Abstract
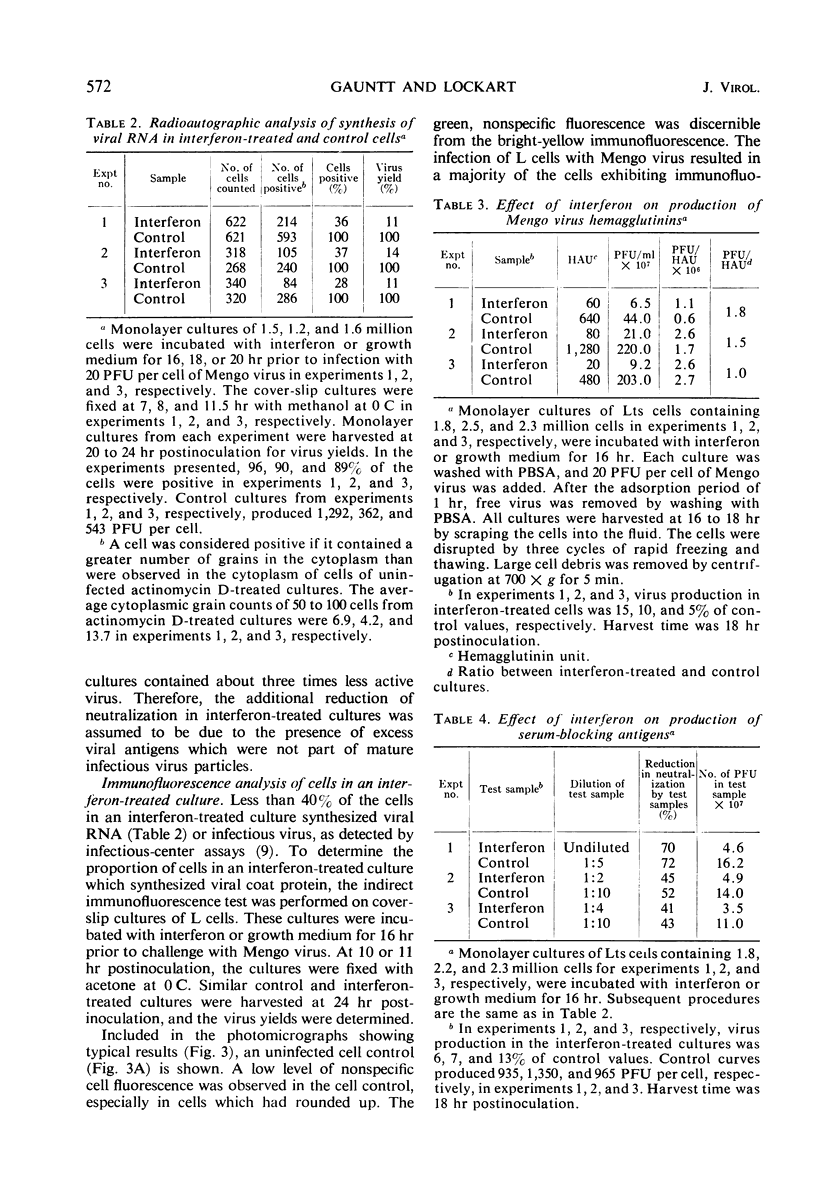
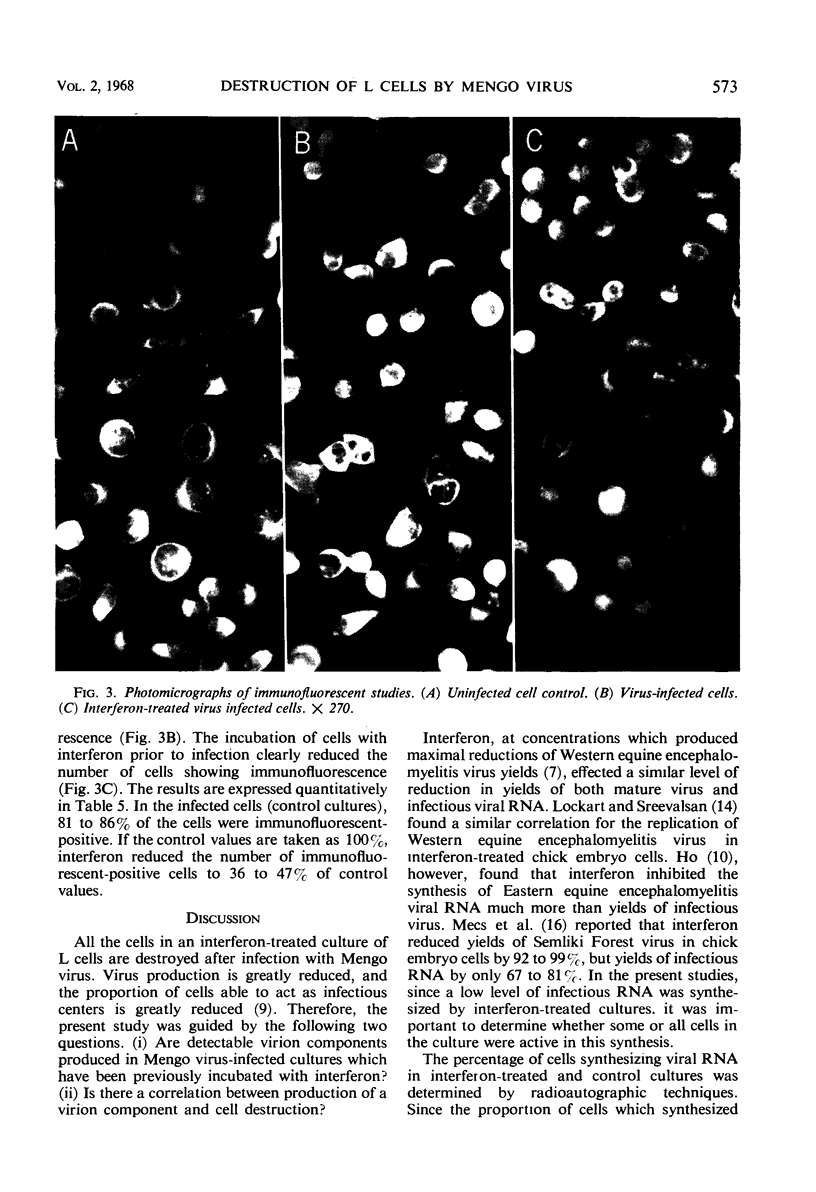
Interferon, when added to L cells, inhibited the synthesis of infectious Mengo viral ribonucleic acid, hemagglutinins, and infectious virus by 85 to 95%. Serum-blocking antigens were also reduced by the action of interferon, but threefold excess amounts of these antigens accumulated in interferon-treated cultures above the amounts expected for the quantity of infectious virus that was produced in these cultures. Radioautographic analysis showed that 28 to 36% of the cells of an interferon-treated population synthesized viral ribonucleic acid and 36 to 47% produced viral antigens as determined by an immunofluorescence technique. Despite the reductions in synthesis of viral components, all cells in an interferon-treated culture underwent cytopathic effects at the same time as cells in infected cultures which had not been treated with interferon. The results are compatible with the hypothesis that the cell destruction which results from the infection of L cells with Mengo virus is due to a protein which is coded for by the virus but is not a component of the mature virion.
Full text
PDF


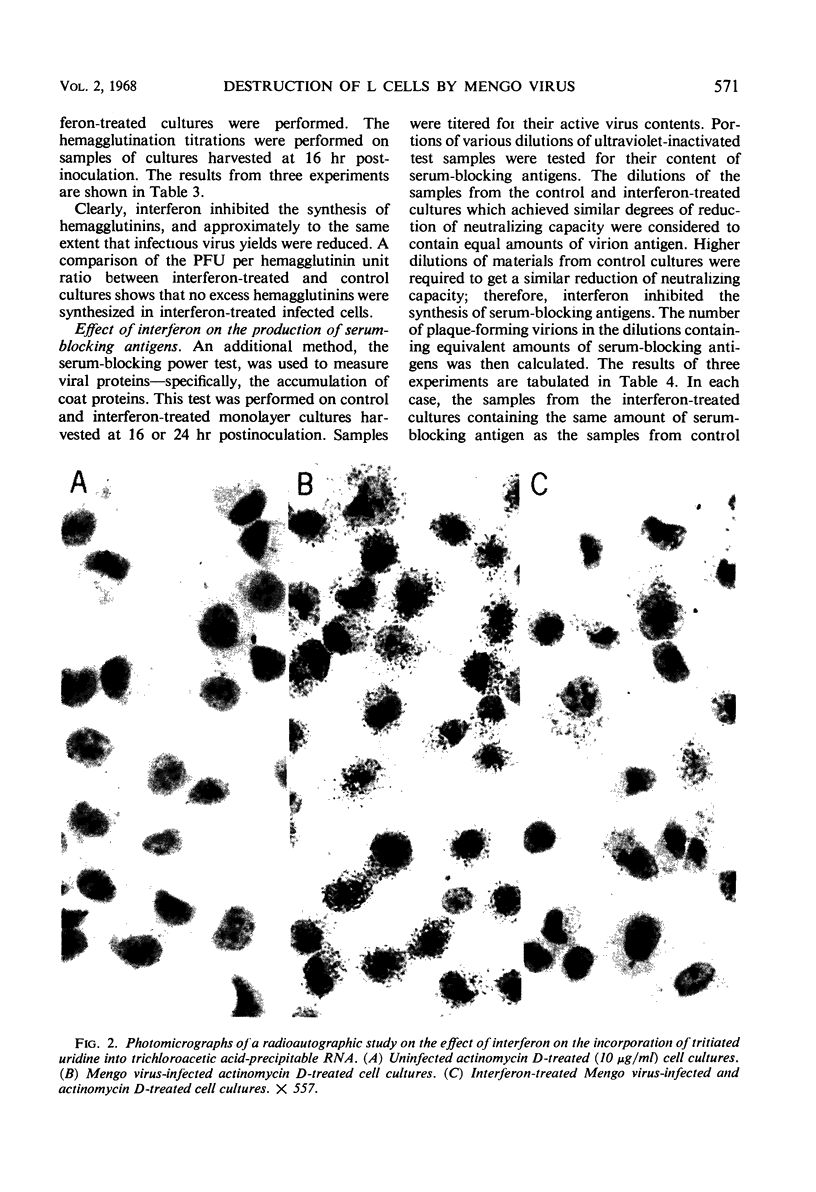


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amako K., Dales S. Cytopathology of Mengovirus infection. I. Relationship between cellular disintegration and virulence. Virology. 1967 Jun;32(2):184–200. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(67)90269-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BABLANIAN R., EGGERS H. J., TAMM I. STUDIES ON THE MECHANISM OF POLIOVIRUS-INDUCED CELL DAMAGE. II. THE RELATION BETWEEN POLIOVIRUS GROWTH AND VIRUS-INDUCED MORPHOLOGICAL CHANGES IN CELLS. Virology. 1965 May;26:114–121. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(65)90031-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter W. A., Levy H. B. Ribosomes: effect of interferon on their interaction with rapidly labeled cellular and viral RNA's. Science. 1967 Mar 10;155(3767):1254–1257. doi: 10.1126/science.155.3767.1254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DE SOMER P., PRINZIE A., DENYS P., Jr, SCHONNE E. Mechanism of action of interferon. I. Relationship with viral ribonucleic acid. Virology. 1962 Jan;16:63–70. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(62)90202-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DULBECCO R., VOGT M. One-step growth curve of Western equine encephalomyelitis virus on chicken embryo cells grown in vitro and analysis of virus yields from single cells. J Exp Med. 1954 Feb;99(2):183–199. doi: 10.1084/jem.99.2.183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANKLIN R. M. A cytochemical description of the multiplication of mengovirus in L-929 cells. J Cell Biol. 1962 Jan;12:1–15. doi: 10.1083/jcb.12.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANKLIN R. M., BALTIMORE D. Patterns of macromolecular synthesis in normal and virus-infected mammalian cells. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1962;27:175–198. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1962.027.001.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gauntt C. J., Lockart R. Z., Jr Inhibition of Mengo virus by interferon. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jan;91(1):176–182. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.1.176-182.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HO M. Effect of an interferon on synthesis of viral ribonucleic acid and plaque formation. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1963 Feb;112:511–515. doi: 10.3181/00379727-112-28090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOMMA M., GRAHAM A. F. SYNTHESIS OF RNA IN L CELLS INFECTED WITH MENGO VIRUS. J Cell Physiol. 1963 Oct;62:179–192. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1030620207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joklik W. K., Merigan T. C. Concerning the mechanism of action of interferon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Aug;56(2):558–565. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.2.558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus P. I., Salb J. M. Molecular basis of interferon action: inhibition of viral RNA translation. Virology. 1966 Nov;30(3):502–516. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(66)90126-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miner N., Ray W. J., Jr, Simon E. H. Effect of interferon on the production and action of viral RNA polymerase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Jul 20;24(2):264–268. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90730-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mécs E., Sonnabend J. A., Martin E. M., Fantes K. H. The effect of interferon on the synthesis of RNA in chick cells infected with Semliki forest virus. J Gen Virol. 1967 Jan;1(1):25–40. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-1-1-25. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REICH E., FRANKLIN R. M., SHATKIN A. J., TATUM E. L. Effect of actinomycin D on cellular nucleic acid synthesis and virus production. Science. 1961 Aug 25;134(3478):556–557. doi: 10.1126/science.134.3478.556. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHERRER K., DARNELL J. E. Sedimentation characteristics of rapidly labelled RNA from HeLa cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1962 Jun 4;7:486–490. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(62)90341-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonnabend J. A., Martin E. M., Mécs E., Fantes K. H. The effect of interferon on the synthesis and activity of an RNA polymerase isolated from chick cells infected with Semliki forest virus. J Gen Virol. 1967 Jan;1(1):41–48. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-1-1-41. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TOBEY R. A. MENGOVIRUS REPLICATION. II. ISOLATION OF POLYRIBOSOMES CONTAINING THE INFECTING VIRAL GENOME. Virology. 1964 May;23:23–29. doi: 10.1016/s0042-6822(64)80004-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor J. Inhibition of interferon action by actinomycin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1964;14:447–451. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(64)90084-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobey R. A., Campbell E. W. Mengovirus replication. 3. Virus reproduction in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Virology. 1965 Sep;27(1):11–16. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(65)90137-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]