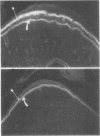
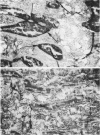
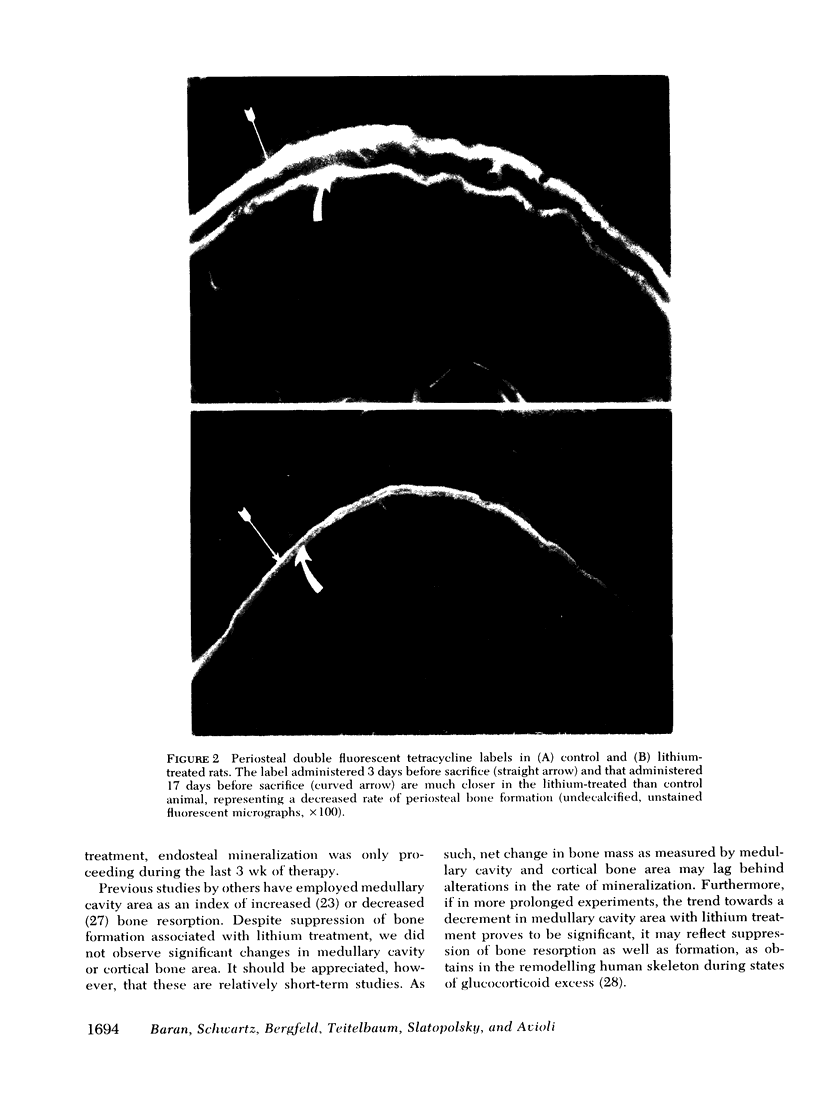
Abstract
Lithium chloride administration to growing rats, which resulted in circulating lithium levels of 1.4 meq/liter, was attended by significant suppression of bone mineralization and organic matrix synthesis as assessed by tetracycline labeling and histological quantitation of osteoid, respectively. These effects of lithium were not associated with changes in animal behavior, nor were there any significant differences in blood levels of calcium, phosphorus, alkaline phosphatase, creatinine, pH, or parathyroid hormone. The data suggest that lithium inhibition of bone mineralization is secondary to suppression of osteoid formation.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andreoli V. M., Villani F., Brambilla G. Increased calcium and magnesium excretion induced by lithium carbonate. Psychopharmacologia. 1972;25(1):77–85. doi: 10.1007/BF00422619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baylink D., Morey E., Rich C. Effect of calcitonin on the rates of bone formation and resorption in the rat. Endocrinology. 1969 Feb;84(2):261–269. doi: 10.1210/endo-84-2-261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baylink D., Stauffer M., Wergedal J., Rich C. Formation, mineralization, and resorption of bone in vitamin D-deficient rats. J Clin Invest. 1970 Jun;49(6):1122–1134. doi: 10.1172/JCI106328. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellwinkel S., Schäfer A., Minne H., Ziegler R. The effect of chronic lithium application on the mineral content of rat bone and soft tissues. Int Pharmacopsychiatry. 1975;10(1):9–16. doi: 10.1159/000468163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowers G. N., Jr, McComb R. B. A continuous spectrophotometric method for measuring the activity of serum alkaline phosphatase. Clin Chem. 1966 Feb;12(2):70–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chanard J., Black R., Purkerson M., Lewis J., Klahr S., Slatopolsky E. The effects of colchicine and vinblastine on parathyroid hormone secretion in the rat. Endocrinology. 1977 Dec;101(6):1792–1800. doi: 10.1210/endo-101-6-1792. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammond R. H., Storey E. Measurement of growth and resorption of bone in rats fed meat diet. Calcif Tissue Res. 1970;4(4):291–304. doi: 10.1007/BF02279132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammond R. H., Storey E. Measurement of growth and resorption of bone in the seventh caudal vertebra of the rat. Calcif Tissue Res. 1974 Jun 11;15(1):11–20. doi: 10.1007/BF02059039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henneman D., Zimmerberg J. J. Lack of effect of chronic lithium chloride on bone composition and metabolism. Endocrinology. 1974 Mar;94(3):915–917. doi: 10.1210/endo-94-3-915. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KLEIN M., VILLANUEVA A. R., FROST H. M. A QUANTITATIVE HISTOLOGICAL STUDY OF RIB FROM 18 PATIENTS TREATED WITH ADRENAL CORTICAL STEROIDS. Acta Orthop Scand. 1965;35:171–184. doi: 10.3109/17453676508989351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraml M. A semi-automated determination of phospholipids. Clin Chim Acta. 1966 Apr;13(4):442–448. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(66)90235-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merz W. A., Schenk R. K. Quantitative structural analysis of human cancellous bone. Acta Anat (Basel) 1970;75(1):54–66. doi: 10.1159/000143440. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohabbat O., Younos M. S., Merzad A. A., Srivastava R. N., Sediq G. G., Aram G. N. An outbreak of hepatic veno-occlusive disease in north-western Afghanistan. Lancet. 1976 Aug 7;2(7980):269–271. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)90726-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olesen O. V., Thomsen K. Effect of prolonged lithium ingestion on glucagon and parathyroid hormone responses in rats. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol (Copenh) 1974 Apr;34(4):225–231. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0773.1974.tb03517.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perez G. O., Oster J. R., Vaamonde C. A. Incomplete syndrome of renal tubular acidosis induced by lithium carbonate. J Lab Clin Med. 1975 Sep;86(3):386–394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pybus J., Feldman F. J., Bowers G. N., Jr Measurement of total calcium in serum by atomic absorption spectrophotometry, with use of a strontium internal reference. Clin Chem. 1970 Dec;16(12):998–1007. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schou M. Lithium in psychiatric therapy and prophylaxis. J Psychiatr Res. 1968 Jun;6(1):67–95. doi: 10.1016/0022-3956(68)90047-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiegel A. M., Gerner R. H., Murphy D. L., Aurbach G. D. Lithium does not inhibit the parathyroid hormone-mediated rise in urinary cyclic AMP and phosphate in humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1976 Dec;43(6):1390–1393. doi: 10.1210/jcem-43-6-1390. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stauffer M., Baylink D., Wergedal J., Rich C. Bone repletion in calcium deficient rats fed a high calcium diet. Calcif Tissue Res. 1972;9(2):163–172. doi: 10.1007/BF02061954. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steele T. H. Selective lithium inhibition of hormonal phosphaturic responses. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1976 Apr;197(1):206–214. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenström A., Hansson L. I., Thorngren K. G. Cortical bone remodeling in normal rat. Calcif Tissue Res. 1977 Jun 28;23(2):161–170. doi: 10.1007/BF02012782. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]