Abstract
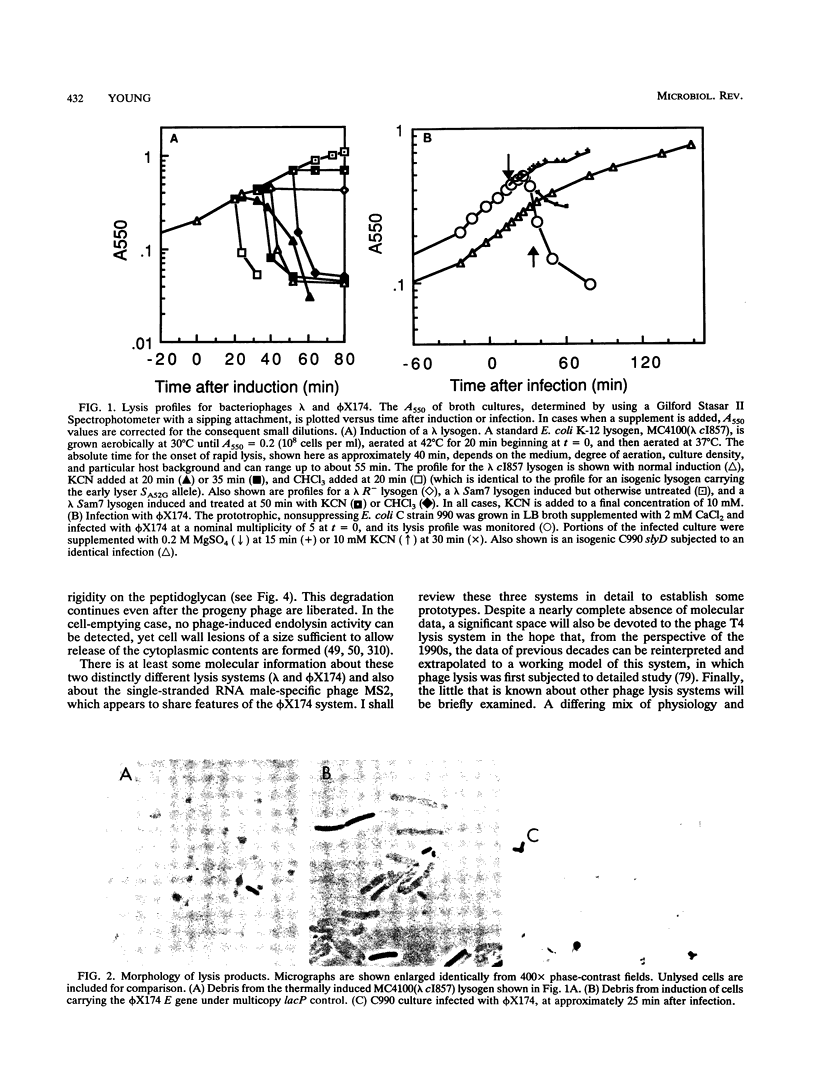
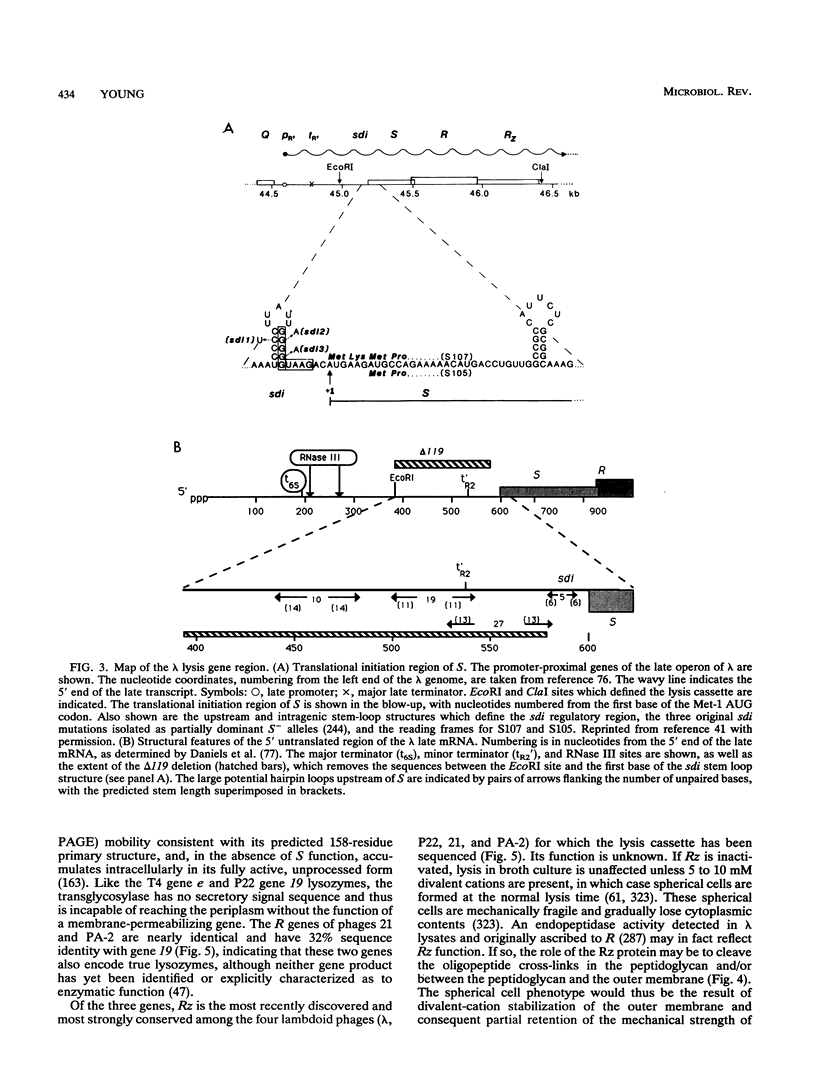
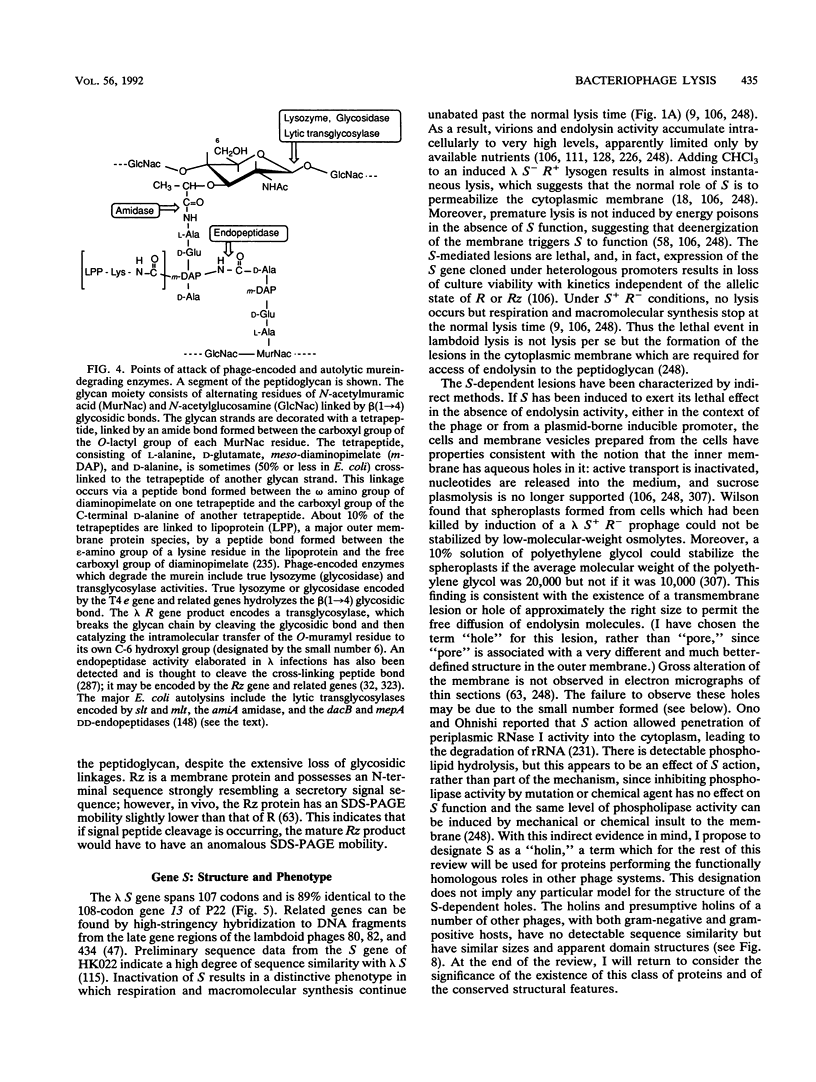
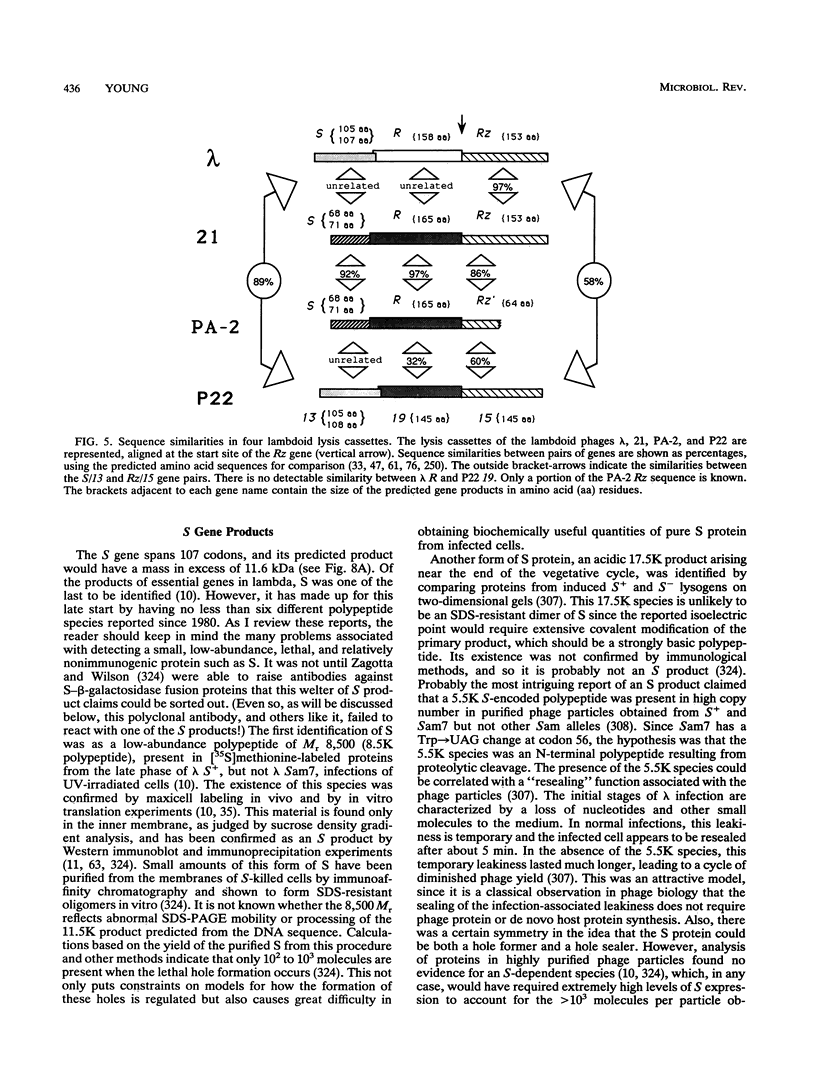
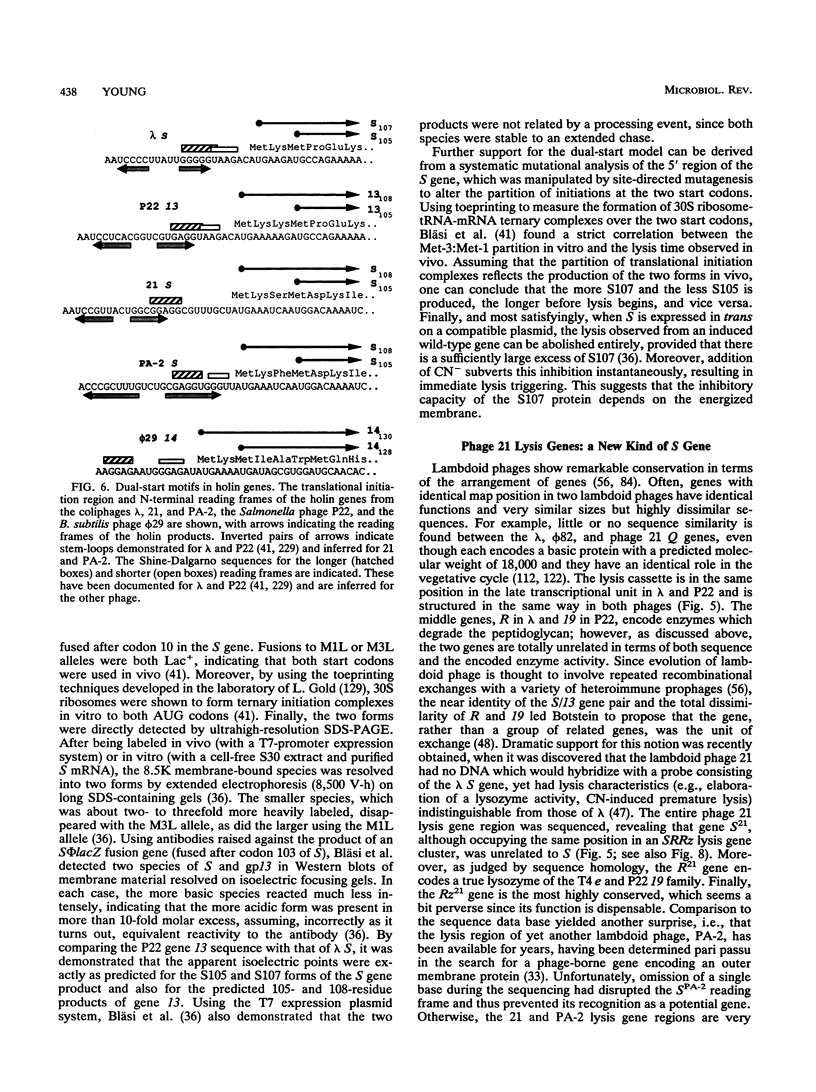
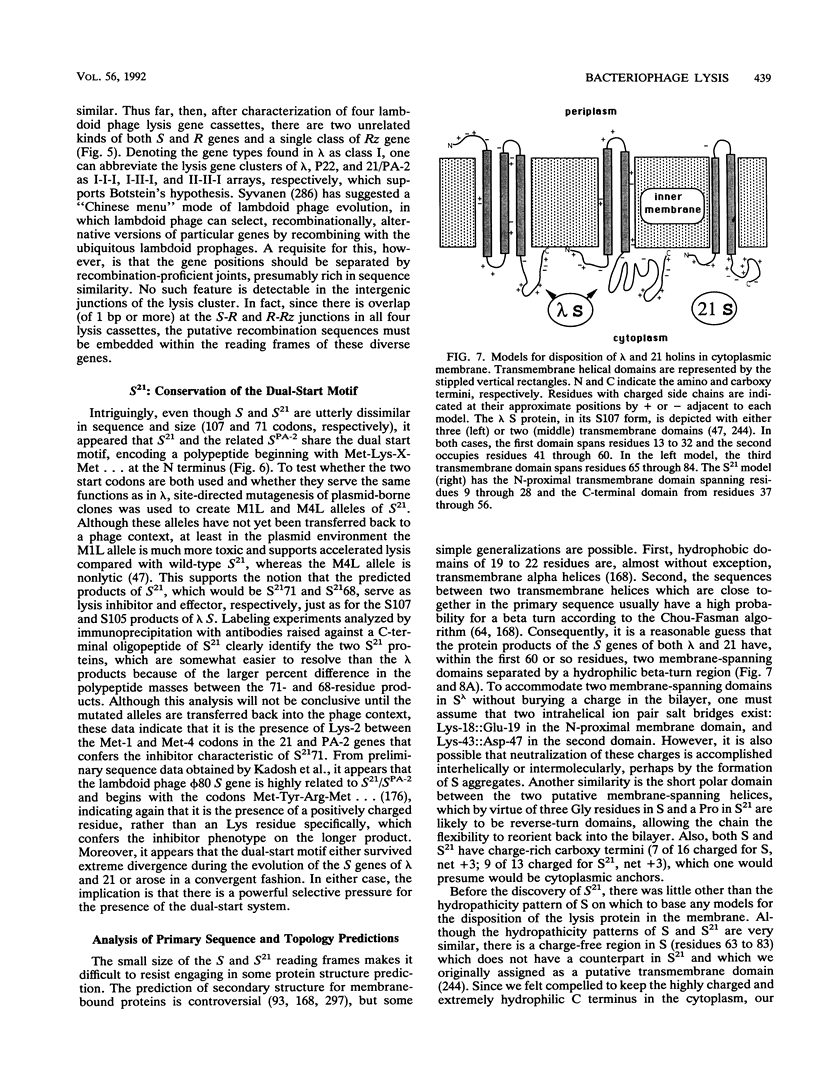
Bacteriophage lysis involves at least two fundamentally different strategies. Most phages elaborate at least two proteins, one of which is a murein hydrolase, or lysin, and the other is a membrane protein, which is given the designation holin in this review. The function of the holin is to create a lesion in the cytoplasmic membrane through which the murein hydrolase passes to gain access to the murein layer. This is necessary because phage-encoded lysins never have secretory signal sequences and are thus incapable of unassisted escape from the cytoplasm. The holins, whose prototype is the lambda S protein, share a common organization in terms of the arrangement of charged and hydrophobic residues, and they may all contain at least two transmembrane helical domains. The available evidence suggests that holins oligomerize to form nonspecific holes and that this hole-forming step is the regulated step in phage lysis. The correct scheduling of the lysis event is as much an essential feature of holin function as is the hole formation itself. In the second strategy of lysis, used by the small single-stranded DNA phage phi X174 and the single-stranded RNA phage MS2, no murein hydrolase activity is synthesized. Instead, there is a single species of small membrane protein, unlike the holins in primary structure, which somehow causes disruption of the envelope. These lysis proteins function by activation of cellular autolysins. A host locus is required for the lytic function of the phi X174 lysis gene E.
Full text
PDF







































Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abedon S. T. Selection for lysis inhibition in bacteriophage. J Theor Biol. 1990 Oct 21;146(4):501–511. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5193(05)80375-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adhin M. R., Avots A., Berzin V., Overbeek G. P., van Duin J. Complete nucleotide sequence of the group I RNA bacteriophage fr. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Aug 27;1050(1-3):104–109. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(90)90149-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adhin M. R., Hirashima A., van Duin J. Nucleotide sequence from the ssRNA bacteriophage JP34 resolves the discrepancy between serological and biophysical classification. Virology. 1989 May;170(1):238–242. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90371-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adhin M. R., van Duin J. Scanning model for translational reinitiation in eubacteria. J Mol Biol. 1990 Jun 20;213(4):811–818. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80265-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adhin M. R., van Duin J. Translational regulation of the lysis gene in RNA bacteriophage fr requires a UUG initiation codon. Mol Gen Genet. 1989 Jul;218(1):137–142. doi: 10.1007/BF00330576. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altman E., Altman R. K., Garrett J. M., Grimaila R. J., Young R. S gene product: identification and membrane localization of a lysis control protein. J Bacteriol. 1983 Sep;155(3):1130–1137. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.3.1130-1137.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altman E., Young K., Garrett J., Altman R., Young R. Subcellular localization of lethal lysis proteins of bacteriophages lambda and phiX174. J Virol. 1985 Mar;53(3):1008–1011. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.3.1008-1011.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armour G. A., Brewer G. J. Membrane morphogenesis from cloned fragments of bacteriophage PM2 DNA that contain the sp6.6 gene. FASEB J. 1990 Mar;4(5):1488–1493. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.4.5.2407591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atkins J. F., Steitz J. A., Anderson C. W., Model P. Binding of mammalian ribosomes to MS2 phage RNA reveals an overlapping gene encoding a lysis function. Cell. 1979 Oct;18(2):247–256. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90044-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERTANI G. Studies on lysogenesis. I. The mode of phage liberation by lysogenic Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1951 Sep;62(3):293–300. doi: 10.1128/jb.62.3.293-300.1951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachmann B. J. Pedigrees of some mutant strains of Escherichia coli K-12. Bacteriol Rev. 1972 Dec;36(4):525–557. doi: 10.1128/br.36.4.525-557.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bamford D. H., Palva E. T. Structure of the lipid-containing bacteriophage phi 6. Disruption by Triton X-100 treatment. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Sep 18;601(2):245–259. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90530-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bamford J. K., Hänninen A. L., Pakula T. M., Ojala P. M., Kalkkinen N., Frilander M., Bamford D. H. Genome organization of membrane-containing bacteriophage PRD1. Virology. 1991 Aug;183(2):658–676. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90995-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrell B. G., Air G. M., Hutchison C. A., 3rd Overlapping genes in bacteriophage phiX174. Nature. 1976 Nov 4;264(5581):34–41. doi: 10.1038/264034a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benjamin R. C., Fitzmaurice W. P., Huang P. C., Scocca J. J. Nucleotide sequence of cloned DNA segments of the Haemophilus influenzae bacteriophage HP1c1. Gene. 1984 Nov;31(1-3):173–185. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90208-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett J., Glavinovich J., Liskay R., Wulff D. L., Cronan J. E., Jr Phospholipid hydrolysis in Escherichia coli infected with rapid lysis mutants of Phage T4. Virology. 1971 Feb;43(2):516–518. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90326-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beremand M. N., Blumenthal T. Overlapping genes in RNA phage: a new protein implicated in lysis. Cell. 1979 Oct;18(2):257–266. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90045-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkhout B., Kastelein R. A., van Duin J. Translational interference at overlapping reading frames in prokaryotic messenger RNA. Gene. 1985;37(1-3):171–179. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90270-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkhout B., Schmidt B. F., van Strien A., van Boom J., van Westrenen J., van Duin J. Lysis gene of bacteriophage MS2 is activated by translation termination at the overlapping coat gene. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jun 5;195(3):517–524. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90180-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkhout B., de Smit M. H., Spanjaard R. A., Blom T., van Duin J. The amino terminal half of the MS2-coded lysis protein is dispensable for function: implications for our understanding of coding region overlaps. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 1;4(12):3315–3320. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04082.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkhout B., van der Laken C. J., van Knippenberg P. H. Formylmethionyl-tRNA binding to 30 S ribosomes programmed with homopolynucleotides and the effect of translational initiation factor 3. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Mar 26;866(2-3):144–153. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(86)90111-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bienkowska-Szewczyk K., Lipinska B., Taylor A. The R gene product of bacteriophage lambda is the murein transglycosylase. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;184(1):111–114. doi: 10.1007/BF00271205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blasband A. J., Marcotte W. R., Jr, Schnaitman C. A. Structure of the lc and nmpC outer membrane porin protein genes of lambdoid bacteriophage. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 25;261(27):12723–12732. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blattner F. R., Dahlberg J. E. RNA synthesis startpoints in bacteriophage lambda: are the promoter and operator transcribed? Nat New Biol. 1972 Jun 21;237(77):227–232. doi: 10.1038/newbio237227a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bläsi U., Chang C. Y., Zagotta M. T., Nam K. B., Young R. The lethal lambda S gene encodes its own inhibitor. EMBO J. 1990 Apr;9(4):981–989. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08200.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bläsi U., Henrich B., Lubitz W. Lysis of Escherichia coli by cloned phi X174 gene E depends on its expression. J Gen Microbiol. 1985 May;131(5):1107–1114. doi: 10.1099/00221287-131-5-1107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bläsi U., Linke R. P., Lubitz W. Evidence for membrane-bound oligomerization of bacteriophage phi X174 lysis protein-E. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 15;264(8):4552–4558. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bläsi U., Lubitz W. Influence of C-terminal modifications of phi X174 lysis gene E on its lysis-inducing properties. J Gen Virol. 1985 Jun;66(Pt 6):1209–1213. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-6-1209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bläsi U., Nam K., Hartz D., Gold L., Young R. Dual translational initiation sites control function of the lambda S gene. EMBO J. 1989 Nov;8(11):3501–3510. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08515.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bläsi U., Nam K., Lubitz W., Young R. Translational efficiency of phi X174 lysis gene E is unaffected by upstream translation of the overlapping gene D reading frame. J Bacteriol. 1990 Oct;172(10):5617–5623. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.10.5617-5623.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bläsi U., Young R., Lubitz W. Evaluation of the interaction of phi X174 gene products E and K in E-mediated lysis of Escherichia coli. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):4362–4364. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.4362-4364.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bode W. Lysis inhibition in Escherichia coli infected with bacteriophage T4. J Virol. 1967 Oct;1(5):948–955. doi: 10.1128/jvi.1.5.948-955.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boizet B., Lahbib-Mansais Y., Dupont L., Ritzenthaler P., Mata M. Cloning, expression and sequence analysis of an endolysin-encoding gene of Lactobacillus bulgaricus bacteriophage mv1. Gene. 1990 Sep 28;94(1):61–67. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90468-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonovich M. T., Young R. Dual start motif in two lambdoid S genes unrelated to lambda S. J Bacteriol. 1991 May;173(9):2897–2905. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.9.2897-2905.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botstein D. A theory of modular evolution for bacteriophages. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1980;354:484–490. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1980.tb27987.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley D. E., Dewar C. A., Robertson D. Structural changes in Escherichia coli infected with a phi X174 type bacteriophage. J Gen Virol. 1969 Jul;5(1):113–121. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-5-1-113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley D. E. Spheroplast formation in cells of Escherichia coli infected with a phi-X 174 type bacteriophage. J Gen Virol. 1968 Jul;3(1):141–142. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-3-1-141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewer G. J. Characterization of temperature-sensitive mutants of bacteriophage PM2: membrane mutants. Mol Gen Genet. 1978 Nov 16;167(1):65–74. doi: 10.1007/BF00270322. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewer G. J., Singh M. Kinetics and characterization of the proteins synthesized during infection by bacteriophage PM2. J Gen Virol. 1982 May;60(Pt 1):135–146. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-60-1-135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckley K. J., Hayashi M. Lytic activity localized to membrane-spanning region of phi X174 E protein. Mol Gen Genet. 1986 Jul;204(1):120–125. doi: 10.1007/BF00330198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckley K. J., Hayashi M. Role of premature translational termination in the regulation of expression of the phi X174 lysis gene. J Mol Biol. 1987 Dec 20;198(4):599–607. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90203-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAMPBELL A., DELCAMPILLO-CAMPBELL A. MUTANT OF LAMBDA BACTERIOPHAGE PRODUCING A THERMOLABILE ENDOLYSIN. J Bacteriol. 1963 Jun;85:1202–1207. doi: 10.1128/jb.85.6.1202-1207.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHAMPE S. P. BACTERIOPHAGE REPRODUCTION. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1963;17:87–114. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.17.100163.000511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camacho A., Jiménez F., De La Torre J., Carrascosa J. L., Mellado R. P., Vásquez C., Viñuela E., Salas M. Assembly of Bacillus subtilis phage phi29. 1. Mutants in the cistrons coding for the structural proteins. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Feb 15;73(1):39–55. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11290.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell J. H., Rolfe B. G. Evidence for a dual control of the initiation of host-cell lysis caused by phage lambda. Mol Gen Genet. 1975 Aug 5;139(1):1–8. doi: 10.1007/BF00267990. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrascosa J. L., Camacho A., Moreno F., Jiménez F., Mellado R. P., Viñuela E., Salas M. Bacillus subtilis phage phi29. Characterization of gene products and functions. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Jul 1;66(2):229–241. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10512.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrascosa J. L., Viñuela E., Salas M. Proteins induced in Bacillus subtilis infected with bacteriophage phi 29. Virology. 1973 Nov;56(1):291–299. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casjens S., Eppler K., Parr R., Poteete A. R. Nucleotide sequence of the bacteriophage P22 gene 19 to 3 region: identification of a new gene required for lysis. Virology. 1989 Aug;171(2):588–598. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90628-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Empirical predictions of protein conformation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:251–276. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.001343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Prediction of beta-turns. Biophys J. 1979 Jun;26(3):367–383. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(79)85259-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cody J. D., Conway T. W. Leakage induced in Escherichia coli cells by A protein-RNA complexes from bacteriophage f2. J Virol. 1981 Jul;39(1):60–66. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.1.60-66.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman J., Inouye M., Atkins J. Bacteriophage MS2 lysis protein does not require coat protein to mediate cell lysis. J Bacteriol. 1983 Feb;153(2):1098–1100. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.2.1098-1100.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cone K. C., Steege D. A. Messenger RNA conformation and ribosome selection of translational reinitiation sites in the lac repressor mRNA. J Mol Biol. 1985 Dec 20;186(4):725–732. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90392-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cronan J. E., Jr, Wulff D. L. A role for phospholipid hydrolysis in the lysis of Escherichia coli infected with bacteriophage T4. Virology. 1969 Jun;38(2):241–246. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90365-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOERMANN A. H. The intracellular growth of bacteriophages. I. Liberation of intracellular bacteriophage T4 by premature lysis with another phage or with cyanide. J Gen Physiol. 1952 Mar;35(4):645–656. doi: 10.1085/jgp.35.4.645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dabora R. L., Cooney C. L. Intracellular lytic enzyme systems and their use for disruption of Escherichia coli. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol. 1990;43:11–30. doi: 10.1007/BFb0009077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daegelen P., Brody E. The rIIA gene of bacteriophage T4. I. Its DNA sequence and discovery of a new open reading frame between genes 60 and rIIA. Genetics. 1990 Jun;125(2):237–248. doi: 10.1093/genetics/125.2.237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dai D., Ishiguro E. E. Two new mutant loci (smhB and lytD) in Escherichia coli which confer temperature-sensitive growth and lysis phenotypes. Can J Microbiol. 1990 Dec;36(12):827–833. doi: 10.1139/m90-143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniels D. L., Subbarao M. N., Blattner F. R., Lozeron H. A. Q-mediated late gene transcription of bacteriophage lambda: RNA start point and RNase III processing sites in vivo. Virology. 1988 Dec;167(2):568–577. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Mars Cody J., Conway T. W. Defective lysis of streptomycin-resistant escherichia coli cells infected with bacteriophage f2. J Virol. 1981 Feb;37(2):813–820. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.2.813-820.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLong A., Syvanen M. Membrane association of the Tnp and Inh proteins of IS50R. J Bacteriol. 1990 Sep;172(9):5516–5519. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.9.5516-5519.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denhardt D. T., Sinsheimer R. L. The process of infection with bacteriophage phi-X174. 3. Phage maturation and lysis after synchronized infection. J Mol Biol. 1965 Jul;12(3):641–646. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80318-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doermann A. H. Lysis and Lysis Inhibition with Escherichia coli Bacteriophage. J Bacteriol. 1948 Feb;55(2):257–276. doi: 10.1128/jb.55.2.257-276.1948. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn J. J., Studier F. W. Complete nucleotide sequence of bacteriophage T7 DNA and the locations of T7 genetic elements. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):477–535. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80282-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emrich J. Lysis of T4-infected bacteria in the absence of lysozyme. Virology. 1968 May;35(1):158–165. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(68)90315-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emrich J., Streisinger G. The role of phage lysozyme in the life cycle of phage T4. Virology. 1968 Nov;36(3):387–391. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(68)90163-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelberg H., Soudry E. Ribonucleic acid bacteriophage release: requirement for host-controlled protein synthesis. J Virol. 1971 Sep;8(3):257–264. doi: 10.1128/jvi.8.3.257-264.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ennis H. L., Kievitt K. D. Alteration of the Escherichia coli membrane by addition of bacteriophage T4 protein synthesized after infection. J Virol. 1977 May;22(2):553–560. doi: 10.1128/jvi.22.2.553-560.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ennis H. L., Kievitt K. D. Association of the rIIA protein with the bacterial membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 May;70(5):1468–1472. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.5.1468. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faelen M., Toussaint A. Isolation of conditional defective mutants of temperate phage Mu-1 and deletion mapping of the Mu-1 prophage. Virology. 1973 Jul;54(1):117–124. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90121-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fasman G. D., Gilbert W. A. The prediction of transmembrane protein sequences and their conformation: an evaluation. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Mar;15(3):89–92. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90187-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiers W., Contreras R., Duerinck F., Haegeman G., Iserentant D., Merregaert J., Min Jou W., Molemans F., Raeymaekers A., Van den Berghe A. Complete nucleotide sequence of bacteriophage MS2 RNA: primary and secondary structure of the replicase gene. Nature. 1976 Apr 8;260(5551):500–507. doi: 10.1038/260500a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fromageot H. P., Zinder N. D. Growth of bacteriophage f2 in E. coli treated with rifampicin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Sep;61(1):184–191. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.1.184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froshauer S., Green G. N., Boyd D., McGovern K., Beckwith J. Genetic analysis of the membrane insertion and topology of MalF, a cytoplasmic membrane protein of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1988 Apr 5;200(3):501–511. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90539-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GAREN A. Physiological effects of rII mutations in bacteriophage T4. Virology. 1961 Jun;14:151–163. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(61)90190-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galvez A., Valdivia E., Maqueda M., Montoya E. Production of bacteriocin-like substances by group D streptococci of human origin. Microbios. 1985;43(176S):223–232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia P., Lopez R., Ronda C., Garcia E., Tomasz A. Mechanism of phage-induced lysis in pneumococci. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 Feb;129(2):479–487. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-2-479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- García E., García J. L., García P., Arrarás A., Sánchez-Puelles J. M., López R. Molecular evolution of lytic enzymes of Streptococcus pneumoniae and its bacteriophages. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(3):914–918. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.3.914. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- García J. L., García E., Arrarás A., García P., Ronda C., López R. Cloning, purification, and biochemical characterization of the pneumococcal bacteriophage Cp-1 lysin. J Virol. 1987 Aug;61(8):2573–2580. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.8.2573-2580.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garnier J., Osguthorpe D. J., Robson B. Analysis of the accuracy and implications of simple methods for predicting the secondary structure of globular proteins. J Mol Biol. 1978 Mar 25;120(1):97–120. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90297-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrett J. M., Young R. Lethal action of bacteriophage lambda S gene. J Virol. 1982 Dec;44(3):886–892. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.3.886-892.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrett J., Bruno C., Young R. Lysis protein S of phage lambda functions in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1990 Dec;172(12):7275–7277. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.12.7275-7277.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrett J., Fusselman R., Hise J., Chiou L., Smith-Grillo D., Schulz J., Young R. Cell lysis by induction of cloned lambda lysis genes. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;182(2):326–331. doi: 10.1007/BF00269678. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgiou C. D., Dueweke T. J., Gennis R. B. Beta-galactosidase gene fusions as probes for the cytoplasmic regions of subunits I and II of the membrane-bound cytochrome d terminal oxidase from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 15;263(26):13130–13137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillam S., Atkinson T., Markham A., Smith M. Gene K of bacteriophage phi X174 codes for a protein which affects the burst size of phage production. J Virol. 1985 Feb;53(2):708–709. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.2.708-709.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goessens W. H., Driessen A. J., Wilschut J., van Duin J. A synthetic peptide corresponding to the C-terminal 25 residues of phage MS2 coded lysis protein dissipates the protonmotive force in Escherichia coli membrane vesicles by generating hydrophilic pores. EMBO J. 1988 Mar;7(3):867–873. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02886.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg A. R., Howe M. New mutations in the S cistron of bacteriophage lambda affecting host cell lysis. Virology. 1969 May;38(1):200–202. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90148-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goliger J. A., Roberts J. W. Sequences required for antitermination by phage 82 Q protein. J Mol Biol. 1989 Dec 5;210(3):461–471. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90123-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodell E. W., Lopez R., Tomasz A. Suppression of lytic effect of beta lactams on Escherichia coli and other bacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Sep;73(9):3293–3297. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.9.3293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottlieb P., Metzger S., Romantschuk M., Carton J., Strassman J., Bamford D. H., Kalkkinen N., Mindich L. Nucleotide sequence of the middle dsRNA segment of bacteriophage phi 6: placement of the genes of membrane-associated proteins. Virology. 1988 Mar;163(1):183–190. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90245-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groman N. B., Suzuki G. Effect of spermine on lysis and reproduction by bacteriophages phi-X174, lambda, and f2. J Bacteriol. 1966 Dec;92(6):1735–1740. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.6.1735-1740.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gschwender H. H., Hofschneider P. H. Lysis inhibition of phi-X174-, M12-, and Q-beta-infected Escherichia coli bacteria by magnesium ions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Oct 22;190(2):454–459. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(69)90094-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gualerzi C., Pon C. L., Kaji A. Initiation factor dependent release of aminoacyl-tRNAs from complexes of 30S ribosomal subunits, synthetic polynucleotide and aminoacyl tRNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Dec 3;45(5):1312–1319. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90162-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guidolin A., Zingg J. M., Lehnherr H., Arber W. Bacteriophage P1 tail-fibre and dar operons are expressed from homologous phage-specific late promoter sequences. J Mol Biol. 1989 Aug 20;208(4):615–622. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90152-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guo H. C., Kainz M., Roberts J. W. Characterization of the late-gene regulatory region of phage 21. J Bacteriol. 1991 Feb;173(4):1554–1560. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.4.1554-1560.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEAGY F. C. The effect of 2,4-dinitrophenol and phage T2 on Escherichia coli B. J Bacteriol. 1950 Mar;59(3):367–373. doi: 10.1128/jb.59.3.367-373.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERRIOTT R. M., BARLOW J. L. The protein coats or ghosts of coli phage T2. II. The biological functions. J Gen Physiol. 1957 Nov 20;41(2):307–331. doi: 10.1085/jgp.41.2.307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOFFMANN BERLING H., MAZE R. RELEASE OF MALE-SPECIFIC BACTERIOPHAGES FROM SURVIVING HOST BACTERIA. Virology. 1964 Mar;22:305–313. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(64)90021-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUTCHISON C. A., SINSHEIMER R. L. KINETICS OF BACTERIOPHAGE RELEASE BY SINGLE CELLS OF PHI X174-INFECTED E. COLI. J Mol Biol. 1963 Aug;7:206–208. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(63)80046-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall J. E., Vodyanoy I., Balasubramanian T. M., Marshall G. R. Alamethicin. A rich model for channel behavior. Biophys J. 1984 Jan;45(1):233–247. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84151-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall M. N., Gabay J., Débarbouillé M., Schwartz M. A role for mRNA secondary structure in the control of translation initiation. Nature. 1982 Feb 18;295(5850):616–618. doi: 10.1038/295616a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardaway K. L., Maten M. V., Buller C. S. Phospholipase activity in bacteriophage-infected Escherichia coli. III. Phopholipase A involvement in lysis of T4-infected cells. J Virol. 1975 Oct;16(4):867–871. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.4.867-871.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harkness R. E., Ishiguro E. E. Temperature-sensitive autolysis-defective mutants of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jul;155(1):15–21. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.1.15-21.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartz D., McPheeters D. S., Traut R., Gold L. Extension inhibition analysis of translation initiation complexes. Methods Enzymol. 1988;164:419–425. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(88)64058-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hausmann R. Bacteriophage T7 genetics. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1976;75:77–110. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-66530-1_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi M. N., Hayashi M. Stability of bacteriophage phi X174-specific mRNA in vivo. J Virol. 1981 Jan;37(1):506–510. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.1.506-510.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henrich B., Lubitz W., Plapp R. Lysis of Escherichia coli by induction of cloned phi X174 genes. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;185(3):493–497. doi: 10.1007/BF00334146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershey A. D. Mutation of Bacteriophage with Respect to Type of Plaque. Genetics. 1946 Nov;31(6):620–640. doi: 10.1093/genetics/31.6.620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershey A. D., Rotman R. Linkage Among Genes Controlling Inhibition of Lysis in a Bacterial Virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1948 Mar;34(3):89–96. doi: 10.1073/pnas.34.3.89. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herskowitz I., Signer E. R. A site essential for expression of all late genes in bacteriophage lambda. J Mol Biol. 1970 Feb 14;47(3):545–556. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90321-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill J. E., Wannamaker L. W. Identification of a lysin associated with a bacteriophage (A25) virulent for group A streptococci. J Bacteriol. 1981 Feb;145(2):696–703. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.2.696-703.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hocking S. M., Egan J. B. Genetic studies of coliphage 186. II. Genes associated with phage replication and host cell lysis. J Virol. 1982 Dec;44(3):1068–1071. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.3.1068-1071.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooper I., Woods W. H., Egan B. Coliphage 186 Replication is delayed when the host cell is UV irradiated before infection. J Virol. 1981 Nov;40(2):341–349. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.2.341-349.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard B. D. Phage lambda mutants deficient in r-II exclusion. Science. 1967 Dec 22;158(3808):1588–1589. doi: 10.1126/science.158.3808.1588. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard L. V., Gooder H. Specificity of the autolysin of Streptococcus (Diplococcus) pneumoniae. J Bacteriol. 1974 Feb;117(2):796–804. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.2.796-804.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang W. M., Buchanan J. M. Synergistic interactions of T4 early proteins concerned with their binding to DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jun;71(6):2226–2230. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.6.2226. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang W. M. Membrane-associated proteins of T4-infected Escherichia coli. Virology. 1975 Aug;66(2):508–521. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90223-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang W. M. The 52-protein subunit of T4 DNA topoisomerase is homologous to the gyrA-protein of gyrase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Sep 25;14(18):7379–7390. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutchison C. A., 3rd, Sinsheimer R. L. The process of infection with bacteriophage phi-X174. X. Mutations in a phi-X Lysis gene. J Mol Biol. 1966 Jul;18(3):429–447. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80035-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Höltje J. V., Fiedler W., Rotering H., Walderich B., van Duin J. Lysis induction of Escherichia coli by the cloned lysis protein of the phage MS2 depends on the presence of osmoregulatory membrane-derived oligosaccharides. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 15;263(8):3539–3541. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Höltje J. V., Tuomanen E. I. The murein hydrolases of Escherichia coli: properties, functions and impact on the course of infections in vivo. J Gen Microbiol. 1991 Mar;137(3):441–454. doi: 10.1099/00221287-137-3-441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iba H., Nanno M., Kakitani H., Emori Y., Okada Y. A lytic enzyme in the bacteriophage phi 6 virion. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1981;64:491–502. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iida K., Hirota Y., Schwarz U. Mutants of Escherichia coli defective in penicillin-insensitive murein DD-endopeptidase. Mol Gen Genet. 1983;189(2):215–221. doi: 10.1007/BF00337807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iida S., Arber W. Plaque forming specialized transducing phage P1: isolation of P1CmSmSu, a precursor of P1Cm. Mol Gen Genet. 1977 Jun 24;153(3):259–269. doi: 10.1007/BF00431591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inouye M., Arnheim N., Sternglanz R. Bacteriophage T7 lysozyme is an N-acetylmuramyl-L-alanine amidase. J Biol Chem. 1973 Oct 25;248(20):7247–7252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isberg R. R., Lazaar A. L., Syvanen M. Regulation of Tn5 by the right-repeat proteins: control at the level of the transposition reaction? Cell. 1982 Oct;30(3):883–892. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90293-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isberg R. R., Syvanen M. Compartmentalization of the proteins encoded by IS50R. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3645–3651. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JACOB F., FUERST C. R. The mechanism of lysis by phage studied with defective lysogenic bacteria. J Gen Microbiol. 1958 Apr;18(2):518–526. doi: 10.1099/00221287-18-2-518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiménez F., Camacho A., De La Torre J., Viñuela E., Salas M. Assembly of Bacillus subtilis phage phe29. 2. Mutants in the cistrons coding for the non-structural proteins. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Feb 15;73(1):57–72. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11291.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston H. M., Roth J. R. DNA sequence changes of mutations altering attenuation control of the histidine operon of Salmonella typhimurium. J Mol Biol. 1981 Feb 5;145(4):735–756. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90312-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Josslin R. Physiological studies on the t gene defect in T4-infected Escherichia coli. Virology. 1971 Apr;44(1):101–107. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90157-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Josslin R. The effect of phage T4 infection on phospholipid hydrolysis in Escherichia coli. Virology. 1971 Apr;44(1):94–100. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90156-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Josslin R. The lysis mechanism of phage T4: mutants affecting lysis. Virology. 1970 Mar;40(3):719–726. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90216-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jähnig F. Structure predictions of membrane proteins are not that bad. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Mar;15(3):93–95. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90188-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaback H. R. Transport in isolated bacterial membrane vesicles. Methods Enzymol. 1974;31:698–709. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)31075-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao S. H., McClain W. H. Baseplate protein of bacteriophage T4 with both structural and lytic functions. J Virol. 1980 Apr;34(1):95–103. doi: 10.1128/jvi.34.1.95-103.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao S. H., McClain W. H. Roles of bacteriophage T4 gene 5 and gene s products in cell lysis. J Virol. 1980 Apr;34(1):104–107. doi: 10.1128/jvi.34.1.104-107.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karnik S., Billeter M. The lysis function of RNA bacteriophage Qbeta is mediated by the maturation (A2) protein. EMBO J. 1983;2(9):1521–1526. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01617.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kastelein R. A., Remaut E., Fiers W., van Duin J. Lysis gene expression of RNA phage MS2 depends on a frameshift during translation of the overlapping coat protein gene. Nature. 1982 Jan 7;295(5844):35–41. doi: 10.1038/295035a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keck W., Schwarz U. Escherichia coli murein-DD-endopeptidase insensitive to beta-lactam antibiotics. J Bacteriol. 1979 Sep;139(3):770–774. doi: 10.1128/jb.139.3.770-774.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krebs M. P., Reznikoff W. S. Transcriptional and translational initiation sites of IS50. Control of transposase and inhibitor expression. J Mol Biol. 1986 Dec 20;192(4):781–791. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90028-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krylov V. N., Yankovsky N. K. Mutations in the new gene stIII of bacteriophage T4B suppressing the lysis defect of gene stII and a gene e mutant. J Virol. 1975 Jan;15(1):22–26. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.1.22-26.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kusser W., Ishiguro E. E. Suppression of mutations conferring penicillin tolerance by interference with the stringent control mechanism of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1987 Sep;169(9):4396–4398. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.9.4396-4398.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrer R. I., Ganz T., Selsted M. E., Babior B. M., Curnutte J. T. Neutrophils and host defense. Ann Intern Med. 1988 Jul 15;109(2):127–142. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-109-2-127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner T. J., Zinder N. D. Discontinuous release of phage f2. Virology. 1977 Jun 1;79(1):236–238. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90348-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl G. Characterization of conditional lethal mutants of bacteriophage P2. Mol Gen Genet. 1974 Feb 6;128(3):249–260. doi: 10.1007/BF00267114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linder C. H., Carlson K. Escherichia coli Rho factor is involved in lysis of bacteriophage T4-infected cells. Genetics. 1985 Oct;111(2):197–218. doi: 10.1093/genetics/111.2.197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lubitz W., Harkness R. E., Ishiguro E. E. Requirement for a functional host cell autolytic enzyme system for lysis of Escherichia coli by bacteriophage phi X174. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jul;159(1):385–387. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.1.385-387.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luk K. C., Szybalski W. Tandem transcription-termination sites in the late rightward operon of bacteriophage lambda. Mol Gen Genet. 1983;189(2):289–297. doi: 10.1007/BF00337819. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARKERT A., ZILLIG W. STUDIES ON THE LYSIS OF ESCHERICHIA COLI C BY BACTERIOPHAGE PHI-X174. Virology. 1965 Jan;25:88–97. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(65)90256-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manoil C., Mekalanos J. J., Beckwith J. Alkaline phosphatase fusions: sensors of subcellular location. J Bacteriol. 1990 Feb;172(2):515–518. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.2.515-518.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manoil C., Sinha N., Alberts B. Intracellular DNA-protein complexes from bacteriophage T4-infected cells isolated by a rapid two-step procedure. Characterization and identification of the protein components. J Biol Chem. 1977 Apr 25;252(8):2734–2741. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maratea D., Young K., Young R. Deletion and fusion analysis of the phage phi X174 lysis gene E. Gene. 1985;40(1):39–46. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90022-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuhashi M., Maruyama I. N., Takagaki Y., Tamaki S., Nishimura Y., Hirota Y. Isolation of a mutant of Escherichia coli lacking penicillin-sensitive D-alanine carboxypeptidase IA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2631–2635. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matz K., Schmandt M., Gussin G. N. The rex gene of bacteriophage lambda is really two genes. Genetics. 1982 Nov;102(3):319–327. doi: 10.1093/genetics/102.3.319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCommas S. A., Syvanen M. Temporal control of transposition in Tn5. J Bacteriol. 1988 Feb;170(2):889–894. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.2.889-894.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFALL E., STENT G. S. Three star mutants of coliphage T2. J Gen Microbiol. 1958 Apr;18(2):346–363. doi: 10.1099/00221287-18-2-346. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
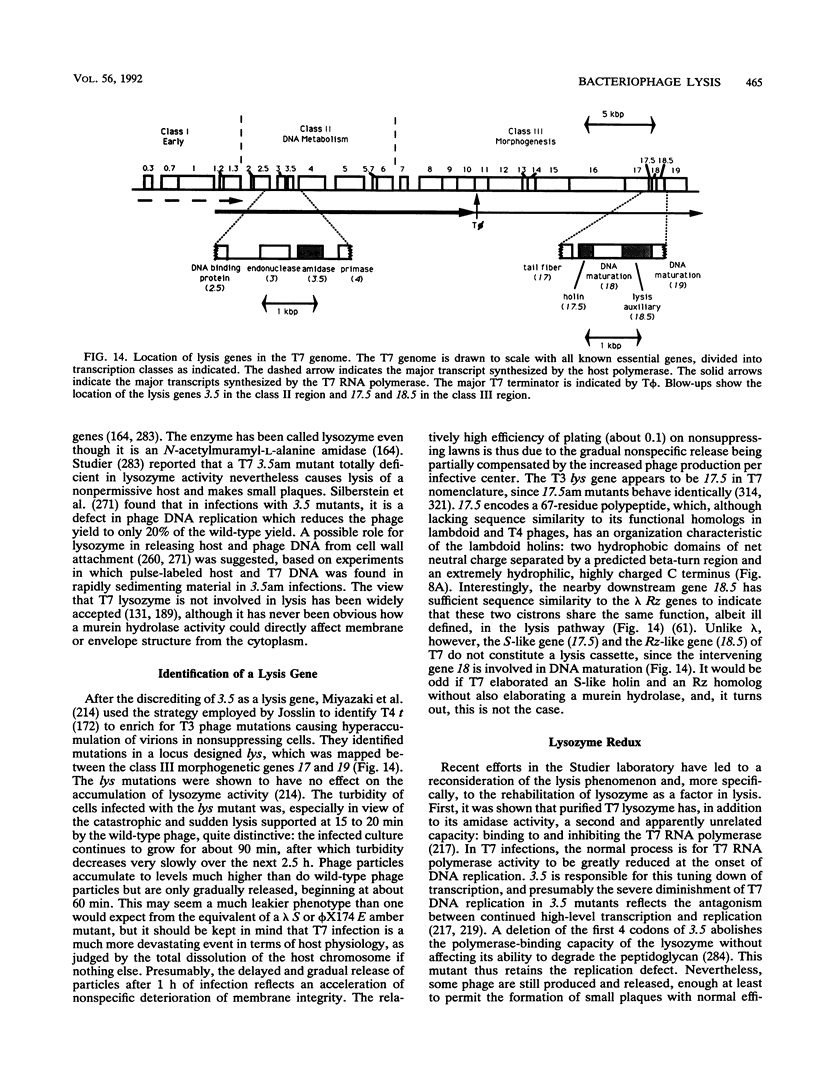
- McPheeters D. S., Christensen A., Young E. T., Stormo G., Gold L. Translational regulation of expression of the bacteriophage T4 lysozyme gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jul 25;14(14):5813–5826. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.14.5813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller F. D., Winkfein R. J., Rattner J. B., van de Sande J. H. Sequence analysis of a PM2-DNA anti-Z-IgG-binding region. Biosci Rep. 1984 Oct;4(10):885–895. doi: 10.1007/BF01138171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mindich L., Bamford D., Goldthwaite C., Laverty M., Mackenzie G. Isolation of nonsense mutants of lipid-containing bacteriophage PRD1. J Virol. 1982 Dec;44(3):1013–1020. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.3.1013-1020.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mindich L., Lehman J. Cell wall lysin as a component of the bacteriophage phi 6 virion. J Virol. 1979 May;30(2):489–496. doi: 10.1128/jvi.30.2.489-496.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyazaki J. I., Ryo Y., Fujisawa H., Minagawa T. Mutation in bacteriophage T3 affecting host cell lysis. Virology. 1978 Aug;89(1):327–329. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90067-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Model P., Webster R. E., Zinder N. D. Characterization of Op3, a lysis-defective mutant of bacteriophage f2. Cell. 1979 Oct;18(2):235–246. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90043-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moffatt B. A., Studier F. W. T7 lysozyme inhibits transcription by T7 RNA polymerase. Cell. 1987 Apr 24;49(2):221–227. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90563-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohana Rao J. K., Argos P. A conformational preference parameter to predict helices in integral membrane proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Jan 30;869(2):197–214. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(86)90295-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montag D., Degen M., Henning U. Nucleotide sequence of gene t (lysis gene) of the E. coli phage T4. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Aug 25;15(16):6736–6736. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.16.6736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreillon P., Markiewicz Z., Nachman S., Tomasz A. Two bactericidal targets for penicillin in pneumococci: autolysis-dependent and autolysis-independent killing mechanisms. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Jan;34(1):33–39. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.1.33. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreillon P., Tomasz A. Penicillin resistance and defective lysis in clinical isolates of pneumococci: evidence for two kinds of antibiotic pressure operating in the clinical environment. J Infect Dis. 1988 Jun;157(6):1150–1157. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.6.1150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosig G., Lin G. W., Franklin J., Fan W. H. Functional relationships and structural determinants of two bacteriophage T4 lysozymes: a soluble (gene e) and a baseplate-associated (gene 5) protein. New Biol. 1989 Nov;1(2):171–179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukai F., Streisinger G., Miller B. The mechanism of lysis in phage T4-infected cells. Virology. 1967 Nov;33(3):398–404. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(67)90115-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukherjee P. K., Mandal R. K. Role of S gene of bacteriophage lambda in host lysis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 May 3;70(1):302–309. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)91142-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagai K., Thøgersen H. C. Synthesis and sequence-specific proteolysis of hybrid proteins produced in Escherichia coli. Methods Enzymol. 1987;153:461–481. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)53072-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nam K., Bläsi U., Zagotta M. T., Young R. Conservation of a dual-start motif in P22 lysis gene regulation. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jan;172(1):204–211. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.1.204-211.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obringer J., McCreary P., Bernstein H. Bacteriophage T4 genes sp and 40 apparently are the same. J Virol. 1988 Aug;62(8):3043–3045. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.8.3043-3045.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono T., Ohnishi Y. Degradation of ribosomal RNA in bacteriophage lambda lysogens after thermal induction. Microbiol Immunol. 1981;25(5):433–444. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1981.tb00046.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozaki M., Valentine R. C. Inhibition of bacterial cell wall mucopeptide synthesis: a new function of RNA bacteriophage Qbeta. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 May 28;304(3):707–714. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(73)90216-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paces V., Vlcek C., Urbánek P., Hostomský Z. Nucleotide sequence of the right early region of Bacillus subtilis phage PZA completes the 19366-bp sequence of PZA genome. Comparison with the homologous sequence of phage phi 29. Gene. 1986;44(1):115–120. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90049-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pakula T. M., Savilahti H., Bamford D. H. Comparison of the amino acid sequence of the lytic enzyme from broad-host-range bacteriophage PRD1 with sequences of other cell-wall-peptidoglycan lytic enzymes. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Mar 1;180(1):149–152. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14625.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson R. F., Kievitt K. D., Ennis H. L. Membrane protein synthesis after infection of Escherichia coli B with phage T4: the rIIB protein. Virology. 1972 Nov;50(2):520–527. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90403-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollock T. J., Tessman E. S., Tessman I. Identification of lysis protein E of bacteriophage phiX174. J Virol. 1978 Oct;28(1):408–410. doi: 10.1128/jvi.28.1.408-410.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poteete A. R., Rennell D., Bouvier S. E. Functional significance of conserved amino acid residues. Proteins. 1992 May;13(1):38–40. doi: 10.1002/prot.340130104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell J. K., Young K. D. Lysis of Escherichia coli by beta-lactams which bind penicillin-binding proteins 1a and 1b: inhibition by heat shock proteins. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jul;173(13):4021–4026. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.13.4021-4026.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pribnow D., Sigurdson D. C., Gold L., Singer B. S., Napoli C., Brosius J., Dull T. J., Noller H. F. rII cistrons of bacteriophage T4. DNA sequence around the intercistronic divide and positions of genetic landmarks. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jul 5;149(3):337–376. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90477-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raab R., Neal G., Garrett J., Grimaila R., Fusselman R., Young R. Mutational analysis of bacteriophage lambda lysis gene S. J Bacteriol. 1986 Sep;167(3):1035–1042. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.3.1035-1042.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raab R., Neal G., Sohaskey C., Smith J., Young R. Dominance in lambda S mutations and evidence for translational control. J Mol Biol. 1988 Jan 5;199(1):95–105. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rae M. E., Stodolsky M. Chromosome breakage, fusion and reconstruction during P1dl transduction. Virology. 1974 Mar;58(1):32–54. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90139-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray P. N., Pearson M. L. Evidence for post-transcriptional control of the morphogenetic genes of bacteriophage lambda. J Mol Biol. 1974 May 5;85(1):163–175. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90135-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reader R. W., Siminovitch L. Lysis defective mutants of bacteriophage lambda: on the role of the S function in lysis. Virology. 1971 Mar;43(3):623–637. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90287-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redfield R. J., Campbell A. M. Structure of cryptic lambda prophages. J Mol Biol. 1987 Dec 5;198(3):393–404. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90289-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rennell D., Poteete A. R. Phage P22 lysis genes: nucleotide sequences and functional relationships with T4 and lambda genes. Virology. 1985 May;143(1):280–289. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90115-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riede I. Lysis gene t of T-even bacteriophages: evidence that colicins and bacteriophage genes have common ancestors. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jul;169(7):2956–2961. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.7.2956-2961.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts J. W. Transcription termination and late control in phage lambda. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Sep;72(9):3300–3304. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.9.3300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rolfe B. G., Campbell J. H. A relationship between tolerance to colicin K and the mechanism of phage-induced host cell lysis. Mol Gen Genet. 1974;133(4):293–297. doi: 10.1007/BF00332705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rolfe B. G., Campbell J. H. Genetic and physiological control of host cell lysis by bacteriophage lambda. J Virol. 1977 Sep;23(3):626–636. doi: 10.1128/jvi.23.3.626-636.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romantschuk M., Olkkonen V. M., Bamford D. H. The nucleocapsid of bacteriophage phi 6 penetrates the host cytoplasmic membrane. EMBO J. 1988 Jun;7(6):1821–1829. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03014.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romero A., Lopez R., Garcia P. Characterization of the pneumococcal bacteriophage HB-3 amidase: cloning and expression in Escherichia coli. J Virol. 1990 Jan;64(1):137–142. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.1.137-142.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ronda-Lain C., Lopez R., Tapia A., Tomasz A. Role of the pneumococcal autolysin (murein hydrolase) in the release of progeny bacteriophage and in the bacteriophage-induced lysis of the host cells. J Virol. 1977 Jan;21(1):366–374. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.1.366-374.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutberg B., Rutberg L. Role of superinfecting phage in lysis inhibition with phage T4 in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1965 Oct;90(4):891–894. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.4.891-894.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STENT G. S., MAAL|OE O. Radioactive phosphorus tracer studies on the reproduction of T4 bacteriophage. II. Kinetics of phosphorus assimilation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1953 Jan;10(1):55–69. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(53)90210-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STREISINGER G., MUKAI F., DREYER W. J., MILLER B., HORIUCHI S. Mutations affecting the lysozyme of phage T4. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1961;26:25–30. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1961.026.01.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SYMONDS N. The properties of a star mutant of phage T2. J Gen Microbiol. 1958 Apr;18(2):330–345. doi: 10.1099/00221287-18-2-330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadowski P. D., Kerr C. Degradation of Escherichia coli B deoxyribonucleic acid after infection with deoxyribonucleic acid-defective amber mutants of bacteriophage T7. J Virol. 1970 Aug;6(2):149–155. doi: 10.1128/jvi.6.2.149-155.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sampson L. L., Hendrix R. W., Huang W. M., Casjens S. R. Translation initiation controls the relative rates of expression of the bacteriophage lambda late genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(15):5439–5443. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.15.5439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R., Friedmann T., Air G. M., Barrell B. G., Brown N. L., Fiddes J. C., Hutchison C. A., 3rd, Slocombe P. M., Smith M. The nucleotide sequence of bacteriophage phiX174. J Mol Biol. 1978 Oct 25;125(2):225–246. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90346-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sauer B., Calendar R., Ljungquist E., Six E., Sunshine M. G. Interaction of satellite phage P4 with phage 186 helper. Virology. 1982 Jan 30;116(2):523–534. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90145-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt B. F., Berkhout B., Overbeek G. P., van Strien A., van Duin J. Determination of the RNA secondary structure that regulates lysis gene expression in bacteriophage MS2. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jun 5;195(3):505–516. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90179-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholtissek S., Grosse F. A plasmid vector system for the expression of a triprotein consisting of beta-galactosidase, a collagenase recognition site and a foreign gene product. Gene. 1988;62(1):55–64. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90579-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schüller A., Harkness R. E., Rüther U., Lubitz W. Deletion of C-terminal amino acid codons of PhiX174 gene E: effect on its lysis inducing properties. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jun 11;13(11):4143–4153. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.11.4143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shearman C., Underwood H., Jury K., Gasson M. Cloning and DNA sequence analysis of a Lactococcus bacteriophage lysin gene. Mol Gen Genet. 1989 Aug;218(2):214–221. doi: 10.1007/BF00331271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinedling S., Parma D., Gold L. Wild-type bacteriophage T4 is restricted by the lambda rex genes. J Virol. 1987 Dec;61(12):3790–3794. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.12.3790-3794.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinedling S., Singer B. S., Gayle M., Pribnow D., Jarvis E., Edgar B., Gold L. Sequences and studies of bacteriophage T4 rII mutants. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jun 5;195(3):471–480. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90176-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silberstein S., Inouye M. Studies on the role of bacteriophage T7 lysozyme during phage infection. J Mol Biol. 1975 Jul 25;96(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90178-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinsheimer R. L. Bacteriophage phi-X174 and related viruses. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1968;8:115–169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Six E. W. The helper dependence of satellite bacteriophage P4: which gene functions of bacteriophage P2 are needed by P4? Virology. 1975 Sep;67(1):249–263. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90422-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sklar J., Yot P., Weissman S. M. Determination of genes, restriction sites, and DNA sequences surrounding the 6S RNA template of bacteriophage lambda. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 May;72(5):1817–1821. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.5.1817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder L., McWilliams K. The rex genes of bacteriophage lambda can inhibit cell function without phage superinfection. Gene. 1989 Sep 1;81(1):17–24. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90332-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W. Bacteriophage T7. Science. 1972 Apr 28;176(4033):367–376. doi: 10.1126/science.176.4033.367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor A. Endopeptidase activity of phage lamba-endolysin. Nat New Biol. 1971 Dec 1;234(48):144–145. doi: 10.1038/newbio234144a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasz A. Choline in the cell wall of a bacterium: novel type of polymer-linked choline in Pneumococcus. Science. 1967 Aug 11;157(3789):694–697. doi: 10.1126/science.157.3789.694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomioka S., Matsuhashi M. Purification of penicillin-insensitive DD-endopeptidase, a new cell wall peptidoglycan-hydrolyzing enzyme in Escherichia coli, and its inhibition by deoxyribonucleic acids. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Oct 30;84(4):978–984. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91679-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tosi M. E., Reilly B. E., Anderson D. L. Morphogenesis of bacteriophage phi29 of Bacillus subtilis: cleavage and assembly of the neck appendage protein. J Virol. 1975 Nov;16(5):1282–1295. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.5.1282-1295.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsugita A., Inouye M. Complete primary structure of phage lysozyme from Escherichia coli T4. J Mol Biol. 1968 Oct 14;37(1):201–212. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90083-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukagoshi N., Schäfer R., Franklin R. M. Structure and synthesis of a lipid-containing bacteriophage. An endolysin activity associated with bacteriophage PM2. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Aug 1;77(3):585–588. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11702.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VISCONTI N. Resistance to lysis from without in bacteria infected with T2 bacteriophage. J Bacteriol. 1953 Sep;66(3):247–253. doi: 10.1128/jb.66.3.247-253.1953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlcek C., Paces V. Nucleotide sequence of the late region of Bacillus phage phi 29 completes the 19,285-bp sequence of phi 29 genome. Comparison with the homologous sequence of phage PZA. Gene. 1986;46(2-3):215–225. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90406-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WATSON J. D. The properties of x-ray inactivated bacteriophage. I. Inactivation by direct effect. J Bacteriol. 1950 Dec;60(6):697–718. doi: 10.1128/jb.60.6.697-718.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walderich B., Höltje J. V. Specific localization of the lysis protein of bacteriophage MS2 in membrane adhesion sites of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jun;171(6):3331–3336. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.6.3331-3336.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walderich B., Ursinus-Wössner A., van Duin J., Höltje J. V. Induction of the autolytic system of Escherichia coli by specific insertion of bacteriophage MS2 lysis protein into the bacterial cell envelope. J Bacteriol. 1988 Nov;170(11):5027–5033. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.11.5027-5033.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. T., Walker D. H. Mutations in coliphage p1 affecting host cell lysis. J Virol. 1980 Aug;35(2):519–530. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.2.519-530.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver L. H., Rennell D., Poteete A. R., Mathews B. W. Structure of phage P22 gene 19 lysozyme inferred from its homology with phage T4 lysozyme. Implications for lysozyme evolution. J Mol Biol. 1985 Aug 20;184(4):739–741. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90318-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub S. B., Frankel F. R. Identification of the T4rIIB gene product as a membrane protein. J Mol Biol. 1972 Oct 14;70(3):589–615. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90561-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson D. B. Effect of the lambda S gene product on properties of the Escherichia coli inner membrane. J Bacteriol. 1982 Sep;151(3):1403–1410. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.3.1403-1410.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson D. B., Okabe A. A second function of the S gene of bacteriophage lambda. J Bacteriol. 1982 Dec;152(3):1091–1095. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.3.1091-1095.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winter R. B., Gold L. Overproduction of bacteriophage Q beta maturation (A2) protein leads to cell lysis. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):877–885. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90030-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witte A., Bläsi U., Halfmann G., Szostak M., Wanner G., Lubitz W. Phi X174 protein E-mediated lysis of Escherichia coli. Biochimie. 1990 Feb-Mar;72(2-3):191–200. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(90)90145-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witte A., Lubitz W., Bakker E. P. Proton-motive-force-dependent step in the pathway to lysis of Escherichia coli induced by bacteriophage phi X174 gene E product. J Bacteriol. 1987 Apr;169(4):1750–1752. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.4.1750-1752.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witte A., Lubitz W. Biochemical characterization of phi X174-protein-E-mediated lysis of Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Mar 15;180(2):393–398. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14661.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witte A., Wanner G., Bläsi U., Halfmann G., Szostak M., Lubitz W. Endogenous transmembrane tunnel formation mediated by phi X174 lysis protein E. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jul;172(7):4109–4114. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.7.4109-4114.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada M., Fujisawa H., Kato H., Hamada K., Minagawa T. Cloning and sequencing of the genetic right end of bacteriophage T3 DNA. Virology. 1986 Jun;151(2):350–361. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90055-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamazaki Y. Enzymatic activities on cell walls in bacteriophage T4. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 May 27;178(3):542–550. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(69)90223-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young K. D., Anderson R. J., Hafner R. J. Lysis of Escherichia coli by the bacteriophage phi X174 E protein: inhibition of lysis by heat shock proteins. J Bacteriol. 1989 Aug;171(8):4334–4341. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.8.4334-4341.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young K. D., Young R. Lytic action of cloned phi X174 gene E. J Virol. 1982 Dec;44(3):993–1002. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.3.993-1002.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R., Way J., Way S., Yin J., Syvanen M. Transposition mutagenesis of bacteriophage lambda: a new gene affecting cell lysis. J Mol Biol. 1979 Aug 15;132(3):307–322. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90262-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zagotta M. T., Wilson D. B. Oligomerization of the bacteriophage lambda S protein in the inner membrane of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1990 Feb;172(2):912–921. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.2.912-921.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinder N. D., Lyons L. B. Cell Lysis: Another Function of the Coat Protein of the Bacteriophage f2. Science. 1968 Jan 5;159(3810):84–86. doi: 10.1126/science.159.3810.84. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Boer P. A., Cook W. R., Rothfield L. I. Bacterial cell division. Annu Rev Genet. 1990;24:249–274. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.24.120190.001341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G., Manoil C. Membrane proteins: from sequence to structure. Protein Eng. 1990 Dec;4(2):109–112. doi: 10.1093/protein/4.2.109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]