Abstract
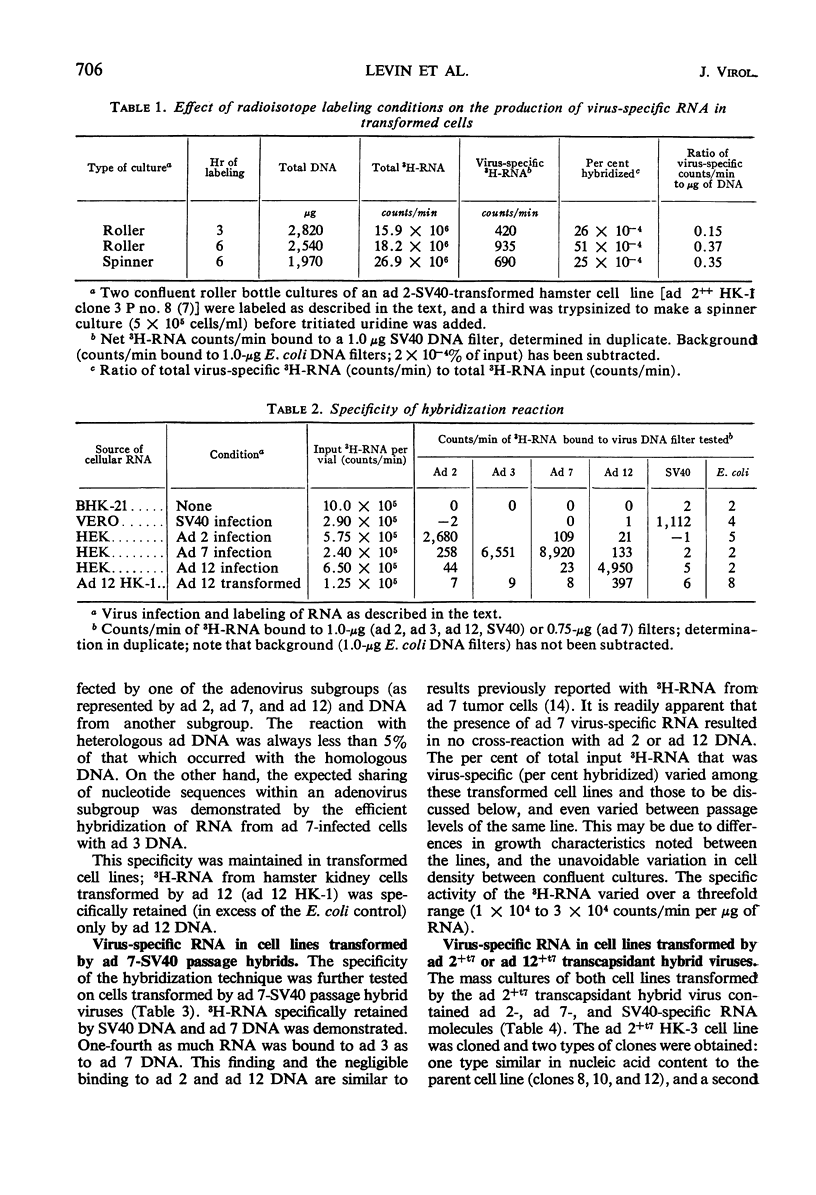
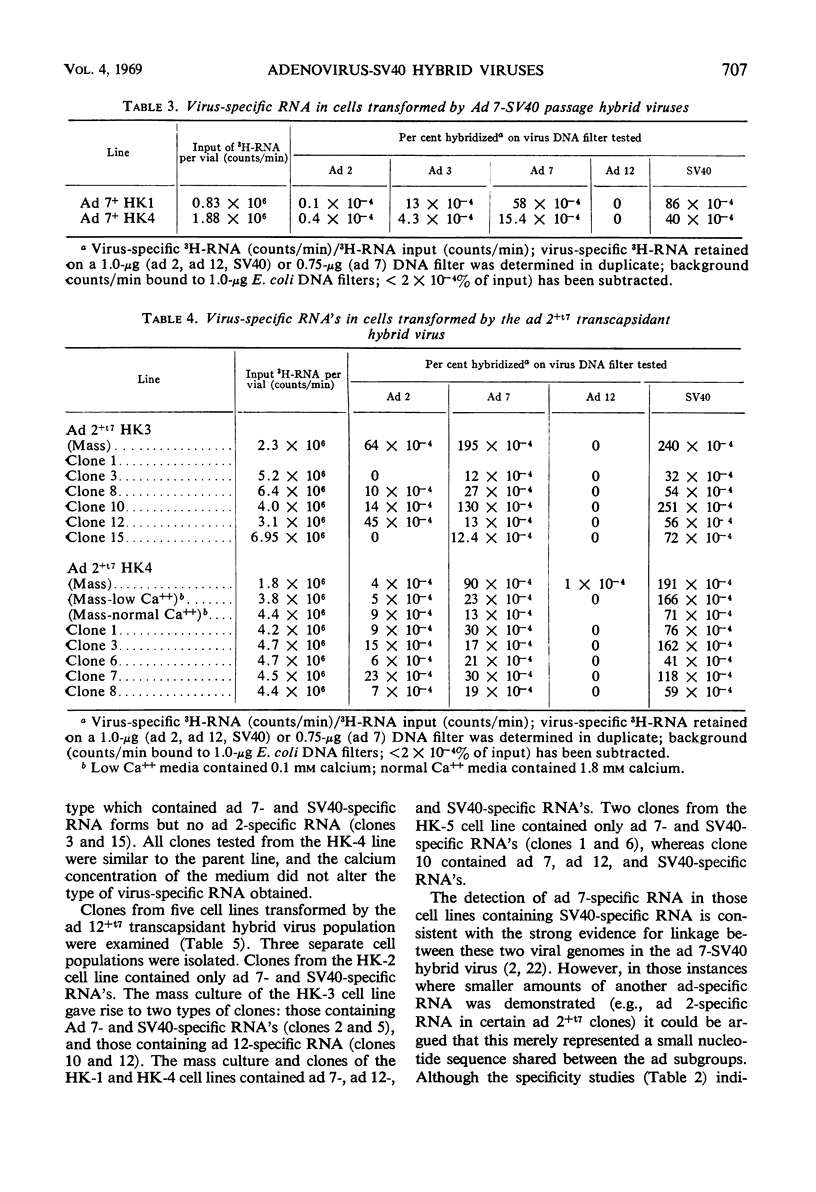
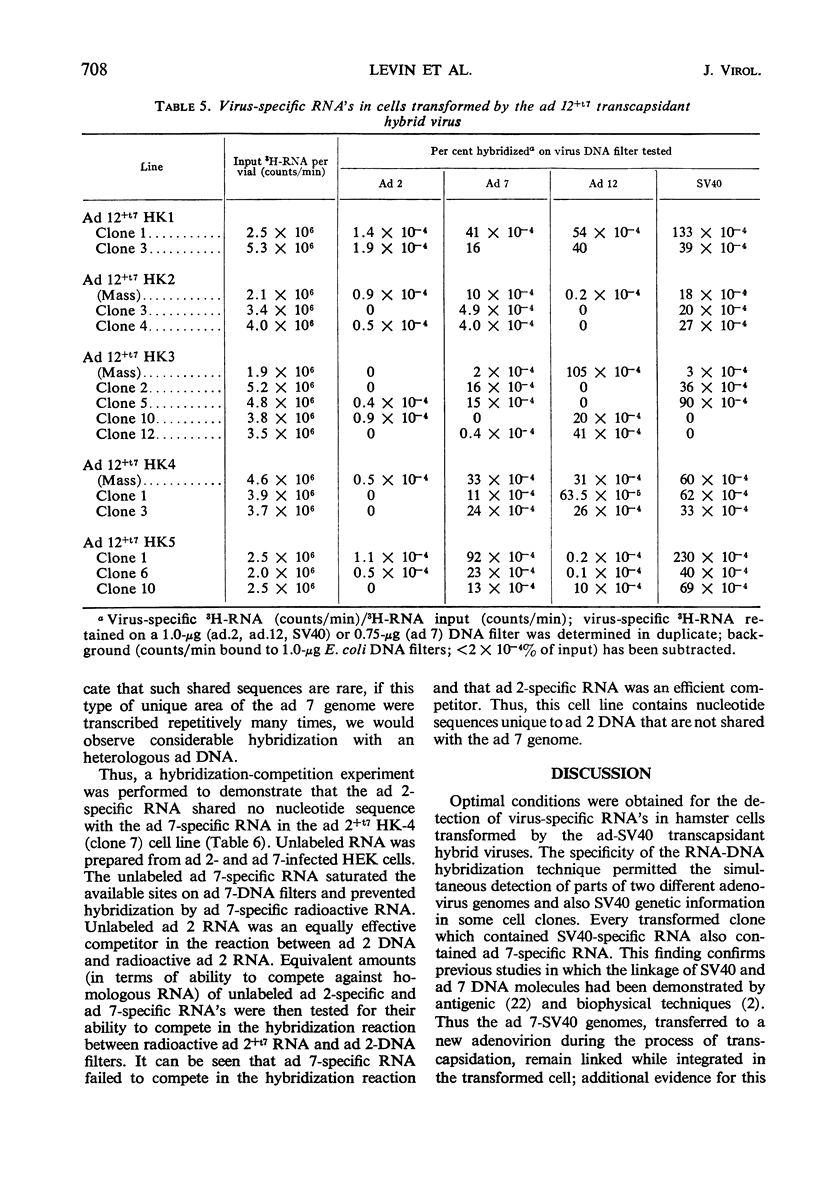
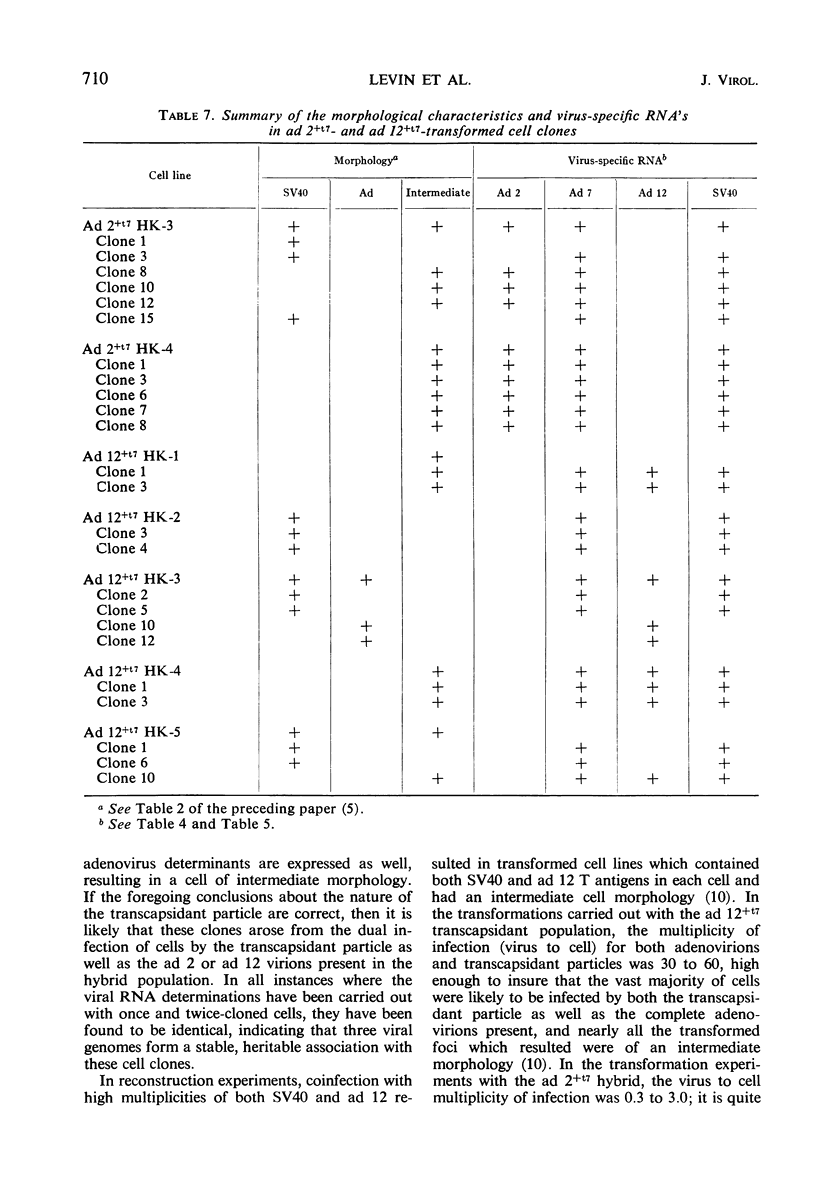
The ribonucleic acid-deoxyribonucleic acid hybridization technique was utilized to determine the presence of adenovirus (ad) and SV40 genetic information and to determine which ad genomes were present in clones of hamster cells transformed with the ad 2-SV40 and ad 12-SV40 transcapsidant hybrid virus populations. The results were correlated with the morphology of the transformed cells and colonies. It was found that cells transformed by either transcapsidant virus which had an SV40 morphology contained the ad 7 and SV40 genomes, whereas cells with a typical ad morphology contained only ad genetic information. Cells and colonies with morphological features of both ad- and SV40-transformed cells contained either the ad 2, or ad 12 genomes, depending on the transcapsidant used, together with the ad 7 and SV40 genomes. The results indicate the following: at least three different events occurred during transformation of hamster cells by the transcapsidant virus populations; the morphology of the resulting clones is determined by the viral genome(s) present; the linkage of the ad 7-SV40 genomes is confirmed since the ad 7- SV40 genomes were never found to be dissociated; the defective ad 7-SV40 genomes are capable of causing transformation; and the transcapsidant particle is probably composed of only ad 7 and SV40 genetic information.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aloni Y., Winocour E., Sachs L. Characterization of the simian virus 40-specific RNA in virus-yielding and transformed cells. J Mol Biol. 1968 Feb 14;31(3):415–429. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90418-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLACK P. H., CRAWFORD E. M., CRAWFORD L. V. THE PURIFICATION OF SIMIAN VIRUS 40. Virology. 1964 Nov;24:381–387. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(64)90175-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLACK P. H., ROWE W. P. VIRAL STUDIES OF SV40 TUMORIGENESIS IN HAMSTERS. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1964 Jan;32:253–265. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURTON K. A study of the conditions and mechanism of the diphenylamine reaction for the colorimetric estimation of deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochem J. 1956 Feb;62(2):315–323. doi: 10.1042/bj0620315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baum S. G., Reich P. R., Hybner C. J., Rowe W. P., Weissman S. M. Biophysical evidence for linkage of adenovirus and SV40 DNA's in adenovirus 7-SV40 hybrid particles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Nov;56(5):1509–1515. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.5.1509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benjamin T. L. Virus-specific RNA in cells productively infected or transformed by polyoma virus. J Mol Biol. 1966 Apr;16(2):359–373. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80179-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black P. H., Berman L. D., Dixon C. B. In vitro transformation by adenovirus-simiam virus 40 hybrid viruses. IV. Properties of clones isolated from cell lines transformed by adenovirus 2-simiam virus 40 and adenovirus 12-simiam virus 40 transcapsidant hybird viruses. J Virol. 1969 Nov;4(5):694–703. doi: 10.1128/jvi.4.5.694-703.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black P. H., Lewis A. M., Jr, Blacklow N. R., Austin J. B., Rowe W. P. The presence of adenovirus-specific antigens in hamster cells rendered neoplastic by adenovirus 1-SV40 and adenovirus 2-SV40 hybrid viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 May;57(5):1324–1330. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.5.1324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black P. H., Todaro G. J. In vitro transformation of hamster and human cells with the adeno 7-SV 40 hybrid virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Aug;54(2):374–381. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.2.374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black P. H., White B. J. In vitro transformation by the adenovirus-SV40 hybrid viruses. II. Characteristics of the transformation of hamster cells by the adeno 2-, adeno 3-, and adeno 12-SV40 viruses. J Exp Med. 1967 Apr 1;125(4):629–646. doi: 10.1084/jem.125.4.629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnett J. P., Summers A. O., Harrington J. A., Dwyer A. C. Production of highly labeled adenoviruses. Appl Microbiol. 1968 Aug;16(8):1245–1250. doi: 10.1128/am.16.8.1245-1250.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman A. E., Black P. H., Vanderpool E. A., Henry P. H., Austin J. B., Huebner R. J. Transformation of primary rat embryo cells by adenovirus type 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Sep;58(3):1205–1212. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.3.1205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujinaga K., Green M. Mechanism of viral carcinogenesis by DNA Mammalian viruses, ii. Viral-specific RNA in tumor cells induced by "weakly" oncogenic human adenoviruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Mar;57(3):806–812. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.3.806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujinaga K., Green M. Mechanism of viral carcinogenesis by deoxyribonucleic acid mammalian viruses. IV. Related virus-specific ribonucleic acids in tumor cells induced by "highly" oncogenic adenovirus types 12, 18, and 31. J Virol. 1967 Jun;1(3):576–582. doi: 10.1128/jvi.1.3.576-582.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillespie D., Spiegelman S. A quantitative assay for DNA-RNA hybrids with DNA immobilized on a membrane. J Mol Biol. 1965 Jul;12(3):829–842. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80331-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIRBY K. S. ISOLATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF RIBOSOMAL RIBONUCLEIC ACID. Biochem J. 1965 Jul;96:266–269. doi: 10.1042/bj0960266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin M. J., Oxman M. N., Diamandopoulos G. T., Levine A. S., Henry P. H., Enders J. F. Virus-specific nucleic acids in SV40-exposed hamster embryo cell lines: correlation with S and T antigens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Feb;62(2):589–596. doi: 10.1073/pnas.62.2.589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oda K., Dulbecco R. Regulation of transcription of the SV40 DNA in productively infected and in transformed cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Jun;60(2):525–532. doi: 10.1073/pnas.60.2.525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose J. A., Reich P. R., Weissman S. M. RNA production in adenovirus-infected KB cells. Virology. 1965 Dec;27(4):571–579. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(65)90183-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe W. P., Pugh W. E. Studies of adenovirus-SV40 hybrid viruses. V. Evidence for linkage between adenovirus and SV40 genetic materials. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 May;55(5):1126–1132. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.5.1126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe W. P. Studies of adenovirus-SV40 hybrid viruses. 3. Transfer of SV40 gene between adenovirus types. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Sep;54(3):711–717. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.3.711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHERRER K., DARNELL J. E. Sedimentation characteristics of rapidly labelled RNA from HeLa cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1962 Jun 4;7:486–490. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(62)90341-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


