Abstract
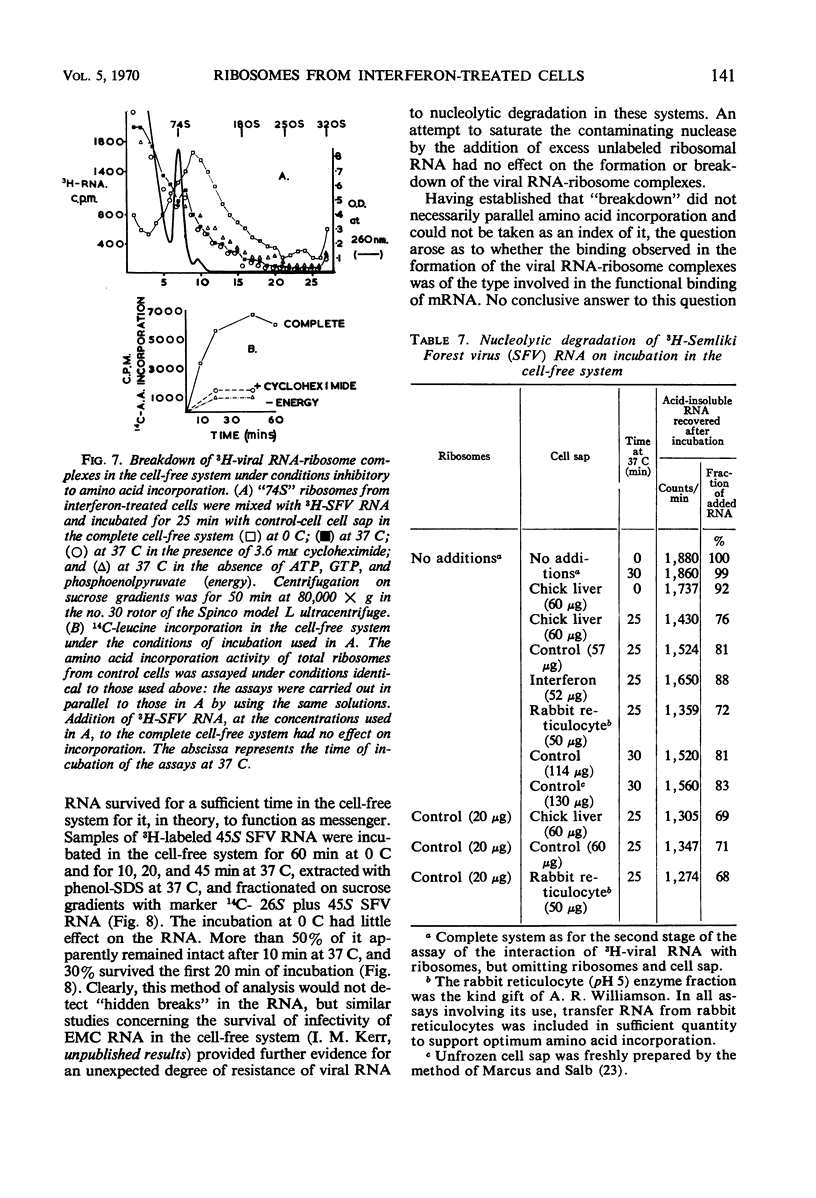
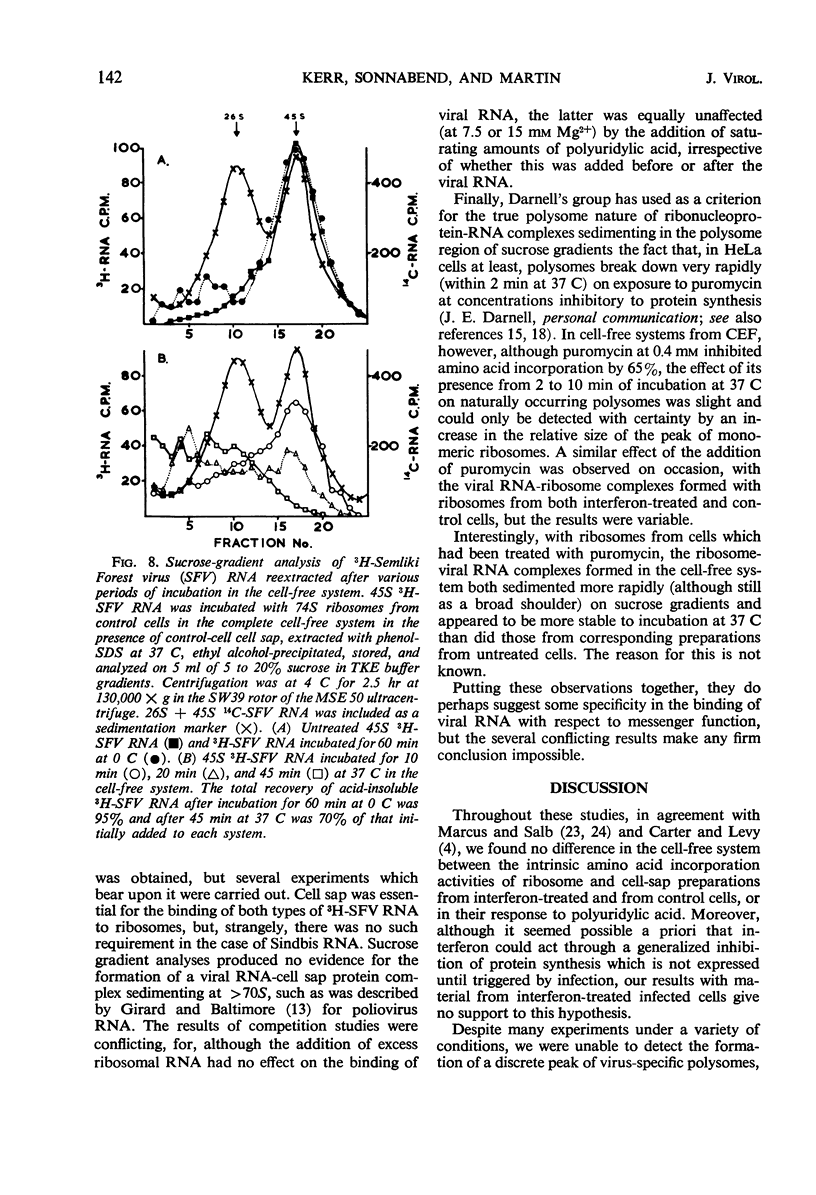
Cell-free protein-synthetic systems from normal and interferon-treated chick cells were compared. No difference was found in the amino acid incorporation activities of such ribosome-cell sap systems or in their response to polyuridylic acid. Throughout a variety of experiments we failed to detect the formation of a discrete peak of virus-specific polysomes, when ribosome monomers and subunits (from interferon-treated or control cells) were incubated with labeled Sindbis or Semliki Forest virus ribonucleic acid (RNA). Some binding of viral RNA did occur, but the complexes formed were evident in sucrose gradients as a broad, rapidly sedimenting shoulder on the ribosome monomer peak. Interferon pretreatment of cells did not affect the formation of these complexes in vitro, nor did it alter their rate of breakdown on incubation under amino acid incorporation conditions. Experiments with inhibitors of protein synthesis showed that such “breakdown” was not dependent upon amino acid incorporation and was not an index of translation. In these respects, our results are in marked contrast to those of Marcus and Salb. These results, together with our failure to detect any significant change in the protein composition of ribosomes from interferon-treated cells, suggest that such treatment does not result in a modification of the ribosome per se. They do not, however, rule out the involvement of a factor(s) required for ribosomes and viral RNA to function in viral protein synthesis. Indeed, it remains likely that interferon acts through such a mechanism, although the precise level at which the inhibition occurs remains to be elucidated.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beard N. S., Jr, Armentrout S. A. Protein synthesis by reticulocyte ribosomes. 3. Description of a ribonucleoprotein fraction which stimulates messenger RNA-ribosomal interaction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Aug;58(2):750–757. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.2.750. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter W. A., Levy H. B. Ribosomes: effect of interferon on their interaction with rapidly labeled cellular and viral RNA's. Science. 1967 Mar 10;155(3767):1254–1257. doi: 10.1126/science.155.3767.1254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter W. A., Levy H. B. The recognition of viral RNA by mammalian ribosomes. An effect of interferon. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Feb 26;155(2):437–443. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(68)90189-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FAULKNER P., MARTIN E. M., SVED S., VALENTINE R. C., WORK T. S. Studies on protein and nucleic acid metabolism in virus-infected mammalian cells. 2. The isolation, crystallization and chemical characterization of mouse encephalomyocarditis virus. Biochem J. 1961 Sep;80:597–605. doi: 10.1042/bj0800597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRAENKEL-CONRAT H., SINGER B., TSUGITA A. Purification of viral RNA by means of bentonite. Virology. 1961 May;14:54–58. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(61)90131-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRIEDMAN R. M., SONNABEND J. A. INHIBITION OF INTERFERON ACTION BY P-FLUOROPHENYLALANINE. Nature. 1964 Jul 25;203:366–367. doi: 10.1038/203366a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fantes K. H. Purification of interferon from chick embryonic allantoic fluids and fibroblast tissue infected with influenza virus. J Gen Virol. 1967 Jul;1(3):257–267. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-1-3-257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox S. M., Birnie G. D., Harvey D. R., Martin E. M., Sonnabend J. A. The use of batch-type zonal ultracentrifuge rotors for the isolation and purification of viruses. J Gen Virol. 1968 May;2(3):455–459. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-2-3-455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman R. M., Sonnabend J. A. Inhibition of interferon action by puromycin. J Immunol. 1965 Oct;95(4):696–703. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuhr J. E., London I. M., Grayzel A. I. A factor promoting the initiation of globin synthesis in a rabbit reticulocyte cell-free system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 May;63(1):129–134. doi: 10.1073/pnas.63.1.129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girard M., Baltimore D. The effect of HeLa cell cytoplasm on the rate of sedimentation of RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Sep;56(3):999–1002. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.3.999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guggenheim M. A., Friedman R. M., Rabson A. S. Interferon action in heterokaryons. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1969 Apr;130(4):1242–1245. doi: 10.3181/00379727-130-33763. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joklik W. K., Becker Y. Studies on the genesis of polyribosomes. I. Origin and significance of the subribosomal particles. J Mol Biol. 1965 Sep;13(2):496–510. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80112-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joklik W. K., Merigan T. C. Concerning the mechanism of action of interferon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Aug;56(2):558–565. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.2.558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr I. M., Cohen N., Work T. S. Factors controlling amino acid incorporation by ribosomes from krebs II mouse ascites-tumour cells. Biochem J. 1966 Mar;98(3):826–835. doi: 10.1042/bj0980826. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latham H., Darnell J. E. Entrance of mRNA into HeLa cell cytoplasm in puromycin-treated cells. J Mol Biol. 1965 Nov;14(1):13–22. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80225-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy H. B., Carter W. A. Molecular basis of the action of interferon. J Mol Biol. 1968 Feb 14;31(3):561–577. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90428-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy H. B., Merigan T. C. Interferon and uninfected cells. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1966 Jan;121(1):53–55. doi: 10.3181/00379727-121-30695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus P. I., Salb J. M. Molecular basis of interferon action: inhibition of viral RNA translation. Virology. 1966 Nov;30(3):502–516. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(66)90126-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. L., Schweet R. Isolation of a protein fraction from reticulocyte ribosomes required for de novo synthesis of hemoglobin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1968 May;125(2):632–646. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(68)90622-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miner N., Ray W. J., Jr, Simon E. H. Effect of interferon on the production and action of viral RNA polymerase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Jul 20;24(2):264–268. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90730-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mécs E., Sonnabend J. A., Martin E. M., Fantes K. H. The effect of interferon on the synthesis of RNA in chick cells infected with Semliki forest virus. J Gen Virol. 1967 Jan;1(1):25–40. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-1-1-25. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skogerson L., Moldave K. Characterization of the interaction of aminoacyltransferase II with ribosomes. Binding of transferase II and translocation of peptidyl transfer ribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1968 Oct 25;243(20):5354–5360. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonnabend J. A., Martin E. M., Mécs E., Fantes K. H. The effect of interferon on the synthesis and activity of an RNA polymerase isolated from chick cells infected with Semliki forest virus. J Gen Virol. 1967 Jan;1(1):41–48. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-1-1-41. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAYLOR J. STUDIES ON THE MECHANISM OF ACTION OF INTERFERON. I. INTERFERON ACTION AND RNA SYNTHESIS IN CHICK EMBRYO FIBROBLASTS INFECTED WITH SEMLIKI FOREST VIRUS. Virology. 1965 Mar;25:340–349. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(65)90053-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor J. Inhibition of interferon action by actinomycin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1964;14:447–451. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(64)90084-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zwartouw H. T., Algar D. J. Growth of high-titre Semliki forest virus in concentrated suspensions of chick embryo cells. J Gen Virol. 1968 Mar;2(2):243–250. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-2-2-243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


