Abstract
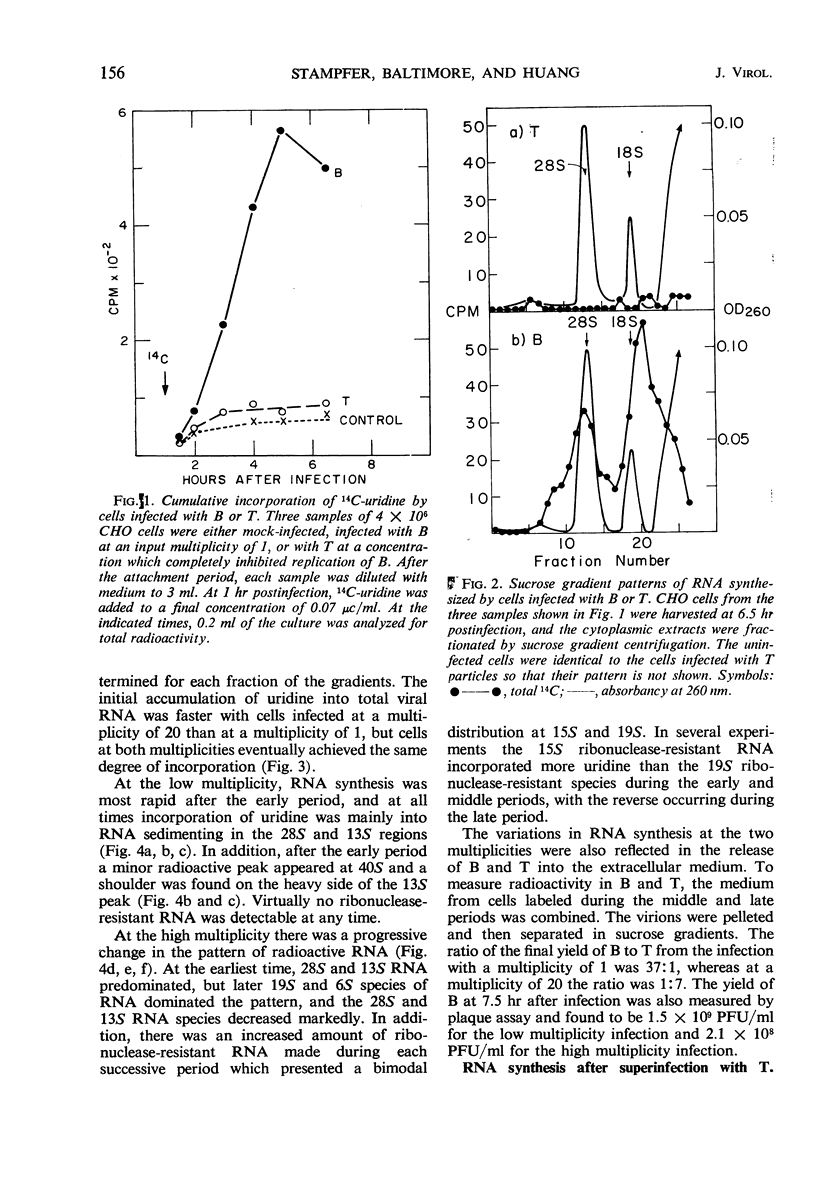
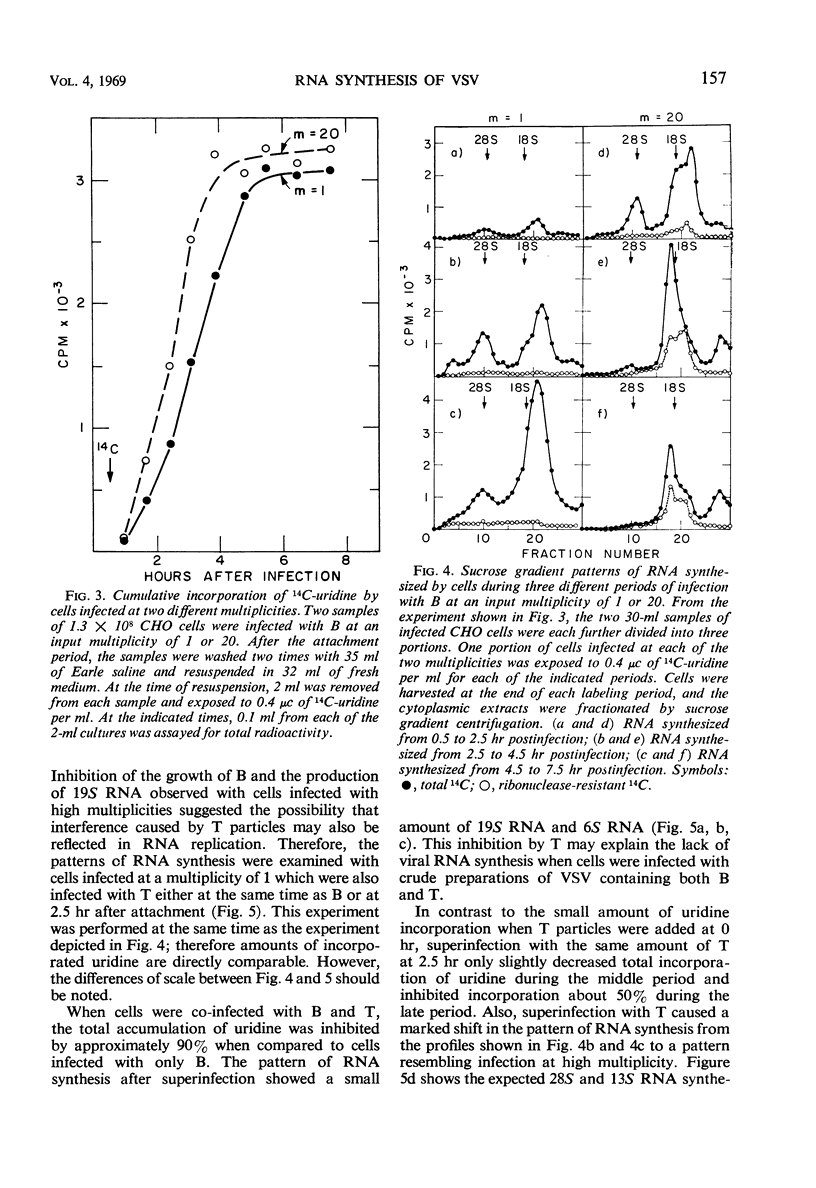
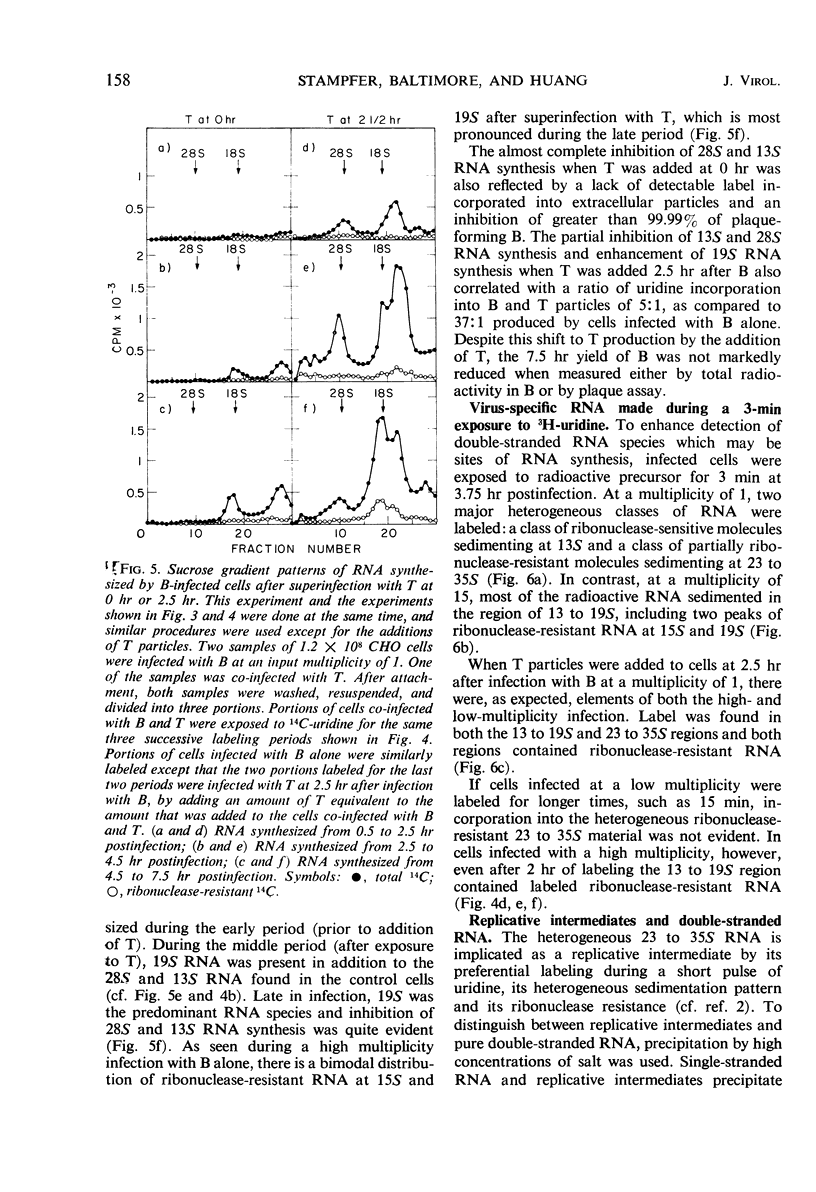
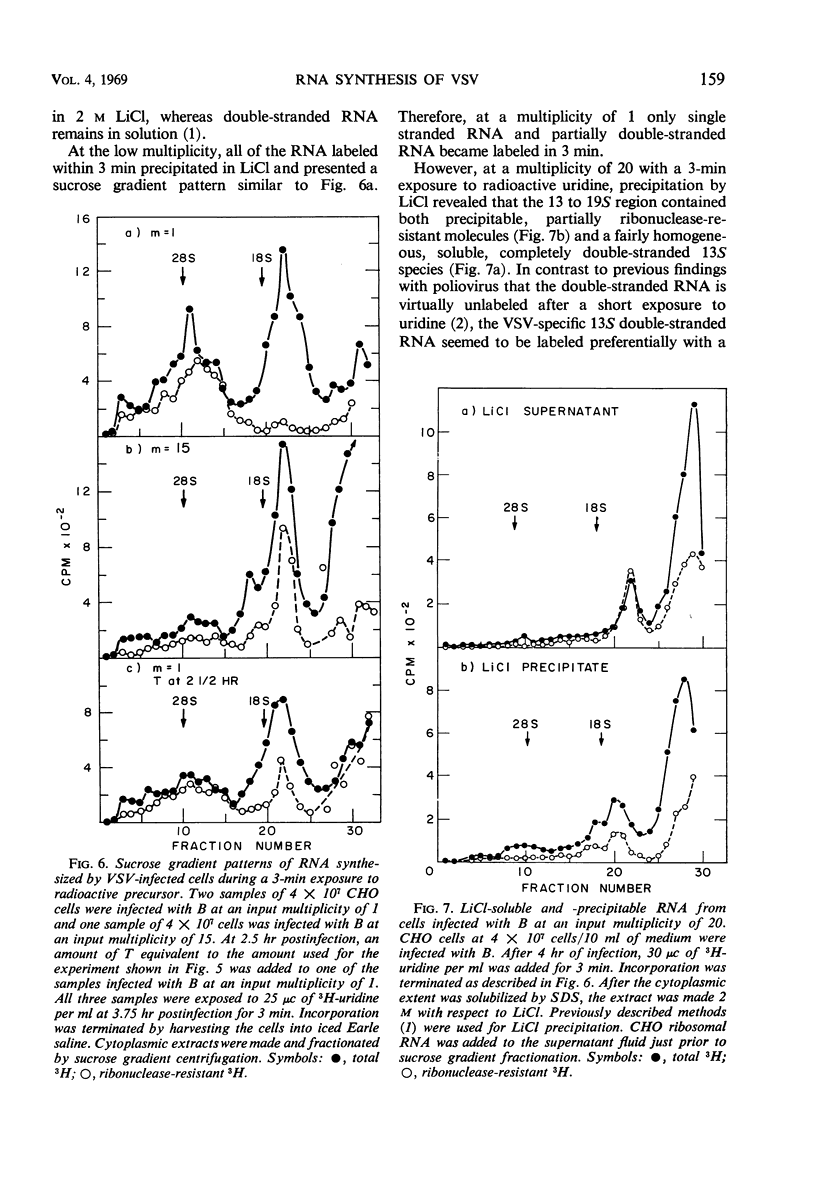
Plaque-forming B particles of vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV) induce the synthesis of virus-specific ribonucleic acid (RNA) in Chinese hamster ovary cells, whereas defective T particles do not. Infection with low input multiplicities of B results in the formation of four species of RNA. During infection with high multiplicities, RNA synthesis begins with mainly these four species of RNA but gradually shifts to a new pattern of RNA synthesis involving five other species of RNA. The change can also be induced by superinfection with T at 2.5 hr after infection with a low multiplicity of B. T added at the same time as B prevents virtually all RNA synthesis. Synthesis of the first group of RNA species correlates with the formation of B particles, whereas synthesis of the second group correlates with the formation of T particles. The various species of RNA formed after infection with VSV particles include single-stranded RNA, a completely double-stranded RNA, and RNA with partially double-stranded regions. These observations begin to establish a molecular basis for understanding the ability of T particles to interfere with the growth of B particles.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baltimore D., Girard M. An intermediate in the synthesis of poliovirus RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Aug;56(2):741–748. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.2.741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baltimore D. Purification and properties of poliovirus double-stranded ribonucleic acid. J Mol Biol. 1966 Jul;18(3):421–428. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80034-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown F., Martin S. J., Cartwright B., Crick J. The ribonucleic acids of the infective and interfering components of vesicular stomatitis virus. J Gen Virol. 1967 Oct;1(4):479–486. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-1-4-479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HACKETT A. J. A POSSIBLE MORPHOLOGIC BASIS FOR THE AUTOINTERFERENCE PHENOMENON IN VESICULAR STOMATITIS VIRUS. Virology. 1964 Sep;24:51–59. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(64)90147-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hackett A. J., Schaffer F. L., Madin S. H. The separation of infectious and autointerfering particles in vesicular stomatitis virus preparations. Virology. 1967 Jan;31(1):114–119. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(67)90014-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang A. S., Greenawalt J. W., Wagner R. R. Defective T particles of vesicular stomatitis virus. I. Preparation, morphology, and some biologic properties. Virology. 1966 Oct;30(2):161–172. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(66)90092-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang A. S., Wagner R. R. Comparative sedimentation coefficients of RNA extracted from plaque-forming and defective particles of vesicular stomatitis virus. J Mol Biol. 1966 Dec 28;22(2):381–384. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(66)90143-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang A. S., Wagner R. R. Defective T particles of vesicular stomatitis virus. II. Biologic role in homologous interference. Virology. 1966 Oct;30(2):173–181. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(66)90093-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang A. S., Wagner R. R. Inhibition of cellular RNA synthesis by nonreplicating vesicular stomatitis virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Dec;54(6):1579–1584. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.6.1579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang C. Y., Prevec L. Proteins of vesicular stomatitis virus. I. Polyacrylamide gel analysis of viral antigens. J Virol. 1969 Apr;3(4):404–413. doi: 10.1128/jvi.3.4.404-413.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingsbury D. W. Newcastle disease virus RNA. II. Preferential synthesis of RNA complementary to parental viral RNA by chick embryo cells. J Mol Biol. 1966 Jun;18(1):204–214. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80086-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills D. R., Peterson R. L., Spiegelman S. An extracellular Darwinian experiment with a self-duplicating nucleic acid molecule. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Jul;58(1):217–224. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.1.217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PUCK T. T., SANDERS P., PETERSEN D. LIFE CYCLE ANALYSIS OF MAMMALIAN CELLS. II. CELLS FROM THE CHINESE HAMSTER OVARY GROWN IN SUSPENSION CULTURE. Biophys J. 1964 Nov;4:441–450. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3495(64)86794-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penman S., Scherrer K., Becker Y., Darnell J. E. POLYRIBOSOMES IN NORMAL AND POLIOVIRUS-INFECTED HELA CELLS AND THEIR RELATIONSHIP TO MESSENGER-RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 May;49(5):654–662. doi: 10.1073/pnas.49.5.654. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffer F. L., Hackett A. J., Soergel M. E. Vesicular stomatitis virus RNA: complementarity between infected cell RNA and RNA's from infectious and autointerfering viral fractions. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 Jun 10;31(5):685–692. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90616-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WAGNER R. R., LEVEY A. H., SNYDER R. M., RATCLIFF G. A., Jr, HYATT D. F. BIOLOGIC PROPERTIES OF TWO PLAQUE VARIANTS OF VESICULAR STOMATITIS VIRUS (INDIANA SEROTYPE). J Immunol. 1963 Jul;91:112–122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner R. R., Schnaitman T. A., Snyder R. M. Structural proteins of vesicular stomatitis viruses. J Virol. 1969 Apr;3(4):395–403. doi: 10.1128/jvi.3.4.395-403.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


