Abstract
The removal of cell-bound water through air drying and the addition of water to air-dried cells are forces that have played a pivotal role in the evolution of the prokaryotes. In bacterial cells that have been subjected to air drying, the evaporation of free cytoplasmic water (Vf) can be instantaneous, and an equilibrium between cell-bound water (Vb) and the environmental water (vapor) potential (psi wv) may be achieved rapidly. In the air-dried state some bacteria survive only for seconds whereas others can tolerate desiccation for thousands, perhaps millions, of years. The desiccated (anhydrobiotic) cell is characterized by its singular lack of water--with contents as low as 0.02 g of H2O g (dry weight)-1. At these levels the monolayer coverage by water of macromolecules, including DNA and proteins, is disturbed. As a consequence the mechanisms that confer desiccation tolerance upon air-dried bacteria are markedly different from those, such as the mechanism of preferential exclusion of compatible solutes, that preserve the integrity of salt-, osmotically, and freeze-thaw-stressed cells. Desiccation tolerance reflects a complex array of interactions at the structural, physiological, and molecular levels. Many of the mechanisms remain cryptic, but it is clear that they involve interactions, such as those between proteins and co-solvents, that derive from the unique properties of the water molecule. A water replacement hypothesis accounts for how the nonreducing disaccharides trehalose and sucrose preserve the integrity of membranes and proteins. Nevertheless, we have virtually no insight into the state of the cytoplasm of an air-dried cell. There is no evidence for any obvious adaptations of proteins that can counter the effects of air drying or for the occurrence of any proteins that provide a direct and a tangible contribution to cell stability. Among the prokaryotes that can exist as anhydrobiotic cells, the cyanobacteria have a marked capacity to do so. One form, Nostoc commune, encompasses a number of the features that appear to be critical to the withstanding of a long-term water deficit, including the elaboration of a conspicuous extracellular glycan, synthesis of abundant UV-absorbing pigments, and maintenance of protein stability and structural integrity. There are indications of a growing technology for air-dried cells and enzymes. Paradoxically, desiccation tolerance of bacteria has virtually been ignored for the past quarter century. The present review considers what is known, and what is not known, about desiccation, a phenomenon that impinges upon every facet of the distributions and activities of prokaryotic cells.
Full text
PDF
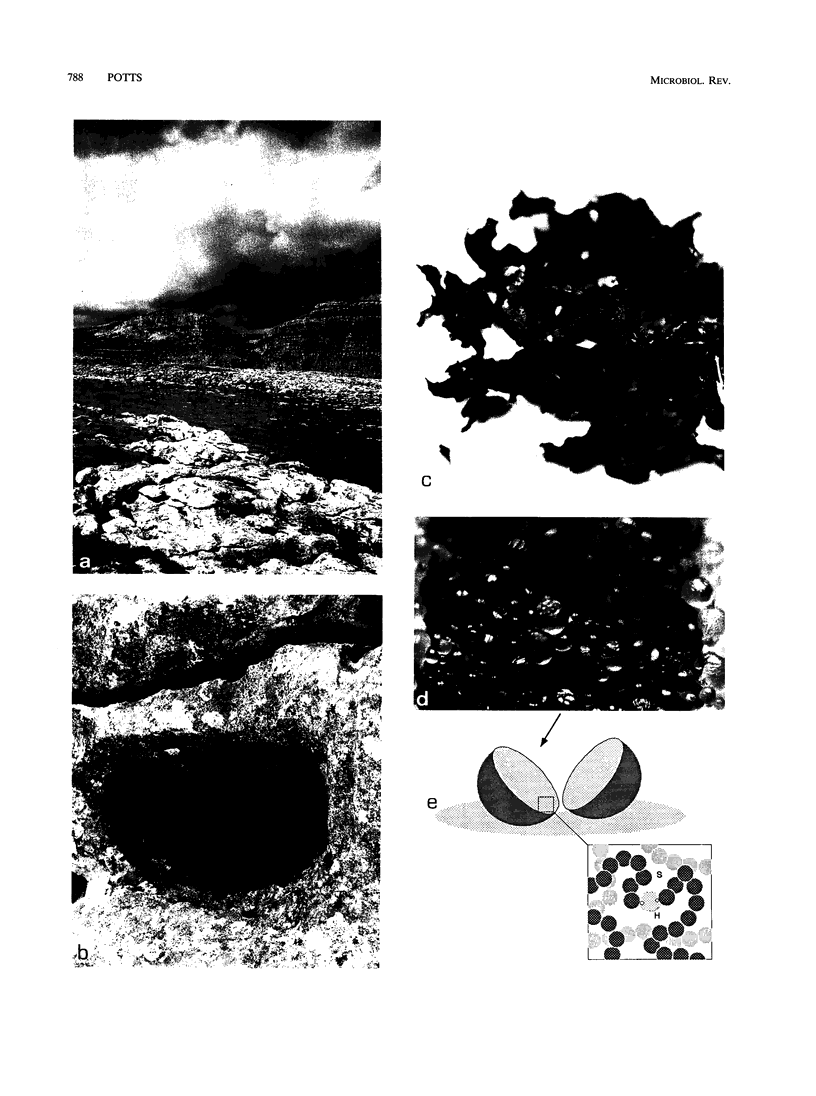


































Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agarwal S., Sohal R. S. Relationship between aging and susceptibility to protein oxidative damage. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 Aug 16;194(3):1203–1206. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.1950. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen M. M. Cyanobacterial cell inclusions. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1984;38:1–25. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.38.100184.000245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angeloni S. V., Potts M. Polysome turnover in immobilized cells of Nostoc commune (cyanobacteria) exposed to water stress. J Bacteriol. 1986 Nov;168(2):1036–1039. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.2.1036-1039.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Antheunisse J., Arkesteijn-Dijksman L. Rate of drying and the survival of microorganisms. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1979;45(2):177–184. doi: 10.1007/BF00418582. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Antheunisse J., de Bruin-Tol J. W., van der Pol-van Soest M. E. Survival of microorganisms after drying and storage. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1981;47(6):539–545. doi: 10.1007/BF00443240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Argall M. E., Smith G. D. The use of trehalose-stabilized lyophilized methanol dehydrogenase from Hyphomicrobium X for the detection of methanol. Biochem Mol Biol Int. 1993 Jul;30(3):491–497. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asada S., Takano M., Shibasaki I. Mutation induced by drying of Escherichia coli on a hydrophobic filter membrane. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Aug;40(2):274–281. doi: 10.1128/aem.40.2.274-281.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bakaltcheva I., Williams W. P., Schmitt J. M., Hincha D. K. The solute permeability of thylakoid membranes is reduced by low concentrations of trehalose as a co-solute. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1994 Jan 3;1189(1):38–44. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(94)90277-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartlett D. H., Wright M. E., Silverman M. Variable expression of extracellular polysaccharide in the marine bacterium Pseudomonas atlantica is controlled by genome rearrangement. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(11):3923–3927. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.11.3923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berry A. M., Harriott O. T., Moreau R. A., Osman S. F., Benson D. R., Jones A. D. Hopanoid lipids compose the Frankia vesicle envelope, presumptive barrier of oxygen diffusion to nitrogenase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 1;90(13):6091–6094. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.13.6091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Besra G. S., Bolton R. C., McNeil M. R., Ridell M., Simpson K. E., Glushka J., van Halbeek H., Brennan P. J., Minnikin D. E. Structural elucidation of a novel family of acyltrehaloses from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Biochemistry. 1992 Oct 13;31(40):9832–9837. doi: 10.1021/bi00155a040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bieger-Dose A., Dose K., Meffert R., Mehler M., Risi S. Extreme dryness and DNA-protein cross-links. Adv Space Res. 1992;12(4):265–270. doi: 10.1016/0273-1177(92)90181-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonani G., Friedmann E. I., Ocampo-Friedmann R., McKay C. P., Woelfli W. Preliminary report on radiocarbon dating of cryptoendolithic microorganisms. Polarforschung. 1988;58(2-3):199–200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boos W., Ehmann U., Bremer E., Middendorf A., Postma P. Trehalase of Escherichia coli. Mapping and cloning of its structural gene and identification of the enzyme as a periplasmic protein induced under high osmolarity growth conditions. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 25;262(27):13212–13218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braune W., Sanke H. Interferometrische Untersuchungen zur Dynamik von Hydratur und Trockenmassegehalt während der lichtabhängigen Keimung der Akineten von Anabaena variabilis Kützing. Z Allg Mikrobiol. 1979;19(8):535–546. doi: 10.1002/jobm.3630190803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brawn K., Fridovich I. DNA strand scission by enzymically generated oxygen radicals. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1981 Feb;206(2):414–419. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(81)90108-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breedveld M. W., Zevenhuizen L. P., Zehnder A. J. Synthesis of cyclic beta-(1,2)-glucans by Rhizobium leguminosarum biovar trifolii TA-1: factors influencing excretion. J Bacteriol. 1992 Oct;174(20):6336–6342. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.20.6336-6342.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bronner D., Sieberth V., Pazzani C., Roberts I. S., Boulnois G. J., Jann B., Jann K. Expression of the capsular K5 polysaccharide of Escherichia coli: biochemical and electron microscopic analyses of mutants with defects in region 1 of the K5 gene cluster. J Bacteriol. 1993 Sep;175(18):5984–5992. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.18.5984-5992.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burlacu E., David C., Vasilescu T. Comparative evaluation of three in vacuo dessication procedures on bacterial cultures. Arch Roum Pathol Exp Microbiol. 1989 Jan-Mar;48(1):65–78. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camphausen R. T., McNeil M., Jardine I., Brennan P. J. Location of acyl groups of trehalose-containing lipooligosaccharides of mycobacteria. J Bacteriol. 1987 Dec;169(12):5473–5480. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.12.5473-5480.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carducci C., Ellul L., Antonozzi I., Pontecorvi A. DNA elution and amplification by polymerase chain reaction from dried blood spots. Biotechniques. 1992 Nov;13(5):735–737. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter J. F., Crowe J. H. An infrared spectroscopic study of the interactions of carbohydrates with dried proteins. Biochemistry. 1989 May 2;28(9):3916–3922. doi: 10.1021/bi00435a044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter J. F., Martin B., Crowe L. M., Crowe J. H. Stabilization of phosphofructokinase during air-drying with sugars and sugar/transition metal mixtures. Cryobiology. 1987 Oct;24(5):455–464. doi: 10.1016/0011-2240(87)90049-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cayley S., Lewis B. A., Guttman H. J., Record M. T., Jr Characterization of the cytoplasm of Escherichia coli K-12 as a function of external osmolarity. Implications for protein-DNA interactions in vivo. J Mol Biol. 1991 Nov 20;222(2):281–300. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90212-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cayley S., Lewis B. A., Record M. T., Jr Origins of the osmoprotective properties of betaine and proline in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1992 Mar;174(5):1586–1595. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.5.1586-1595.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chuang S. E., Daniels D. L., Blattner F. R. Global regulation of gene expression in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1993 Apr;175(7):2026–2036. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.7.2026-2036.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciferri O. Spirulina, the edible microorganism. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Dec;47(4):551–578. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.4.551-578.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clegg J. S. Intracellular water and the cytomatrix: some methods of study and current views. J Cell Biol. 1984 Jul;99(1 Pt 2):167s–171s. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.1.167s. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clegg J. S. Properties and metabolism of the aqueous cytoplasm and its boundaries. Am J Physiol. 1984 Feb;246(2 Pt 2):R133–R151. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1984.246.2.R133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Close T. J., Lammers P. J. An osmotic stress protein of cyanobacteria is immunologically related to plant dehydrins. Plant Physiol. 1993 Mar;101(3):773–779. doi: 10.1104/pp.101.3.773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colombo M. F., Rau D. C., Parsegian V. A. Protein solvation in allosteric regulation: a water effect on hemoglobin. Science. 1992 May 1;256(5057):655–659. doi: 10.1126/science.1585178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Compan I., Touati D. Interaction of six global transcription regulators in expression of manganese superoxide dismutase in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1993 Mar;175(6):1687–1696. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.6.1687-1696.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox C. S., Baxter J., Maidment B. J. A mathematical expression for oxygen-induced death in dehydrated bacteria. J Gen Microbiol. 1973 Mar;75(1):179–185. doi: 10.1099/00221287-75-1-179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowe J. H., Crowe L. M., Carpenter J. F., Aurell Wistrom C. Stabilization of dry phospholipid bilayers and proteins by sugars. Biochem J. 1987 Feb 15;242(1):1–10. doi: 10.1042/bj2420001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowe J. H., Crowe L. M., Carpenter J. F., Rudolph A. S., Wistrom C. A., Spargo B. J., Anchordoguy T. J. Interactions of sugars with membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Jun 9;947(2):367–384. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(88)90015-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowe J. H., Hoekstra F. A., Crowe L. M. Anhydrobiosis. Annu Rev Physiol. 1992;54:579–599. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.54.030192.003051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowe J. H., Spargo B. J., Crowe L. M. Preservation of dry liposomes does not require retention of residual water. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(6):1537–1540. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.6.1537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowe L. M., Crowe J. H. Anhydrobiosis: a strategy for survival. Adv Space Res. 1992;12(4):239–247. doi: 10.1016/0273-1177(92)90178-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Csonka L. N., Hanson A. D. Prokaryotic osmoregulation: genetics and physiology. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1991;45:569–606. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.45.100191.003033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Csonka L. N. Physiological and genetic responses of bacteria to osmotic stress. Microbiol Rev. 1989 Mar;53(1):121–147. doi: 10.1128/mr.53.1.121-147.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlbäck B., Hermansson M., Kjelleberg S., Norkrans B. The hydrophobicity of bacteria - an important factor in their initial adhesion at the air-water interface. Arch Microbiol. 1981 Jan;128(3):267–270. doi: 10.1007/BF00422527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Primo C., Sligar S. G., Hoa G. H., Douzou P. A critical role of protein-bound water in the catalytic cycle of cytochrome P-450 camphor. FEBS Lett. 1992 Nov 9;312(2-3):252–254. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80946-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dose K., Bieger-Dose A., Labusch M., Gill M. Survival in extreme dryness and DNA-single-strand breaks. Adv Space Res. 1992;12(4):221–229. doi: 10.1016/0273-1177(92)90176-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drake C. R., Roberts I. S., Jann B., Jann K., Boulnois G. J. Molecular cloning and expression of the genes encoding the Escherichia coli K4 capsular polysaccharide, a fructose-substituted chondroitin. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1990 Jan 1;54(1-3):227–230. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(90)90287-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg D., McLachlan A. D. Solvation energy in protein folding and binding. Nature. 1986 Jan 16;319(6050):199–203. doi: 10.1038/319199a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eleutherio E. C., Araujo P. S., Panek A. D. Role of the trehalose carrier in dehydration resistance of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Mar 21;1156(3):263–266. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(93)90040-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Errington J. Bacillus subtilis sporulation: regulation of gene expression and control of morphogenesis. Microbiol Rev. 1993 Mar;57(1):1–33. doi: 10.1128/mr.57.1.1-33.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairhead H., Setlow B., Setlow P. Prevention of DNA damage in spores and in vitro by small, acid-soluble proteins from Bacillus species. J Bacteriol. 1993 Mar;175(5):1367–1374. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.5.1367-1374.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairhead H., Setlow P. Binding of DNA to alpha/beta-type small, acid-soluble proteins from spores of Bacillus or Clostridium species prevents formation of cytosine dimers, cytosine-thymine dimers, and bipyrimidine photoadducts after UV irradiation. J Bacteriol. 1992 May;174(9):2874–2880. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.9.2874-2880.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrington M., Brenwald N., Haines D., Walpole E. Resistance to desiccation and skin fatty acids in outbreak strains of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J Med Microbiol. 1992 Jan;36(1):56–60. doi: 10.1099/00222615-36-1-56. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fattom A., Shilo M. Hydrophobicity as an adhesion mechanism of benthic cyanobacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Jan;47(1):135–143. doi: 10.1128/aem.47.1.135-143.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Favinger J., Stadtwald R., Gest H. Rhodospirillum centenum, sp. nov., a thermotolerant cyst-forming anoxygenic photosynthetic bacterium. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1989 Mar;55(3):291–296. doi: 10.1007/BF00393857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finney J. L. The organization and function of water in protein crystals. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1977 Mar 29;278(959):3–32. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1977.0029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frackowiak D., Skibinski A., Zelent B., Leblanc R. M. Skew orientation of biological samples Anacystis nidulans cyanobacteria and their fragments in a polymer matrix. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Apr 15;184(1):441–447. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)91213-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franks F. Solvation interactions of proteins in solution. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1977 Mar 29;278(959):89–96. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1977.0032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedmann E. I. Endolithic microorganisms in the antarctic cold desert. Science. 1982 Feb 26;215(4536):1045–1053. doi: 10.1126/science.215.4536.1045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedmann E. I., Hua M., Ocampo-Friedmann R. Cryptoendolithic lichen and cyanobacterial communities of the Ross Desert, Antarctica. Polarforschung. 1988;58(2-3):251–259. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedmann E. I., Kappen L., Meyer M. A., Nienow J. A. Long-term productivity in the cryptoendolithic microbial community of the Ross Desert, Antarctica. Microb Ecol. 1993 Jan-Feb;25(1):51–69. doi: 10.1007/BF00182129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedmann E. I., Weed R. Microbial trace-fossil formation, biogenous, and abiotic weathering in the Antarctic cold desert. Science. 1987 May 8;236(4802):703–705. doi: 10.1126/science.11536571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiwara S., Zielinski N. A., Chakrabarty A. M. Enhancer-like activity of A1gR1-binding site in alginate gene activation: positional, orientational, and sequence specificity. J Bacteriol. 1993 Sep;175(17):5452–5459. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.17.5452-5459.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulton A. B. How crowded is the cytoplasm? Cell. 1982 Sep;30(2):345–347. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90231-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Pichel F., Castenholz R. W. Occurrence of UV-Absorbing, Mycosporine-Like Compounds among Cyanobacterial Isolates and an Estimate of Their Screening Capacity. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1993 Jan;59(1):163–169. doi: 10.1128/aem.59.1.163-169.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Pichel F., Wingard C. E., Castenholz R. W. Evidence Regarding the UV Sunscreen Role of a Mycosporine-Like Compound in the Cyanobacterium Gloeocapsa sp. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1993 Jan;59(1):170–176. doi: 10.1128/aem.59.1.170-176.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garza-Ramos G., Darszon A., Tuena de Gómez-Puyou M., Gómez-Puyou A. Enzyme catalysis in organic solvents with low water content at high temperatures. The adenosinetriphosphatase of submitochondrial particles. Biochemistry. 1990 Jan 23;29(3):751–757. doi: 10.1021/bi00455a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gautier N., López Marín L. M., Lanéelle M. A., Daffé M. Structure of mycoside F, a family of trehalose-containing glycolipids of Mycobacterium fortuitum. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1992 Nov 1;77(1-3):81–87. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(92)90136-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geiger O., Russo F. D., Silhavy T. J., Kennedy E. P. Membrane-derived oligosaccharides affect porin osmoregulation only in media of low ionic strength. J Bacteriol. 1992 Feb;174(4):1410–1413. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.4.1410-1413.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giaever H. M., Styrvold O. B., Kaasen I., Strøm A. R. Biochemical and genetic characterization of osmoregulatory trehalose synthesis in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jun;170(6):2841–2849. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.6.2841-2849.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilichinsky D. A., Vorobyova E. A., Erokhina L. G., Fyordorov-Davydov D. G., Chaikovskaya N. R., Fyordorov-Dayvdov D. G. Long-term preservation of microbial ecosystems in permafrost. Adv Space Res. 1992;12(4):255–263. doi: 10.1016/0273-1177(92)90180-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glucksmann M. A., Reuber T. L., Walker G. C. Family of glycosyl transferases needed for the synthesis of succinoglycan by Rhizobium meliloti. J Bacteriol. 1993 Nov;175(21):7033–7044. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.21.7033-7044.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodrich R. P., Baldeschwieler J. D. The cryoprotective action of synthetic glycolipids. Cryobiology. 1991 Aug;28(4):327–334. doi: 10.1016/0011-2240(91)90039-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodrich R. P., Crowe J. H., Crowe L. M., Baldeschwieler J. D. Alterations in membrane surfaces induced by attachment of carbohydrates. Biochemistry. 1991 May 28;30(21):5313–5318. doi: 10.1021/bi00235a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodrich R. P., Sowemimo-Coker S. O., Zerez C. R., Tanaka K. R. Preservation of metabolic activity in lyophilized human erythrocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Feb 1;89(3):967–971. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.3.967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodsell D. S. Inside a living cell. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Jun;16(6):203–206. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90083-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gouesbet G., Abaibou H., Wu L. F., Mandrand-Berthelot M. A., Blanco C. Osmotic repression of anaerobic metabolic systems in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1993 Jan;175(1):214–221. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.1.214-221.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg J. T., Monach P., Chou J. H., Josephy P. D., Demple B. Positive control of a global antioxidant defense regulon activated by superoxide-generating agents in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(16):6181–6185. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.16.6181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta A., Morby A. P., Turner J. S., Whitton B. A., Robinson N. J. Deletion within the metallothionein locus of cadmium-tolerant Synechococcus PCC 6301 involving a highly iterated palindrome (HIP1). Mol Microbiol. 1993 Jan;7(2):189–195. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01110.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutierrez C., Ardourel M., Bremer E., Middendorf A., Boos W., Ehmann U. Analysis and DNA sequence of the osmoregulated treA gene encoding the periplasmic trehalase of Escherichia coli K12. Mol Gen Genet. 1989 Jun;217(2-3):347–354. doi: 10.1007/BF02464903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halliwell B. Oxidants and human disease: some new concepts. FASEB J. 1987 Nov;1(5):358–364. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris R. F., Gardner W. R., Adebayo A. A., Sommers L. E. Agar dish isopiestic equilibration method for controlling the water potential of solid substrates. Appl Microbiol. 1970 Mar;19(3):536–537. doi: 10.1128/am.19.3.536-537.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hassan H. M., Sun H. C. Regulatory roles of Fnr, Fur, and Arc in expression of manganese-containing superoxide dismutase in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 15;89(8):3217–3221. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.8.3217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hengge-Aronis R., Klein W., Lange R., Rimmele M., Boos W. Trehalose synthesis genes are controlled by the putative sigma factor encoded by rpoS and are involved in stationary-phase thermotolerance in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1991 Dec;173(24):7918–7924. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.24.7918-7924.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hengge-Aronis R., Lange R., Henneberg N., Fischer D. Osmotic regulation of rpoS-dependent genes in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1993 Jan;175(1):259–265. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.1.259-265.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershkovitz N., Oren A., Cohen Y. Accumulation of trehalose and sucrose in cyanobacteria exposed to matric water stress. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Mar;57(3):645–648. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.3.645-648.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill D. R., Hladun S. L., Scherer S., Potts M. Water stress proteins of Nostoc commune (Cyanobacteria) are secreted with UV-A/B-absorbing pigments and associate with 1,4-beta-D-xylanxylanohydrolase activity. J Biol Chem. 1994 Mar 11;269(10):7726–7734. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoekstra F. A., Crowe J. H., Crowe L. M. Effect of Sucrose on Phase Behavior of Membranes in Intact Pollen of Typha latifolia L., as Measured with Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy. Plant Physiol. 1991 Nov;97(3):1073–1079. doi: 10.1104/pp.97.3.1073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoelzle I., Streeter J. G. Increased Accumulation of Trehalose in Rhizobia Cultured under 1% Oxygen. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Oct;56(10):3213–3215. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.10.3213-3215.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houssin C., Eynard N., Shechter E., Ghazi A. Effect of osmotic pressure on membrane energy-linked functions in Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Jan 3;1056(1):76–84. doi: 10.1016/s0005-2728(05)80075-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imlay J. A., Linn S. DNA damage and oxygen radical toxicity. Science. 1988 Jun 3;240(4857):1302–1309. doi: 10.1126/science.3287616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imshenetsky A. A., Pisarenko N. F., Kuziurina L. A., Yakshina V. M. Physiology of xerophytic micro-organisms growing under Martian conditions. Life Sci Space Res. 1977;15:47–52. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israeli E., Giberman E., Kohn A. Membrane malfunctions in freeze-dried Escherichia coli. Cryobiology. 1974 Oct;11(5):473–477. doi: 10.1016/0011-2240(74)90115-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israeli E., Kohn A., Gitelman J. The molecular nature of damage by oxygen to freeze-dried Escherichia coli. Cryobiology. 1975 Feb;12(1):15–25. doi: 10.1016/0011-2240(75)90037-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israeli E., Shaffer B. T., Hoyt J. A., Lighthart B., Ganio L. M. Survival differences among freeze-dried genetically engineered and wild-type bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1993 Feb;59(2):594–598. doi: 10.1128/aem.59.2.594-598.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito T. The effects of vacuum-UV radiation (50-190nm) on microorganisms and DNA. Adv Space Res. 1992;12(4):249–253. doi: 10.1016/0273-1177(92)90179-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs M., Wnendt S., Stahl U. High-efficiency electro-transformation of Escherichia coli with DNA from ligation mixtures. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Mar 25;18(6):1653–1653. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.6.1653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaenicke R. Folding and association of proteins. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1987;49(2-3):117–237. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(87)90011-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaenicke R. Protein folding: local structures, domains, subunits, and assemblies. Biochemistry. 1991 Apr 2;30(13):3147–3161. doi: 10.1021/bi00227a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaenicke R. Protein stability and molecular adaptation to extreme conditions. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Dec 18;202(3):715–728. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb16426.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaenicke R. Protein stability and protein folding. Ciba Found Symp. 1991;161:206–221. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins D. E., Chaisson S. A., Matin A. Starvation-induced cross protection against osmotic challenge in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1990 May;172(5):2779–2781. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.5.2779-2781.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jernigan R. L., Sarai A., Ting K. L., Nussinov R. Hydrophobic interactions in the major groove can influence DNA local structure. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1986 Aug;4(1):41–48. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1986.10507645. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston C. G., Vestal J. R. Photosynthetic carbon incorporation and turnover in antarctic cryptoendolithic microbial communities: are they the slowest-growing communities on Earth? Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Aug;57(8):2308–2311. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.8.2308-2311.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jung J. U., Gutierrez C., Villarejo M. R. Sequence of an osmotically inducible lipoprotein gene. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jan;171(1):511–520. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.1.511-520.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jäger K., Potts M. Distinct fractions of genomic DNA from cyanobacterium Nostoc commune that differ in the degree of methylation. Gene. 1988 Dec 25;74(1):197–201. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90286-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keenleyside W. J., Bronner D., Jann K., Jann B., Whitfield C. Coexpression of colanic acid and serotype-specific capsular polysaccharides in Escherichia coli strains with group II K antigens. J Bacteriol. 1993 Oct;175(20):6725–6730. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.20.6725-6730.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch A. L., Pinette M. F. Nephelometric determination of turgor pressure in growing gram-negative bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1987 Aug;169(8):3654–3663. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.8.3654-3663.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kogut M., Russell N. J. Life at the limits. Considerations on how bacteria can grow at extremes of temperature and pressure, or with high concentrations of ions and solutes. Sci Prog. 1987;71(283 Pt 3):381–399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koike J., Oshima T., Koike K. A., Taguchi H., Tanaka R., Nishimura K., Miyaji M. Survival rates of some terrestrial microorganisms under simulated space conditions. Adv Space Res. 1992;12(4):271–274. doi: 10.1016/0273-1177(92)90182-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondo T., Strayer C. A., Kulkarni R. D., Taylor W., Ishiura M., Golden S. S., Johnson C. H. Circadian rhythms in prokaryotes: luciferase as a reporter of circadian gene expression in cyanobacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jun 15;90(12):5672–5676. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.12.5672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornblatt J. A., Hoa G. H. A nontraditional role for water in the cytochrome c oxidase reaction. Biochemistry. 1990 Oct 9;29(40):9370–9376. doi: 10.1021/bi00492a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosanke J. W., Osburn R. M., Shuppe G. I., Smith R. S. Slow rehydration improves the recovery of dried bacterial populations. Can J Microbiol. 1992 Jun;38(6):520–525. doi: 10.1139/m92-086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koshi G., Rajeshwari K., Philipose L. Preservation of streptococci and other bacteria by sand desiccation and filter paper techniques. Indian J Med Res. 1977 Apr;65(4):500–502. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuntz I. D., Zipp A. Water in biological systems. N Engl J Med. 1977 Aug 4;297(5):262–266. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197708042970509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lafleur M. V., Retèl J. Contrasting effects of SH-compounds on oxidative DNA damage: repair and increase of damage. Mutat Res. 1993 Jan;295(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0921-8734(93)90006-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laudenbach D. E., Grossman A. R. Characterization and mutagenesis of sulfur-regulated genes in a cyanobacterium: evidence for function in sulfate transport. J Bacteriol. 1991 May;173(9):2739–2750. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.9.2739-2750.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lechner J., Wieland F. Structure and biosynthesis of prokaryotic glycoproteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:173–194. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.001133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. W., Das Gupta S. K., Mattai J., Shipley G. G., Abdel-Mageed O. H., Makriyannis A., Griffin R. G. Characterization of the L lambda phase in trehalose-stabilized dry membranes by solid-state NMR and X-ray diffraction. Biochemistry. 1989 Jun 13;28(12):5000–5009. doi: 10.1021/bi00438a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. W., Waugh J. S., Griffin R. G. Solid-state NMR study of trehalose/1,2-dipalmitoyl-sn-phosphatidylcholine interactions. Biochemistry. 1986 Jul 1;25(13):3737–3742. doi: 10.1021/bi00361a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemassu A., Lanéelle M. A., Daffé M. Revised structure of a trehalose-containing immunoreactive glycolipid of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1991 Mar 1;62(2-3):171–175. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(91)90153-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leslie S. B., Teter S. A., Crowe L. M., Crowe J. H. Trehalose lowers membrane phase transitions in dry yeast cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1994 Jun 1;1192(1):7–13. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(94)90136-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li C., Adler J. Escherichia coli shows two types of behavioral responses to osmotic upshift. J Bacteriol. 1993 May;175(9):2564–2567. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.9.2564-2567.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl T., Nyberg B. Rate of depurination of native deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochemistry. 1972 Sep 12;11(19):3610–3618. doi: 10.1021/bi00769a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg C., Horneck G. Thymine photoproduct formation and inactivation of intact spores of Bacillus subtilis irradiated with short wavelength UV (200-300nm) at atmospheric pressure and in vacuo. Adv Space Res. 1992;12(4):275–279. doi: 10.1016/0273-1177(92)90183-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindsay J. A., Murrell W. G. A comparison of UV induced DNA photoproducts from isolated and non-isolated developing bacterial forespores. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Jun 15;113(2):618–625. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91771-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liochev S. I., Fridovich I. Effects of overproduction of superoxide dismutases in Escherichia coli on inhibition of growth and on induction of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase by paraquat. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1992 Apr;294(1):138–143. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(92)90147-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohman T. M. Kinetics of protein-nucleic acid interactions: use of salt effects to probe mechanisms of interaction. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1986;19(3):191–245. doi: 10.3109/10409238609084656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lounnas V., Pettitt B. M., Phillips G. N., Jr A global model of the protein-solvent interface. Biophys J. 1994 Mar;66(3 Pt 1):601–614. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3495(94)80835-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacIver D. H., Green N. K., Gammage M. D., Durkin H., Izzard A. S., Franklyn J. A., Heagerty A. M. Effect of experimental hypertension on phosphoinositide hydrolysis and proto-oncogene expression in cardiovascular tissues. J Vasc Res. 1993 Jan-Feb;30(1):13–22. doi: 10.1159/000158970. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKenzie A. P. Non-equilibrium freezing behaviour of aqueous systems. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1977 Mar 29;278(959):167–189. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1977.0036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall B., Flynn P., Kamely D., Levy S. B. Survival of Escherichia coli with and without ColE1::Tn5 after aerosol dispersal in a laboratory and a farm environment. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Jul;54(7):1776–1783. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.7.1776-1783.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mary P., Ochin D., Tailliez R. Rates of Drying and Survival of Rhizobium meliloti Strains During Storage at Different Relative Humidities. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Aug;50(2):207–211. doi: 10.1128/aem.50.2.207-211.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathews C. K. The cell-bag of enzymes or network of channels? J Bacteriol. 1993 Oct;175(20):6377–6381. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.20.6377-6381.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazur P. Limits to life at low temperatures and at reduced water contents and water activities. Orig Life. 1980 Jun;10(2):137–159. doi: 10.1007/BF00928665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meury J., Kohiyama M. Potassium ions and changes in bacterial DNA supercoiling under osmotic stress. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1992 Dec 1;78(2-3):159–164. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(92)90018-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel D., Furini A., Salamini F., Bartels D. Structure and regulation of an ABA- and desiccation-responsive gene from the resurrection plant Craterostigma plantagineum. Plant Mol Biol. 1994 Feb;24(4):549–560. doi: 10.1007/BF00023553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller K. J., Kennedy E. P., Reinhold V. N. Osmotic adaptation by gram-negative bacteria: possible role for periplasmic oligosaccharides. Science. 1986 Jan 3;231(4733):48–51. doi: 10.1126/science.3941890. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore B. G., Tischer R. G. Biosynthesis of extracellular polysaccharides by the blue-green alga Anabaena flos-aquae. Can J Microbiol. 1965 Dec;11(6):877–885. doi: 10.1139/m65-117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morikawa M., Daido H., Takao T., Murata S., Shimonishi Y., Imanaka T. A new lipopeptide biosurfactant produced by Arthrobacter sp. strain MIS38. J Bacteriol. 1993 Oct;175(20):6459–6466. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.20.6459-6466.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mugnier J., Jung G. Survival of bacteria and fungi in relation to water activity and the solvent properties of water in biopolymer gels. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Jul;50(1):108–114. doi: 10.1128/aem.50.1.108-114.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson B., Anderson S. Proper and improper folding of proteins in the cellular environment. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1991;45:607–635. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.45.100191.003135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nunoshiba T., Hidalgo E., Li Z., Demple B. Negative autoregulation by the Escherichia coli SoxS protein: a dampening mechanism for the soxRS redox stress response. J Bacteriol. 1993 Nov;175(22):7492–7494. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.22.7492-7494.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor L. T., Savage D. C. Characterization of an activity from the strict anaerobe Roseburia cecicola that degrades DNA when exposed to air. J Bacteriol. 1993 Aug;175(15):4681–4687. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.15.4681-4687.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oksanen C. A., Zografi G. Molecular mobility in mixtures of absorbed water and solid poly(vinylpyrrolidone). Pharm Res. 1993 Jun;10(6):791–799. doi: 10.1023/a:1018988506336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olie J. J., Potts M. Purification and Biochemical Analysis of the Cytoplasmic Membrane from the Desiccation-Tolerant Cyanobacterium Nostoc commune UTEX 584. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Oct;52(4):706–710. doi: 10.1128/aem.52.4.706-710.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver M. J., Bewley J. D. Plant Desiccation and Protein Synthesis : VI. Changes in Protein Synthesis Elicited by Desiccation of the Moss Tortula ruralis are Effected at the Translational Level. Plant Physiol. 1984 Apr;74(4):923–927. doi: 10.1104/pp.74.4.923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osa-Afiana L. O., Alexander M. Differences among cowpea rhizobia in tolerance to high temperature and desiccation in soil. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Feb;43(2):435–439. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.2.435-439.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otting G., Liepinsh E., Wüthrich K. Protein hydration in aqueous solution. Science. 1991 Nov 15;254(5034):974–980. doi: 10.1126/science.1948083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POLLOCK M. R., RICHMOND M. H. Low cyst(e)ine content of bacterial extracellular proteins: its possible physiological significance. Nature. 1962 May 5;194:446–449. doi: 10.1038/194446a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer R. J., Jr, Friedmann E. I. Water relations and photosynthesis in the cryptoendolithic microbial habitat of hot and cold deserts. Microb Ecol. 1990;19:111–118. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer R. J., Jr, Nienow J. A., Friedmann E. I. Control of matric water potential by temperature differential. J Microbiol Methods. 1987;6:323–326. doi: 10.1016/0167-7012(87)90017-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker J. G. On the inactivation of bacteria by singlet oxygen--another view. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Jun 11;1157(2):209–210. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(93)90067-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen J. C., Jacobsen C. S. Fate of Enterobacter cloacae JP120 and Alcaligenes eutrophus AEO106(pRO101) in soil during water stress: effects on culturability and viability. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1993 May;59(5):1560–1564. doi: 10.1128/aem.59.5.1560-1564.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perona J. J., Craik C. S., Fletterick R. J. Locating the catalytic water molecule in serine proteases. Science. 1993 Jul 30;261(5121):620–622. doi: 10.1126/science.8342029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinette M. F., Koch A. L. Variability of the turgor pressure of individual cells of the gram-negative heterotroph Ancylobacter aquaticus. J Bacteriol. 1987 Oct;169(10):4737–4742. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.10.4737-4742.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Platt M. W., Miller K. J., Lane W. S., Kennedy E. P. Isolation and characterization of the constitutive acyl carrier protein from Rhizobium meliloti. J Bacteriol. 1990 Sep;172(9):5440–5444. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.9.5440-5444.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potts M., Angeloni S. V., Ebel R. E., Bassam D. Myoglobin in a cyanobacterium. Science. 1992 Jun 19;256(5064):1690–1691. doi: 10.1126/science.256.5064.1690. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potts M., Olie J. J., Nickels J. S., Parsons J., White D. C. Variation in Phospholipid Ester-Linked Fatty Acids and Carotenoids of Desiccated Nostoc commune (Cyanobacteria) from Different Geographic Locations. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Jan;53(1):4–9. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.1.4-9.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potts M. Protein synthesis and proteolysis in immobilized cells of the cyanobacterium Nostoc commune UTEX 584 exposed to matric water stress. J Bacteriol. 1985 Dec;164(3):1025–1031. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.3.1025-1031.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potts M., Sun H., Mockaitis K., Kennelly P. J., Reed D., Tonks N. K. A protein-tyrosine/serine phosphatase encoded by the genome of the cyanobacterium Nostoc commune UTEX 584. J Biol Chem. 1993 Apr 15;268(11):7632–7635. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proteau P. J., Gerwick W. H., Garcia-Pichel F., Castenholz R. The structure of scytonemin, an ultraviolet sunscreen pigment from the sheaths of cyanobacteria. Experientia. 1993 Sep 15;49(9):825–829. doi: 10.1007/BF01923559. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purcell L. C., Sinclair T. R. Soybean (Glycine max) Nodule Physical Traits Associated with Permeability Responses to Oxygen. Plant Physiol. 1993 Sep;103(1):149–156. doi: 10.1104/pp.103.1.149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quiocho F. A., Wilson D. K., Vyas N. K. Substrate specificity and affinity of a protein modulated by bound water molecules. Nature. 1989 Aug 3;340(6232):404–407. doi: 10.1038/340404a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rand R. P. Raising water to new heights. Science. 1992 May 1;256(5057):618–618. doi: 10.1126/science.256.5057.618. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rau D. C., Lee B., Parsegian V. A. Measurement of the repulsive force between polyelectrolyte molecules in ionic solution: hydration forces between parallel DNA double helices. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2621–2625. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeck G. R., Fisher L. A statistical analysis of the amino acid compositions of proteins. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1973;5(2):109–117. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1973.tb02325.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reslow M., Adlercreutz P., Mattiasson B. The influence of water on protease-catalyzed peptide synthesis in acetonitrile/water mixtures. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Nov 1;177(2):313–318. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14378.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards W. G., King P. M., Reynolds C. A. Solvation effects. Protein Eng. 1989 Jan;2(5):319–327. doi: 10.1093/protein/2.5.319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberson E. B., Firestone M. K. Relationship between Desiccation and Exopolysaccharide Production in a Soil Pseudomonas sp. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Apr;58(4):1284–1291. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.4.1284-1291.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez-Valera F. Biotechnological potential of halobacteria. Biochem Soc Symp. 1992;58:135–147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romeo T., Moore J., Smith J. A simple method for cloning genes involved in glucan biosynthesis: isolation of structural and regulatory genes for glycogen synthesis in Escherichia coli. Gene. 1991 Dec 1;108(1):23–29. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90483-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roszak D. B., Colwell R. R. Survival strategies of bacteria in the natural environment. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Sep;51(3):365–379. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.3.365-379.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudolph A. S. The freeze-dried preservation of liposome encapsulated hemoglobin: a potential blood substitute. Cryobiology. 1988 Aug;25(4):277–284. doi: 10.1016/0011-2240(88)90036-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rumley M. K., Therisod H., Weissborn A. C., Kennedy E. P. Mechanisms of regulation of the biosynthesis of membrane-derived oligosaccharides in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 15;267(17):11806–11810. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell N. J. Cold adaptation of microorganisms. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1990 Jan 30;326(1237):595-608, discussion 608-11. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1990.0034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SNEATH P. H. Longevity of micro-organisms. Nature. 1962 Aug 18;195:643–646. doi: 10.1038/195643a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STANIER R. Y., VAN NIEL C. B. The concept of a bacterium. Arch Mikrobiol. 1962;42:17–35. doi: 10.1007/BF00425185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadasivan L., Neyra C. A. Flocculation in Azospirillum brasilense and Azospirillum lipoferum: exopolysaccharides and cyst formation. J Bacteriol. 1985 Aug;163(2):716–723. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.2.716-723.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santell L., Rubin R. L., Levin E. G. Enhanced phosphorylation and dephosphorylation of a histone-like protein in response to hyperosmotic and hypoosmotic conditions. J Biol Chem. 1993 Oct 5;268(28):21443–21447. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherer S., Chen T. W., Böger P. A New UV-A/B Protecting Pigment in the Terrestrial Cyanobacterium Nostoc commune. Plant Physiol. 1988 Dec;88(4):1055–1057. doi: 10.1104/pp.88.4.1055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherer S., Potts M. Novel water stress protein from a desiccation-tolerant cyanobacterium. Purification and partial characterization. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 25;264(21):12546–12553. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid E. N. Fate of the Escherichia coli capsule during embedding procedures for electron microscopical studies. Microsc Acta. 1981 Jul;84(4):353–360. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seckler R., Jaenicke R. Protein folding and protein refolding. FASEB J. 1992 May;6(8):2545–2552. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.6.8.1592207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setlow B., Setlow P. Most of the coenzyme A in dormant spores of Bacillus megaterium is in disulfide linkage to protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Mar 7;75(1):45–50. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)91286-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setlow P. I will survive: protecting and repairing spore DNA. J Bacteriol. 1992 May;174(9):2737–2741. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.9.2737-2741.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegele D. A., Kolter R. Life after log. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jan;174(2):345–348. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.2.345-348.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skriver K., Mundy J. Gene expression in response to abscisic acid and osmotic stress. Plant Cell. 1990 Jun;2(6):503–512. doi: 10.1105/tpc.2.6.503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slade L., Levine H. Beyond water activity: recent advances based on an alternative approach to the assessment of food quality and safety. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 1991;30(2-3):115–360. doi: 10.1080/10408399109527543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sohal R. S., Agarwal S., Dubey A., Orr W. C. Protein oxidative damage is associated with life expectancy of houseflies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Aug 1;90(15):7255–7259. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.15.7255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southam G., Beveridge T. J. Characterization of novel, phenol-soluble polypeptides which confer rigidity to the sheath of Methanospirillum hungatei GP1. J Bacteriol. 1992 Feb;174(3):935–946. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.3.935-946.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southam G., Beveridge T. J. Detection of growth sites in and protomer pools for the sheath of Methanospirillum hungatei GP1 by use of constituent organosulfur and immunogold labeling. J Bacteriol. 1992 Oct;174(20):6460–6470. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.20.6460-6470.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spaink H. P., Sheeley D. M., van Brussel A. A., Glushka J., York W. S., Tak T., Geiger O., Kennedy E. P., Reinhold V. N., Lugtenberg B. J. A novel highly unsaturated fatty acid moiety of lipo-oligosaccharide signals determines host specificity of Rhizobium. Nature. 1991 Nov 14;354(6349):125–130. doi: 10.1038/354125a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spargo B. J., Crowe L. M., Ioneda T., Beaman B. L., Crowe J. H. Cord factor (alpha,alpha-trehalose 6,6'-dimycolate) inhibits fusion between phospholipid vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 1;88(3):737–740. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.3.737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stadtman E. R., Oliver C. N. Metal-catalyzed oxidation of proteins. Physiological consequences. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 5;266(4):2005–2008. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner B. M., Wong G. H., Sutrave P., Graves S. Oxygen toxicity in Treponema pallidum: deoxyribonucleic acid single-stranded breakage induced by low doses of hydrogen peroxide. Can J Microbiol. 1984 Dec;30(12):1467–1476. doi: 10.1139/m84-234. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storz G., Christman M. F., Sies H., Ames B. N. Spontaneous mutagenesis and oxidative damage to DNA in Salmonella typhimurium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):8917–8921. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.8917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stout V., Torres-Cabassa A., Maurizi M. R., Gutnick D., Gottesman S. RcsA, an unstable positive regulator of capsular polysaccharide synthesis. J Bacteriol. 1991 Mar;173(5):1738–1747. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.5.1738-1747.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streeter J. G. Accumulation of alpha,alpha-trehalose by Rhizobium bacteria and bacteroids. J Bacteriol. 1985 Oct;164(1):78–84. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.1.78-84.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Styrvold O. B., Strøm A. R. Synthesis, accumulation, and excretion of trehalose in osmotically stressed Escherichia coli K-12 strains: influence of amber suppressors and function of the periplasmic trehalase. J Bacteriol. 1991 Feb;173(3):1187–1192. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.3.1187-1192.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tadolini B., Motta P., Sechi A. M. Phospholipid polar heads affect the generation of oxygen active species by Fe2+ autoxidation. Biochem Int. 1992 May;26(6):987–994. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka K., Takayanagi Y., Fujita N., Ishihama A., Takahashi H. Heterogeneity of the principal sigma factor in Escherichia coli: the rpoS gene product, sigma 38, is a second principal sigma factor of RNA polymerase in stationary-phase Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 15;90(8):3511–3515. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.8.3511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taranto P. A., Keenan T. W., Potts M. Rehydration induces rapid onset of lipid biosynthesis in desiccated Nostoc commune (Cyanobacteria). Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Jun 12;1168(2):228–237. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(93)90129-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tartaglia L. A., Gimeno C. J., Storz G., Ames B. N. Multidegenerate DNA recognition by the OxyR transcriptional regulator. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 25;267(3):2038–2045. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Therisod H., Weissborn A. C., Kennedy E. P. An essential function for acyl carrier protein in the biosynthesis of membrane-derived oligosaccharides of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7236–7240. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsaneva I. R., Weiss B. soxR, a locus governing a superoxide response regulon in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1990 Aug;172(8):4197–4205. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.8.4197-4205.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsvetkov T. D., Tsonev L. I., Tsvetkova N. M., Koynova R. D., Tenchov B. G. Effect of trehalose on the phase properties of hydrated and lyophilized dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine multilayers. Cryobiology. 1989 Apr;26(2):162–169. doi: 10.1016/0011-2240(89)90047-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tudor J. J., Conti S. F. Characterization of bdellocysts of Bdellovibrio sp. J Bacteriol. 1977 Jul;131(1):314–322. doi: 10.1128/jb.131.1.314-322.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEBB S. J., DUMASIA M. D., BHORJEE J. S. BOUND WATER, INOSITOL, AND THE BIOSYNTHESIS OF TEMPERATE AND VIRULENT BACTERIOPHAGES BY AIR-DRIED ESCHERICHIA COLI. Can J Microbiol. 1965 Apr;11:141–150. doi: 10.1139/m65-020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEBB S. J. Factors affecting the viability of air-borne bacteria. II. The effect of chemical additives on the behavior of air-borne cells. Can J Microbiol. 1960 Feb;6:71–87. doi: 10.1139/m60-010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEBB S. J. Factors affecting the viability of air-borne bacteria. III. The role of bonded water and protein structure in the death of air-borne cells. Can J Microbiol. 1960 Feb;6:89–105. doi: 10.1139/m60-011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wada A., Yamazaki Y., Fujita N., Ishihama A. Structure and probable genetic location of a "ribosome modulation factor" associated with 100S ribosomes in stationary-phase Escherichia coli cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(7):2657–2661. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.7.2657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waks M. Proteins and peptides in water-restricted environments. Proteins. 1986 Sep;1(1):4–15. doi: 10.1002/prot.340010104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb S. J. Effect of dehydration on bacterial recombination. Nature. 1968 Mar 30;217(5135):1231–1234. doi: 10.1038/2171231a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb S. J. Mutation of bacterial cells by controlled desiccation. Nature. 1967 Mar 18;213(5081):1137–1139. doi: 10.1038/2131137b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb S. J. The effects of oxygen on the possible repair of dehydration damage by Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1969 Nov;58(3):317–326. doi: 10.1099/00221287-58-3-317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb S. J., Walker J. L. The influence of cell water content on the inactivation of RNA by partial desiccation and ultraviolet light. Can J Microbiol. 1968 May;14(5):565–572. doi: 10.1139/m68-095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissenborn D. L., Wittekindt N., Larson T. J. Structure and regulation of the glpFK operon encoding glycerol diffusion facilitator and glycerol kinase of Escherichia coli K-12. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 25;267(9):6122–6131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch T. J., Farewell A., Neidhardt F. C., Bartlett D. H. Stress response of Escherichia coli to elevated hydrostatic pressure. J Bacteriol. 1993 Nov;175(22):7170–7177. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.22.7170-7177.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitley P., von Heijne G. The DsbA-DsbB system affects the formation of disulfide bonds in periplasmic but not in intramembraneous protein domains. FEBS Lett. 1993 Oct 11;332(1-2):49–51. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)80481-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whyte W., Niven L. Airborne bacteria sampling: the effect of dehydration and sampling time. J Parenter Sci Technol. 1986 Sep-Oct;40(5):182–188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiggins P. M. Role of water in some biological processes. Microbiol Rev. 1990 Dec;54(4):432–449. doi: 10.1128/mr.54.4.432-449.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wildhaber I., Santarius U., Baumeister W. Three-dimensional structure of the surface protein of Desulfurococcus mobilis. J Bacteriol. 1987 Dec;169(12):5563–5568. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.12.5563-5568.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfenden R. V., Cullis P. M., Southgate C. C. Water, protein folding, and the genetic code. Science. 1979 Nov 2;206(4418):575–577. doi: 10.1126/science.493962. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wunderlich M., Jaenicke R., Glockshuber R. The redox properties of protein disulfide isomerase (DsbA) of Escherichia coli result from a tense conformation of its oxidized form. J Mol Biol. 1993 Oct 20;233(4):559–566. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xie W. Q., Whitton B. A., Simon J. W., Jäger K., Reed D., Potts M. Nostoc commune UTEX 584 gene expressing indole phosphate hydrolase activity in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1989 Feb;171(2):708–713. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.2.708-713.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeilmaker G. H., Verhamme C. M. A simplified method for freezing mouse embryos. Cryobiology. 1979 Feb;16(1):6–10. doi: 10.1016/0011-2240(79)90003-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerberg J., Parsegian V. A. Polymer inaccessible volume changes during opening and closing of a voltage-dependent ionic channel. Nature. 1986 Sep 4;323(6083):36–39. doi: 10.1038/323036a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Araujo P. S., Panek A. D. The interaction of Saccharomyces cerevisiae trehalase with membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Jun 5;1148(2):303–307. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(93)90143-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Chazal N. M., Smaglinski S., Smith G. D. Methods involving light variation for isolation of cyanobacteria: characterization of isolates from central australia. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Nov;58(11):3561–3566. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.11.3561-3566.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Loosdrecht M. C., Lyklema J., Norde W., Zehnder A. J. Influence of interfaces on microbial activity. Microbiol Rev. 1990 Mar;54(1):75–87. doi: 10.1128/mr.54.1.75-87.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Tilbeurgh H., Pettersson G., Bhikabhai R., De Boeck H., Claeyssens M. Studies of the cellulolytic system of Trichoderma reesei QM 9414. Reaction specificity and thermodynamics of interactions of small substrates and ligands with the 1,4-beta-glucan cellobiohydrolase II. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Apr 15;148(2):329–334. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08843.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Hippel P. H., Berg O. G. Facilitated target location in biological systems. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 15;264(2):675–678. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]