Abstract
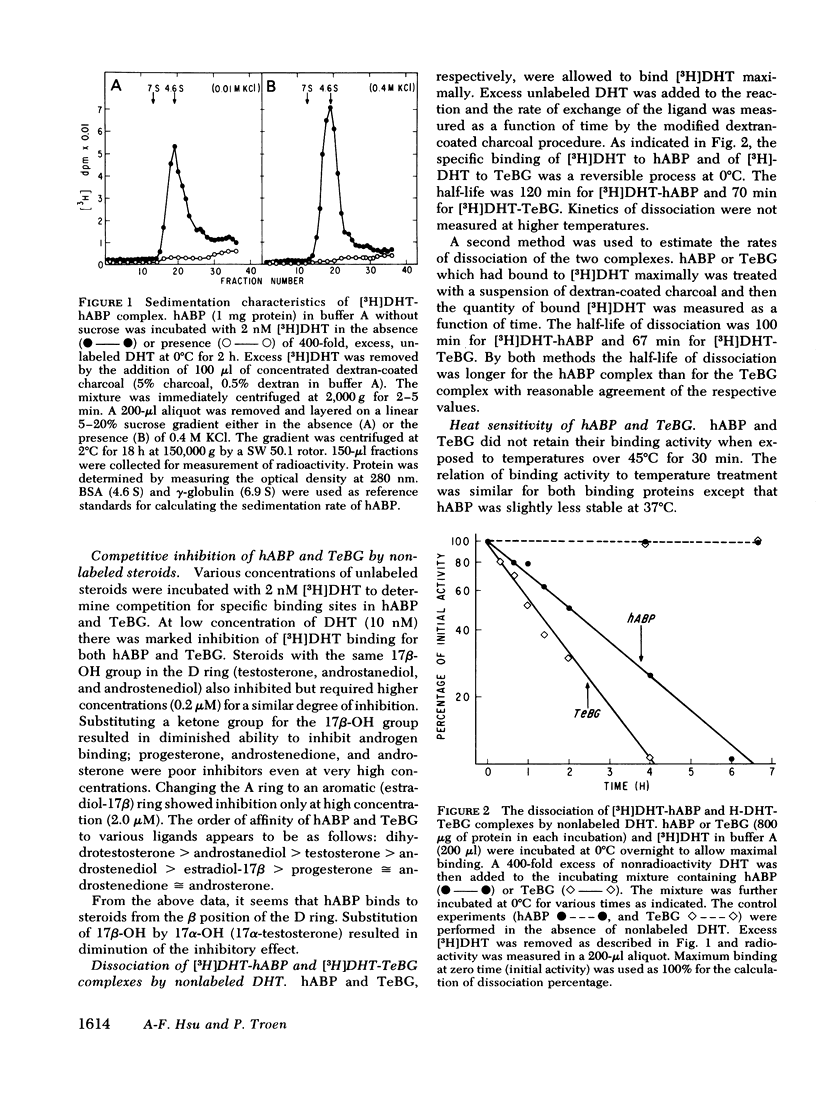
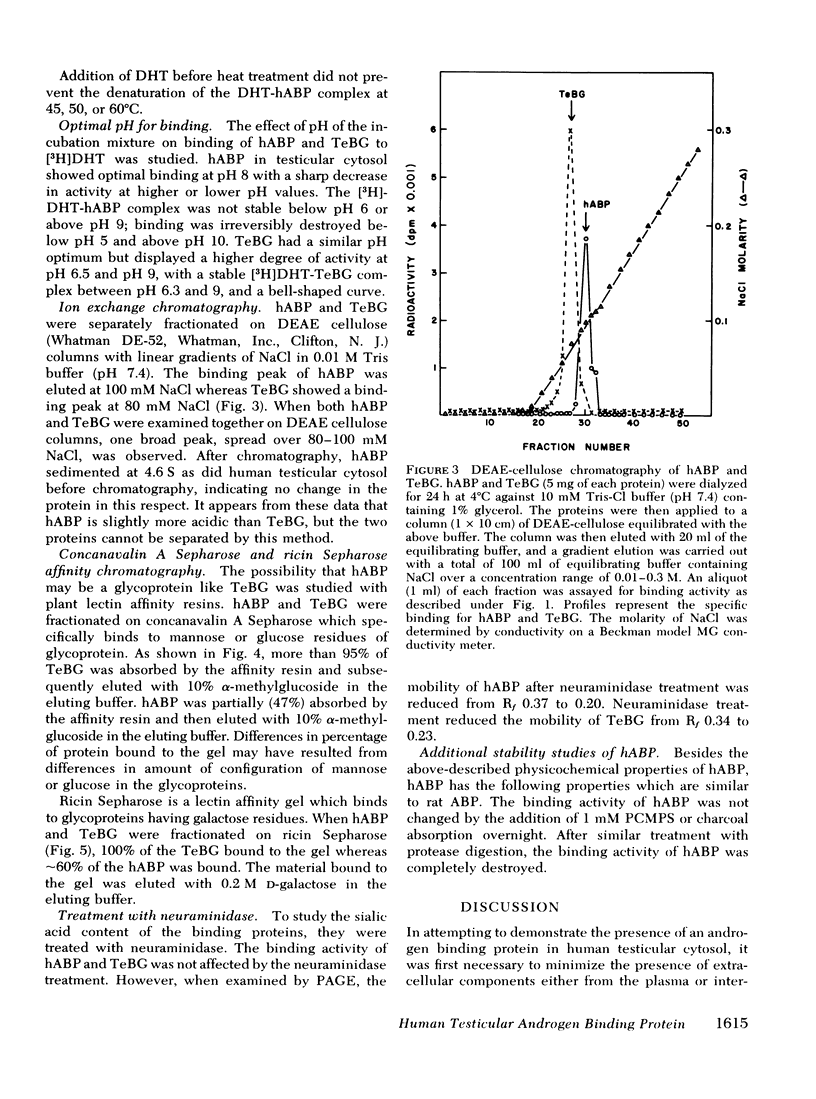
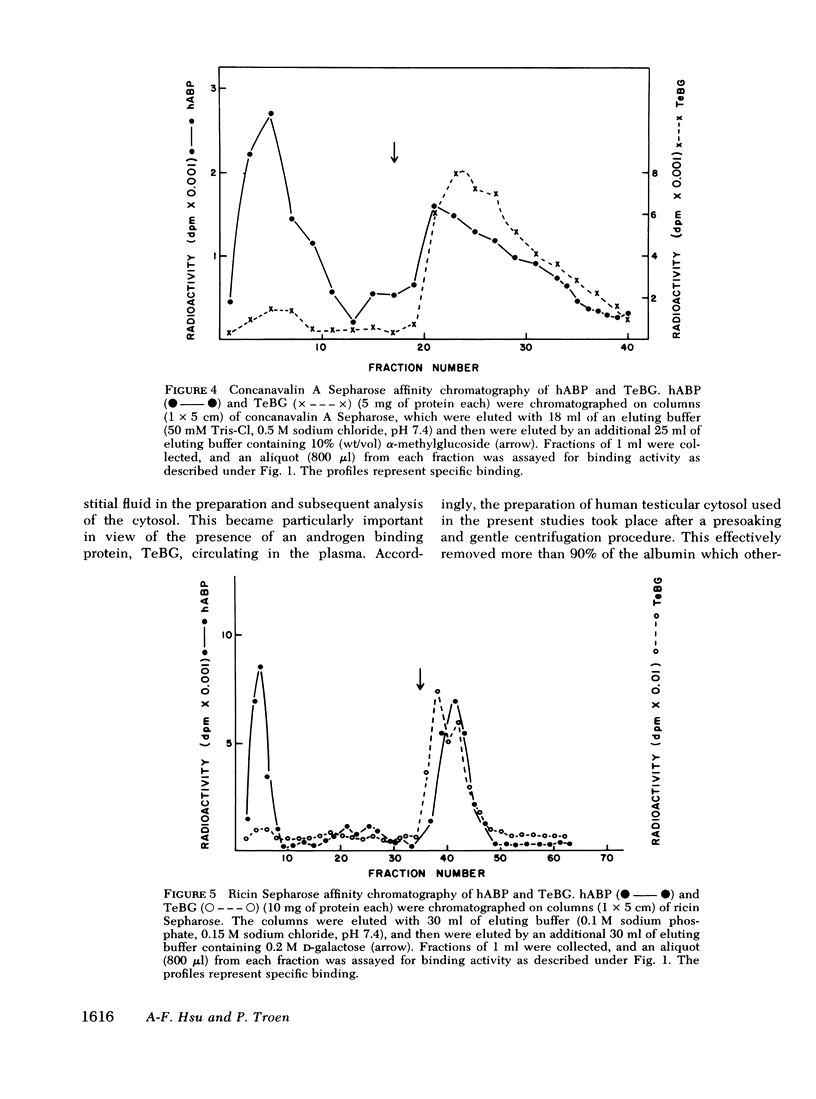
After removal of plasma contamination, an androgen binding protein (hABP) was detected in a 105,000-g supernate of human testicular homogenate. The physicochemical properties of hABP have been compared with a similar androgen binding protein in human plasma, testosterone-estrogen binding globulin (TeBG). hABP had high affinity (Kd = 7.8 nM) and low capacity (0.27 pmol/mg protein) for 5α-dihydrotestosterone (DHT). Binding affinity of human TeBG for DHT was greater (Kd = 0.66 nM, binding capacity 0.68 pmol/mg protein). On the basis of sedimentation rates and Einstein Stokes radii of hABP and TeBG, the mol wt of the two proteins were similar in the range of 87,000-92,000. The ligand specificities of hABP and TeBG were the same. The binding of [3H]DHT to hABP and TeBG were reversible processes at 0°C. The half-lives for the dissociation of [3H]DHT from hABP and TeBG were 100-120 min and 67-70 min, respectively. Heat sensitivity of hABP and TeBG were similar. hABP had a sharp pH binding curve with an optimum at 8, whereas TeBG had a stable pH optimum between 6.5 and 9. hABP and TeBG were eluted from an ion exchange column at 100 mM and 80 mM sodium chloride concentrations, respectively. Concanavalin A and ricin Sepharose affinity chromatography showed that TeBG is bound to the columns nearly quantitatively, whereas hABP is bound to the columns only partially.
Differences between hABP and TeBG, plus the reduction of plasma contamination as marked by albumin, suggest that the human mature testis contains an androgen binding protein separate from that circulating in plasma.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- French F. S., McLean W. S., Smith A. A., Tindall D. J., Weddington S. C., Petrusz P., Nayfeh S. N., Ritzén E. M., Hansson V., Trystad O. Androgen transport and receptor mechanisms in testis and epididymis. Nature. 1974 Aug 2;250(465):387–391. doi: 10.1038/250387a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- French F. S., Ritzén E. M. A high-affinity androgen-binding protein (ABP) in rat testis: evidence for secretion into efferent duct fluid and absorption by epididymis. Endocrinology. 1973 Jul;93(1):88–95. doi: 10.1210/endo-93-1-88. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansson V., Djoseland O., Reusch E., Attramadal A., Torgersen O. An androgen binding protein in the testis cytosol fraction of adult rats. Comparison with the androgen binding protein in the epididymis. Steroids. 1973 Mar;21(3):457–474. doi: 10.1016/0039-128x(73)90037-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansson V., Djoseland O., Reusch E., Attramadal A., Torgersen O. Intracellular receptors for 5alpha-dihydrostestosterone in the epididymis of adult rats. Comparison with the androgenic receptors in the ventral prostate and the androgen binding protein (ABP) in the testicular and epididymal fluid. Steroids. 1973 Jul;22(1):19–33. doi: 10.1016/0039-128x(73)90068-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansson V., McLean W. S., Smith A. A., Tindall D. J., Weddington S. C., Nayfeh S. N., French F. S., Ritzen E. M. Androgen receptors in rat testis. Steroids. 1974 Jun;23(6):823–832. doi: 10.1016/0039-128x(74)90056-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopkinson D. A. Isozymes. J Clin Pathol Suppl (R Coll Pathol) 1974;8:122–127. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTIN R. G., AMES B. N. A method for determining the sedimentation behavior of enzymes: application to protein mixtures. J Biol Chem. 1961 May;236:1372–1379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy B. E. Some studies of the protein-binding of steroids and their application to the routine micro and ultramicro measurement of various steroids in body fluids by competitive protein-binding radioassay. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1967 Jul;27(7):973–990. doi: 10.1210/jcem-27-7-973. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearlman W. H., Crépy O. Steroid-protein interaction with particular reference to testosterone binding by human serum. J Biol Chem. 1967 Jan 25;242(2):182–189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritzén E. M., Dobbins M. C., Tindall D. J., French F. S., Nayfeh S. N. Characterization of an androgen binding protein (ABP) in rat testis and epididymis. Steroids. 1973 Apr;21(4):593–608. doi: 10.1016/0039-128x(73)90047-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritzén E. M., French F. S., Weddington S. C., Nayfeh S. N., Hansson V. Steroid binding in polyacrylamide gels. Quantitation at steady state conditions. J Biol Chem. 1974 Oct 25;249(20):6597–6604. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tindall D. J., Means A. R. Concerning the hormonal regulation of androgen binding protein in rat testis. Endocrinology. 1976 Sep;99(3):809–818. doi: 10.1210/endo-99-3-809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vigersky R. A., Loriaux D. L., Howards S. S., Hodgen G. B., Lipsett M. B., Chrambach A. Androgen binding proteins of testis, epididymis, and plasma in man and monkey. J Clin Invest. 1976 Nov;58(5):1061–1068. doi: 10.1172/JCI108557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner R. K., Jungblut P. W. Differentiation between steroid hormone receptors CBG and SHBG in human target organ extracts by a single-step assay. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1975 Dec;4(1):13–24. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(76)90003-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weddington S. C., Hansson V., Ritzen E. M., Hagenas L., French F. S., Nayfeh S. N. Sertoli cell secretory function after hypophysectomy. Nature. 1975 Mar 13;254(5496):145–146. doi: 10.1038/254145a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weddington S. C., McLean W. S., Nayfeh S. N., French F. S. Androgen binding protein (ABP) in rabbit testis and epididymis. Steroids. 1974 Jul;24(1):123–134. doi: 10.1016/0039-128x(74)90050-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


