Abstract
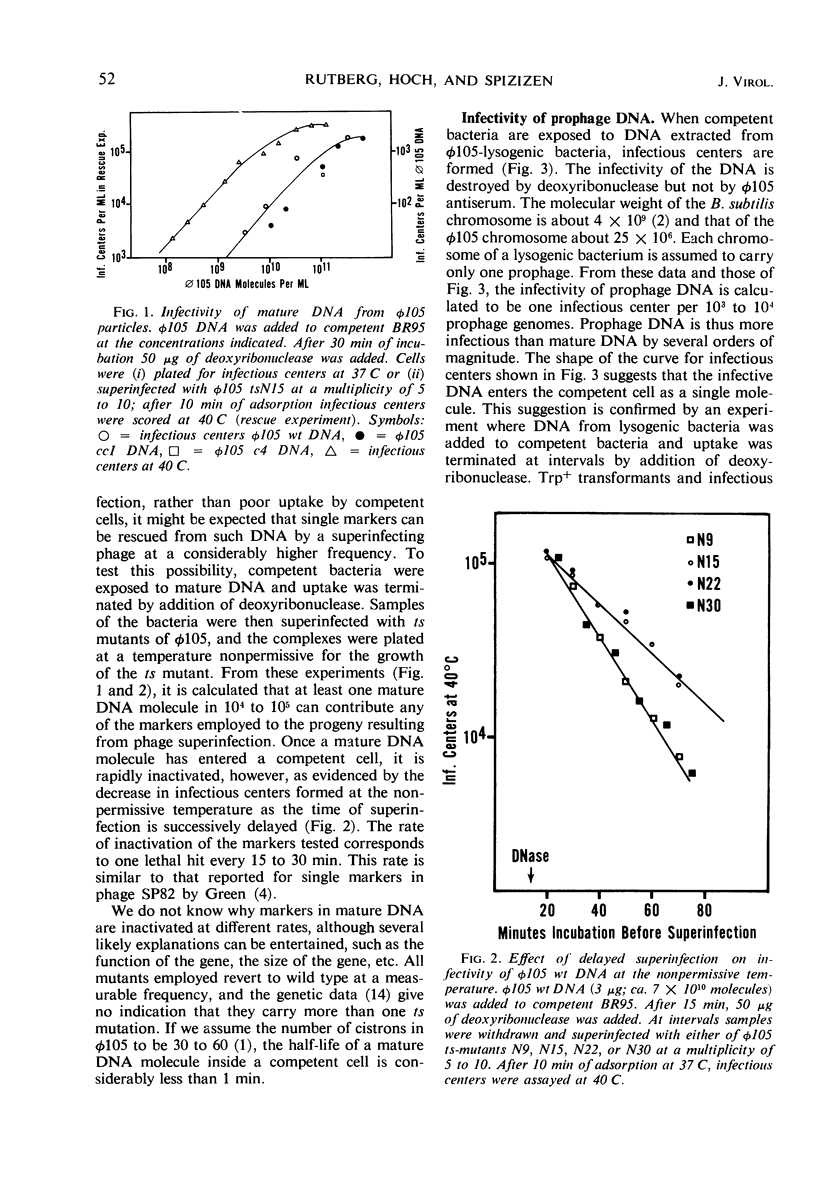
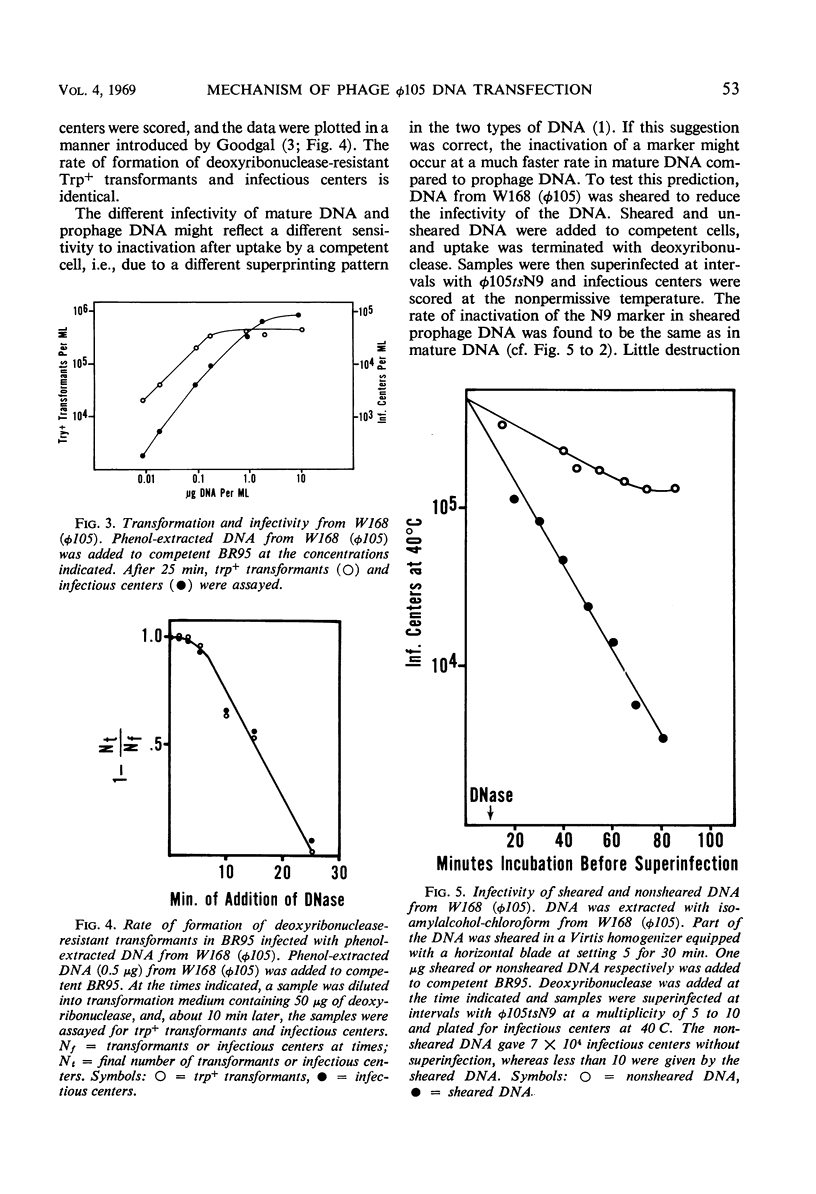
Bacteriophage φ105 is a temperate phage for the transformable Bacillus subtilis 168. The infectivity of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) extracted from mature φ105 phage particles, from bacteria lysogenic for φ105 (prophage DNA), and from induced lysogenic bacteria (vegetative DNA) was examined in the B. subtilis transformation system. About one infectious center was formed per 108 mature DNA molecules added to competent cells, but single markers could be rescued from mature DNA by a superinfecting phage at a 103- to 104-fold higher frequency. Single markers in mature DNA were inactivated at an exponential rate after uptake by a competent cell. Prophage and vegetative DNA gave about one infectious center per 103 molecules added to competent cells. Infectious prophage DNA entered competent cells as a single molecule; it gave a majority of lytic responses. Single markers in sheared prophage DNA were inactivated at the same rate as markers in mature DNA. Prophage DNA was dependent on the bacterial rec-1 function for its infectivity, whereas vegetative DNA was not. The mechanism of transfection of B. subtilis with viral DNA is discussed, and a model for transfection with φ105 DNA is proposed.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dubnau D., Goldthwaite C., Smith I., Marmur J. Genetic mapping in Bacillus subtilis. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jul 14;27(1):163–185. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90358-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOODGAL S. H. Studies on transformations of Hemophilus influenzae. IV. Linked and unlinked transformations. J Gen Physiol. 1961 Nov;45:205–228. doi: 10.1085/jgp.45.2.205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARM W., RUPERT C. S. INFECTION OF TRANSFORMABLE CELLS OF HAEMOPHILUS INFLUENZAE BY BACTERIOPHAGE AND BACTERIOPHAGE DNA. Z Vererbungsl. 1963 Dec 30;94:336–348. doi: 10.1007/BF00897593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERSHEY A. D., CHASE M. Independent functions of viral protein and nucleic acid in growth of bacteriophage. J Gen Physiol. 1952 May;36(1):39–56. doi: 10.1085/jgp.36.1.39. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoch J. A., Barat M., Anagnostopoulos C. Transformation and transduction in recombination-defective mutants of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1967 Jun;93(6):1925–1937. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.6.1925-1937.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Javor G. T., Tomasz A. An autoradiographic study of genetic transformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Aug;60(4):1216–1222. doi: 10.1073/pnas.60.4.1216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahan E. A genetic study of temperature-sensitive mutants of the subtilis phage SP82. Virology. 1966 Dec;30(4):650–660. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(66)90170-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser A. D., Inman R. B. Cohesion and the biological activity of bacteriophage lambda DNA. J Mol Biol. 1965 Aug;13(1):78–91. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80081-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okubo S., Romig W. R. Comparison of ultraviolet sensitivity of Bacillus subtilis bacteriophage SPO2 and its infectious DNA. J Mol Biol. 1965 Nov;14(1):130–142. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80235-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REILLY B. E., SPIZIZEN J. BACTERIOPHAGE DEOXYRIBONUCLEATE INFECTION OF COMPETENT BACILLUS SUBTILIS. J Bacteriol. 1965 Mar;89:782–790. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.3.782-790.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutberg L. Mapping of a temperate bacteriophage active on Bacillus subtilis. J Virol. 1969 Jan;3(1):38–44. doi: 10.1128/jvi.3.1.38-44.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Signer E. R. Lysogeny: the integration problem. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1968;22:451–488. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.22.100168.002315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spizizen J., Reilly B. E., Evans A. H. Microbial transformation and transfection. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1966;20:371–400. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.20.100166.002103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOLLMAN E. L., JACOB F. Sur les processus de conjugaison et de recombinaison chez Escherichia coli. II. La localisation chromosomique du prophage lambda et les conséquences génétiques de l'induction zygotique. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1957 Sep;93(3):323–339. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolstenholme D. R., Vermeulen C. A., Venema G. Evidence for the involvement of membranous bodies in the processes leading to genetic transformation in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1966 Oct;92(4):1111–1121. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.4.1111-1121.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young E. T., 2nd, Sinsheimer R. L. Vegetative bacteriophage lambda-DNA. I. Infectivity in a spheroplast assay. J Mol Biol. 1967 Nov 28;30(1):147–164. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90250-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


