon: patterns in patients with chronic renal failure and diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1976 Jan;42(1):173–176. doi: 10.1210/jcem-42-1-173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller W. A., Faloona G. R., Unger R. H. Hyperglucagonemia in diabetic ketoacidosis. Its prevalence and significance. Am J Med. 1973 Jan;54(1):52–57. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(73)90083-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olefsky J. M. Decreased insulin binding to adipocytes and circulating monocytes from obese subjects. J Clin Invest. 1976 May;57(5):1165–1172. doi: 10.1172/JCI108384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olefsky J. M., Reaven G. M. Decreased insulin binding to lymphocytes from diabetic subjects. J Clin Invest. 1974 Dec;54(6):1323–1328. doi: 10.1172/JCI107878. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker M. L., Pildes R. S., Chao K. L., Cornblath M., Kipnis D. M. Juvenile diabetes mellitus, a deficiency in insulin. Diabetes. 1968 Jan;17(1):27–32. doi: 10.2337/diab.17.1.27. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perley M., Kipnis D. M. Plasma insulin responses to glucose and tolbutamide of normal weight and obese diabetic and nondiabetic subjects. Diabetes. 1966 Dec;15(12):867–874. doi: 10.2337/diab.15.12.867. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilkis S. J., Exton J. H., Johnson R. A., Park C. R. Effects of glucagon on cyclic AMP and carbohydrate metabolism in livers from diabetic rats. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Mar 20;343(1):250–267. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(74)90258-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pohl S. L. The glucagon receptor and its relationship to adenylate cyclase. Fed Proc. 1977 Jul;36(8):2115–2118. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raskin P., Aydin I., Unger R. H. Effect of insulin on the exaggerated glucagon response to arginine stimulation in diabetes mellitus. Diabetes. 1976 Mar;25(3):227–229. doi: 10.2337/diab.25.3.227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Recant L., Perrino P. V., Bhathena S. J., Danforth D. N., Jr, Lavine R. L. Plasma immunoreactive glucagon fractions in four cases of glucagonoma: increased "large glucagon-immunoreactivity". Diabetologia. 1976 Aug;12(4):319–326. doi: 10.1007/BF00420975. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selawry H., Gutman R., Fink G., Recant L. The effect of starvation on tissue adenosine 3'-5' monophosphate levels. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Mar 5;51(1):198–204. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90528-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorrentino R. N., Florini J. R. Variations among individual mice in binding of growth hormone and insulin to membranes from animals of different ages. Exp Aging Res. 1976 May;2(3):191–205. doi: 10.1080/03610737608257176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- UNGER R. H., EISENTRAUT A. M., McCALL M. S., KELLER S., LANZ H. C., MADISON L. L. Glucagon antibodies and their use for immunoassay for glucagon. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1959 Oct-Dec;102:621–623. doi: 10.3181/00379727-102-25338. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unger R. H., Aguilar-Parada E., Müller W. A., Eisentraut A. M. Studies of pancreatic alpha cell function in normal and diabetic subjects. J Clin Invest. 1970 Apr;49(4):837–848. doi: 10.1172/JCI106297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unger R. H., Orci L. Physiology and pathophysiology of glucagon. Physiol Rev. 1976 Oct;56(4):778–826. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1976.56.4.778. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valverde I., Villanueva M. L. Heterogeneity of plasma immunoreactive glucagon. Metabolism. 1976 Nov;25(11 Suppl 1):1393–1395. doi: 10.1016/s0026-0495(76)80149-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zahlten R. N., Stratman F. W. The isolation of hormone-sensitive rat hepatocytes by a modified enzymatic technique. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1974 Aug;163(2):600–608. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(74)90519-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Meyts P., Roth J., Neville D. M., Jr, Gavin J. R., 3rd, Lesniak M. A. Insulin interactions with its receptors: experimental evidence for negative cooperativity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Nov 1;55(1):154–161. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(73)80072-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


