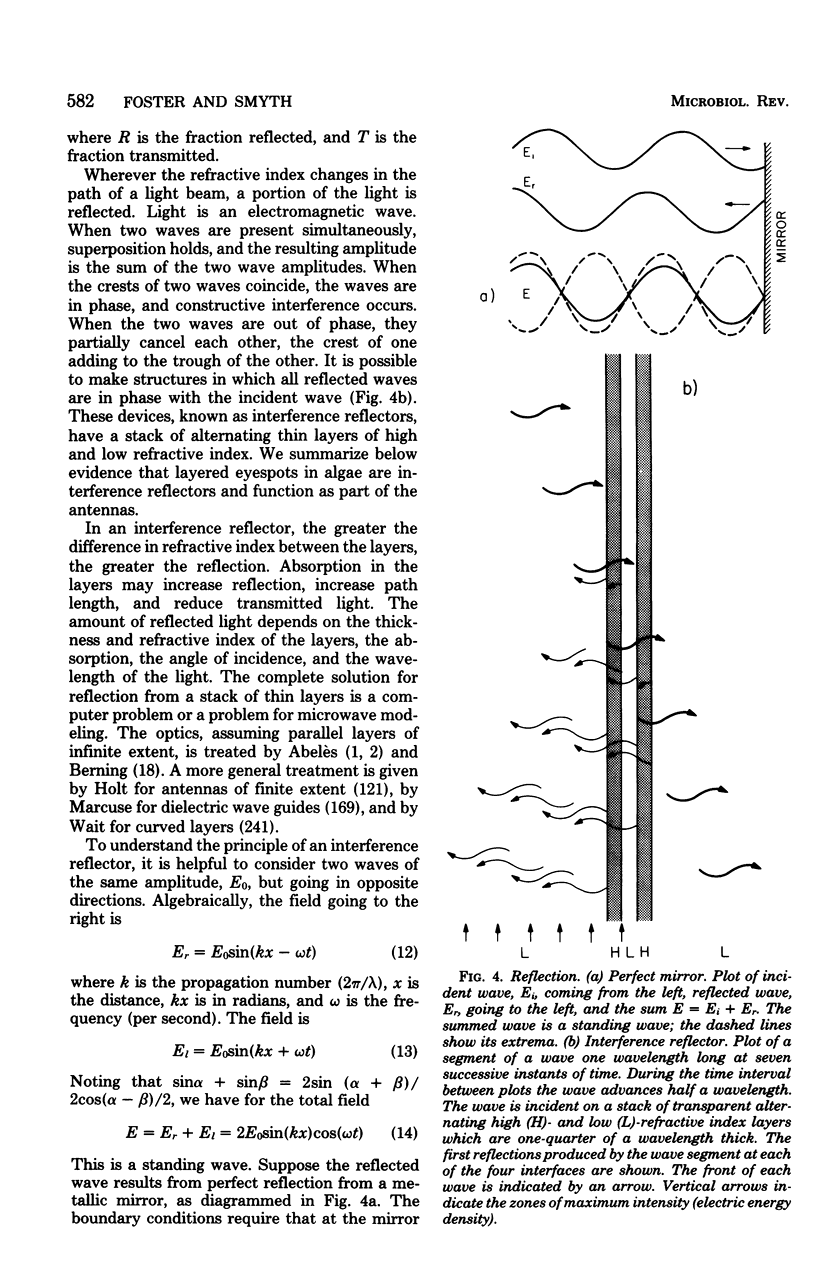
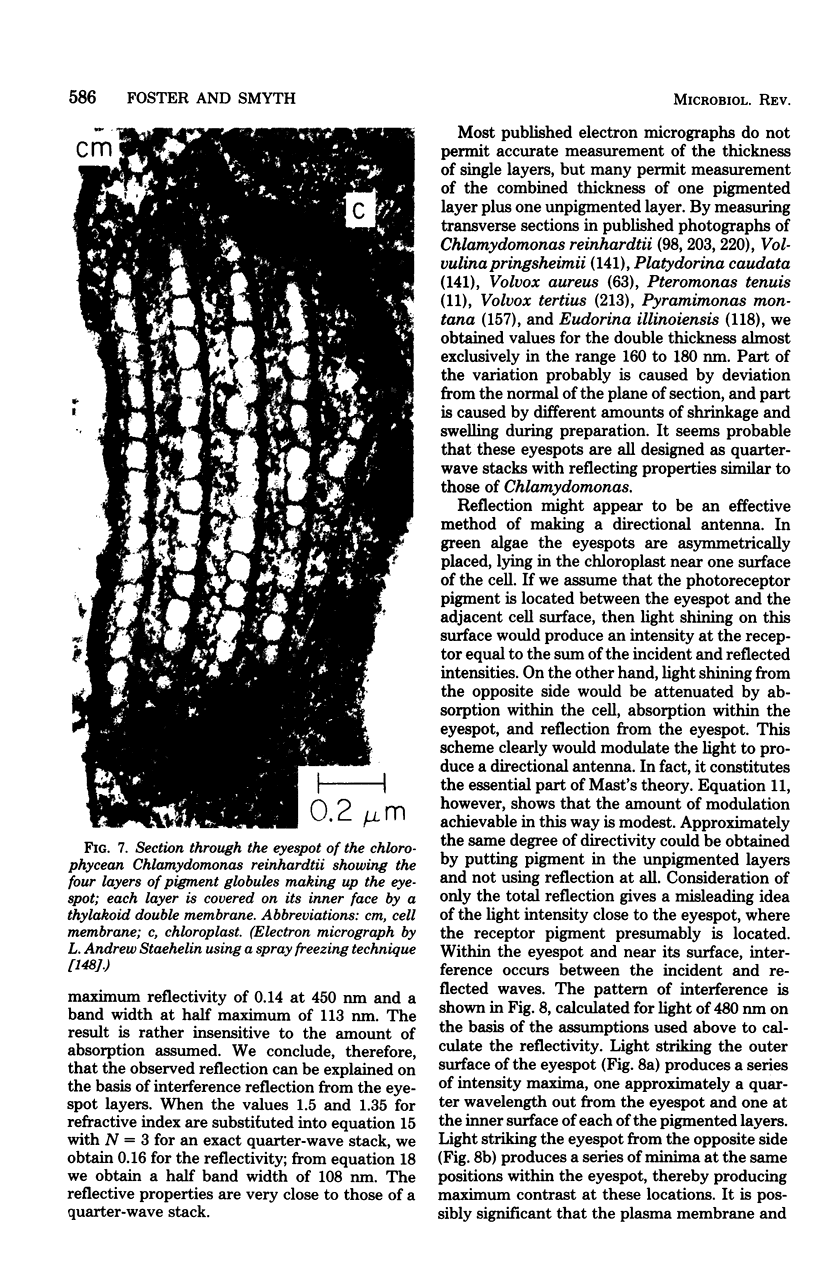
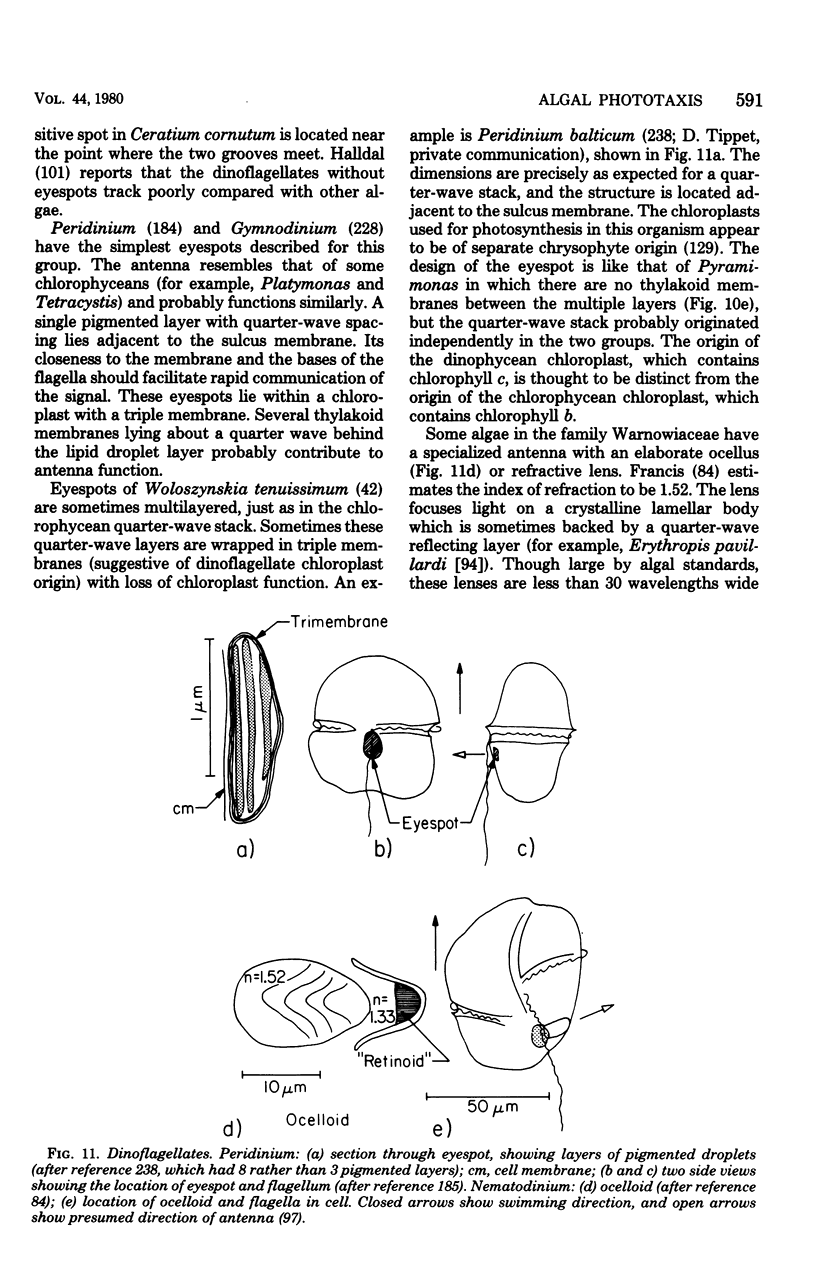
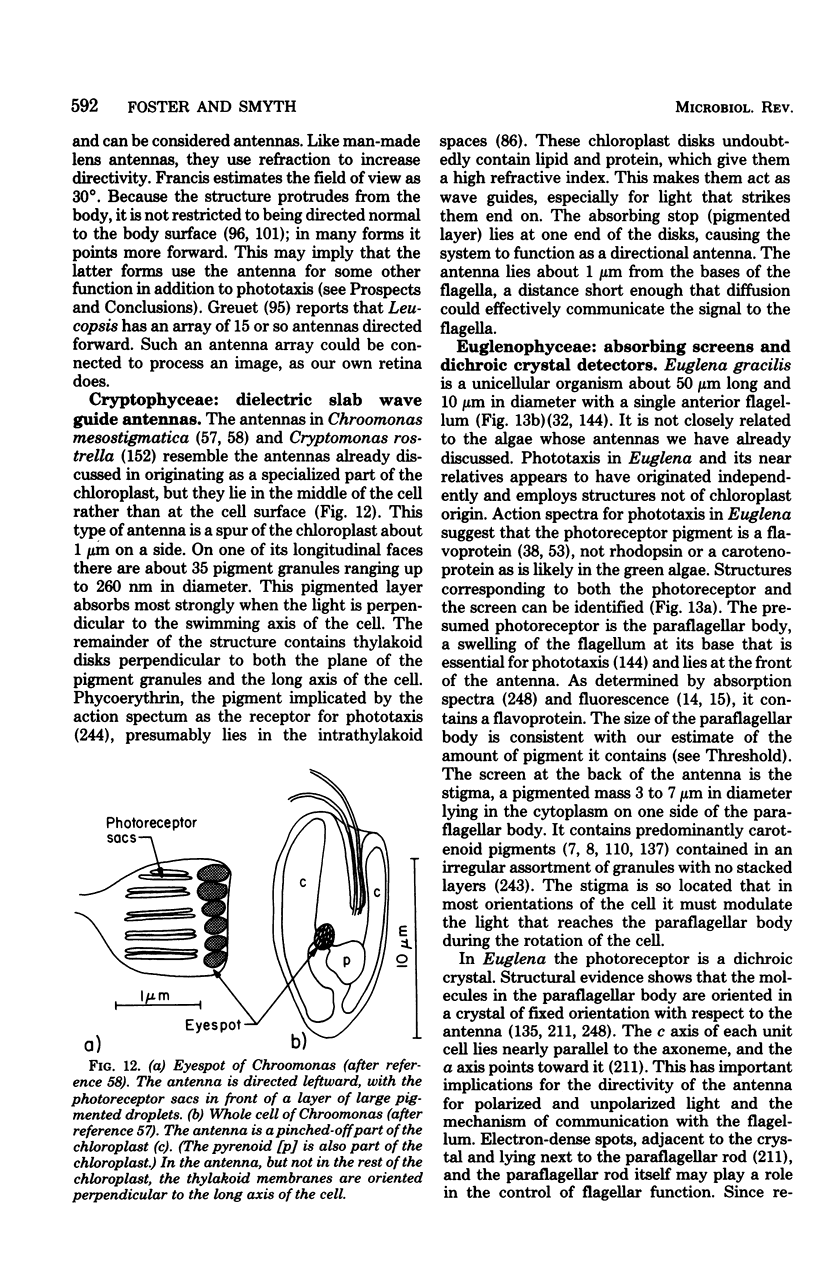
Full text
PDF


















































Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alpern M., Pugh E. N., Jr The density and photosensitivity of human rhodopsin in the living retina. J Physiol. 1974 Mar;237(2):341–370. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ascoli C., Barbi M., Frediani C., Murè A. Measurements of Euglena motion parameters by laser light scattering. Biophys J. 1978 Dec;24(3):585–599. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(78)85406-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BATRA P. P., TOLLIN G. PHOTOTAXIS IN EUGLENA. I. ISOLATION OF THE EYE-SPOT GRANULES AND IDENTIFICATION OF THE EYE-SPOT PIGMENTS. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Mar 30;79:371–378. doi: 10.1016/0926-6585(64)90017-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bader C. R., Macleish P. R., Schwartz E. A. A voltage-clamp study of the light response in solitary rods of the tiger salamander. J Physiol. 1979 Nov;296:1–26. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartlett C. J., Walne P. L., Schwarz O. J., Brown D. H. Large Scale Isolation and Purification of Eyespot Granules from Euglena gracilis var. bacillaris. Plant Physiol. 1972 Jun;49(6):881–885. doi: 10.1104/pp.49.6.881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg H. C., Tedesco P. M. Transient response to chemotactic stimuli in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Aug;72(8):3235–3239. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.8.3235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonting S. L., van Breugel P. J., Daemen F. J. Influence of the lipid environment of the properties of rhodopsin in the photoreceptor membrane. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1977;83:175–189. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-3276-3_16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bray D. F., Nakamura K., Costerton J. W., Wagenaar E. B. Ultrastructure of Chlamydomonas eugametos as revealed by freeze-etching: cell wall, plasmalemma and chloroplast membrane. J Ultrastruct Res. 1974 May;47(2):125–141. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(74)80065-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. A., Berg H. C. Temporal stimulation of chemotaxis in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1388–1392. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CASTLE E. S. DIFFERENTIAL GROWTH AND PHOTOTROPIC BENDING IN PHYCOMYCES. J Gen Physiol. 1965 Jan;48:409–423. doi: 10.1085/jgp.48.3.409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLAYTON R. K. On the interplay of environmental factors affecting taxis and motility in Rhodospirillum rubrum. Arch Mikrobiol. 1958;29(2):189–212. doi: 10.1007/BF00409860. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlquist F. W., Elwell R. A., Lovely P. S. Studies of bacterial chemotaxis in defined concentration gradients. A model for chemotaxis toward L-serine. J Supramol Struct. 1976;4(3):329–342. doi: 10.1002/jss.400040304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delbrück M., Shropshire W. Action and Transmission Spectra of Phycomyces. Plant Physiol. 1960 Mar;35(2):194–204. doi: 10.1104/pp.35.2.194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennison D. S., Foster K. W. Intracellular rotation and the phototropic response of Phycomyces. Biophys J. 1977 Apr;18(1):103–123. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(77)85599-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diehn B. Action spectra of the phototactic responses in Euglena. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Feb 18;177(1):136–143. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(69)90073-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodge J. D. Fine structure and phylogeny in the algae. Sci Prog. 1974 Summer;61(242):257–274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckert R., Brehm P. Ionic mechanisms of excitation in Paramecium. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1979;8:353–383. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.08.060179.002033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enoch J. M., Birch D. G., Birch E. E. Monocular light exclusion for a period of days reduces directional sensitivity of the human retina. Science. 1979 Nov 9;206(4419):705–707. doi: 10.1126/science.493976. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fain G. L., Quandt F. N., Bastian B. L., Gerschenfeld H. M. Contribution of a caesium-sensitive conductance increase to the rod photoresponse. Nature. 1978 Mar 30;272(5652):466–469. doi: 10.1038/272467a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forward R. B., Jr Phototaxis by the dinoflagellate Gymnodinium splendens Lebour. J Protozool. 1974 May;21(2):312–315. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1974.tb03659.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster K. W., Lipson E. D. The light growth response of Phycomyces. J Gen Physiol. 1973 Nov;62(5):590–617. doi: 10.1085/jgp.62.5.590. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster K. W. Phototropism of coprophilous zygomycetes. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1977;6:419–443. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.06.060177.002223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francis D. On the eyespot of the dinoflagellate, Nematodinium. J Exp Biol. 1967 Dec;47(3):495–501. doi: 10.1242/jeb.47.3.495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOSSEL I. Uber das Aktionsspektrum der Phototaxis chlorophyllfreier Euglenen und über die Absorption des Augenflecks. Arch Mikrobiol. 1957;27(3):288–305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gantt E., Edwards M. R., Provasoli L. Chloroplast structure of the Cryptophyceae. Evidence for phycobiliproteins within intrathylakoidal spaces. J Cell Biol. 1971 Feb;48(2):280–290. doi: 10.1083/jcb.48.2.280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruber H. E., Rosario B. Variation in eyespot ultrastructure in Chlamydomonas reinhardi (ac-31). J Cell Sci. 1974 Aug;15(3):481–494. doi: 10.1242/jcs.15.3.481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagins W. A., Penn R. D., Yoshikami S. Dark current and photocurrent in retinal rods. Biophys J. 1970 May;10(5):380–412. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(70)86308-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagins W. A., Yoshikami S. Proceedings: A role for Ca2+ in excitation of retinal rods and cones. Exp Eye Res. 1974 Mar;18(3):299–305. doi: 10.1016/0014-4835(74)90157-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hecht S., Shlaer S., Pirenne M. H. ENERGY, QUANTA, AND VISION. J Gen Physiol. 1942 Jul 20;25(6):819–840. doi: 10.1085/jgp.25.6.819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heelis D. V., Kernick W., Phillips G. O., Davies K. Separation and identification of the carotenoid pigments of stigmata isolated from light-grown cells of Euglena gracilis strain Z. Arch Microbiol. 1979 Jun;121(3):207–211. doi: 10.1007/BF00425057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemmerich P. The present status of flavin and flavocoenzyme chemistry. Fortschr Chem Org Naturst. 1976;33:451–527. doi: 10.1007/978-3-7091-3262-3_5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson R. The purple membrane from Halobacterium halobium. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1977;6:87–109. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.06.060177.000511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hibberd D. J. The structure and phylogenetic significance of the flagellar transition region in the chlorophyll c-containing algae. Biosystems. 1979 Dec;11(4):243–261. doi: 10.1016/0303-2647(79)90025-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huskey R. J. Mutants affecting vegetative cell orientation in Volvox carteri. Dev Biol. 1979 Oct;72(2):236–243. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(79)90114-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyams J. S., Borisy G. G. Isolated flagellar apparatus of Chlamydomonas: characterization of forward swimming and alteration of waveform and reversal of motion by calcium ions in vitro. J Cell Sci. 1978 Oct;33:235–253. doi: 10.1242/jcs.33.1.235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahn T. L., Bovee E. C. Movement and locomotion of microorganisms. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1965;19:21–58. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.19.100165.000321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jesaitis A. J. Linear dichroism and orientation of the Phycomyces photopigment. J Gen Physiol. 1974 Jan;63(1):1–21. doi: 10.1085/jgp.63.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRINSKY N. I., GOLDSMITH T. H. The carotenoids of the flagellated alga. Euglena gracilis. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1960 Dec;91:271–279. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(60)90501-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krebs W., Kühn H. Structure of isolated bovine rod outer segment membranes. Exp Eye Res. 1977 Nov;25(5):511–526. doi: 10.1016/0014-4835(77)90180-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Land M. F. The physics and biology of animal reflectors. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1972;24:75–106. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(72)90004-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenci F., Colombetti G. Photobehavior of microorganisms: a biophysical approach. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1978;7:341–361. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.07.060178.002013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linder J. C., Staehelin L. A. A novel model for fluid secretion by the trypanosomatid contractile vacuole apparatus. J Cell Biol. 1979 Nov;83(2 Pt 1):371–382. doi: 10.1083/jcb.83.2.371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipson E. D. White noise analysis of Phycomyces light growth response system. II. Extended intensity ranges. Biophys J. 1975 Oct;15(10):1013–1031. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(75)85880-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litvin F. F., Sineshchekov O. A., Sineshchekov V. A. Photoreceptor electric potential in the phototaxis of the alga Haematococcus pluvialis. Nature. 1978 Feb 2;271(5644):476–478. doi: 10.1038/271476a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus M. A., Lewis A. Kinetic resonance Raman spectroscopy: dynamics of deprotonation of the Schiff base of bacteriorhodopsin. Science. 1977 Mar 25;195(4284):1328–1330. doi: 10.1126/science.841330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick D. B. Interactions of flavins with amino acid residues: assessments from spectral and photochemical studies. Photochem Photobiol. 1977 Aug;26(2):169–182. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1977.tb07471.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mesibov R., Ordal G. W., Adler J. The range of attractant concentrations for bacterial chemotaxis and the threshold and size of response over this range. Weber law and related phenomena. J Gen Physiol. 1973 Aug;62(2):203–223. doi: 10.1085/jgp.62.2.203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moestrup O. On the phylogenetic validity of the flagellar apparatus in green algae and other chlorophyll A and B containing plants. Biosystems. 1978 Apr;10(1-2):117–144. doi: 10.1016/0303-2647(78)90035-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols K. M., Rikmenspoel R. Control of flagellar motion in Chlamydomonas and Euglena by mechanical microinjection of Mg2+ and Ca2+ and by electric current injection. J Cell Sci. 1978 Feb;29:233–247. doi: 10.1242/jcs.29.1.233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nultsch W. Effect of external factors on phototaxis of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. II. Charbon dioxide, oxygen and pH. Arch Microbiol. 1977 Mar 1;112(2):179–185. doi: 10.1007/BF00429333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohad I., Siekevitz P., Palade G. E. Biogenesis of chloroplast membranes. I. Plastid dedifferentiation in a dark-grown algal mutant (Chlamydomonas reinhardi). J Cell Biol. 1967 Dec;35(3):521–552. doi: 10.1083/jcb.35.3.521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Retallack B., Butler R. D. Reproduction in Bulbochaete hiloensis (nordst.) tiffany. I. Structure of the zoospore. Arch Mikrobiol. 1972;86(4):265–280. doi: 10.1007/BF00424984. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rushton W. A., Henry G. H. Bleaching and regeneration of cone pigments in man. Vision Res. 1968 Jun;8(6):617–631. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(68)90040-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAGER R., PALADE G. E. Chloroplast structure in green and yellow strains of Chlamydomonas. Exp Cell Res. 1954 Nov;7(2):584–588. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4827(54)80107-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt J. A., Eckert R. Calcium couples flagellar reversal to photostimulation in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Nature. 1976 Aug 19;262(5570):713–715. doi: 10.1038/262713a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Song P. S., Koka P., Prézelin B. B., Haxo F. T. Molecular topology of the photosynthetic light-harvesting pigment complex, peridinin-chlorophyll a-protein, from marine dinoflagellates. Biochemistry. 1976 Oct 5;15(20):4422–4427. doi: 10.1021/bi00665a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer M. S., Goy M. F., Adler J. Protein methylation in behavioural control mechanisms and in signal transduction. Nature. 1979 Jul 26;280(5720):279–284. doi: 10.1038/280279a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoeckenius W., Lozier R. H., Bogomolni R. A. Bacteriorhodopsin and the purple membrane of halobacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Mar 14;505(3-4):215–278. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(79)90006-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALD G., BROWN P. K. The molar extinction of rhodopsin. J Gen Physiol. 1953 Nov 20;37(2):189–200. doi: 10.1085/jgp.37.2.189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolken J. J. Euglena: the photoreceptor system for phototaxis. J Protozool. 1977 Nov;24(4):518–522. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1977.tb01004.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




