Abstract
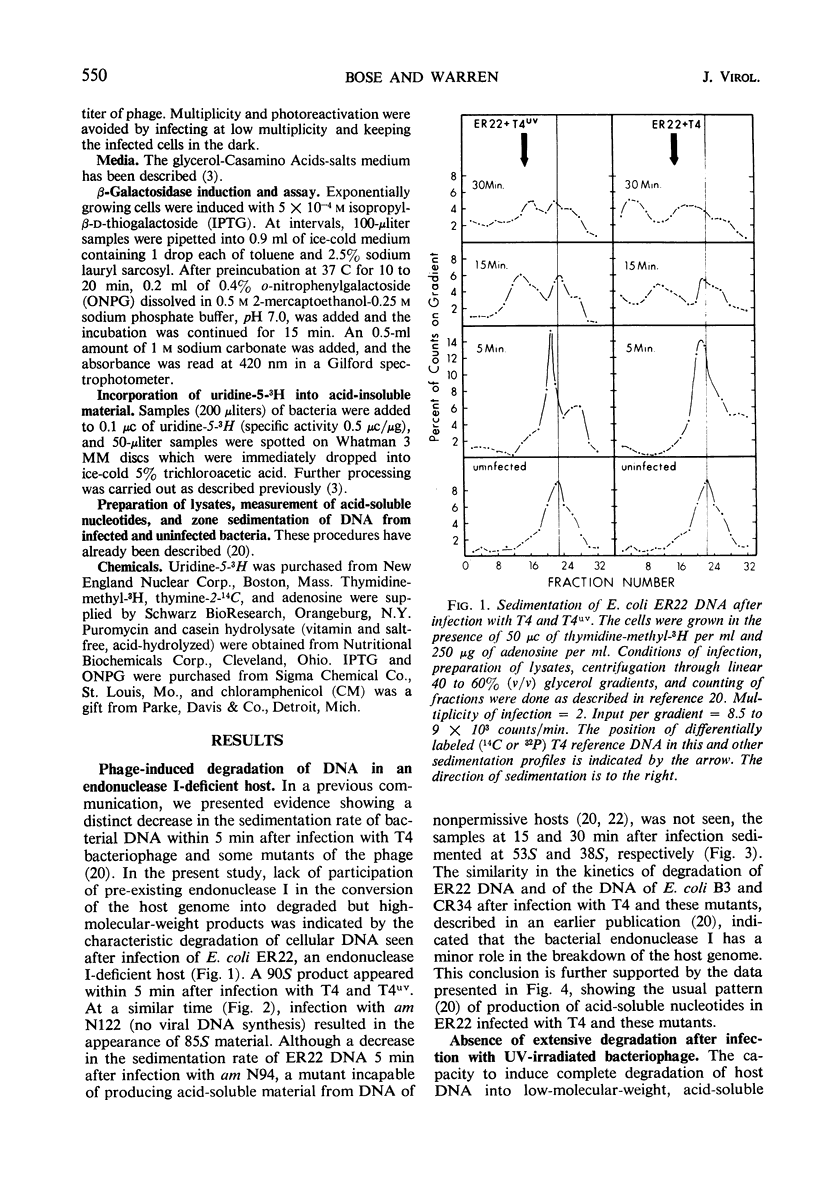
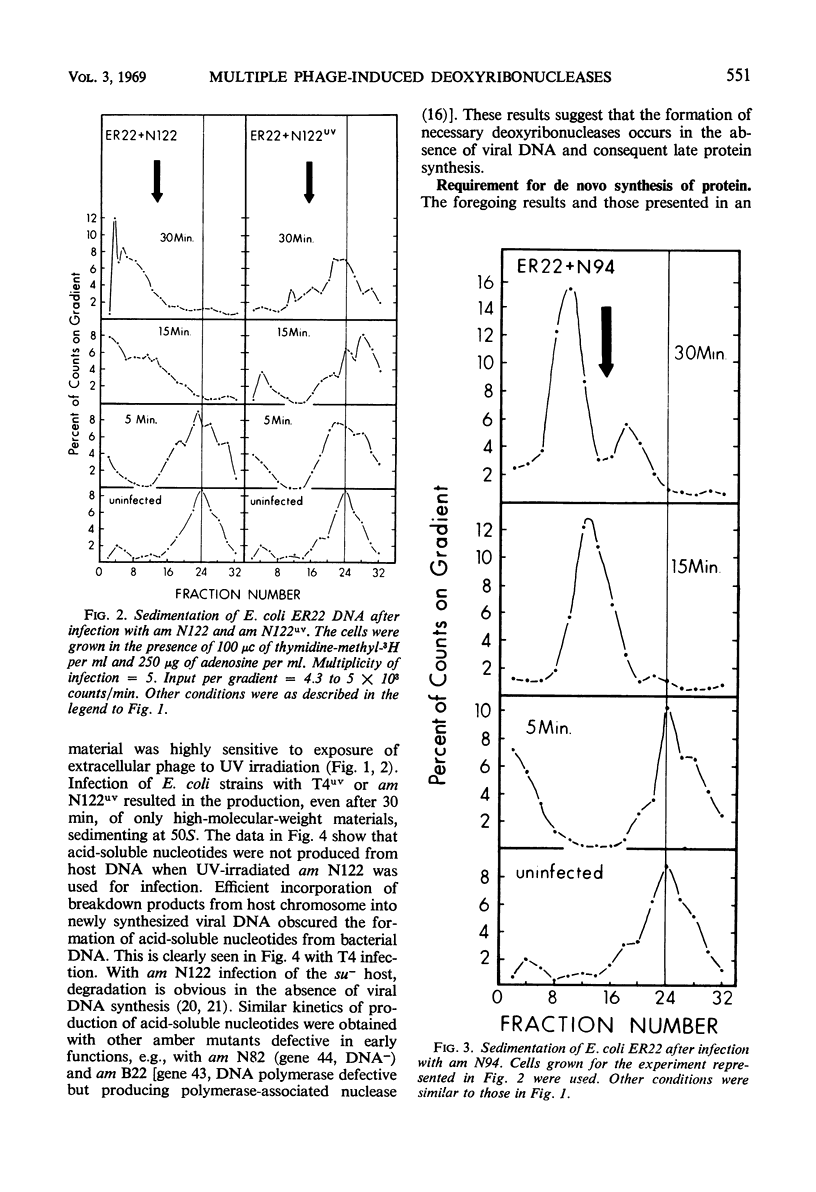
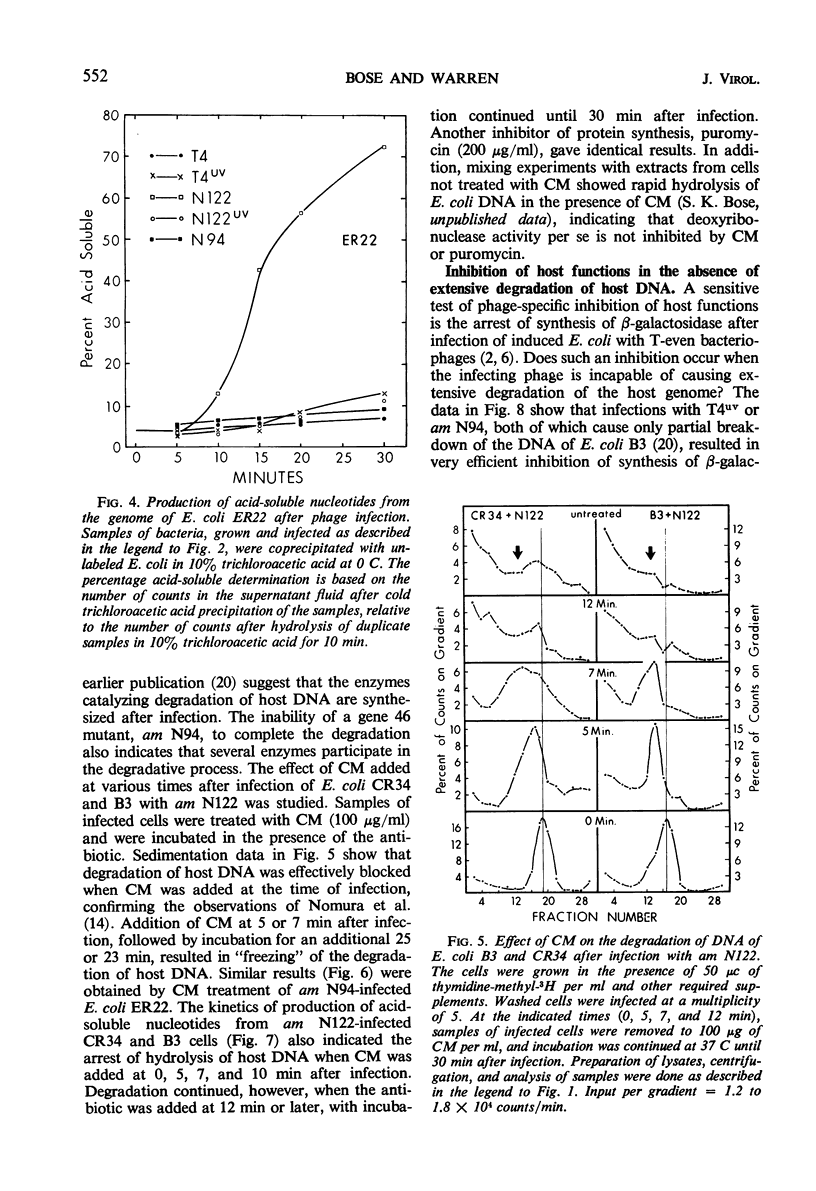
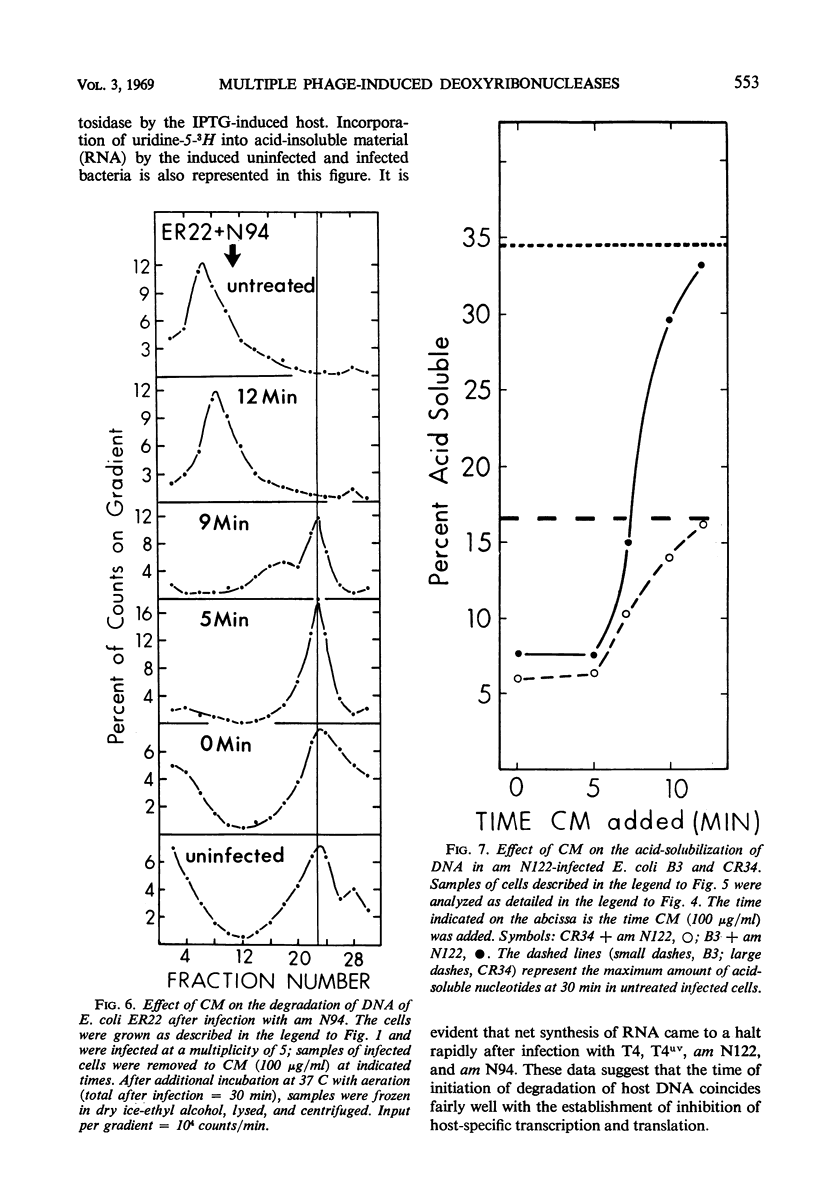
Degradation of bacterial deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) after infection with T4 bacteriophage was studied in an endonuclease I-deficient host. The kinetics of degradation were similar to those seen in other hosts with a normal level of this enzyme. Irradiation of extracellular phage with ultraviolet (UV) destroyed the capacity of the infecting virus to induce extensive breakdown of host DNA, which was, however, converted to high-molecular-weight material. Addition of chloramphenicol to T4-infected cells provided data which can be interpreted to indicate the involvement of at least two endodeoxyribonucleases and one exodeoxyribonuclease having a high degree of specificity. A model is proposed showing the sequential action of two endodeoxyribonucleases followed by an exodeoxyribonuclease in the degradation of host DNA. The appearance of these hydrolytic enzymes requires protein synthesis. Infections leading to partial degradation only (UV-irradiated phages, gene 46 mutants) effectively inhibited the synthesis of bacterial messenger ribonucleic acid and of β-galactosidase.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ASTRACHAN L., VOLKIN E. Properties of ribonucleic acid turnover in T2-infected Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1958 Sep;29(3):536–544. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(58)90010-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BENZER S. Induced synthesis of enzymes in bacteria analyzed at the cellular level. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1953 Jul;11(3):383–395. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(53)90057-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bose S. K., Warren R. J. On the stability of phage messenger RNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Feb 21;26(4):385–391. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(67)90557-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eigner J., Block S. Host-controlled restriction of T-even bacteriophages: relation of four bacterial deoxyribonucleases to restriction. J Virol. 1968 Apr;2(4):320–326. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.4.320-326.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOZLOFF L. M. Origin and fate of bacteriophage material. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1953;18:209–220. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1953.018.01.032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUNKEE R. E., PARDEE A. B. Studies on the role of deoxyribonuclease in T2 bacteriophage development. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1956 Feb;19(2):236–246. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(56)90424-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaempfer R. O., Magasanik B. Effect of infection with T-even phage on the inducible synthesis of beta-glactosidase in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1967 Aug 14;27(3):453–468. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90051-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennell D. Inhibition of host protein synthesis during infection of Escherichia coli by bacteriophage T4. I. Continued synthesis of host ribonucleic acid. J Virol. 1968 Nov;2(11):1262–1271. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.11.1262-1271.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kutter E. M., Wiberg J. S. Degradation of cytosin-containing bacterial and bacteriophage DNA after infection of Escherichia coli B with bacteriophage T4D wild type and with mutants defective in genes 46, 47 and 56. J Mol Biol. 1968 Dec;38(3):395–411. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90394-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LURIA S. E., HUMAN M. L. Chromatin staining of bacteria during bacteriophage infection. J Bacteriol. 1950 Apr;59(4):551–560. doi: 10.1128/jb.59.4.551-560.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landy A., Spiegelman S. Exhaustive hybridization and its application to an analysis of the ribonucleic acid synthesized in T4-infected cells. Biochemistry. 1968 Feb;7(2):585–591. doi: 10.1021/bi00842a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomura M., Witten C., Mantei N., Echols H. Inhibition of host nucleic acid synthesis by bacteriophage T4: effect of chloramphenicol at various multiplicities of infection. J Mol Biol. 1966 May;17(1):273–278. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80107-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nossal N. G. A T4 bacteriophage mutant which lacks deoxyribonucleic acid polymerase but retains the polymerase-associated nuclease. J Biol Chem. 1969 Jan 10;244(1):218–220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OLESON A. E., KOERNER J. F. A DEOXYRIBONUCLEASE INDUCED BY INFECTION WITH BACTERIOPHAGE T2. J Biol Chem. 1964 Sep;239:2935–2943. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STONE A. B., BURTON K. Studies on the deoxyribonucleases of bacteriophage-infected Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1962 Dec;85:600–606. doi: 10.1042/bj0850600. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOLKIN E., ASTRACHAN L. Phosphorus incorporation in Escherichia coli ribo-nucleic acid after infection with bacteriophage T2. Virology. 1956 Apr;2(2):149–161. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(56)90016-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WIBERG J. S., DIRKSEN M. L., EPSTEIN R. H., LURIA S. E., BUCHANAN J. M. Early enzyme synthesis and its control in E. coli infected with some amber mutants of bacteriophage T4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 Feb;48:293–302. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.2.293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren R. J., Bose S. K. Bacteriophage-induced inhibition of host functions. I. Degradation of Escherichia coli deoxyribonucleic acid after T4 infection. J Virol. 1968 Apr;2(4):327–334. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.4.327-334.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiberg J. S. Mutants of bacteriophage T4 unable to cause breakdown of host DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Mar;55(3):614–621. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.3.614. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


