Abstract
When simian virus 40 (SV40)-transformed mouse kidney cells (mKS) were grown in the presence of susceptible indicator cells, SV40 was readily recovered from: (i) 15 transformed cell lines, (ii) transformed cells subcultured 45 times over a 7-month period in medium containing antiviral serum and bromodeoxyuridine (dBU), (iii) 45 of 46 clonal lines isolated in the presence of antiviral serum, (iv) 19 of 19 secondary clones isolated from two clonal lines, and (v) dBU-resistant transformed cell lines. dBU-resistant SV40-transformed mouse kidney cell lines were selected and shown to contain the T antigen and to have normal levels of thymidylate kinase and deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) polymerase, but to be deficient in thymidine (dT) kinase. Radioautographic and biochemical experiments demonstrated that very little 3H-dT was incorporated into DNA of dBU-resistant cells during a 6-hr labeling period. After infection of dT kinase-deficient mKS cells with vaccinia virus, high levels of dT kinase were induced. The properties of SV40 recovered from dBU-sensitive and dBU-resistant cells were studied. SV40 recovered from transformed cells was shown to express in CV-1 cells at least six functions characteristic of parental virus: synthesis of capsid antigen, synthesis of T antigen, synthesis of viral DNA, induction of dT kinase, induction of DNA polymerase, and induction of host cell DNA synthesis. In addition, SV40 recovered from the transformed cells induced T antigen, dT kinase, deoxycytidylate deaminase, thymidylate kinase, and DNA polymerase in abortively infected mouse kidney cultures, and the virus was also capable of transforming primary cultures of mouse kidney cells.
Full text
PDF
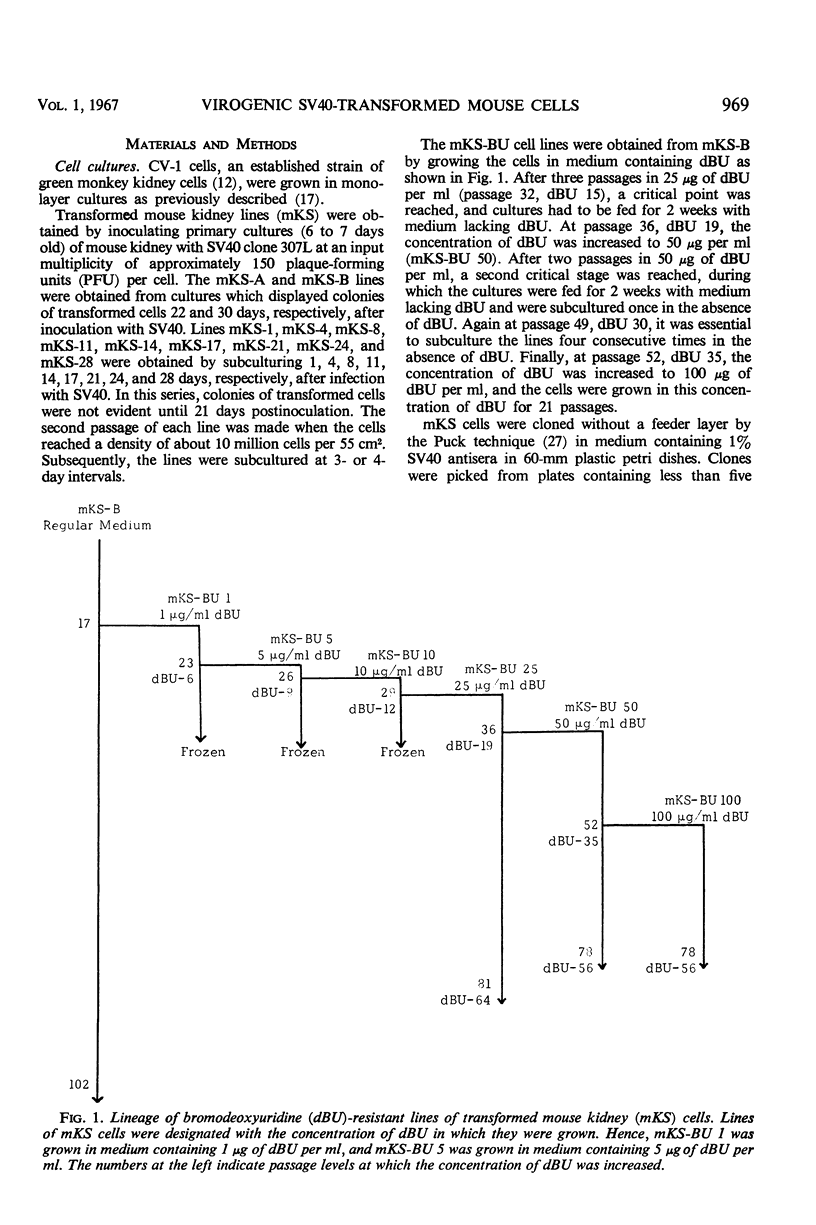

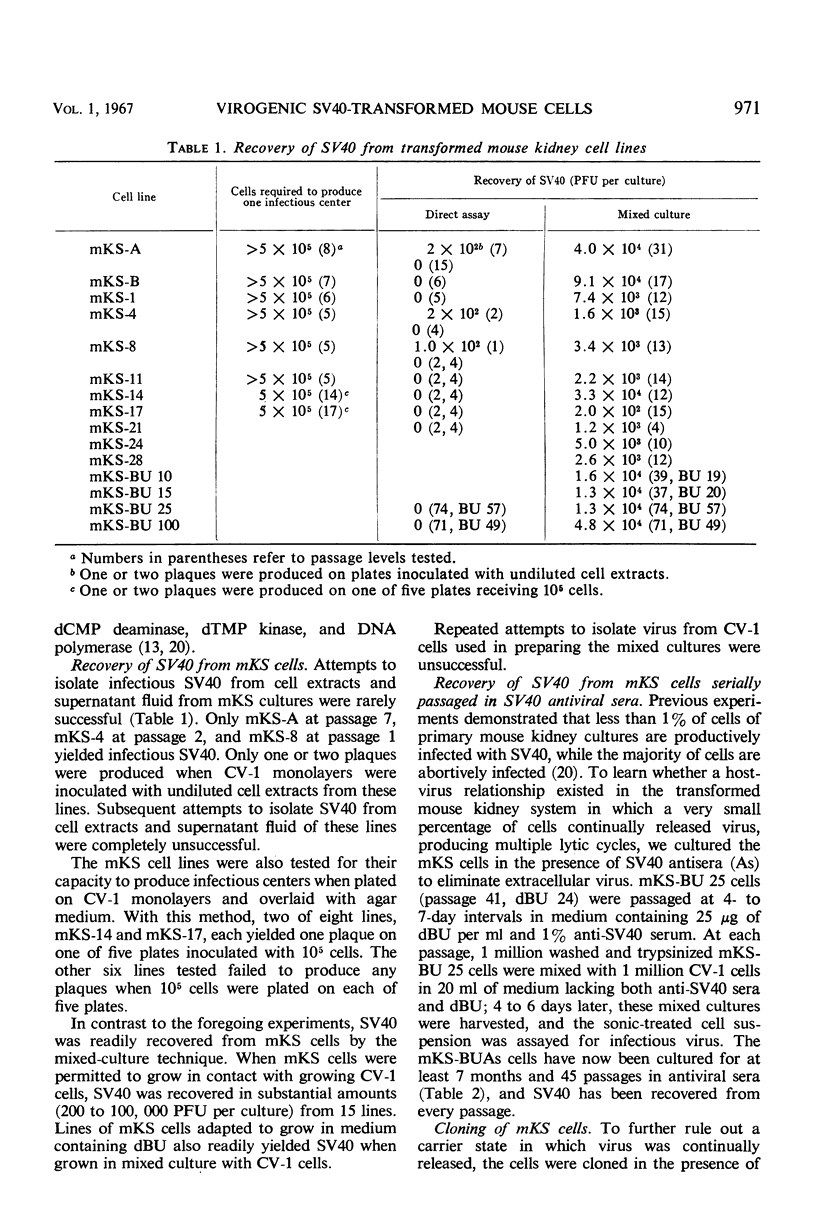
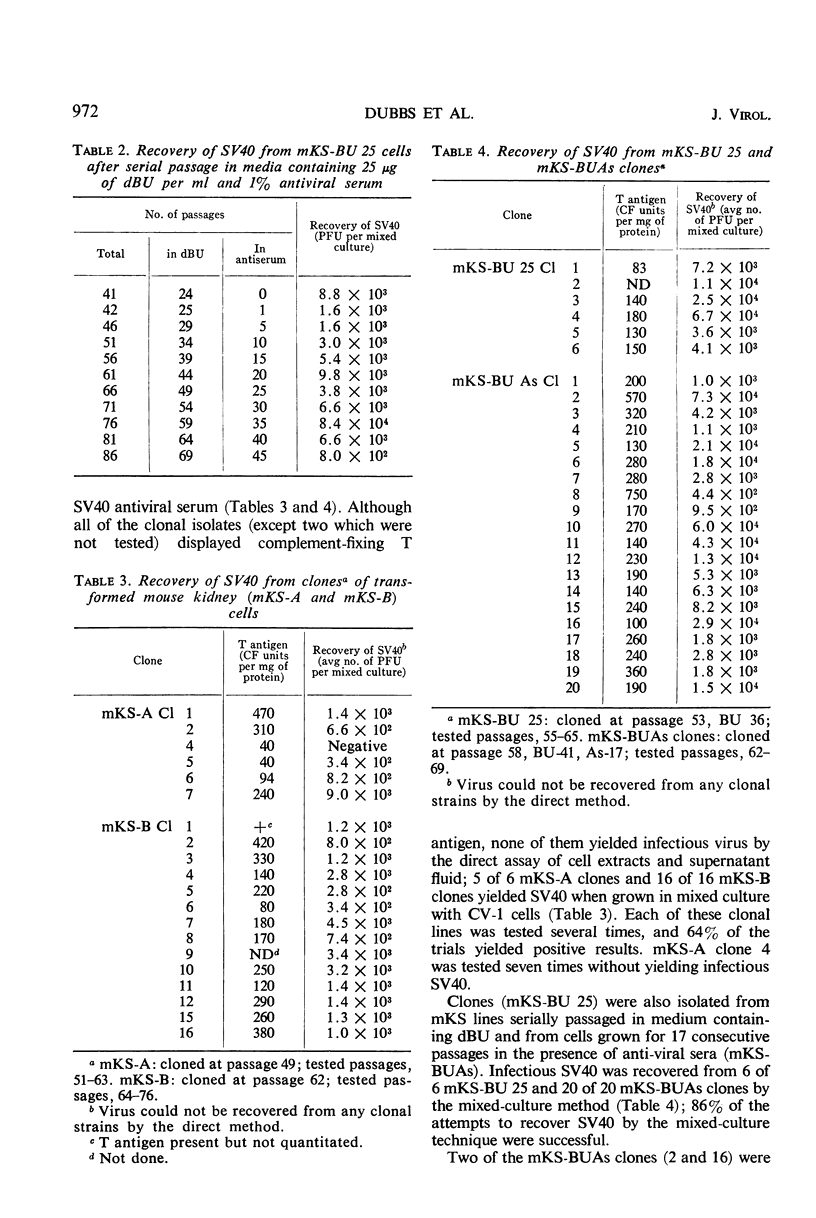
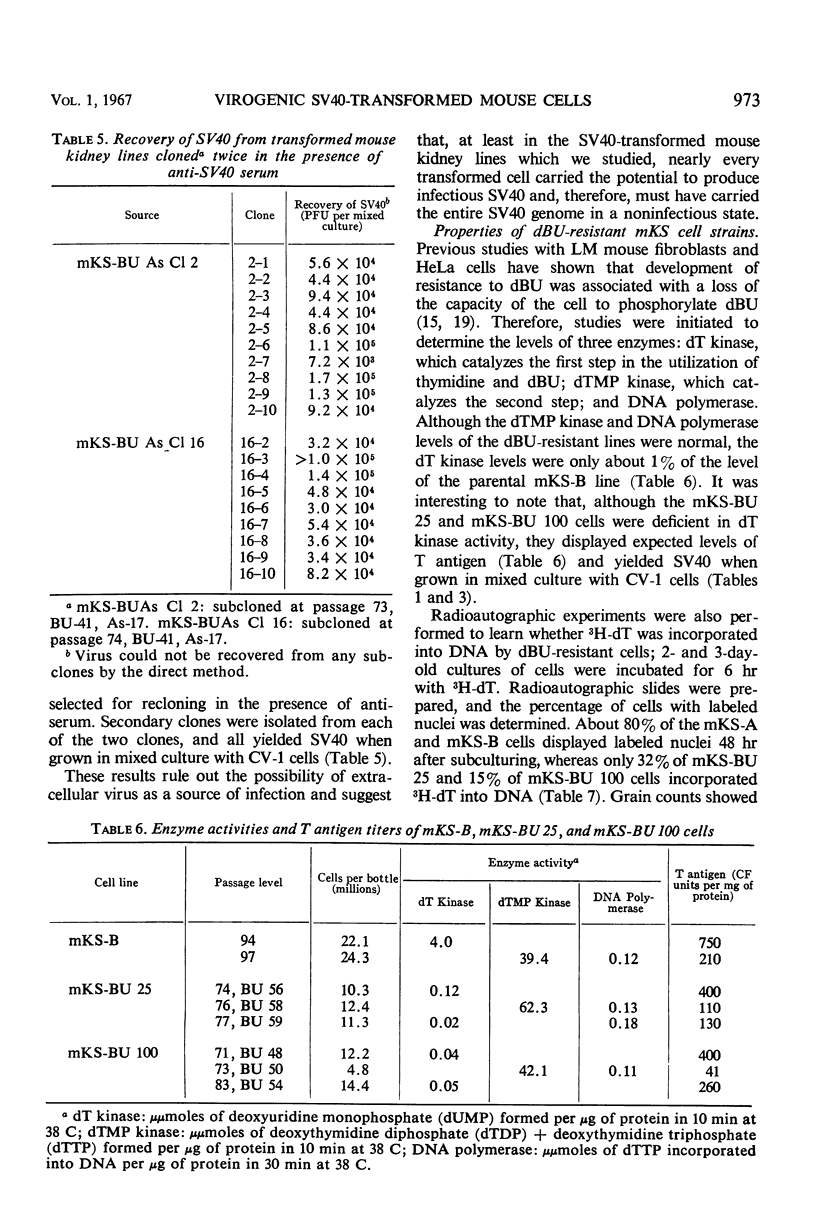



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLACK P. H., ROWE W. P., COOPER H. L. AN ANALYSIS OF SV 40-INDUCED TRANSFORMATION OF HAMSTER KIDNEY TISSUE IN VITRO. II. STUDIES OF THREE CLONES DERIVED FROM A CONTINUOUS LINE OF TRANSFORMED CELLS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Nov;50:847–854. doi: 10.1073/pnas.50.5.847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLACK P. H., ROWE W. P., TURNER H. C., HUEBNER R. J. A SPECIFIC COMPLEMENT-FIXING ANTIGEN PRESENT IN SV40 TUMOR AND TRANSFORMED CELLS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Dec;50:1148–1156. doi: 10.1073/pnas.50.6.1148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black P. H. An analysis of SV40-induced transformation of hamster kidney tissue in vitro. 3. Persistence of SV40 viral genome in clones of transformed hamster cells. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1966 Oct;37(4):487–493. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUBBS D. R., KIT S. ISOLATION AND PROPERTIES OF VACCINIA MUTANTS DEFICIENT IN THYMIDINE KINASE-INDUCING ACTIVITY. Virology. 1964 Feb;22:214–225. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(64)90006-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ephrussi B., Weiss M. C. Interspecific hybridization of somatic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 May;53(5):1040–1042. doi: 10.1073/pnas.53.5.1040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frearson P. M., Kit S., Dubbs D. R. Induction of dihydrofolate reductase activity by SV40 and polyoma virus. Cancer Res. 1966 Aug;26(8):1653–1660. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GERBER P., KIRSCHSTEIN R. L. SV40-induced ependymomas in newborn hamsters. I. Virus-tumor relationships. Virology. 1962 Dec;18:582–588. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(62)90061-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GERBER P. VIROGENIC HAMSTER TUMOR CELLS: INDUCTION OF VIRUS SYNTHESIS. Science. 1964 Aug 21;145(3634):833–833. doi: 10.1126/science.145.3634.833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerber P. Studies on the transfer of subviral infectivity from SV40-induced hamster tumor cells to indicator cells. Virology. 1966 Apr;28(4):501–509. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(66)90234-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOGGAN M. D., ROWE W. P., BLACK P. H., HUEBNER R. J. PRODUCTION OF "TUMOR-SPECIFIC" ANTIGENS BY ONCOGENIC VIRUSES DURING ACUTE CYTOLYTIC INFECTIONS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Jan;53:12–19. doi: 10.1073/pnas.53.1.12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JENSEN F. C., GIRARDI A. J., GILDEN R. V., KOPROWSKI H. INFECTION OF HUMAN AND SIMIAN TISSUE CULTURES WITH ROUS SARCOMA VIRUS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Jul;52:53–59. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.1.53. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIT S., DUBBS D. R., HSU T. C. Biochemistry of vaccinia-infected mouse fibroblasts (strain L-M). III. Radioautographic and biochemical studies of thymidine-H3 uptake into DNA of L-M cells and rabbit cells in primary culture. Virology. 1963 Jan;19:13–22. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(63)90019-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIT S., DUBBS D. R., PIEKARSKI L. J., HSU T. C. DELETION OF THYMIDINE KINASE ACTIVITY FROM L CELLS RESISTANT TO BROMODEOXYURIDINE. Exp Cell Res. 1963 Aug;31:297–312. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(63)90007-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIT S., DUBBS D. R. PROPERTIES OF DEOXYTHYMIDINE KINASE PARTIALLY PURIFIED FROM NONINFECTED MOUSE FIBROBLAST CELLS. Virology. 1965 May;26:16–27. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(65)90021-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kit S., De Torres R. A., Dubbs D. R., Salvi M. L. Induction of cellular deoxyribonuleic acid synthesis by simian virus 40. J Virol. 1967 Aug;1(4):738–746. doi: 10.1128/jvi.1.4.738-746.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kit S., Dubbs D. R., Frearson P. M. Enzymes of nucleic acid metabolism in cells infected with polyoma virus. Cancer Res. 1966 Apr;26(4):638–646. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kit S., Dubbs D. R., Frearson P. M. HeLa cells resistant to bromodeoxyuridine and deficient in thymidine kinase activity. Int J Cancer. 1966 Jan;1(1):19–30. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910010105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kit S., Dubbs D. R., Frearson P. M., Melnick J. L. Enzyme induction in SV40-infected green monkey kidney cultures. Virology. 1966 May;29(1):69–83. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(66)90197-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kit S., Dubbs D. R., Piekarski L. J., de Torres R. A., Melnick J. L. Acquisition of enzyme function by mouse kidney cells abortively infected with papovavirus SV40. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Aug;56(2):463–470. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.2.463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kit S., Melnick J. L., Anken M., Dubbs D. R., De Torres R. A., Kitahara T. Nonidentiy of some simian virus 40-induced enzymes with tumor antigen. J Virol. 1967 Aug;1(4):684–692. doi: 10.1128/jvi.1.4.684-692.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kit S., Piekarski L. J., Dubbs D. R. DNA polymerase induced by Simian virus 40. J Gen Virol. 1967 Apr;1(2):163–173. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-1-2-163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MELNICK J. L., KHERA K. S., RAPP F. PAPOVAVIRUS SV40: FAILURE TO ISOLATE INFECTIOUS VIRUS FROM TRANSFORMED HAMSTER CELLS SYNTHESIZING SV40-INDUCED ANTIGENS. Virology. 1964 Jul;23:430–432. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(64)90267-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PUCK T. T., MARCUS P. I., CIECIURA S. J. Clonal growth of mammalian cells in vitro; growth characteristics of colonies from single HeLa cells with and without a feeder layer. J Exp Med. 1956 Feb 1;103(2):273–283. doi: 10.1084/jem.103.2.273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAPP F., BUTEL J. S., MELNICK J. L. VIRUS-INDUCED INTRANUCLEAR ANTIGEN IN CELLS TRANSFORMED BY PAPOVAVIRUS SV40. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1964 Aug-Sep;116:1131–1135. doi: 10.3181/00379727-116-29472. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAPP F., KITAHARA T., BUTEL J. S., MELNICK J. L. SYNTHESIS OF SV40 TUMOR ANTIGEN DURING REPLICATION OF SIMIAN PAPOVAVIRUS (SV40). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Nov;52:1138–1142. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.5.1138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SABIN A. B., KOCH M. A. BEHAVIOR OF NONINFECTIOUS SV 40 VIRAL GENOME IN HAMSTER TUMOR CELLS: INDUCTION OF SYNTHESIS OF INFECTIOUS VIRUS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Sep;50:407–417. doi: 10.1073/pnas.50.3.407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SABIN A. B., KOCH M. A. Evidence of continuous transmission of non-infectious SV 40 viral genome in most or all SV 40 hamster tumor cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Mar 15;49:304–311. doi: 10.1073/pnas.49.3.304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SABIN A. B., KOCH M. A. SOURCE OF GENETIC INFORMATION FOR SPECIFIC COMPLEMENT-FIXING ANTIGENS IN SV40 VIRUS-INDUCED TUMORS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Nov;52:1131–1138. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.5.1131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tournier P., Cassingena R., Wicker R., Coppey J., Suarez H. Etude du mécanisme de l'induction chez des cellules de hamster syrien transformées par le virus SV40. I. Propriétés d'une lignée cellulaire clonale. Int J Cancer. 1967 Mar 15;2(2):117–132. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910020207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


