Abstract
The preparation and properties of cell cultures derived from human placental tissue are described and their usefulness for the propagation of animal viruses and as “feeder layers” is indicated.
Full text
PDF
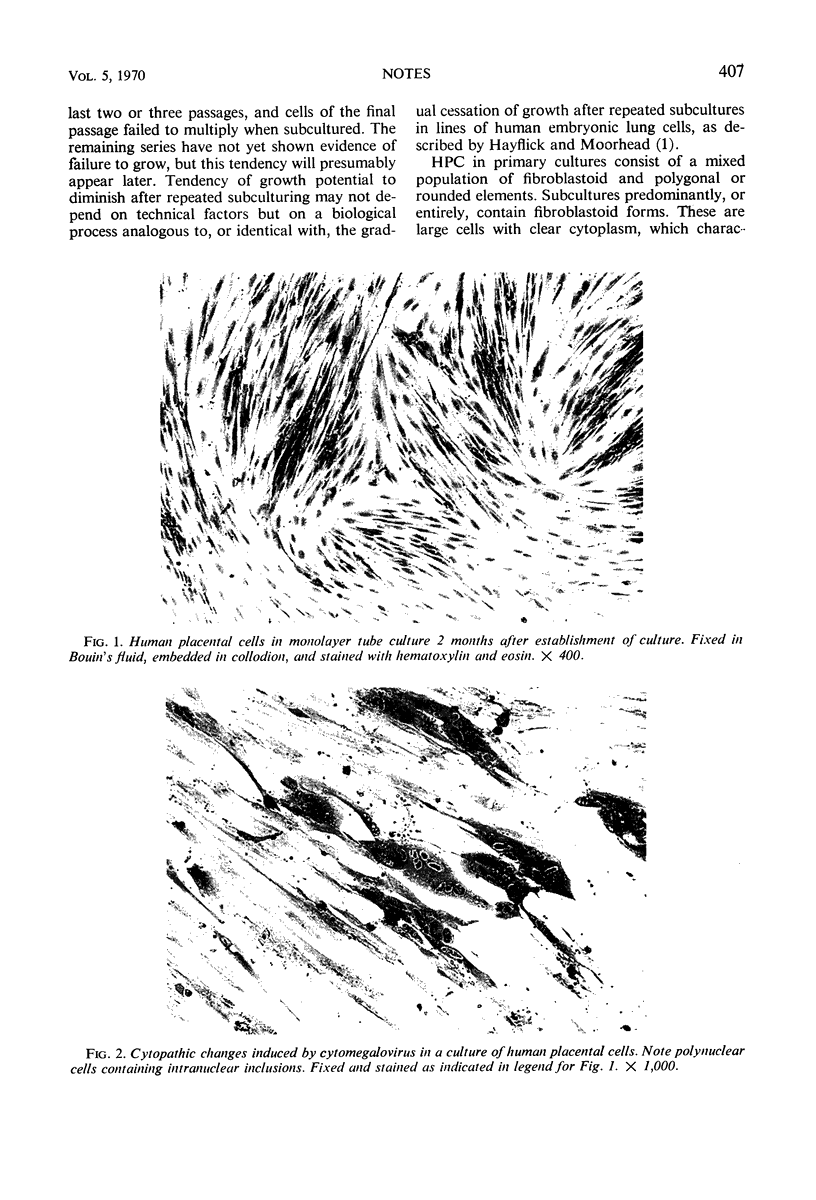
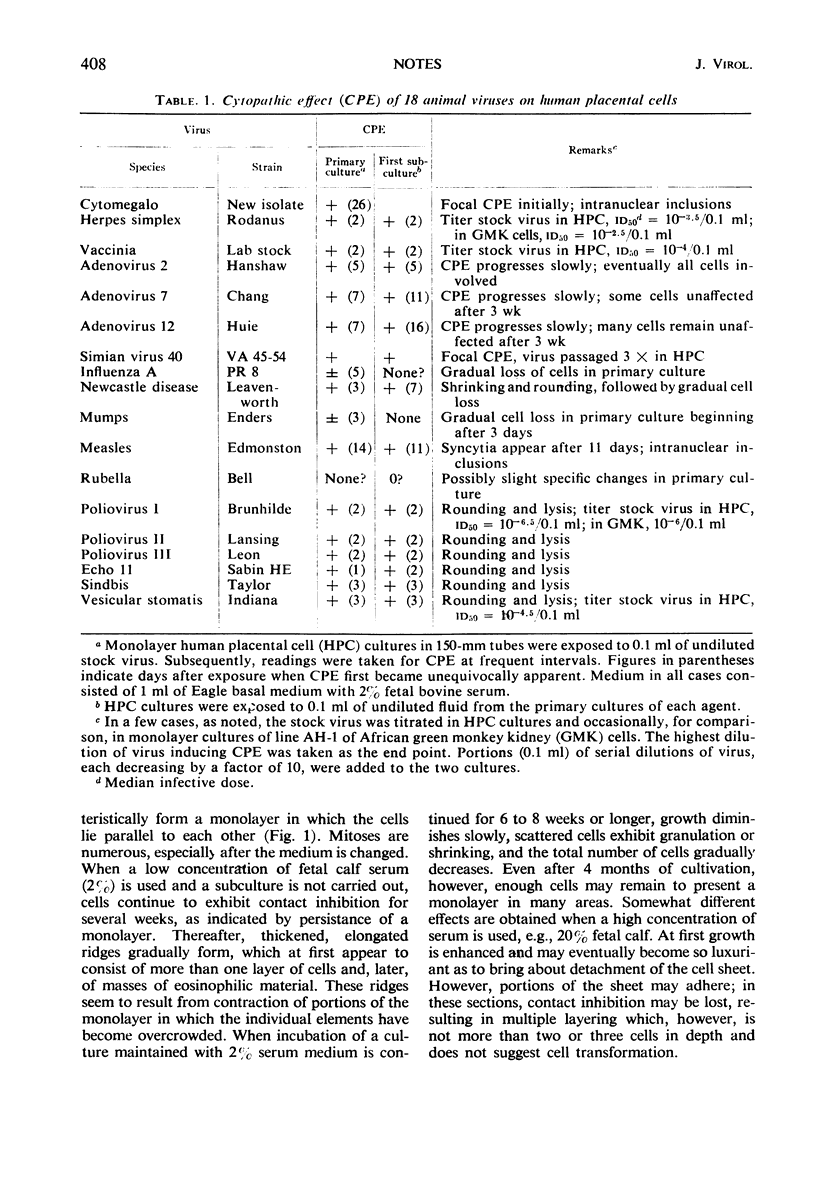

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- HAYFLICK L., MOORHEAD P. S. The serial cultivation of human diploid cell strains. Exp Cell Res. 1961 Dec;25:585–621. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(61)90192-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson T. C., McLaren L. C. Plaque Development and Induction of Interferon Synthesis by RMC Poliovirus. J Bacteriol. 1965 Sep;90(3):565–570. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.3.565-570.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller G., Enders J. F., Lisco H., Kohn H. I. Establishment of lines from normal human blood leukocytes by co-cultivation with a leukocyte line derived from a leukemic child. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1969 Oct;132(1):247–252. doi: 10.3181/00379727-132-34189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neff J. M., Enders J. F. Poliovirus replication and cytopathogenicity in monolayer hamster cell cultures fused with beta propiolactone-inactivated Sendai virus. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1968 Jan;127(1):260–267. doi: 10.3181/00379727-127-32668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZITCER E. M., FOGH J., DUNNEBACKE T. H. Human amnion cells for large-scale production of polio virus. Science. 1955 Jul 1;122(3157):30–30. doi: 10.1126/science.122.3157.30. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




