Abstract
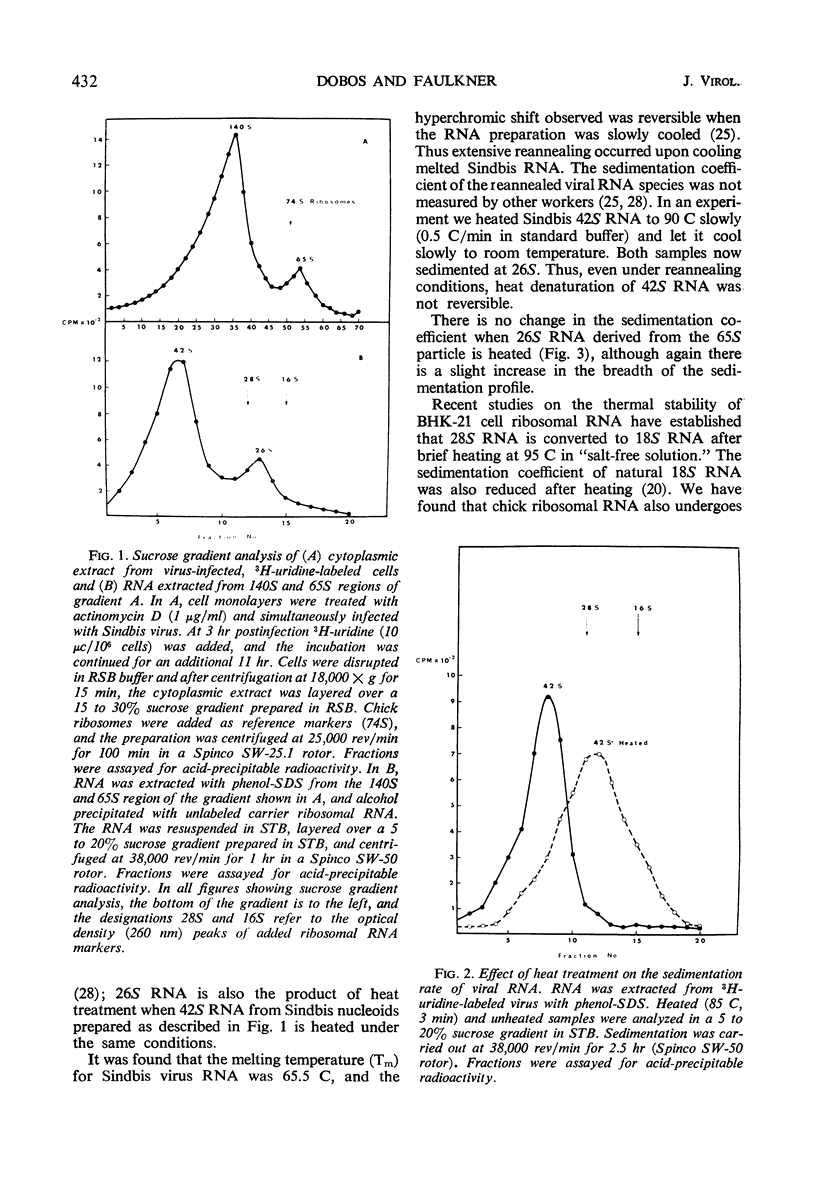
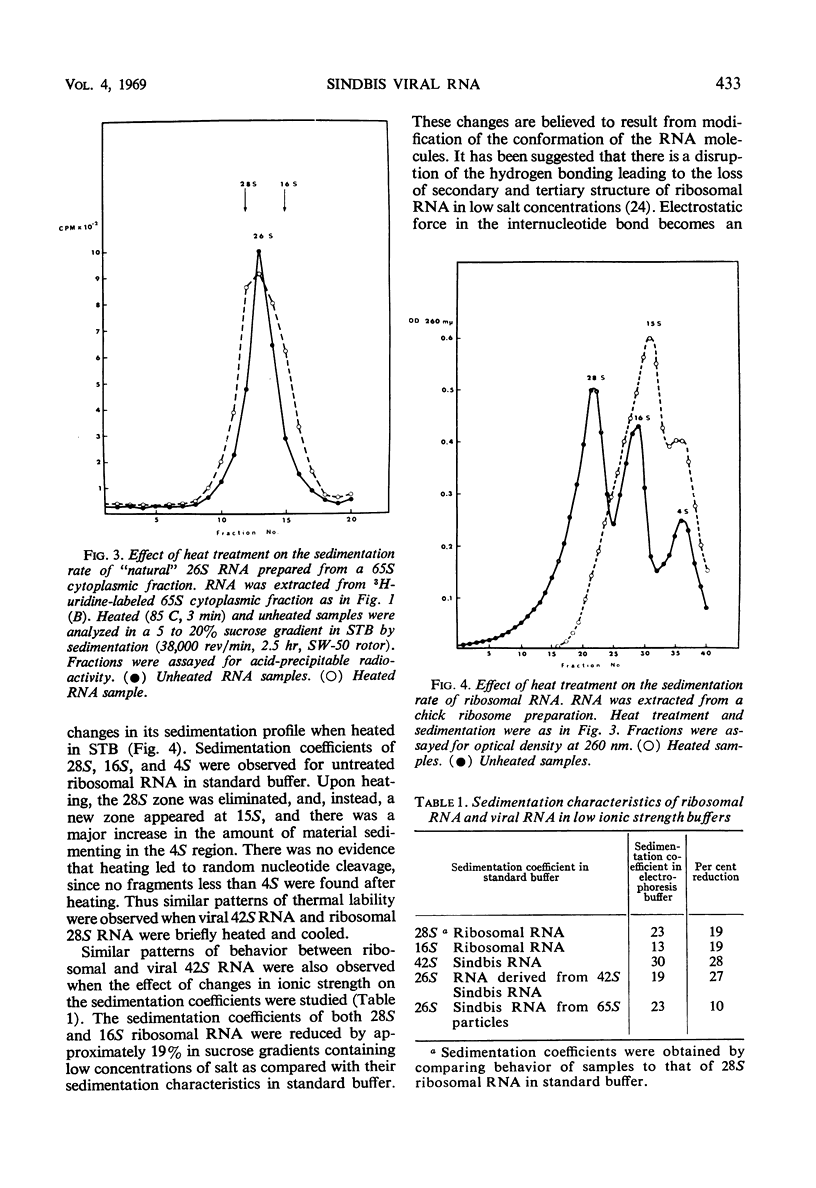
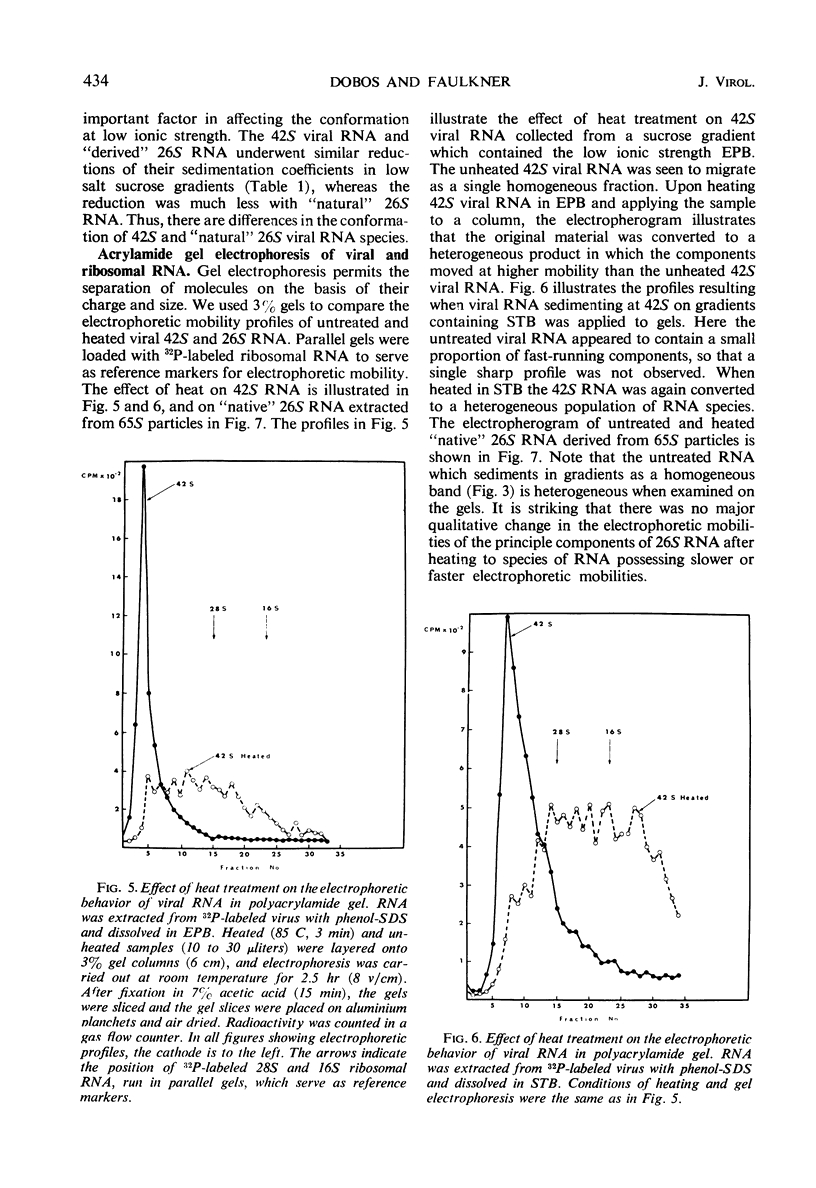
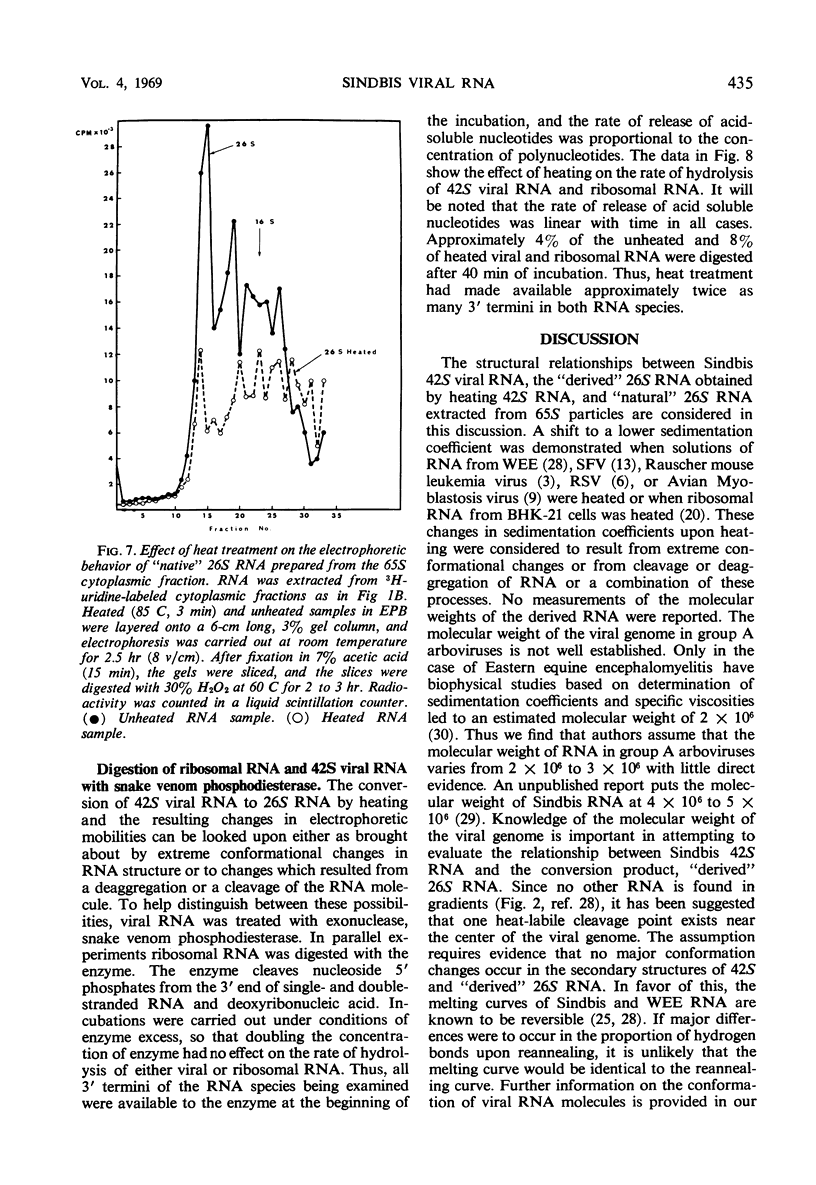
Two species of ribonuclease-sensitive Sindbis viral ribonucleic acids which sedimented at 42S and 26S were studied. 42S RNA, derived either from virions or from viral nucleoids extracted from infected cultures, was converted by heating to an RNA which sedimented at 26S. The sedimentation patterns of 42S RNA and “derived” 26S RNA were similarly affected in low ionic strength buffers. 42S RNA ran as a homogeneous fraction on polyacrylamide gels; the “derived” 26S RNA as well as “natural” 26S RNA from infected cultures showed similar electrophoretic patterns of heterogeneity. A doubling of 3′ polynucleotide termini was observed when 42S RNA was heated. Two possibilities concerning the structure of 42S RNA are considered. (i) It may consist of an aggregate of subunits, joined by means of hydrogen bonds to form a complex molecule. (ii) A heat-labile covalent bond of unknown type may link viral RNA subunits. Although 26S RNA from infected cultures and “derived” 26S RNA from 42S RNA behaved in a similar qualitative manner on gels, their sedimentation characteristics were affected differently in low ionic strength buffers. “Natural” and “derived” 26S RNA appear to consist of a population of fragments. and their behavior in gradients and in gels is probably dictated by the experimental conditions of the analytical methods used.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ben-Ishai Z., Goldblum N., Becker Y. The intracellular site and sequence of Sindbis virus replication. J Gen Virol. 1968 May;2(3):365–375. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-2-3-365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop D. H., Claybrook J. R., Spiegelman S. Electrophoretic separation of viral nucleic acids on polyacrylamide gels. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 28;26(3):373–387. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90310-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blair C. D., Duesberg P. H. Structure of Rauscher mouse leukaemia virus RNA. Nature. 1968 Oct 26;220(5165):396–399. doi: 10.1038/220396a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DULBECCO R., VOGT M. One-step growth curve of Western equine encephalomyelitis virus on chicken embryo cells grown in vitro and analysis of virus yields from single cells. J Exp Med. 1954 Feb;99(2):183–199. doi: 10.1084/jem.99.2.183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalgarno L., Martin E. M., Liu S. L., Work T. S. Characterization of the products formed by the RNA polymerases of cells infected with encephalomyocarditis virus. J Mol Biol. 1966 Jan;15(1):77–91. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80210-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobos P., Faulkner P. Characterization of a cytoplasmic fraction from Sindbis virus-infected cultures. Can J Microbiol. 1969 Feb;15(2):215–222. doi: 10.1139/m69-036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duesberg P. H., Cardiff R. D. Structural relationships between the RNA of mammary tumor virus and those of other RNA tumor viruses. Virology. 1968 Dec;36(4):696–700. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(68)90206-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duesberg P. H. Physical properties of Rous Sarcoma Virus RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Aug;60(4):1511–1518. doi: 10.1073/pnas.60.4.1511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erikson R. L. Studies on the RNA from avian myeloblastosis virus. Virology. 1969 Jan;37(1):124–131. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90313-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRAENKEL-CONRAT H., SINGER B., TSUGITA A. Purification of viral RNA by means of bentonite. Virology. 1961 May;14:54–58. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(61)90131-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faulkner P., Dobos P. Investigations on the formation and interconversion of Sindbis virus hemagglutinins. Can J Microbiol. 1968 Jan;14(1):45–51. doi: 10.1139/m68-008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman R. M., Berezesky I. K. Cytoplasmic fractions associated with Semliki Forest virus ribonucleic acid replication. J Virol. 1967 Apr;1(2):374–383. doi: 10.1128/jvi.1.2.374-383.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman R. M., Fantes K. H., Levy H. B., Carter W. B. Interferon action on parental Semliki forest virus ribonucleic acid. J Virol. 1967 Dec;1(6):1168–1173. doi: 10.1128/jvi.1.6.1168-1173.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman R. M., Levy H. B., Carter W. B. Replication of semliki forest virus: three forms of viral RNA produced during infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Aug;56(2):440–446. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.2.440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadjiolov A. A., Venkov P. V., Dolapchiev L. B., Genchev D. D. The action of snake venom phosphodiesterase on liver ribosomal ribonucleic acids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Jun 20;142(1):111–127. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(67)90520-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay A. J., Skehel J. J., Burke D. C. Proteins synthesized in chick cells following infection with Semliki Forest virus. J Gen Virol. 1968 Sep;3(2):175–184. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-3-2-175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loening U. E. The fractionation of high-molecular-weight ribonucleic acid by polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis. Biochem J. 1967 Jan;102(1):251–257. doi: 10.1042/bj1020251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTIN R. G., AMES B. N. A method for determining the sedimentation behavior of enzymes: application to protein mixtures. J Biol Chem. 1961 May;236:1372–1379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin S. J. Thermal stability of ribosomal ribonucleic acid from baby hamster kidney cells. Biochem J. 1966 Dec;101(3):721–726. doi: 10.1042/bj1010721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Midgley J. E. Studies on the structure of 23-S ribosomal ribonucleic acid from Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Nov 8;108(3):348–354. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(65)90027-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pene J. J., Knight E., Jr, Darnell J. E., Jr Characterization of a new low molecular weight RNA in HeLa cell ribosomes. J Mol Biol. 1968 May 14;33(3):609–623. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90309-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonnabend J. A., Martin E. M., Mécs E. Viral specific RNAs in infected cells. Nature. 1967 Jan 28;213(5074):365–367. doi: 10.1038/213365a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprecher-Goldberger S. Differences between the structures of poliovirus and Sindbis virus infectious ribonucleic acids. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1967;20(2):225–234. doi: 10.1007/BF01241276. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sreevalsan T., Allen P. T. Replication of Western equine encephalomyelitis virus. II. Cytoplasmic structure involved in the synthesis and development of the virions. J Virol. 1968 Oct;2(10):1038–1046. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.10.1038-1046.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sreevalsan T., Lockart R. Z., Jr, Dodson M. L., Jr, Hartman K. A. Replication of Western equine encephalomyelitis virus. I. Some chemical and physical characteristics of viral ribonucleic acid. J Virol. 1968 Jun;2(6):558–566. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.6.558-566.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sreevalsan T., Lockart R. Z., Jr Heterogeneous RNA's occurring during the replication of Western equine encephalomyelitis virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Apr;55(4):974–981. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.4.974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauss J. H., Jr, Burge B. W., Darnell J. E. Sindbis virus infection of chick and hamster cells: synthesis of virus-specific proteins. Virology. 1969 Mar;37(3):367–376. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90220-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WECKER E. [Features of an infectious nucleic acid fraction from chick embryos infected with encephalitis virus. I. Physical and chemical featurs]. Z Naturforsch B. 1959 Jun;14B:370–378. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


