Full text
PDF



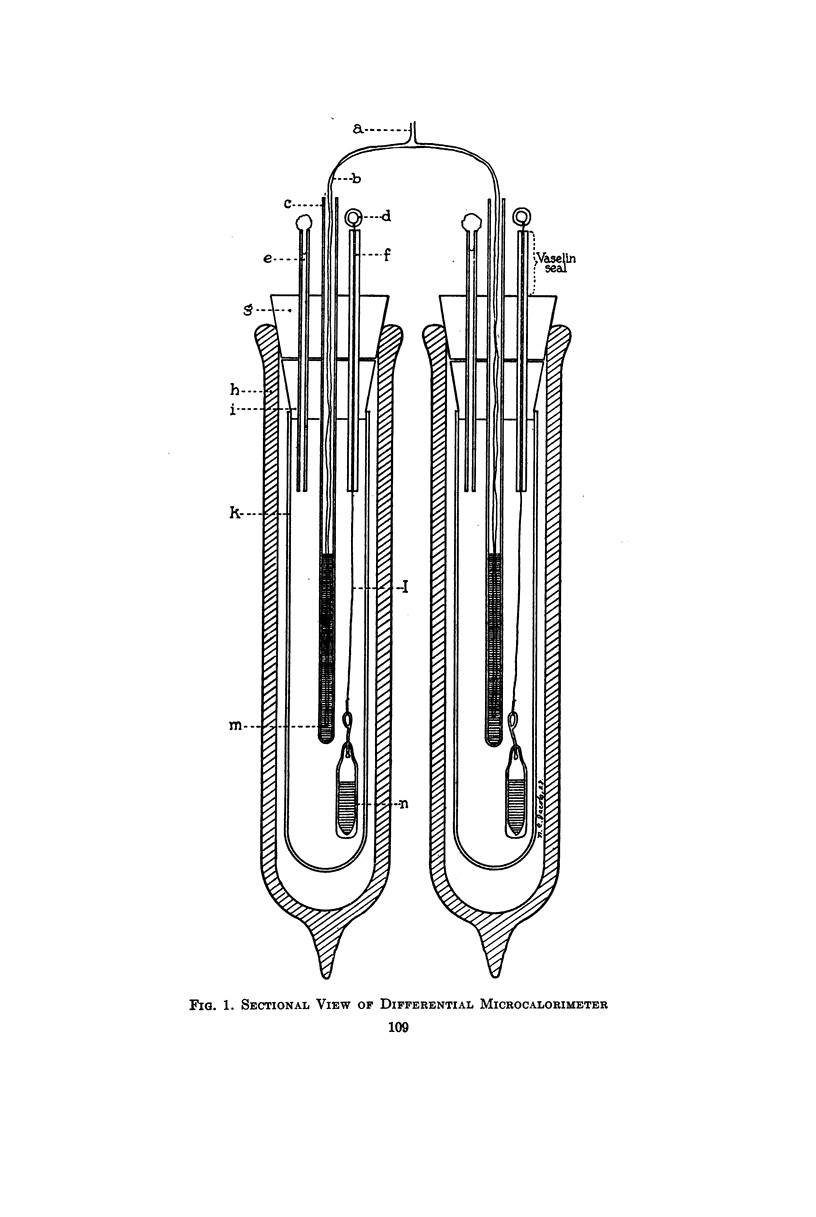





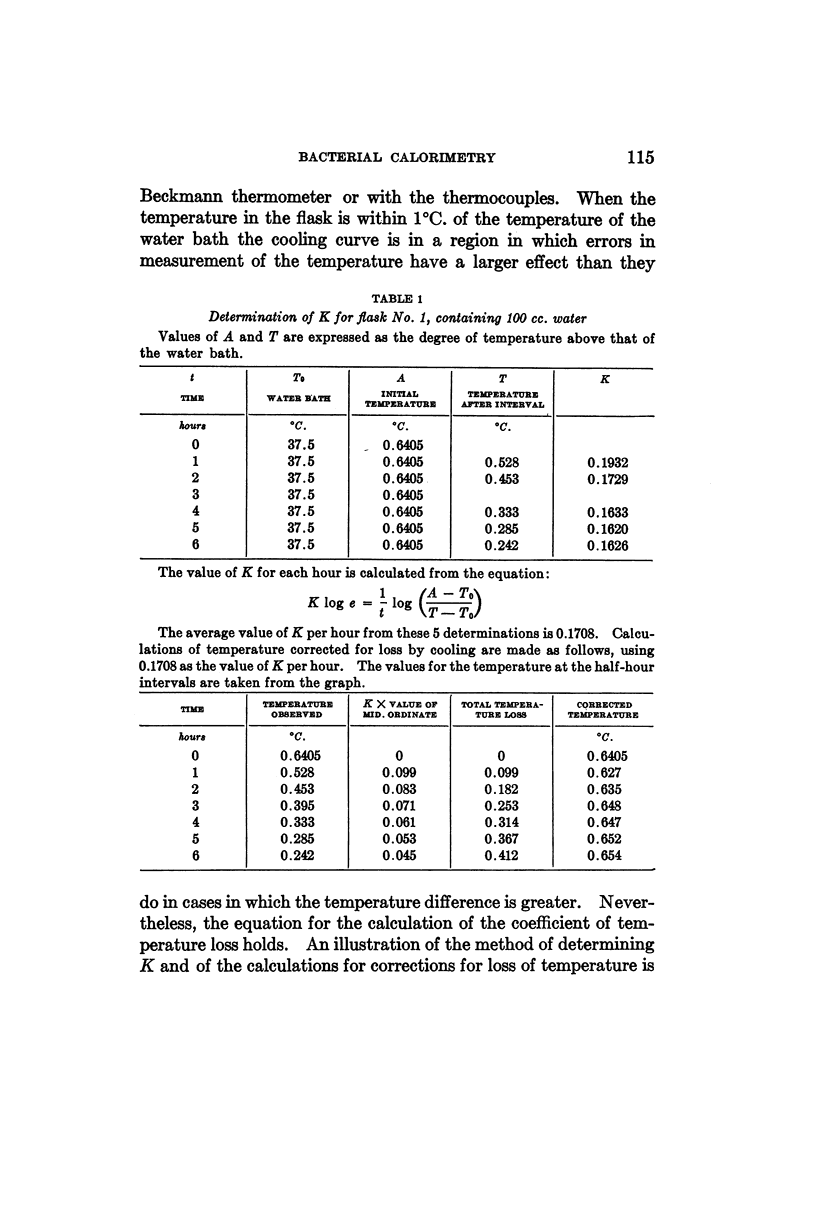
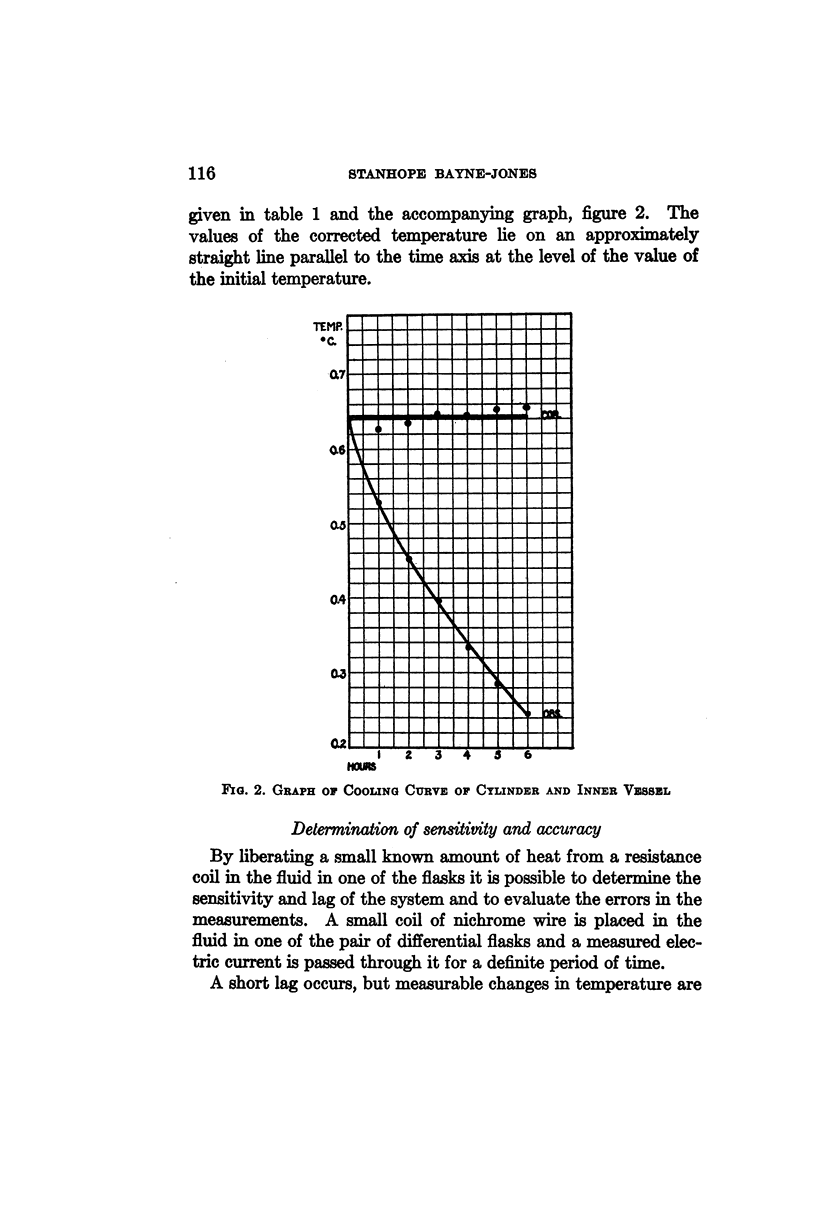

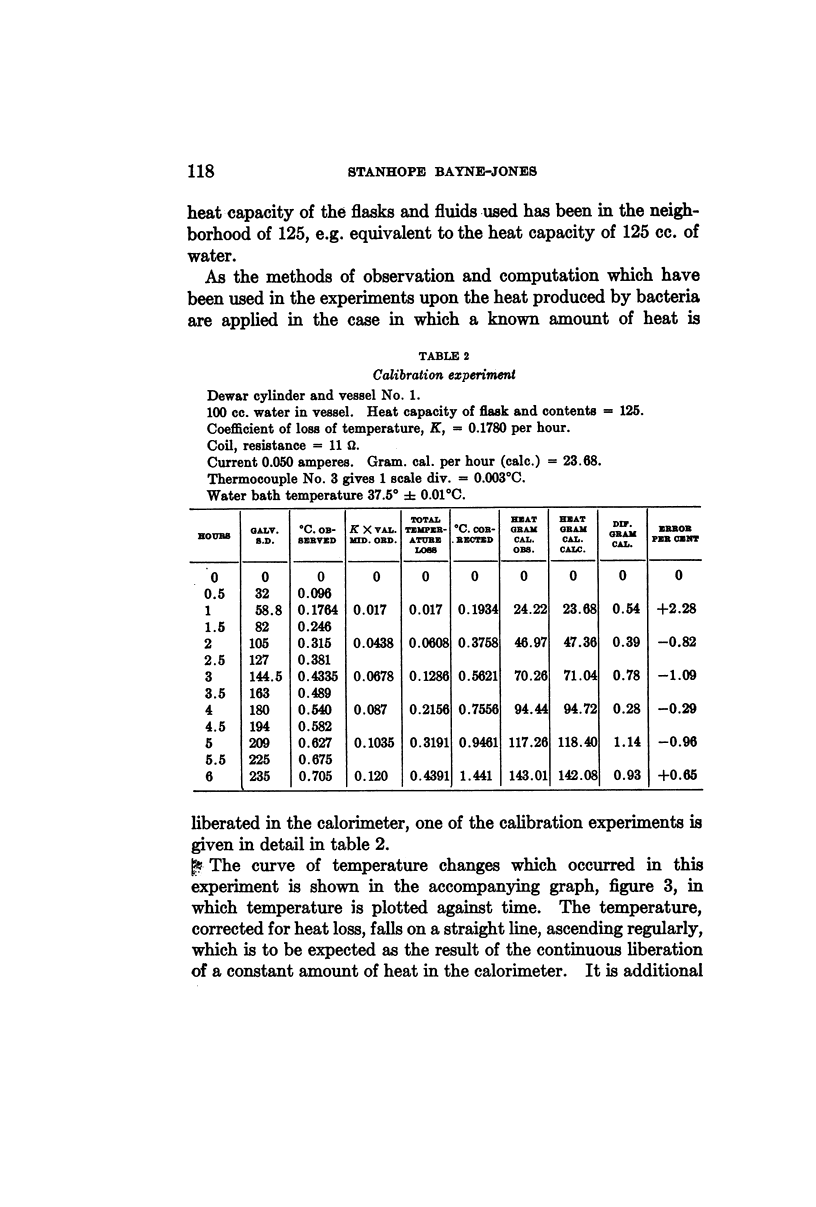



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Hill A. V. A new form of differential micro-calorimeter, for the estimation of heat production in physiological, bacteriological, or ferment actions. J Physiol. 1911 Nov 20;43(3-4):261–285. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1911.sp001472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill A. V. The heat-producton of surviving amphibian muscles, during rest, activity, and rigor. J Physiol. 1912 Jul 15;44(5-6):466–513. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1912.sp001526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James L. H., James L. H. STUDIES IN MICROBIAL THERMOGENESIS. Science. 1927 May 20;65(1690):504–506. doi: 10.1126/science.65.1690.504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James L. H., Rettger L. F., Thom C. MICROBIAL THERMOGENESIS II. HEAT PRODUCTION IN MOIST ORGANIC MATERIALS WITH SPECIAL REFERENCE TO THE PART PLAYED BY MICROORGANISMS. J Bacteriol. 1928 Feb;15(2):117–141. doi: 10.1128/jb.15.2.117-141.1928. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shearer C. On the amount of heat liberated by bacillus coli when grown in the presence of free amino-acids. J Physiol. 1921 May 24;55(1-2):50–60. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1921.sp001955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


