Abstract
The ABC transporters (also called traffic ATPases) make up a large superfamily of proteins which share a common function and a common ATP-binding domain. ABC transporters are classified into three major groups: bacterial importers (the periplasmic permeases), eukaryotic transporters, and bacterial exporters. We present a comprehensive review of the bacterial ABC exporter group, which currently includes over 40 systems. The bacterial ABC exporter systems are functionally subdivided on the basis of the type of substrate that each translocates. We describe three main groups: protein exporters, peptide exporters, and systems that transport nonprotein substrates. Prototype exporters from each group are described in detail to illustrate our current understanding of this protein family. The prototype systems include the alpha-hemolysin, colicin V, and capsular polysaccharide exporters from Escherichia coli, the protease exporter from Erwinia chrysanthemi, and the glucan exporters from Agrobacterium tumefaciens and Rhizobium meliloti. Phylogenetic analysis of the ATP-binding domains from 29 bacterial ABC exporters indicates that the bacterial ABC exporters can be divided into two primary branches. One branch contains the transport systems where the ATP-binding domain and the membrane-spanning domain are present on the same polypeptide, and the other branch contains the systems where these domains are found on separate polypeptides. Differences in substrate specificity do not correlate with evolutionary relatedness. A complete survey of the known and putative bacterial ABC exporters is included at the end of the review.
Full text
PDF

















Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albright L. M., Ronson C. W., Nixon B. T., Ausubel F. M. Identification of a gene linked to Rhizobium meliloti ntrA whose product is homologous to a family to ATP-binding proteins. J Bacteriol. 1989 Apr;171(4):1932–1941. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.4.1932-1941.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ames G. F. Bacterial periplasmic transport systems: structure, mechanism, and evolution. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:397–425. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.002145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ames G. F., Mimura C. S., Shyamala V. Bacterial periplasmic permeases belong to a family of transport proteins operating from Escherichia coli to human: Traffic ATPases. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 1990 Aug;6(4):429–446. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1990.tb04110.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Augustin J., Rosenstein R., Wieland B., Schneider U., Schnell N., Engelke G., Entian K. D., Götz F. Genetic analysis of epidermin biosynthetic genes and epidermin-negative mutants of Staphylococcus epidermidis. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Mar 15;204(3):1149–1154. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb16740.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barry E. M., Weiss A. A., Ehrmann I. E., Gray M. C., Hewlett E. L., Goodwin M. S. Bordetella pertussis adenylate cyclase toxin and hemolytic activities require a second gene, cyaC, for activation. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jan;173(2):720–726. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.2.720-726.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker K. F., Allmeier H., Höllt V. New mechanisms of hormone secretion: MDR-like gene products as extrusion pumps for hormones? Horm Metab Res. 1992 May;24(5):210–213. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1003295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beckman D. L., Trawick D. R., Kranz R. G. Bacterial cytochromes c biogenesis. Genes Dev. 1992 Feb;6(2):268–283. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.2.268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blight M. A., Holland I. B. Structure and function of haemolysin B,P-glycoprotein and other members of a novel family of membrane translocators. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Jun;4(6):873–880. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00660.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulnois G. J., Roberts I. S. Genetics of capsular polysaccharide production in bacteria. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1990;150:1–18. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-74694-9_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley M. K., Smith T. F., Lathrop R. H., Livingston D. M., Webster T. A. Consensus topography in the ATP binding site of the simian virus 40 and polyomavirus large tumor antigens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(12):4026–4030. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.12.4026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burrows L. L., Lo R. Y. Molecular characterization of an RTX toxin determinant from Actinobacillus suis. Infect Immun. 1992 Jun;60(6):2166–2173. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.6.2166-2173.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cangelosi G. A., Martinetti G., Leigh J. A., Lee C. C., Thienes C., Theines C., Nester E. W. Role for [corrected] Agrobacterium tumefaciens ChvA protein in export of beta-1,2-glucan. J Bacteriol. 1989 Mar;171(3):1609–1615. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.3.1609-1615.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler M. S., Morrison D. A. Competence for genetic transformation in Streptococcus pneumoniae: molecular cloning of com, a competence control locus. J Bacteriol. 1987 May;169(5):2005–2011. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.5.2005-2011.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang Y. F., Ma D. P., Shi J., Chengappa M. M. Molecular characterization of a leukotoxin gene from a Pasteurella haemolytica-like organism, encoding a new member of the RTX toxin family. Infect Immun. 1993 May;61(5):2089–2095. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.5.2089-2095.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang Y. F., Shi J., Ma D. P., Shin S. J., Lein D. H. Molecular analysis of the Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae RTX toxin-III gene cluster. DNA Cell Biol. 1993 May;12(4):351–362. doi: 10.1089/dna.1993.12.351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang Y. F., Young R., Moulds T. L., Struck D. K. Secretion of the Pasteurella leukotoxin by Escherichia coli. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1989 Jul 15;51(1):169–173. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(89)90502-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang Y. F., Young R., Struck D. K. Cloning and characterization of a hemolysin gene from Actinobacillus (Haemophilus) pleuropneumoniae. DNA. 1989 Nov;8(9):635–647. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1989.8.635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang Y. F., Young R., Struck D. K. The Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae hemolysin determinant: unlinked appCA and appBD loci flanked by pseudogenes. J Bacteriol. 1991 Aug;173(16):5151–5158. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.16.5151-5158.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu S., Trust T. J. An Aeromonas salmonicida gene which influences a-protein expression in Escherichia coli encodes a protein containing an ATP-binding cassette and maps beside the surface array protein gene. J Bacteriol. 1993 May;175(10):3105–3114. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.10.3105-3114.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung Y. J., Steen M. T., Hansen J. N. The subtilin gene of Bacillus subtilis ATCC 6633 is encoded in an operon that contains a homolog of the hemolysin B transport protein. J Bacteriol. 1992 Feb;174(4):1417–1422. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.4.1417-1422.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coote J. G. Structural and functional relationships among the RTX toxin determinants of gram-negative bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 1992 Feb;8(2):137–161. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1992.tb04961.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crisel R. M., Baker R. S., Dorman D. E. Capsular polymer of Haemophilus influenzae, type b. I. Structural characterization of the capsular polymer of strain Eagan. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jul 10;250(13):4926–4930. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davagnino J., Herrero M., Furlong D., Moreno F., Kolter R. The DNA replication inhibitor microcin B17 is a forty-three-amino-acid protein containing sixty percent glycine. Proteins. 1986 Nov;1(3):230–238. doi: 10.1002/prot.340010305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delepelaire P., Wandersman C. Characterization, localization and transmembrane organization of the three proteins PrtD, PrtE and PrtF necessary for protease secretion by the gram-negative bacterium Erwinia chrysanthemi. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Oct;5(10):2427–2434. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb02088.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delepelaire P., Wandersman C. Protease secretion by Erwinia chrysanthemi. Proteases B and C are synthesized and secreted as zymogens without a signal peptide. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 25;264(15):9083–9089. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delepelaire P., Wandersman C. Protein secretion in gram-negative bacteria. The extracellular metalloprotease B from Erwinia chrysanthemi contains a C-terminal secretion signal analogous to that of Escherichia coli alpha-hemolysin. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 5;265(28):17118–17125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devenish J., Rosendal S., Johnson R., Hubler S. Immunoserological comparison of 104-kilodalton proteins associated with hemolysis and cytolysis in Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae, Actinobacillus suis, Pasteurella haemolytica, and Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1989 Oct;57(10):3210–3213. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.10.3210-3213.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deverson E. V., Gow I. R., Coadwell W. J., Monaco J. J., Butcher G. W., Howard J. C. MHC class II region encoding proteins related to the multidrug resistance family of transmembrane transporters. Nature. 1990 Dec 20;348(6303):738–741. doi: 10.1038/348738a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doolittle R. F., Johnson M. S., Husain I., Van Houten B., Thomas D. C., Sancar A. Domainal evolution of a prokaryotic DNA repair protein and its relationship to active-transport proteins. Nature. 1986 Oct 2;323(6087):451–453. doi: 10.1038/323451a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas C. J., Staneloni R. J., Rubin R. A., Nester E. W. Identification and genetic analysis of an Agrobacterium tumefaciens chromosomal virulence region. J Bacteriol. 1985 Mar;161(3):850–860. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.3.850-860.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudler R., Hertig C. Structure of an mdr-like gene from Arabidopsis thaliana. Evolutionary implications. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 25;267(9):5882–5888. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duong F., Lazdunski A., Cami B., Murgier M. Sequence of a cluster of genes controlling synthesis and secretion of alkaline protease in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: relationships to other secretory pathways. Gene. 1992 Nov 2;121(1):47–54. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(92)90160-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dylan T., Ielpi L., Stanfield S., Kashyap L., Douglas C., Yanofsky M., Nester E., Helinski D. R., Ditta G. Rhizobium meliloti genes required for nodule development are related to chromosomal virulence genes in Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4403–4407. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eberspächer B., Hugo F., Pohl M., Bhakdi S. Functional similarity between the haemolysins of Escherichia coli and Morganella morganii. J Med Microbiol. 1990 Nov;33(3):165–170. doi: 10.1099/00222615-33-3-165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Economou A., Hamilton W. D., Johnston A. W., Downie J. A. The Rhizobium nodulation gene nodO encodes a Ca2(+)-binding protein that is exported without N-terminal cleavage and is homologous to haemolysin and related proteins. EMBO J. 1990 Feb;9(2):349–354. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08117.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endicott J. A., Ling V. The biochemistry of P-glycoprotein-mediated multidrug resistance. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:137–171. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.001033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelke G., Gutowski-Eckel Z., Hammelmann M., Entian K. D. Biosynthesis of the lantibiotic nisin: genomic organization and membrane localization of the NisB protein. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Nov;58(11):3730–3743. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.11.3730-3743.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ernst A., Black T., Cai Y., Panoff J. M., Tiwari D. N., Wolk C. P. Synthesis of nitrogenase in mutants of the cyanobacterium Anabaena sp. strain PCC 7120 affected in heterocyst development or metabolism. J Bacteriol. 1992 Oct;174(19):6025–6032. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.19.6025-6032.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans I. J., Downie J. A. The nodI gene product of Rhizobium leguminosarum is closely related to ATP-binding bacterial transport proteins; nucleotide sequence analysis of the nodI and nodJ genes. Gene. 1986;43(1-2):95–101. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90012-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fath M. J., Skvirsky R. C., Kolter R. Functional complementation between bacterial MDR-like export systems: colicin V, alpha-hemolysin, and Erwinia protease. J Bacteriol. 1991 Dec;173(23):7549–7556. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.23.7549-7556.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faulkner D. V., Jurka J. Multiple aligned sequence editor (MASE). Trends Biochem Sci. 1988 Aug;13(8):321–322. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(88)90129-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felmlee T., Pellett S., Lee E. Y., Welch R. A. Escherichia coli hemolysin is released extracellularly without cleavage of a signal peptide. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jul;163(1):88–93. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.1.88-93.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felmlee T., Pellett S., Welch R. A. Nucleotide sequence of an Escherichia coli chromosomal hemolysin. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jul;163(1):94–105. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.1.94-105.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felmlee T., Welch R. A. Alterations of amino acid repeats in the Escherichia coli hemolysin affect cytolytic activity and secretion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(14):5269–5273. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.14.5269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foote S. J., Thompson J. K., Cowman A. F., Kemp D. J. Amplification of the multidrug resistance gene in some chloroquine-resistant isolates of P. falciparum. Cell. 1989 Jun 16;57(6):921–930. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90330-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frey J., Beck M., Stucki U., Nicolet J. Analysis of hemolysin operons in Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae. Gene. 1993 Jan 15;123(1):51–58. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(93)90538-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frey J., van den Bosch H., Segers R., Nicolet J. Identification of a second hemolysin (HlyII) in Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae serotype 1 and expression of the gene in Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1992 Apr;60(4):1671–1676. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.4.1671-1676.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frosch M., Edwards U., Bousset K., Krausse B., Weisgerber C. Evidence for a common molecular origin of the capsule gene loci in gram-negative bacteria expressing group II capsular polysaccharides. Mol Microbiol. 1991 May;5(5):1251–1263. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb01899.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frosch M., Weisgerber C., Meyer T. F. Molecular characterization and expression in Escherichia coli of the gene complex encoding the polysaccharide capsule of Neisseria meningitidis group B. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(5):1669–1673. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.5.1669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrido M. C., Herrero M., Kolter R., Moreno F. The export of the DNA replication inhibitor Microcin B17 provides immunity for the host cell. EMBO J. 1988 Jun;7(6):1853–1862. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03018.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gentschev I., Goebel W. Topological and functional studies on HlyB of Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1992 Mar;232(1):40–48. doi: 10.1007/BF00299135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gentschev I., Hess J., Goebel W. Change in the cellular localization of alkaline phosphatase by alteration of its carboxy-terminal sequence. Mol Gen Genet. 1990 Jul;222(2-3):211–216. doi: 10.1007/BF00633820. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geremia R. A., Cavaignac S., Zorreguieta A., Toro N., Olivares J., Ugalde R. A. A Rhizobium meliloti mutant that forms ineffective pseudonodules in alfalfa produces exopolysaccharide but fails to form beta-(1----2) glucan. J Bacteriol. 1987 Feb;169(2):880–884. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.2.880-884.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghigo J. M., Wandersman C. Cloning, nucleotide sequence and characterization of the gene encoding the Erwinia chrysanthemi B374 PrtA metalloprotease: a third metalloprotease secreted via a C-terminal secretion signal. Mol Gen Genet. 1992 Dec;236(1):135–144. doi: 10.1007/BF00279652. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs T. W., Gill D. R., Salmond G. P. Localised mutagenesis of the fts YEX operon: conditionally lethal missense substitutions in the FtsE cell division protein of Escherichia coli are similar to those found in the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator protein (CFTR) of human patients. Mol Gen Genet. 1992 Jul;234(1):121–128. doi: 10.1007/BF00272353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill D. R., Hatfull G. F., Salmond G. P. A new cell division operon in Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1986 Oct;205(1):134–145. doi: 10.1007/BF02428043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill D. R., Salmond G. P. The Escherichia coli cell division proteins FtsY, FtsE and FtsX are inner membrane-associated. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Dec;210(3):504–508. doi: 10.1007/BF00327204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill D. R., Salmond G. P. The identification of the Escherichia coli ftsY gene product: an unusual protein. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Apr;4(4):575–583. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00626.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmore M. S., Segarra R. A., Booth M. C. An HlyB-type function is required for expression of the Enterococcus faecalis hemolysin/bacteriocin. Infect Immun. 1990 Dec;58(12):3914–3923. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.12.3914-3923.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilson L., Mahanty H. K., Kolter R. Four plasmid genes are required for colicin V synthesis, export, and immunity. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jun;169(6):2466–2470. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.6.2466-2470.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilson L., Mahanty H. K., Kolter R. Genetic analysis of an MDR-like export system: the secretion of colicin V. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(12):3875–3884. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07606.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glaser P., Sakamoto H., Bellalou J., Ullmann A., Danchin A. Secretion of cyclolysin, the calmodulin-sensitive adenylate cyclase-haemolysin bifunctional protein of Bordetella pertussis. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 1;7(12):3997–4004. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03288.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granato P. A., Jackson R. W. Bicomponent nature of lysin from Streptococcus zymogenes. J Bacteriol. 1969 Nov;100(2):865–868. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.2.865-868.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray L., Baker K., Kenny B., Mackman N., Haigh R., Holland I. B. A novel C-terminal signal sequence targets Escherichia coli haemolysin directly to the medium. J Cell Sci Suppl. 1989;11:45–57. doi: 10.1242/jcs.1989.supplement_11.4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray L., Mackman N., Nicaud J. M., Holland I. B. The carboxy-terminal region of haemolysin 2001 is required for secretion of the toxin from Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1986 Oct;205(1):127–133. doi: 10.1007/BF02428042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guilfoile P. G., Hutchinson C. R. A bacterial analog of the mdr gene of mammalian tumor cells is present in Streptomyces peucetius, the producer of daunorubicin and doxorubicin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 1;88(19):8553–8557. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.19.8553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guthmiller J. M., Kolodrubetz D., Cagle M. P., Kraig E. Sequence of the lktB gene from Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Sep 11;18(17):5291–5291. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.17.5291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guzzo J., Duong F., Wandersman C., Murgier M., Lazdunski A. The secretion genes of Pseudomonas aeruginosa alkaline protease are functionally related to those of Erwinia chrysanthemi proteases and Escherichia coli alpha-haemolysin. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Feb;5(2):447–453. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb02128.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guzzo J., Murgier M., Filloux A., Lazdunski A. Cloning of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa alkaline protease gene and secretion of the protease into the medium by Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1990 Feb;172(2):942–948. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.2.942-948.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guzzo J., Pages J. M., Duong F., Lazdunski A., Murgier M. Pseudomonas aeruginosa alkaline protease: evidence for secretion genes and study of secretion mechanism. J Bacteriol. 1991 Sep;173(17):5290–5297. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.17.5290-5297.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gygi D., Nicolet J., Frey J., Cross M., Koronakis V., Hughes C. Isolation of the Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae haemolysin gene and the activation and secretion of the prohaemolysin by the HlyC, HlyB and HlyD proteins of Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Jan;4(1):123–128. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb02021.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson D. M., Sifri C. D., Rodgers M., Wirth D. F., Hendrickson N., Ullman B. Multidrug resistance in Leishmania donovani is conferred by amplification of a gene homologous to the mammalian mdr1 gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jun;12(6):2855–2865. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.6.2855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson J. T., Chopko A. L., van Wassenaar P. D. Purification and primary structure of pediocin PA-1 produced by Pediococcus acidilactici PAC-1.0. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1992 May 15;295(1):5–12. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(92)90480-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess J., Gentschev I., Goebel W., Jarchau T. Analysis of the haemolysin secretion system by PhoA-HlyA fusion proteins. Mol Gen Genet. 1990 Nov;224(2):201–208. doi: 10.1007/BF00271553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewlett E. L., Gordon V. M., McCaffery J. D., Sutherland W. M., Gray M. C. Adenylate cyclase toxin from Bordetella pertussis. Identification and purification of the holotoxin molecule. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 15;264(32):19379–19384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
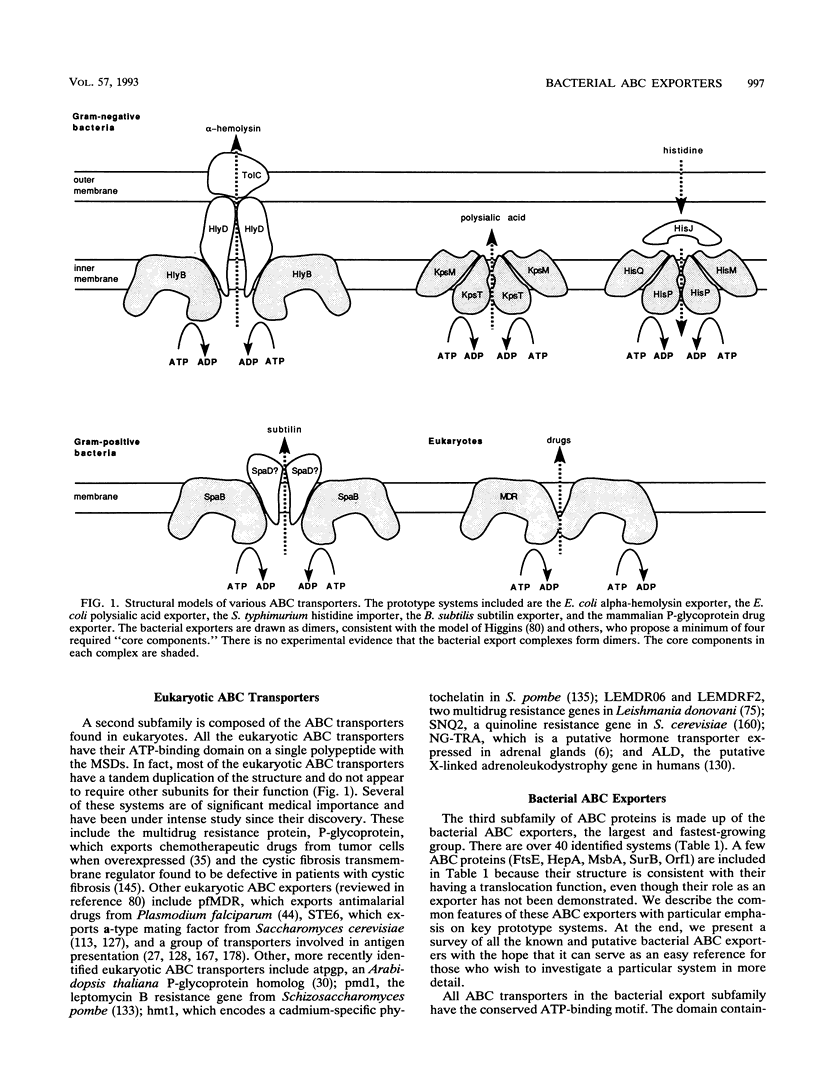
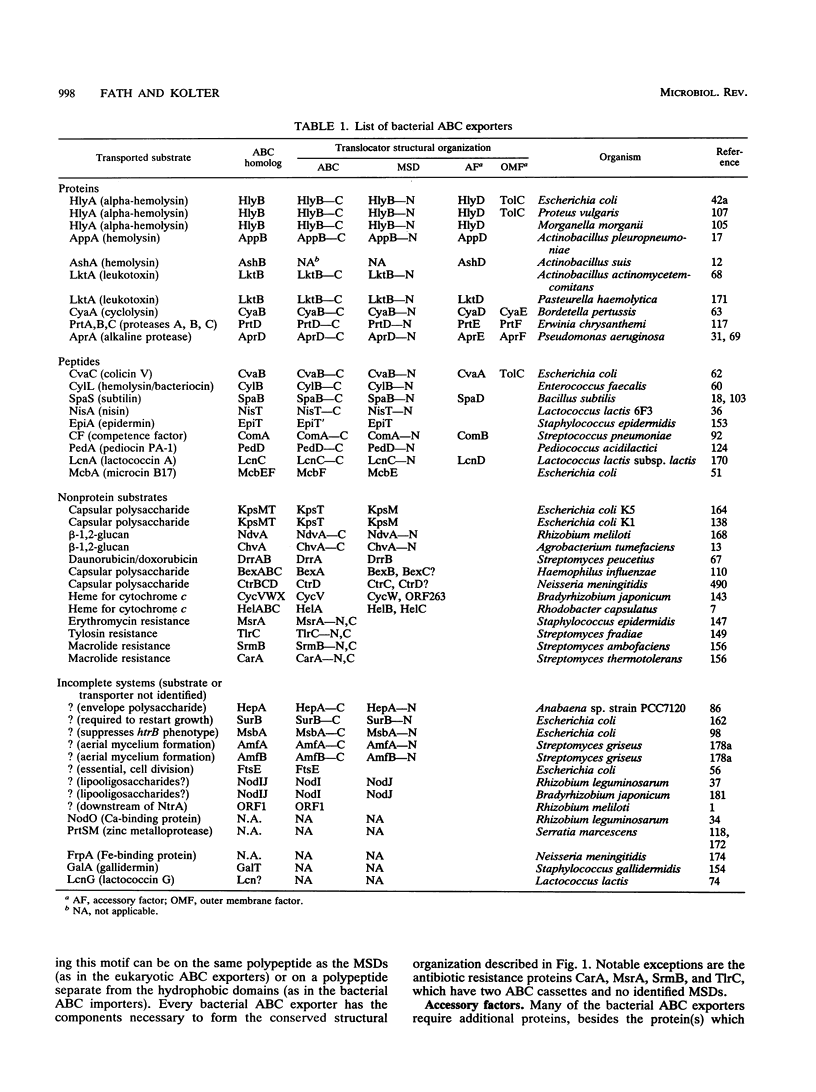
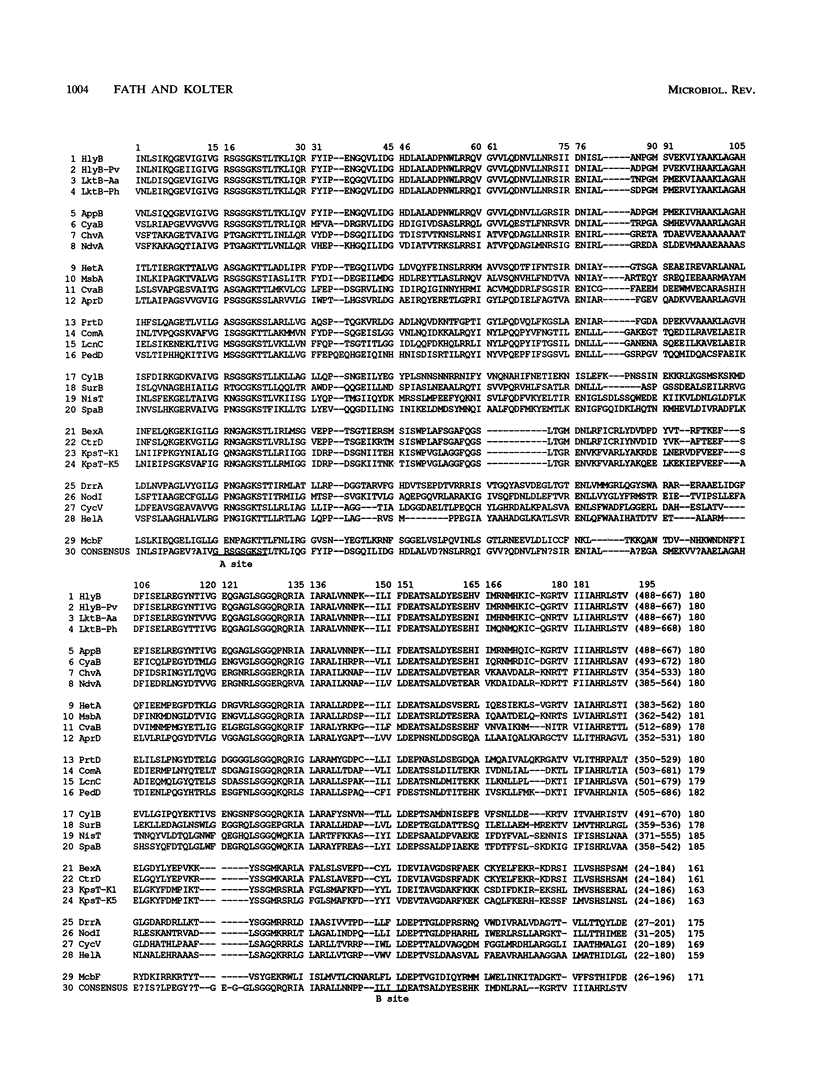
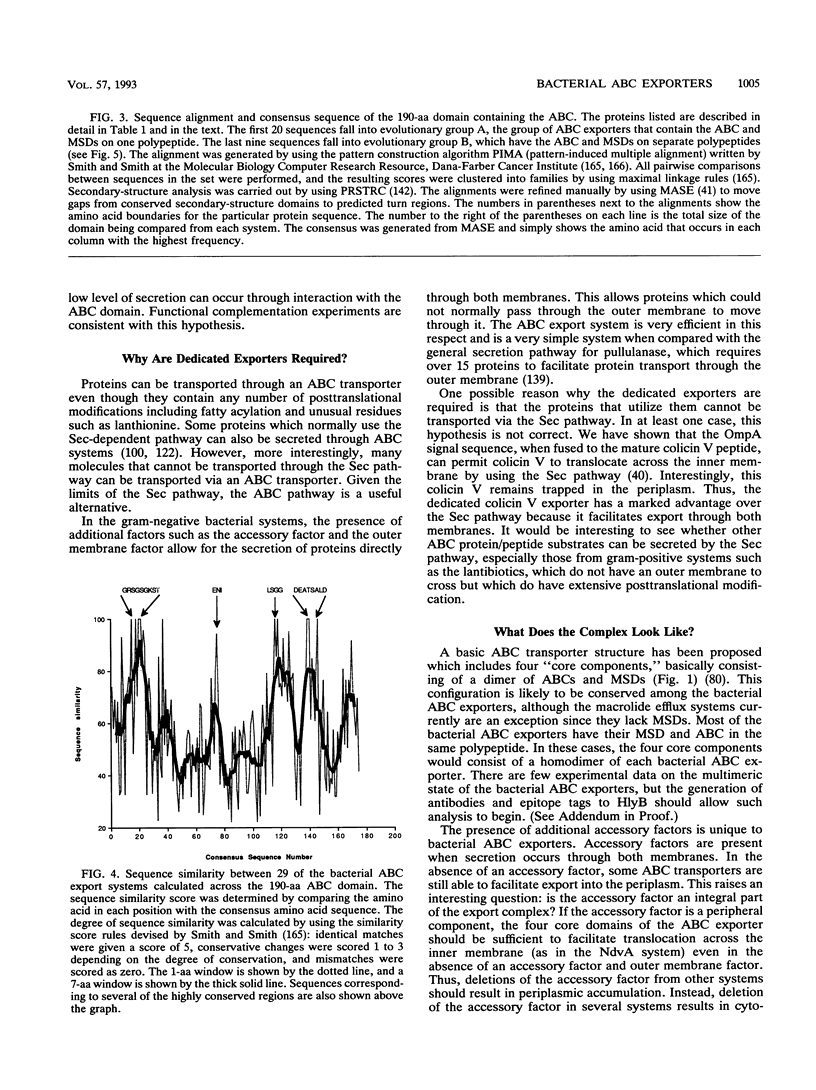
- Higgins C. F. ABC transporters: from microorganisms to man. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1992;8:67–113. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.08.110192.000435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins C. F., Gottesman M. M. Is the multidrug transporter a flippase? Trends Biochem Sci. 1992 Jan;17(1):18–21. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(92)90419-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins C. F., Hiles I. D., Salmond G. P., Gill D. R., Downie J. A., Evans I. J., Holland I. B., Gray L., Buckel S. D., Bell A. W. A family of related ATP-binding subunits coupled to many distinct biological processes in bacteria. Nature. 1986 Oct 2;323(6087):448–450. doi: 10.1038/323448a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins C. F., Hyde S. C., Mimmack M. M., Gileadi U., Gill D. R., Gallagher M. P. Binding protein-dependent transport systems. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 1990 Aug;22(4):571–592. doi: 10.1007/BF00762962. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Highlander S. K., Chidambaram M., Engler M. J., Weinstock G. M. DNA sequence of the Pasteurella haemolytica leukotoxin gene cluster. DNA. 1989 Jan-Feb;8(1):15–28. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1989.8.15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoiseth S. K., Connelly C. J., Moxon E. R. Genetics of spontaneous, high-frequency loss of b capsule expression in Haemophilus influenzae. Infect Immun. 1985 Aug;49(2):389–395. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.2.389-395.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland D., Wolk C. P. Identification and characterization of hetA, a gene that acts early in the process of morphological differentiation of heterocysts. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jun;172(6):3131–3137. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.6.3131-3137.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland I. B., Blight M. A., Kenny B. The mechanism of secretion of hemolysin and other polypeptides from gram-negative bacteria. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 1990 Jun;22(3):473–491. doi: 10.1007/BF00763178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland I. B., Kenny B., Blight M. Haemolysin secretion from E coli. Biochimie. 1990 Feb-Mar;72(2-3):131–141. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(90)90138-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holo H., Nilssen O., Nes I. F. Lactococcin A, a new bacteriocin from Lactococcus lactis subsp. cremoris: isolation and characterization of the protein and its gene. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jun;173(12):3879–3887. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.12.3879-3887.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe T. R., Iglewski B. H. Isolation and characterization of alkaline protease-deficient mutants of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in vitro and in a mouse eye model. Infect Immun. 1984 Mar;43(3):1058–1063. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.3.1058-1063.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes C., Stanley P., Koronakis V. E. coli hemolysin interactions with prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell membranes. Bioessays. 1992 Aug;14(8):519–525. doi: 10.1002/bies.950140804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hui F. M., Morrison D. A. Genetic transformation in Streptococcus pneumoniae: nucleotide sequence analysis shows comA, a gene required for competence induction, to be a member of the bacterial ATP-dependent transport protein family. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jan;173(1):372–381. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.1.372-381.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ike Y., Clewell D. B., Segarra R. A., Gilmore M. S. Genetic analysis of the pAD1 hemolysin/bacteriocin determinant in Enterococcus faecalis: Tn917 insertional mutagenesis and cloning. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jan;172(1):155–163. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.1.155-163.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Issartel J. P., Koronakis V., Hughes C. Activation of Escherichia coli prohaemolysin to the mature toxin by acyl carrier protein-dependent fatty acylation. Nature. 1991 Jun 27;351(6329):759–761. doi: 10.1038/351759a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansen R., Briaire J., Kamp E. M., Gielkens A. L., Smits M. A. Cloning and characterization of the Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae-RTX-toxin III (ApxIII) gene. Infect Immun. 1993 Mar;61(3):947–954. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.3.947-954.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juranka P., Zhang F., Kulpa J., Endicott J., Blight M., Holland I. B., Ling V. Characterization of the hemolysin transporter, HlyB, using an epitope insertion. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 25;267(6):3764–3770. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaletta C., Entian K. D. Nisin, a peptide antibiotic: cloning and sequencing of the nisA gene and posttranslational processing of its peptide product. J Bacteriol. 1989 Mar;171(3):1597–1601. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.3.1597-1601.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karow M., Georgopoulos C. Isolation and characterization of the Escherichia coli msbB gene, a multicopy suppressor of null mutations in the high-temperature requirement gene htrB. J Bacteriol. 1992 Feb;174(3):702–710. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.3.702-710.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karow M., Georgopoulos C. The essential Escherichia coli msbA gene, a multicopy suppressor of null mutations in the htrB gene, is related to the universally conserved family of ATP-dependent translocators. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Jan;7(1):69–79. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01098.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny B., Haigh R., Holland I. B. Analysis of the haemolysin transport process through the secretion from Escherichia coli of PCM, CAT or beta-galactosidase fused to the Hly C-terminal signal domain. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Oct;5(10):2557–2568. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb02102.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny B., Taylor S., Holland I. B. Identification of individual amino acids required for secretion within the haemolysin (HlyA) C-terminal targeting region. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Jun;6(11):1477–1489. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb00868.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerppola R. E., Shyamala V. K., Klebba P., Ames G. F. The membrane-bound proteins of periplasmic permeases form a complex. Identification of the histidine permease HisQMP complex. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 25;266(15):9857–9865. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein C., Kaletta C., Schnell N., Entian K. D. Analysis of genes involved in biosynthesis of the lantibiotic subtilin. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Jan;58(1):132–142. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.1.132-142.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolter R., Moreno F. Genetics of ribosomally synthesized peptide antibiotics. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1992;46:141–163. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.46.100192.001041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koronakis V., Cross M., Senior B., Koronakis E., Hughes C. The secreted hemolysins of Proteus mirabilis, Proteus vulgaris, and Morganella morganii are genetically related to each other and to the alpha-hemolysin of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1987 Apr;169(4):1509–1515. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.4.1509-1515.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koronakis V., Hughes C., Koronakis E. ATPase activity and ATP/ADP-induced conformational change in the soluble domain of the bacterial protein translocator HlyB. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Jun;8(6):1163–1175. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01661.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koronakis V., Hughes C., Koronakis E. Energetically distinct early and late stages of HlyB/HlyD-dependent secretion across both Escherichia coli membranes. EMBO J. 1991 Nov;10(11):3263–3272. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04890.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koronakis V., Koronakis E., Hughes C. Comparison of the haemolysin secretion protein HlyB from Proteus vulgaris and Escherichia coli; site-directed mutagenesis causing impairment of export function. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 Aug;213(2-3):551–555. doi: 10.1007/BF00339631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koronakis V., Koronakis E., Hughes C. Isolation and analysis of the C-terminal signal directing export of Escherichia coli hemolysin protein across both bacterial membranes. EMBO J. 1989 Feb;8(2):595–605. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03414.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraig E., Dailey T., Kolodrubetz D. Nucleotide sequence of the leukotoxin gene from Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans: homology to the alpha-hemolysin/leukotoxin gene family. Infect Immun. 1990 Apr;58(4):920–929. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.4.920-929.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroll J. S., Hopkins I., Moxon E. R. Capsule loss in H. influenzae type b occurs by recombination-mediated disruption of a gene essential for polysaccharide export. Cell. 1988 May 6;53(3):347–356. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90155-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroll J. S., Loynds B., Brophy L. N., Moxon E. R. The bex locus in encapsulated Haemophilus influenzae: a chromosomal region involved in capsule polysaccharide export. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Nov;4(11):1853–1862. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb02034.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kröncke K. D., Boulnois G., Roberts I., Bitter-Suermann D., Golecki J. R., Jann B., Jann K. Expression of the Escherichia coli K5 capsular antigen: immunoelectron microscopic and biochemical studies with recombinant E. coli. J Bacteriol. 1990 Feb;172(2):1085–1091. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.2.1085-1091.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuchler K., Sterne R. E., Thorner J. Saccharomyces cerevisiae STE6 gene product: a novel pathway for protein export in eukaryotic cells. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 20;8(13):3973–3984. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08580.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ladant D. Interaction of Bordetella pertussis adenylate cyclase with calmodulin. Identification of two separated calmodulin-binding domains. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 25;263(6):2612–2618. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lally E. T., Golub E. E., Kieba I. R., Taichman N. S., Rosenbloom J., Rosenbloom J. C., Gibson C. W., Demuth D. R. Analysis of the Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans leukotoxin gene. Delineation of unique features and comparison to homologous toxins. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 15;264(26):15451–15456. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C., Li P., Inouye H., Brickman E. R., Beckwith J. Genetic studies on the inability of beta-galactosidase to be translocated across the Escherichia coli cytoplasmic membrane. J Bacteriol. 1989 Sep;171(9):4609–4616. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.9.4609-4616.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lory S. Determinants of extracellular protein secretion in gram-negative bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jun;174(11):3423–3428. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.11.3423-3428.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Létoffé S., Delepelaire P., Wandersman C. Cloning and expression in Escherichia coli of the Serratia marcescens metalloprotease gene: secretion of the protease from E. coli in the presence of the Erwinia chrysanthemi protease secretion functions. J Bacteriol. 1991 Apr;173(7):2160–2166. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.7.2160-2166.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Létoffé S., Delepelaire P., Wandersman C. Protease secretion by Erwinia chrysanthemi: the specific secretion functions are analogous to those of Escherichia coli alpha-haemolysin. EMBO J. 1990 May;9(5):1375–1382. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08252.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Létoffé S., Wandersman C. Secretion of CyaA-PrtB and HlyA-PrtB fusion proteins in Escherichia coli: involvement of the glycine-rich repeat domain of Erwinia chrysanthemi protease B. J Bacteriol. 1992 Aug;174(15):4920–4927. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.15.4920-4927.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackman N., Baker K., Gray L., Haigh R., Nicaud J. M., Holland I. B. Release of a chimeric protein into the medium from Escherichia coli using the C-terminal secretion signal of haemolysin. EMBO J. 1987 Sep;6(9):2835–2841. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02580.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackman N., Nicaud J. M., Gray L., Holland I. B. Identification of polypeptides required for the export of haemolysin 2001 from E. coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1985;201(3):529–536. doi: 10.1007/BF00331351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marugg J. D., Gonzalez C. F., Kunka B. S., Ledeboer A. M., Pucci M. J., Toonen M. Y., Walker S. A., Zoetmulder L. C., Vandenbergh P. A. Cloning, expression, and nucleotide sequence of genes involved in production of pediocin PA-1, and bacteriocin from Pediococcus acidilactici PAC1.0. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Aug;58(8):2360–2367. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.8.2360-2367.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masure H. R., Au D. C., Gross M. K., Donovan M. G., Storm D. R. Secretion of the Bordetella pertussis adenylate cyclase from Escherichia coli containing the hemolysin operon. Biochemistry. 1990 Jan 9;29(1):140–145. doi: 10.1021/bi00453a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masure H. R., Storm D. R. Characterization of the bacterial cell associated calmodulin-sensitive adenylate cyclase from Bordetella pertussis. Biochemistry. 1989 Jan 24;28(2):438–442. doi: 10.1021/bi00428a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGrath J. P., Varshavsky A. The yeast STE6 gene encodes a homologue of the mammalian multidrug resistance P-glycoprotein. Nature. 1989 Aug 3;340(6232):400–404. doi: 10.1038/340400a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monaco J. J., Cho S., Attaya M. Transport protein genes in the murine MHC: possible implications for antigen processing. Science. 1990 Dec 21;250(4988):1723–1726. doi: 10.1126/science.2270487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosser J., Douar A. M., Sarde C. O., Kioschis P., Feil R., Moser H., Poustka A. M., Mandel J. L., Aubourg P. Putative X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy gene shares unexpected homology with ABC transporters. Nature. 1993 Feb 25;361(6414):726–730. doi: 10.1038/361726a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakahama K., Yoshimura K., Marumoto R., Kikuchi M., Lee I. S., Hase T., Matsubara H. Cloning and sequencing of Serratia protease gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jul 25;14(14):5843–5855. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.14.5843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nieto Lozano J. C., Meyer J. N., Sletten K., Peláz C., Nes I. F. Purification and amino acid sequence of a bacteriocin produced by Pediococcus acidilactici. J Gen Microbiol. 1992 Sep;138(9):1985–1990. doi: 10.1099/00221287-138-9-1985. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niki H., Imamura R., Ogura T., Hiraga S. Nucleotide sequence of the tolC gene of Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Sep 25;18(18):5547–5547. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.18.5547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishi K., Yoshida M., Nishimura M., Nishikawa M., Nishiyama M., Horinouchi S., Beppu T. A leptomycin B resistance gene of Schizosaccharomyces pombe encodes a protein similar to the mammalian P-glycoproteins. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Mar;6(6):761–769. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01526.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oropeza-Wekerle R. L., Speth W., Imhof B., Gentschev I., Goebel W. Translocation and compartmentalization of Escherichia coli hemolysin (HlyA). J Bacteriol. 1990 Jul;172(7):3711–3717. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.7.3711-3717.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ortiz D. F., Kreppel L., Speiser D. M., Scheel G., McDonald G., Ow D. W. Heavy metal tolerance in the fission yeast requires an ATP-binding cassette-type vacuolar membrane transporter. EMBO J. 1992 Oct;11(10):3491–3499. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05431.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otten S. L., Stutzman-Engwall K. J., Hutchinson C. R. Cloning and expression of daunorubicin biosynthesis genes from Streptomyces peucetius and S. peucetius subsp. caesius. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jun;172(6):3427–3434. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.6.3427-3434.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Page M. D., Ferguson S. J. A bacterial c-type cytochrome can be translocated to the periplasm as an apo form; the biosynthesis of cytochrome cd1 (nitrite reductase) from Paracoccus denitrificans. Mol Microbiol. 1989 May;3(5):653–661. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavelka M. S., Jr, Wright L. F., Silver R. P. Identification of two genes, kpsM and kpsT, in region 3 of the polysialic acid gene cluster of Escherichia coli K1. J Bacteriol. 1991 Aug;173(15):4603–4610. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.15.4603-4610.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugsley A. P. The complete general secretory pathway in gram-negative bacteria. Microbiol Rev. 1993 Mar;57(1):50–108. doi: 10.1128/mr.57.1.50-108.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugsley A. P., d'Enfert C., Reyss I., Kornacker M. G. Genetics of extracellular protein secretion by gram-negative bacteria. Annu Rev Genet. 1990;24:67–90. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.24.120190.000435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puvanesarajah V., Schell F. M., Stacey G., Douglas C. J., Nester E. W. Role for 2-linked-beta-D-glucan in the virulence of Agrobacterium tumefaciens. J Bacteriol. 1985 Oct;164(1):102–106. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.1.102-106.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ralph W. W., Webster T., Smith T. F. A modified Chou and Fasman protein structure algorithm. Comput Appl Biosci. 1987 Sep;3(3):211–216. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/3.3.211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramseier T. M., Winteler H. V., Hennecke H. Discovery and sequence analysis of bacterial genes involved in the biogenesis of c-type cytochromes. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 25;266(12):7793–7803. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reizer J., Reizer A., Saier M. H., Jr A new subfamily of bacterial ABC-type transport systems catalyzing export of drugs and carbohydrates. Protein Sci. 1992 Oct;1(10):1326–1332. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560011012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riordan J. R., Rommens J. M., Kerem B., Alon N., Rozmahel R., Grzelczak Z., Zielenski J., Lok S., Plavsic N., Chou J. L. Identification of the cystic fibrosis gene: cloning and characterization of complementary DNA. Science. 1989 Sep 8;245(4922):1066–1073. doi: 10.1126/science.2475911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts I., Mountford R., High N., Bitter-Suermann D., Jann K., Timmis K., Boulnois G. Molecular cloning and analysis of genes for production of K5, K7, K12, and K92 capsular polysaccharides in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1986 Dec;168(3):1228–1233. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.3.1228-1233.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez A. M., Olano C., Vilches C., Méndez C., Salas J. A. Streptomyces antibioticus contains at least three oleandomycin-resistance determinants, one of which shows similarity with proteins of the ABC-transporter superfamily. Mol Microbiol. 1993 May;8(3):571–582. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01601.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross J. I., Eady E. A., Cove J. H., Cunliffe W. J., Baumberg S., Wootton J. C. Inducible erythromycin resistance in staphylococci is encoded by a member of the ATP-binding transport super-gene family. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Jul;4(7):1207–1214. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00696.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosteck P. R., Jr, Reynolds P. A., Hershberger C. L. Homology between proteins controlling Streptomyces fradiae tylosin resistance and ATP-binding transport. Gene. 1991 Jun 15;102(1):27–32. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90533-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salmond G. P., Reeves P. J. Membrane traffic wardens and protein secretion in gram-negative bacteria. Trends Biochem Sci. 1993 Jan;18(1):7–12. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(93)90080-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schatz P. J., Beckwith J. Genetic analysis of protein export in Escherichia coli. Annu Rev Genet. 1990;24:215–248. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.24.120190.001243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheu A. K., Economou A., Hong G. F., Ghelani S., Johnston A. W., Downie J. A. Secretion of the Rhizobium leguminosarum nodulation protein NodO by haemolysin-type systems. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Jan;6(2):231–238. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb02004.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnell N., Engelke G., Augustin J., Rosenstein R., Ungermann V., Götz F., Entian K. D. Analysis of genes involved in the biosynthesis of lantibiotic epidermin. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Feb 15;204(1):57–68. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb16605.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnell N., Entian K. D., Götz F., Hörner T., Kellner R., Jung G. Structural gene isolation and prepeptide sequence of gallidermin, a new lanthionine containing antibiotic. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1989 Apr;49(2-3):263–267. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(89)90050-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnell N., Entian K. D., Schneider U., Götz F., Zähner H., Kellner R., Jung G. Prepeptide sequence of epidermin, a ribosomally synthesized antibiotic with four sulphide-rings. Nature. 1988 May 19;333(6170):276–278. doi: 10.1038/333276a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoner B., Geistlich M., Rosteck P., Jr, Rao R. N., Seno E., Reynolds P., Cox K., Burgett S., Hershberger C. Sequence similarity between macrolide-resistance determinants and ATP-binding transport proteins. Gene. 1992 Jun 15;115(1-2):93–96. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(92)90545-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schülein R., Gentschev I., Mollenkopf H. J., Goebel W. A topological model for the haemolysin translocator protein HlyD. Mol Gen Genet. 1992 Jul;234(1):155–163. doi: 10.1007/BF00272357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sebo P., Glaser P., Sakamoto H., Ullmann A. High-level synthesis of active adenylate cyclase toxin of Bordetella pertussis in a reconstructed Escherichia coli system. Gene. 1991 Jul 31;104(1):19–24. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90459-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Servos J., Haase E., Brendel M. Gene SNQ2 of Saccharomyces cerevisiae, which confers resistance to 4-nitroquinoline-N-oxide and other chemicals, encodes a 169 kDa protein homologous to ATP-dependent permeases. Mol Gen Genet. 1993 Jan;236(2-3):214–218. doi: 10.1007/BF00277115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegele D. A., Kolter R. Life after log. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jan;174(2):345–348. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.2.345-348.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A. N., Boulnois G. J., Roberts I. S. Molecular analysis of the Escherichia coli K5 kps locus: identification and characterization of an inner-membrane capsular polysaccharide transport system. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Nov;4(11):1863–1869. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb02035.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. F., Smith T. F. Automatic generation of primary sequence patterns from sets of related protein sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(1):118–122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.1.118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. F., Smith T. F. Pattern-induced multi-sequence alignment (PIMA) algorithm employing secondary structure-dependent gap penalties for use in comparative protein modelling. Protein Eng. 1992 Jan;5(1):35–41. doi: 10.1093/protein/5.1.35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spies T., Bresnahan M., Bahram S., Arnold D., Blanck G., Mellins E., Pious D., DeMars R. A gene in the human major histocompatibility complex class II region controlling the class I antigen presentation pathway. Nature. 1990 Dec 20;348(6303):744–747. doi: 10.1038/348744a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanfield S. W., Ielpi L., O'Brochta D., Helinski D. R., Ditta G. S. The ndvA gene product of Rhizobium meliloti is required for beta-(1----2)glucan production and has homology to the ATP-binding export protein HlyB. J Bacteriol. 1988 Aug;170(8):3523–3530. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.8.3523-3530.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley P., Koronakis V., Hughes C. Mutational analysis supports a role for multiple structural features in the C-terminal secretion signal of Escherichia coli haemolysin. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Oct;5(10):2391–2403. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb02085.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoddard G. W., Petzel J. P., van Belkum M. J., Kok J., McKay L. L. Molecular analyses of the lactococcin A gene cluster from Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis biovar diacetylactis WM4. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Jun;58(6):1952–1961. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.6.1952-1961.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strathdee C. A., Lo R. Y. Cloning, nucleotide sequence, and characterization of genes encoding the secretion function of the Pasteurella haemolytica leukotoxin determinant. J Bacteriol. 1989 Feb;171(2):916–928. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.2.916-928.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suh Y., Benedik M. J. Production of active Serratia marcescens metalloprotease from Escherichia coli by alpha-hemolysin HlyB and HlyD. J Bacteriol. 1992 Apr;174(7):2361–2366. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.7.2361-2366.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas W. D., Jr, Wagner S. P., Welch R. A. A heterologous membrane protein domain fused to the C-terminal ATP-binding domain of HlyB can export Escherichia coli hemolysin. J Bacteriol. 1992 Nov;174(21):6771–6779. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.21.6771-6779.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson S. A., Wang L. L., Sparling P. F. Cloning and nucleotide sequence of frpC, a second gene from Neisseria meningitidis encoding a protein similar to RTX cytotoxins. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Jul;9(1):85–96. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01671.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson S. A., Wang L. L., West A., Sparling P. F. Neisseria meningitidis produces iron-regulated proteins related to the RTX family of exoproteins. J Bacteriol. 1993 Feb;175(3):811–818. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.3.811-818.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasz A., Mosser J. L. On the nature of the pneumococcal activator substance. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Jan;55(1):58–66. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.1.58. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tommassen J., Filloux A., Bally M., Murgier M., Lazdunski A. Protein secretion in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 1992 Sep;9(1):73–90. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(92)90336-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tormo A., Almirón M., Kolter R. surA, an Escherichia coli gene essential for survival in stationary phase. J Bacteriol. 1990 Aug;172(8):4339–4347. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.8.4339-4347.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trowsdale J., Hanson I., Mockridge I., Beck S., Townsend A., Kelly A. Sequences encoded in the class II region of the MHC related to the 'ABC' superfamily of transporters. Nature. 1990 Dec 20;348(6303):741–744. doi: 10.1038/348741a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueda K., Miyake K., Horinouchi S., Beppu T. A gene cluster involved in aerial mycelium formation in Streptomyces griseus encodes proteins similar to the response regulators of two-component regulatory systems and membrane translocators. J Bacteriol. 1993 Apr;175(7):2006–2016. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.7.2006-2016.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vázquez M., Santana O., Quinto C. The NodL and NodJ proteins from Rhizobium and Bradyrhizobium strains are similar to capsular polysaccharide secretion proteins from gram-negative bacteria. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Apr;8(2):369–377. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01580.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. E., Saraste M., Runswick M. J., Gay N. J. Distantly related sequences in the alpha- and beta-subunits of ATP synthase, myosin, kinases and other ATP-requiring enzymes and a common nucleotide binding fold. EMBO J. 1982;1(8):945–951. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01276.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wandersman C., Delepelaire P., Letoffe S., Schwartz M. Characterization of Erwinia chrysanthemi extracellular proteases: cloning and expression of the protease genes in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1987 Nov;169(11):5046–5053. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.11.5046-5053.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wandersman C., Delepelaire P. TolC, an Escherichia coli outer membrane protein required for hemolysin secretion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(12):4776–4780. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4776. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wandersman C., Létoffé S. Involvement of lipopolysaccharide in the secretion of Escherichia coli alpha-haemolysin and Erwinia chrysanthemi proteases. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Jan;7(1):141–150. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01105.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wandersman C. Secretion across the bacterial outer membrane. Trends Genet. 1992 Sep;8(9):317–322. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(92)90264-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wandersman C. Secretion, processing and activation of bacterial extracellular proteases. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Dec;3(12):1825–1831. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00169.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang R. C., Seror S. J., Blight M., Pratt J. M., Broome-Smith J. K., Holland I. B. Analysis of the membrane organization of an Escherichia coli protein translocator, HlyB, a member of a large family of prokaryote and eukaryote surface transport proteins. J Mol Biol. 1991 Feb 5;217(3):441–454. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90748-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waters V. L., Crosa J. H. Colicin V virulence plasmids. Microbiol Rev. 1991 Sep;55(3):437–450. doi: 10.1128/mr.55.3.437-450.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch R. A., Forestier C., Lobo A., Pellett S., Thomas W., Jr, Rowe G. The synthesis and function of the Escherichia coli hemolysin and related RTX exotoxins. FEMS Microbiol Immunol. 1992 Sep;5(1-3):29–36. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1992.tb05883.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickner W., Driessen A. J., Hartl F. U. The enzymology of protein translocation across the Escherichia coli plasma membrane. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:101–124. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.60.070191.000533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wootton J. C., Drummond M. H. The Q-linker: a class of interdomain sequences found in bacterial multidomain regulatory proteins. Protein Eng. 1989 May;2(7):535–543. doi: 10.1093/protein/2.7.535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang C. C., Konisky J. Colicin V-treated Escherichia coli does not generate membrane potential. J Bacteriol. 1984 May;158(2):757–759. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.2.757-759.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zevenhuizen L. P., Scholten-Koerselman H. J. Surface carbohydrates of Rhizobium. I. Beta-1, 2-glucans. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1979;45(2):165–175. doi: 10.1007/BF00418581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Maagd R. A., Wijfjes A. H., Spaink H. P., Ruiz-Sainz J. E., Wijffelman C. A., Okker R. J., Lugtenberg B. J. nodO, a new nod gene of the Rhizobium leguminosarum biovar viciae sym plasmid pRL1JI, encodes a secreted protein. J Bacteriol. 1989 Dec;171(12):6764–6770. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.12.6764-6770.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Belkum M. J., Hayema B. J., Geis A., Kok J., Venema G. Cloning of two bacteriocin genes from a lactococcal bacteriocin plasmid. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 May;55(5):1187–1191. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.5.1187-1191.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Belkum M. J., Hayema B. J., Jeeninga R. E., Kok J., Venema G. Organization and nucleotide sequences of two lactococcal bacteriocin operons. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Feb;57(2):492–498. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.2.492-498.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


