Full text
PDF
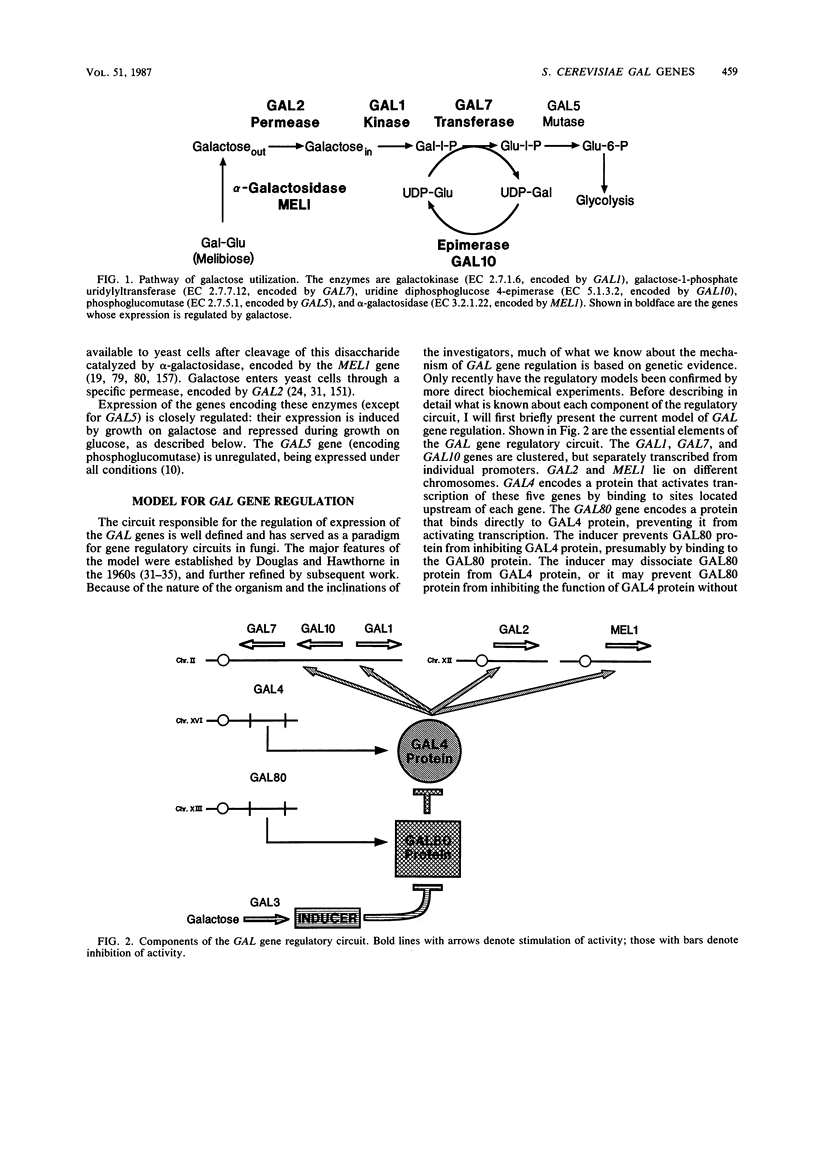



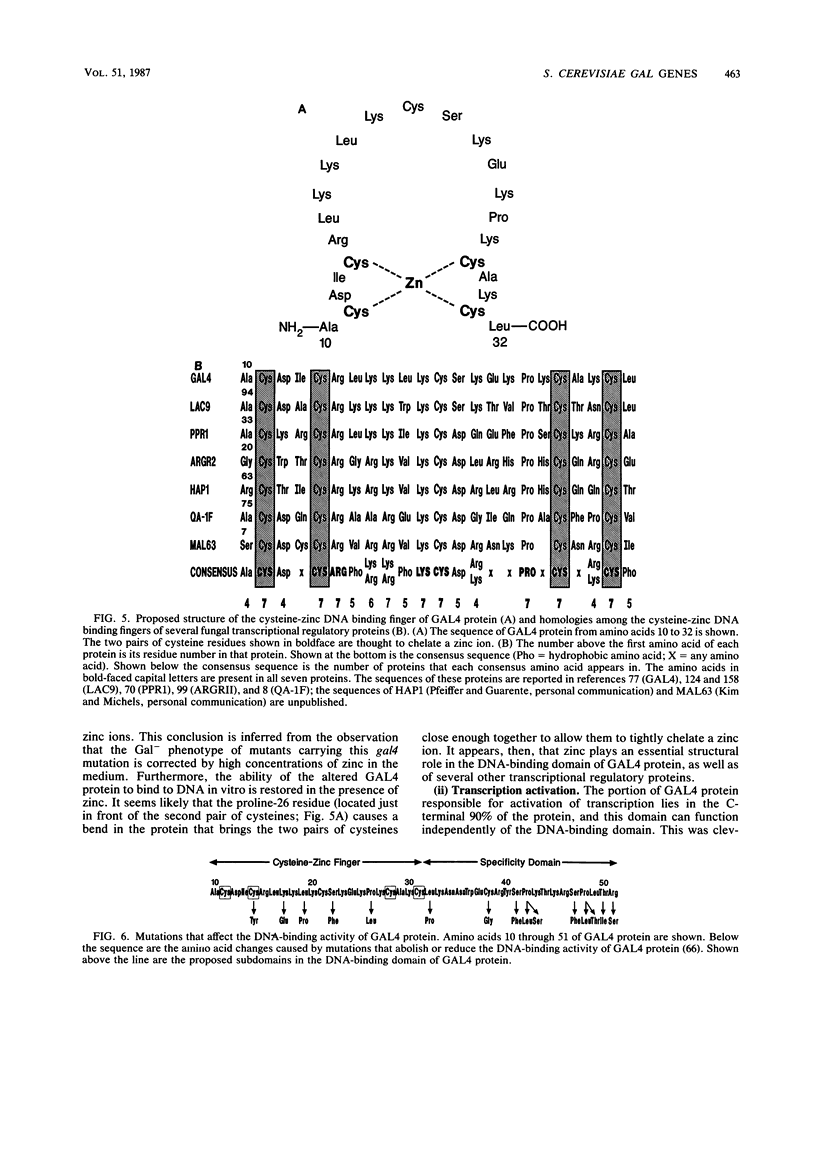


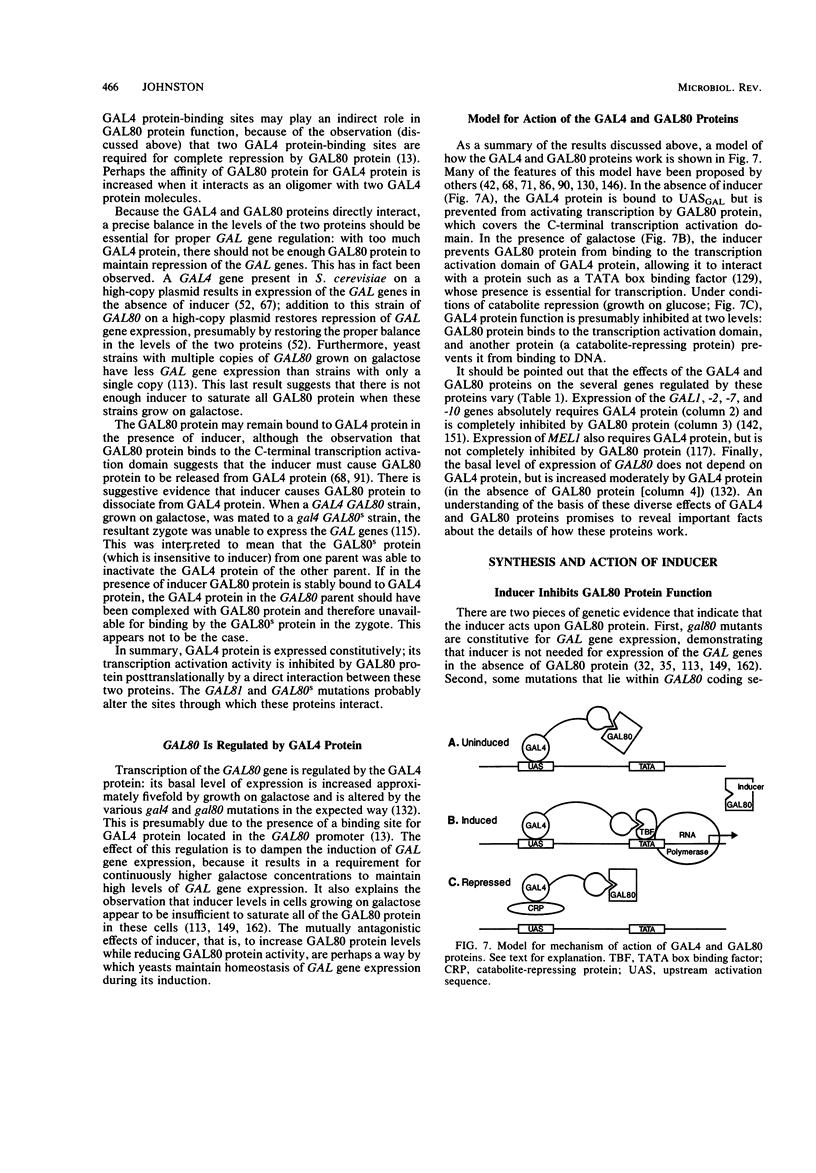

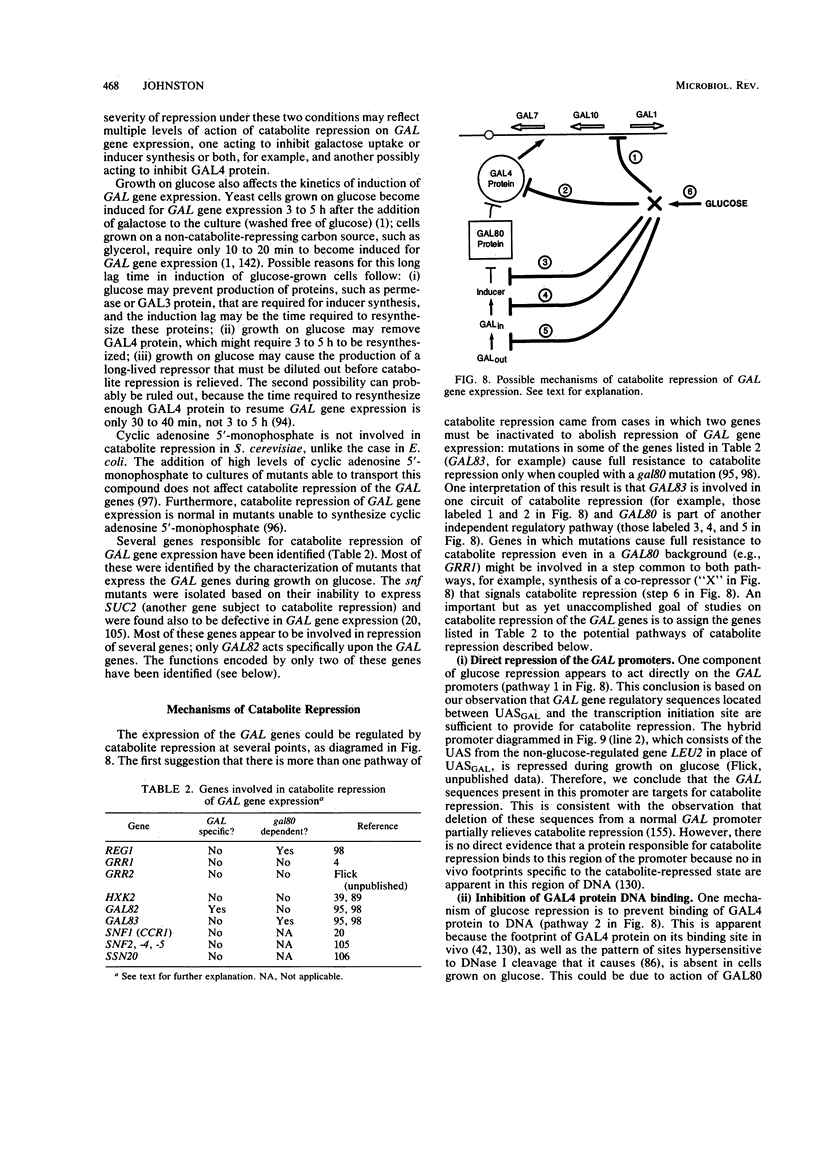








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams B. G., Dalbec J. M. Non- pleiotropic nature of the gal 3 mutation in yeast. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Feb 21;74(4):1348–1354. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)90590-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams B. G. Induction of galactokinase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: kinetics of induction and glucose effects. J Bacteriol. 1972 Aug;111(2):308–315. doi: 10.1128/jb.111.2.308-315.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Algeri A. A., Bianchi L., Viola A. M., Puglisi P. P., Marmiroli N. IMP1/imp1: a gene involved in the nucleo-mitochondrial control of galactose fermentation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1981 Jan;97(1):27–44. doi: 10.1093/genetics/97.1.27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey R. B., Woodword A. Isolation and characterization of a pleiotropic glucose repression resistant mutant of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;193(3):507–512. doi: 10.1007/BF00382091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker S. M., Okkema P. G., Jaehning J. A. Expression of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae GAL7 gene on autonomous plasmids. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Oct;4(10):2062–2071. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.10.2062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes G., Rine J. Regulated expression of endonuclease EcoRI in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: nuclear entry and biological consequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(5):1354–1358. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.5.1354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bassel J., Mortimer R. Genetic order of the galactose structural genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1971 Oct;108(1):179–183. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.1.179-183.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baum J. A., Geever R., Giles N. H. Expression of qa-1F activator protein: identification of upstream binding sites in the qa gene cluster and localization of the DNA-binding domain. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Mar;7(3):1256–1266. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.3.1256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bender A., Sprague G. F., Jr MAT alpha 1 protein, a yeast transcription activator, binds synergistically with a second protein to a set of cell-type-specific genes. Cell. 1987 Aug 28;50(5):681–691. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90326-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bevan P., Douglas H. C. Genetic control of phosphoglucomutase variants in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1969 May;98(2):532–535. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.2.532-535.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boeke J. D., Garfinkel D. J., Styles C. A., Fink G. R. Ty elements transpose through an RNA intermediate. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):491–500. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90197-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bram R. J., Kornberg R. D. Specific protein binding to far upstream activating sequences in polymerase II promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(1):43–47. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.1.43. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bram R. J., Lue N. F., Kornberg R. D. A GAL family of upstream activating sequences in yeast: roles in both induction and repression of transcription. EMBO J. 1986 Mar;5(3):603–608. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04253.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brent R., Ptashne M. A bacterial repressor protein or a yeast transcriptional terminator can block upstream activation of a yeast gene. Nature. 1984 Dec 13;312(5995):612–615. doi: 10.1038/312612a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brent R., Ptashne M. A eukaryotic transcriptional activator bearing the DNA specificity of a prokaryotic repressor. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):729–736. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90246-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broach J. R. Construction of high copy yeast vectors using 2-microns circle sequences. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:307–325. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01024-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckholz R. G., Adams B. G. Induction and genetics of two alpha-galactosidase activities in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;182(1):77–81. doi: 10.1007/BF00422770. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson M., Osmond B. C., Botstein D. Mutants of yeast defective in sucrose utilization. Genetics. 1981 May;98(1):25–40. doi: 10.1093/genetics/98.1.25. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson M., Osmond B. C., Neigeborn L., Botstein D. A suppressor of SNF1 mutations causes constitutive high-level invertase synthesis in yeast. Genetics. 1984 May;107(1):19–32. doi: 10.1093/genetics/107.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celenza J. L., Carlson M. A yeast gene that is essential for release from glucose repression encodes a protein kinase. Science. 1986 Sep 12;233(4769):1175–1180. doi: 10.1126/science.3526554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charron M. J., Michels C. A. The constitutive, glucose-repression-insensitive mutation of the yeast MAL4 locus is an alteration of the MAL43 gene. Genetics. 1987 May;116(1):23–31. doi: 10.1093/genetics/116.1.23. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cirillo V. P. Galactose transport in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. I. Nonmetabolized sugars as substrates and inducers of the galactose transport system. J Bacteriol. 1968 May;95(5):1727–1731. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.5.1727-1731.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Citron B. A., Donelson J. E. Sequence of the Saccharomyces GAL region and its transcription in vivo. J Bacteriol. 1984 Apr;158(1):269–278. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.1.269-278.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Citron B. A., Feiss M., Donelson J. E. Expression of the yeast galactokinase gene in Escherichia coli. Gene. 1979 Jul;6(3):251–264. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(79)90061-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DE ROBICHON-SZULMAJSTER H. Induction of enzymes of the galactose pathway in mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Science. 1958 Jan 3;127(3288):28–29. doi: 10.1126/science.127.3288.28. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOUGLAS H. C. A mutation in saccharomyces that affects phosphoglucomutase activity and galactose utilization. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1961 Sep 2;52:209–211. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(61)90924-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOUGLAS H. C., CONDIE F. The genetic control of galactose utilization in Saccharomyces. J Bacteriol. 1954 Dec;68(6):662–670. doi: 10.1128/jb.68.6.662-670.1954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOUGLAS H. C., HAWTHORNE D. C. ENZYMATIC EXPRESSION AND GENETIC LINKAGE OF GENES CONTROLLING GALACTOSE UTILIZATION IN SACCHAROMYCES. Genetics. 1964 May;49:837–844. doi: 10.1093/genetics/49.5.837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denis C. L., Gallo C. Constitutive RNA synthesis for the yeast activator ADR1 and identification of the ADR1-5c mutation: implications in posttranslational control of ADR1. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):4026–4030. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.4026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas H. C., Hawthorne C. D. Uninducible mutants in the gal i locus of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1972 Mar;109(3):1139–1143. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.3.1139-1143.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas H. C., Hawthorne D. C. Regulation of genes controlling synthesis of the galactose pathway enzymes in yeast. Genetics. 1966 Sep;54(3):911–916. doi: 10.1093/genetics/54.3.911. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Echols H. Multiple DNA-protein interactions governing high-precision DNA transactions. Science. 1986 Sep 5;233(4768):1050–1056. doi: 10.1126/science.2943018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Entian K. D., Fröhlich K. U. Saccharomyces cerevisiae mutants provide evidence of hexokinase PII as a bifunctional enzyme with catalytic and regulatory domains for triggering carbon catabolite repression. J Bacteriol. 1984 Apr;158(1):29–35. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.1.29-35.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Entian K. D. Genetic and biochemical evidence for hexokinase PII as a key enzyme involved in carbon catabolite repression in yeast. Mol Gen Genet. 1980;178(3):633–637. doi: 10.1007/BF00337871. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Entian K. D., Hilberg F., Opitz H., Mecke D. Cloning of hexokinase structural genes from Saccharomyces cerevisiae mutants with regulatory mutations responsible for glucose repression. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;5(11):3035–3040. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.11.3035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukasawa T., Obonai K., Segawa T., Nogi Y. The enzymes of the galactose cluster in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. II. Purification and characterization of uridine diphosphoglucose 4-epimerase. J Biol Chem. 1980 Apr 10;255(7):2705–2707. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giles N. H., Case M. E., Baum J., Geever R., Huiet L., Patel V., Tyler B. Gene organization and regulation in the qa (quinic acid) gene cluster of Neurospora crassa. Microbiol Rev. 1985 Sep;49(3):338–358. doi: 10.1128/mr.49.3.338-358.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill G., Ptashne M. Mutants of GAL4 protein altered in an activation function. Cell. 1987 Oct 9;51(1):121–126. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90016-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giniger E., Varnum S. M., Ptashne M. Specific DNA binding of GAL4, a positive regulatory protein of yeast. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):767–774. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90336-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godowski P. J., Rusconi S., Miesfeld R., Yamamoto K. R. Glucocorticoid receptor mutants that are constitutive activators of transcriptional enhancement. Nature. 1987 Jan 22;325(6102):365–368. doi: 10.1038/325365a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg M. L., Myers P. L., Skvirsky R. C., Greer H. New positive and negative regulators for general control of amino acid biosynthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 May;6(5):1820–1829. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.5.1820. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grove C. L., Gunsalus R. P. Regulation of the aroH operon of Escherichia coli by the tryptophan repressor. J Bacteriol. 1987 May;169(5):2158–2164. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.5.2158-2164.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarente L. Yeast promoters and lacZ fusions designed to study expression of cloned genes in yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:181–191. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01013-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarente L. Yeast promoters: positive and negative elements. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):799–800. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90028-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarente L., Yocum R. R., Gifford P. A GAL10-CYC1 hybrid yeast promoter identifies the GAL4 regulatory region as an upstream site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7410–7414. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanas J. S., Hazuda D. J., Bogenhagen D. F., Wu F. Y., Wu C. W. Xenopus transcription factor A requires zinc for binding to the 5 S RNA gene. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 10;258(23):14120–14125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harashima S., Hinnebusch A. G. Multiple GCD genes required for repression of GCN4, a transcriptional activator of amino acid biosynthetic genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):3990–3998. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.3990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartshorne T. A., Blumberg H., Young E. T. Sequence homology of the yeast regulatory protein ADR1 with Xenopus transcription factor TFIIIA. Nature. 1986 Mar 20;320(6059):283–287. doi: 10.1038/320283a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto H., Kikuchi Y., Nogi Y., Fukasawa T. Regulation of expression of the galactose gene cluster in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Isolation and characterization of the regulatory gene GAL4. Mol Gen Genet. 1983;191(1):31–38. doi: 10.1007/BF00330886. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henry S. A., Klig L. S., Loewy B. S. The genetic regulation and coordination of biosynthetic pathways in yeast: amino acid and phospholipid synthesis. Annu Rev Genet. 1984;18:207–231. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.18.120184.001231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinnebusch A. G. A hierarchy of trans-acting factors modulates translation of an activator of amino acid biosynthetic genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Sep;5(9):2349–2360. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.9.2349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinnebusch A. G. Evidence for translational regulation of the activator of general amino acid control in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(20):6442–6446. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.20.6442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland M. J., Yokoi T., Holland J. P., Myambo K., Innis M. A. The GCR1 gene encodes a positive transcriptional regulator of the enolase and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase gene families in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):813–820. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollenberg S. M., Giguere V., Segui P., Evans R. M. Colocalization of DNA-binding and transcriptional activation functions in the human glucocorticoid receptor. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):39–46. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90753-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hope I. A., Struhl K. Functional dissection of a eukaryotic transcriptional activator protein, GCN4 of yeast. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):885–894. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90070-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hope I. A., Struhl K. GCN4 protein, synthesized in vitro, binds HIS3 regulatory sequences: implications for general control of amino acid biosynthetic genes in yeast. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):177–188. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90022-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopper J. E., Broach J. R., Rowe L. B. Regulation of the galactose pathway in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: induction of uridyl transferase mRNA and dependency on GAL4 gene function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2878–2882. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2878. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopper J. E., Rowe L. B. Molecular expression and regulation of the galactose pathway genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Distinct messenger RNAs specified by the Gali and Gal7 genes in the Gal7-Gal10-Gal1 cluster. J Biol Chem. 1978 Oct 25;253(20):7566–7569. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jayaram M., Li Y. Y., Broach J. R. The yeast plasmid 2mu circle encodes components required for its high copy propagation. Cell. 1983 Aug;34(1):95–104. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90139-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen R. E., Herskowitz I. Directionality and regulation of cassette substitution in yeast. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1984;49:97–104. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1984.049.01.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson A. D., Herskowitz I. A repressor (MAT alpha 2 Product) and its operator control expression of a set of cell type specific genes in yeast. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):237–247. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80119-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston M., Davis R. W. Sequences that regulate the divergent GAL1-GAL10 promoter in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Aug;4(8):1440–1448. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.8.1440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston M., Dover J. Mutations that inactivate a yeast transcriptional regulatory protein cluster in an evolutionarily conserved DNA binding domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2401–2405. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston M. Genetic evidence that zinc is an essential co-factor in the DNA binding domain of GAL4 protein. Nature. 1987 Jul 23;328(6128):353–355. doi: 10.1038/328353a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston S. A., Hopper J. E. Isolation of the yeast regulatory gene GAL4 and analysis of its dosage effects on the galactose/melibiose regulon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6971–6975. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston S. A., Salmeron J. M., Jr, Dincher S. S. Interaction of positive and negative regulatory proteins in the galactose regulon of yeast. Cell. 1987 Jul 3;50(1):143–146. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90671-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston S. A., Zavortink M. J., Debouck C., Hopper J. E. Functional domains of the yeast regulatory protein GAL4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(17):6553–6557. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kammerer B., Guyonvarch A., Hubert J. C. Yeast regulatory gene PPR1. I. Nucleotide sequence, restriction map and codon usage. J Mol Biol. 1984 Dec 5;180(2):239–250. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(84)80002-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keegan L., Gill G., Ptashne M. Separation of DNA binding from the transcription-activating function of a eukaryotic regulatory protein. Science. 1986 Feb 14;231(4739):699–704. doi: 10.1126/science.3080805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kew O. M., Douglas H. C. Genetic co-regulation of galactose and melibiose utilization in Saccharomyces. J Bacteriol. 1976 Jan;125(1):33–41. doi: 10.1128/jb.125.1.33-41.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klar A. J., Halvorson H. O. Effect of GAL4 gene dosage on the level of galactose catabolic enzymes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1976 Jan;125(1):379–381. doi: 10.1128/jb.125.1.379-381.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klar A. J., Halvorson H. O. Studies on the positive regulatory gene, GAL4, in regulation of galactose catabolic enzymes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Gen Genet. 1974;135(3):203–212. doi: 10.1007/BF00268616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosterlitz H. W. The fermentation of galactose and galactose-1-phosphate. Biochem J. 1943 Sep;37(3):322–326. doi: 10.1042/bj0370322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LELOIR L. F. The enzymatic transformation of uridine diphosphate glucose into a galactose derivative. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1951 Sep;33(2):186–190. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(51)90096-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laughon A., Driscoll R., Wills N., Gesteland R. F. Identification of two proteins encoded by the Saccharomyces cerevisiae GAL4 gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Feb;4(2):268–275. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.2.268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laughon A., Gesteland R. F. Isolation and preliminary characterization of the GAL4 gene, a positive regulator of transcription in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6827–6831. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6827. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laughon A., Gesteland R. F. Primary structure of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae GAL4 gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Feb;4(2):260–267. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.2.260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazo P. S., Ochoa A. G., Gascón S. alpha-Galactosidase (melibiase) from Saccharomyces carlsbergensis: structrual and kinetic properties. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1978 Nov;191(1):316–324. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(78)90094-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazo P. S., Ochoa A. G., Gascón S. alpha-Galactosidase from Saccharomyces carlsbergensis. Cellular localization, and purification of the external enzyme. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Jul 15;77(2):375–382. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11677.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legrain M., De Wilde M., Hilger F. Isolation, physical characterization and expression analysis of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae positive regulatory gene PHO4. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Apr 11;14(7):3059–3073. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.7.3059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liljeström P. L. The nucleotide sequence of the yeast MEL1 gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Oct 25;13(20):7257–7268. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.20.7257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lobo Z., Maitra P. K. Genetics of yeast hexokinase. Genetics. 1977 Aug;86(4):727–744. doi: 10.1093/genetics/86.4.727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohr D., Hopper J. E. The relationship of regulatory proteins and DNase I hypersensitive sites in the yeast GAL1-10 genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Dec 9;13(23):8409–8423. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.23.8409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohr D. Organization of the GAL1-GAL10 intergenic control region chromatin. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Nov 26;12(22):8457–8474. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.22.8457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorch Y., Kornberg R. D. A region flanking the GAL7 gene and a binding site for GAL4 protein as upstream activating sequences in yeast. J Mol Biol. 1985 Dec 20;186(4):821–824. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90400-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lue N. F., Chasman D. I., Buchman A. R., Kornberg R. D. Interaction of GAL4 and GAL80 gene regulatory proteins in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;7(10):3446–3451. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.10.3446. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma H., Botstein D. Effects of null mutations in the hexokinase genes of Saccharomyces cerevisiae on catabolite repression. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):4046–4052. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.4046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma J., Ptashne M. A new class of yeast transcriptional activators. Cell. 1987 Oct 9;51(1):113–119. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90015-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma J., Ptashne M. Deletion analysis of GAL4 defines two transcriptional activating segments. Cell. 1987 Mar 13;48(5):847–853. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90081-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma J., Ptashne M. The carboxy-terminal 30 amino acids of GAL4 are recognized by GAL80. Cell. 1987 Jul 3;50(1):137–142. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90670-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matern H., Holzer H. Catabolite inactivation of the galactose uptake system in yeast. J Biol Chem. 1977 Sep 25;252(18):6399–6402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto K., Adachi Y., Toh-e A., Oshima Y. Function of positive regulatory gene gal4 in the synthesis of galactose pathway enzymes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: evidence that the GAL81 region codes for part of the gal4 protein. J Bacteriol. 1980 Feb;141(2):508–527. doi: 10.1128/jb.141.2.508-527.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto K., Toh-e A., Oshima Y. Genetic control of galactokinase synthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: evidence for constitutive expression of the positive regulatory gene gal4. J Bacteriol. 1978 May;134(2):446–457. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.2.446-457.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto K., Toh-e A., Oshima Y. Isolation and characterization of dominant mutations resistant to carbon catabolite repression of galactokinase synthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Feb;1(2):83–93. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.2.83. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto K., Uno I., Ishikawa T., Oshima Y. Cyclic AMP may not be involved in catabolite repression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: evidence from mutants unable to synthesize it. J Bacteriol. 1983 Nov;156(2):898–900. doi: 10.1128/jb.156.2.898-900.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto K., Uno I., Toh-E A., Ishikawa T., Oshima Y. Cyclic AMP may not be involved in catabolite repression in Saccharomyes cerevisiae: evidence from mutants capable of utilizing it as an adenine source. J Bacteriol. 1982 Apr;150(1):277–285. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.1.277-285.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto K., Yoshimatsu T., Oshima Y. Recessive mutations conferring resistance to carbon catabolite repression of galactokinase synthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1983 Mar;153(3):1405–1414. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.3.1405-1414.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messenguy F., Dubois E., Descamps F. Nucleotide sequence of the ARGRII regulatory gene and amino acid sequence homologies between ARGRII PPRI and GAL4 regulatory proteins. Eur J Biochem. 1986 May 15;157(1):77–81. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09640.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metzenberg R. L. Implications of some genetic control mechanisms in Neurospora. Microbiol Rev. 1979 Sep;43(3):361–383. doi: 10.1128/mr.43.3.361-383.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miesfeld R., Godowski P. J., Maler B. A., Yamamoto K. R. Glucocorticoid receptor mutants that define a small region sufficient for enhancer activation. Science. 1987 Apr 24;236(4800):423–427. doi: 10.1126/science.3563519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J., McLachlan A. D., Klug A. Repetitive zinc-binding domains in the protein transcription factor IIIA from Xenopus oocytes. EMBO J. 1985 Jun;4(6):1609–1614. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03825.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mundkur B D. Long Term Adaptation to Galactose by Yeast. Genetics. 1952 Sep;37(5):484–499. doi: 10.1093/genetics/37.5.484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NELSON N. M., DOUGLAS H. C. GENE DOSAGE AND GALACTOSE UTILIZATION BY SACCHAROMYCES TETRAPLOIDS. Genetics. 1963 Dec;48:1585–1591. doi: 10.1093/genetics/48.12.1585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasmyth K. The determination of mother cell-specific mating type switching in yeast by a specific regulator of HO transcription. EMBO J. 1987 Jan;6(1):243–248. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04745.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neigeborn L., Carlson M. Genes affecting the regulation of SUC2 gene expression by glucose repression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1984 Dec;108(4):845–858. doi: 10.1093/genetics/108.4.845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neigeborn L., Rubin K., Carlson M. Suppressors of SNF2 mutations restore invertase derepression and cause temperature-sensitive lethality in yeast. Genetics. 1986 Apr;112(4):741–753. doi: 10.1093/genetics/112.4.741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nogi Y., Fukasawa T. Nucleotide sequence of the transcriptional initiation region of the yeast GAL7 gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Dec 20;11(24):8555–8568. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.24.8555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nogi Y., Fukasawa T. Nucleotide sequence of the yeast regulatory gene GAL80. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Dec 21;12(24):9287–9298. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.24.9287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nogi Y. GAL3 gene product is required for maintenance of the induced state of the GAL cluster genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jan;165(1):101–106. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.1.101-106.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nogi Y., Matsumoto K., Toh-e A., Oshima Y. Interaction of super-repressible and dominant constitutive mutations for the synthesis of galactose pathway enzymes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Gen Genet. 1977 Apr 29;152(3):137–144. doi: 10.1007/BF00268810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nogi Y., Shimada H., Matsuzaki Y., Hashimoto H., Fukasawa T. Regulation of expression of the galactose gene cluster in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. II. The isolation and dosage effect of the regulatory gene GAL80. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;195(1-2):29–34. doi: 10.1007/BF00332719. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlman D., Hopper J. E. Constitutive synthesis of the GAL4 protein, a galactose pathway regulator in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Cell. 1979 Jan;16(1):89–95. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90190-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeifer K., Arcangioli B., Guarente L. Yeast HAP1 activator competes with the factor RC2 for binding to the upstream activation site UAS1 of the CYC1 gene. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):9–18. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90750-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Post-Beittenmiller M. A., Hamilton R. W., Hopper J. E. Regulation of basal and induced levels of the MEL1 transcript in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jul;4(7):1238–1245. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.7.1238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proffitt J. H. DNase I-hypersensitive sites in the galactose gene cluster of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jun;5(6):1522–1524. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.6.1522. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne M. Gene regulation by proteins acting nearby and at a distance. Nature. 1986 Aug 21;322(6081):697–701. doi: 10.1038/322697a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROTMAN B., SPIEGELMAN S. The conversion of negatives to positives in slow adapting populations of yeast. J Bacteriol. 1953 Oct;66(4):492–497. doi: 10.1128/jb.66.4.492-497.1953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raibaud O., Schwartz M. Positive control of transcription initiation in bacteria. Annu Rev Genet. 1984;18:173–206. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.18.120184.001133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riley M. I., Hopper J. E., Johnston S. A., Dickson R. C. GAL4 of Saccharomyces cerevisiae activates the lactose-galactose regulon of Kluyveromyces lactis and creates a new phenotype: glucose repression of the regulon. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):780–786. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.780. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rusconi S., Yamamoto K. R. Functional dissection of the hormone and DNA binding activities of the glucocorticoid receptor. EMBO J. 1987 May;6(5):1309–1315. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02369.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPIEGELMAN S., SUSSMAN R. R., PINSKA E. On the cytoplasmic nature of "long-term adaptation" in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1950 Nov;36(11):591–606. doi: 10.1073/pnas.36.11.591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPIEGELMAN S. The particulate transmission of enzyme-forming capacity in yeast. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1951;16:87–98. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1951.016.01.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salmeron J. M., Jr, Johnston S. A. Analysis of the Kluyveromyces lactis positive regulatory gene LAC9 reveals functional homology to, but sequence divergence from, the Saccharomyces cerevisiae GAL4 gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Oct 10;14(19):7767–7781. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.19.7767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schell M. A., Wilson D. B. Cloning and expression of the yeast galactokinase gene in an Escherichia coli plasmid. Gene. 1979 Apr;5(4):291–303. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(79)90104-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schell M. A., Wilson D. B. Purification and properties of galactokinase from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 25;252(4):1162–1166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segawa T., Fukasawa T. The enzymes of the galactose cluster in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Purification and characterization of galactose-1-phosphate uridylyltransferase. J Biol Chem. 1979 Nov 10;254(21):10707–10709. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selleck S. B., Majors J. E. In vivo DNA-binding properties of a yeast transcription activator protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;7(9):3260–3267. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.9.3260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selleck S. B., Majors J. Photofootprinting in vivo detects transcription-dependent changes in yeast TATA boxes. Nature. 1987 Jan 8;325(7000):173–177. doi: 10.1038/325173a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sengstag C., Hinnen A. The sequence of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae gene PHO2 codes for a regulatory protein with unusual aminoacid composition. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jan 12;15(1):233–246. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.1.233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimada H., Fukasawa T. Controlled transcription of the yeast regulatory gene GAL80. Gene. 1985;39(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90100-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver P. A., Brent R., Ptashne M. DNA binding is not sufficient for nuclear localization of regulatory proteins in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4763–4766. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver P. A., Keegan L. P., Ptashne M. Amino terminus of the yeast GAL4 gene product is sufficient for nuclear localization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(19):5951–5955. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.19.5951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiegelman S., Delorenzo W. F., Campbell A. M. A Single-Cell Analysis of the Transmission of Enzyme-Forming Capacity in Yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1951 Aug;37(8):513–524. doi: 10.1073/pnas.37.8.513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiegelman S., Delorenzo W. F. Substrate Stabilization of Enzyme-Forming Capacity During the Segregation of a Heterozygote. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1952 Jul;38(7):583–592. doi: 10.1073/pnas.38.7.583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St John T. P., Davis R. W. Isolation of galactose-inducible DNA sequences from Saccharomyces cerevisiae by differential plaque filter hybridization. Cell. 1979 Feb;16(2):443–452. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90020-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St John T. P., Davis R. W. The organization and transcription of the galactose gene cluster of Saccharomyces. J Mol Biol. 1981 Oct 25;152(2):285–315. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90244-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St John T. P., Scherer S., McDonell M. W., Davis R. W. Deletion analysis of the Saccharomyces GAL gene cluster. Transcription from three promoters. J Mol Biol. 1981 Oct 25;152(2):317–334. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90245-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl K. Genetic properties and chromatin structure of the yeast gal regulatory element: an enhancer-like sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7865–7869. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl K. Negative control at a distance mediates catabolite repression in yeast. 1985 Oct 31-Nov 6Nature. 317(6040):822–824. doi: 10.1038/317822a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl K. Promoters, activator proteins, and the mechanism of transcriptional initiation in yeast. Cell. 1987 May 8;49(3):295–297. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90277-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tajima M., Nogi Y., Fukasawa T. Duplicate upstream activating sequences in the promoter region of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae GAL7 gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jan;6(1):246–256. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.1.246. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tajima M., Nogi Y., Fukasawa T. Primary structure of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae GAL7 gene. Yeast. 1985 Sep;1(1):67–77. doi: 10.1002/yea.320010108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torchia T. E., Hamilton R. W., Cano C. L., Hopper J. E. Disruption of regulatory gene GAL80 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: effects on carbon-controlled regulation of the galactose/melibiose pathway genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Aug;4(8):1521–1527. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.8.1521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torchia T. E., Hopper J. E. Genetic and molecular analysis of the GAL3 gene in the expression of the galactose/melibiose regulon of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1986 Jun;113(2):229–246. doi: 10.1093/genetics/113.2.229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tschopp J. F., Emr S. D., Field C., Schekman R. GAL2 codes for a membrane-bound subunit of the galactose permease in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1986 Apr;166(1):313–318. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.1.313-318.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuyumu S., Adams B. G. Dilution kinetic studies of yeast populations: in vivo aggregation of galactose utilizing enzymes and positive regulator molecules. Genetics. 1974 Jul;77(3):491–505. doi: 10.1093/genetics/77.3.491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuyumu S., Adams B. G. Population analysis of the deinduction kinetics of galactose long-term adaptation mutants of yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Mar;70(3):919–923. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.3.919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WINGE O., ROBERTS C. Complementary action of melibiase and galactozymase on raffinose fermentation. Nature. 1956 Feb 25;177(4504):383–384. doi: 10.1038/177383a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wen D. Z., Schlesinger M. J. Regulated expression of Sindbis and vesicular stomatitis virus glycoproteins in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):3639–3643. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.3639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West R. W., Jr, Yocum R. R., Ptashne M. Saccharomyces cerevisiae GAL1-GAL10 divergent promoter region: location and function of the upstream activating sequence UASG. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Nov;4(11):2467–2478. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.11.2467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wray L. V., Jr, Witte M. M., Dickson R. C., Riley M. I. Characterization of a positive regulatory gene, LAC9, that controls induction of the lactose-galactose regulon of Kluyveromyces lactis: structural and functional relationships to GAL4 of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Mar;7(3):1111–1121. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.3.1111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K. R. Steroid receptor regulated transcription of specific genes and gene networks. Annu Rev Genet. 1985;19:209–252. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.19.120185.001233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanofsky C., Kelley R. L., Horn V. Repression is relieved before attenuation in the trp operon of Escherichia coli as tryptophan starvation becomes increasingly severe. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jun;158(3):1018–1024. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.3.1018-1024.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yocum R. R., Hanley S., West R., Jr, Ptashne M. Use of lacZ fusions to delimit regulatory elements of the inducible divergent GAL1-GAL10 promoter in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Oct;4(10):1985–1998. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.10.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yocum R. R., Johnston M. Molecular cloning of the GAL80 gene from Saccharomyces cerevisiae and characterization of a gal80 deletion. Gene. 1984 Dec;32(1-2):75–82. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90034-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou K., Brisco P. R., Hinkkanen A. E., Kohlhaw G. B. Structure of yeast regulatory gene LEU3 and evidence that LEU3 itself is under general amino acid control. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 10;15(13):5261–5273. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.13.5261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


