Abstract
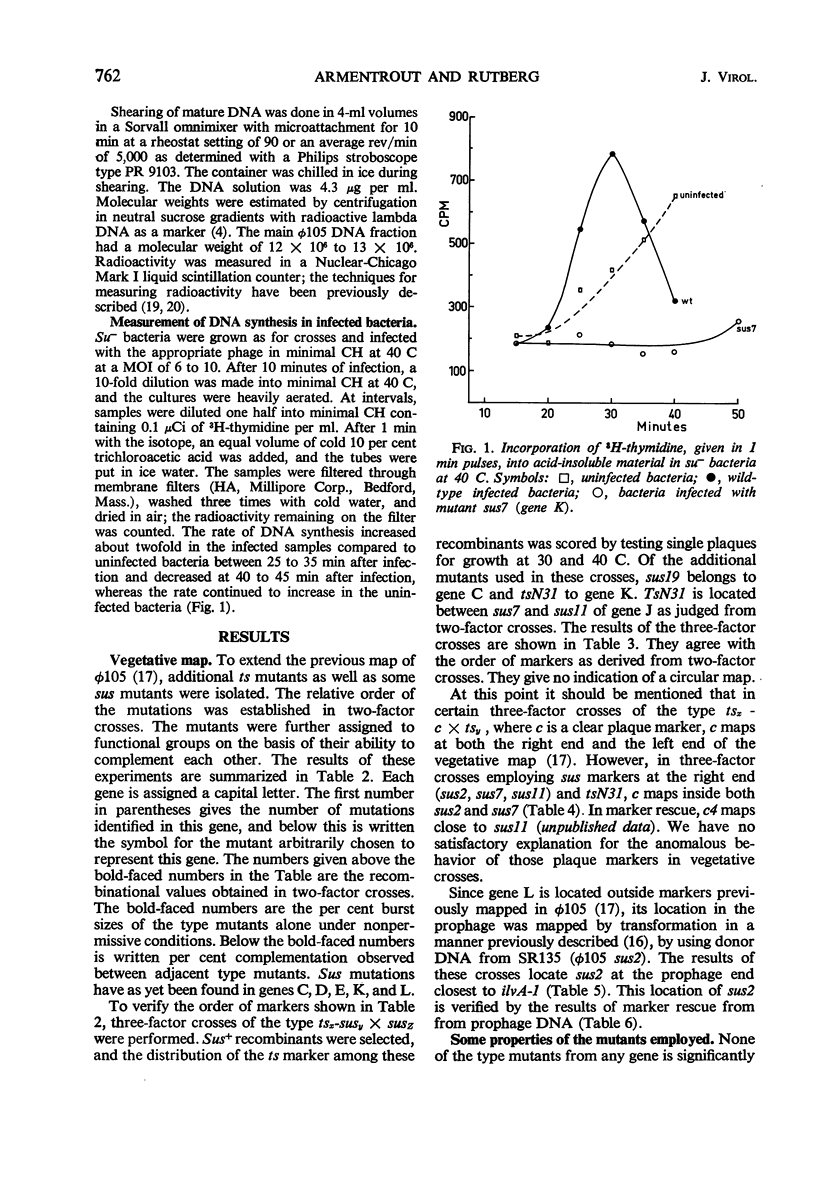
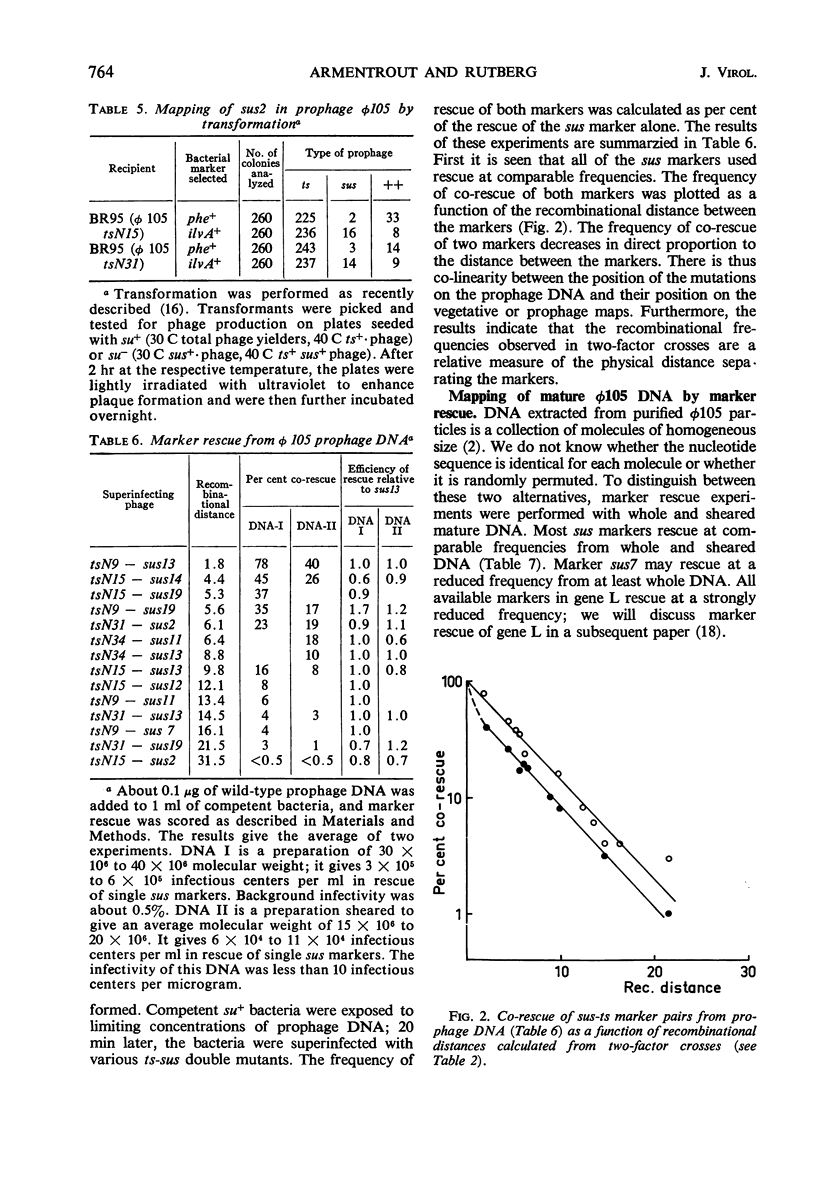
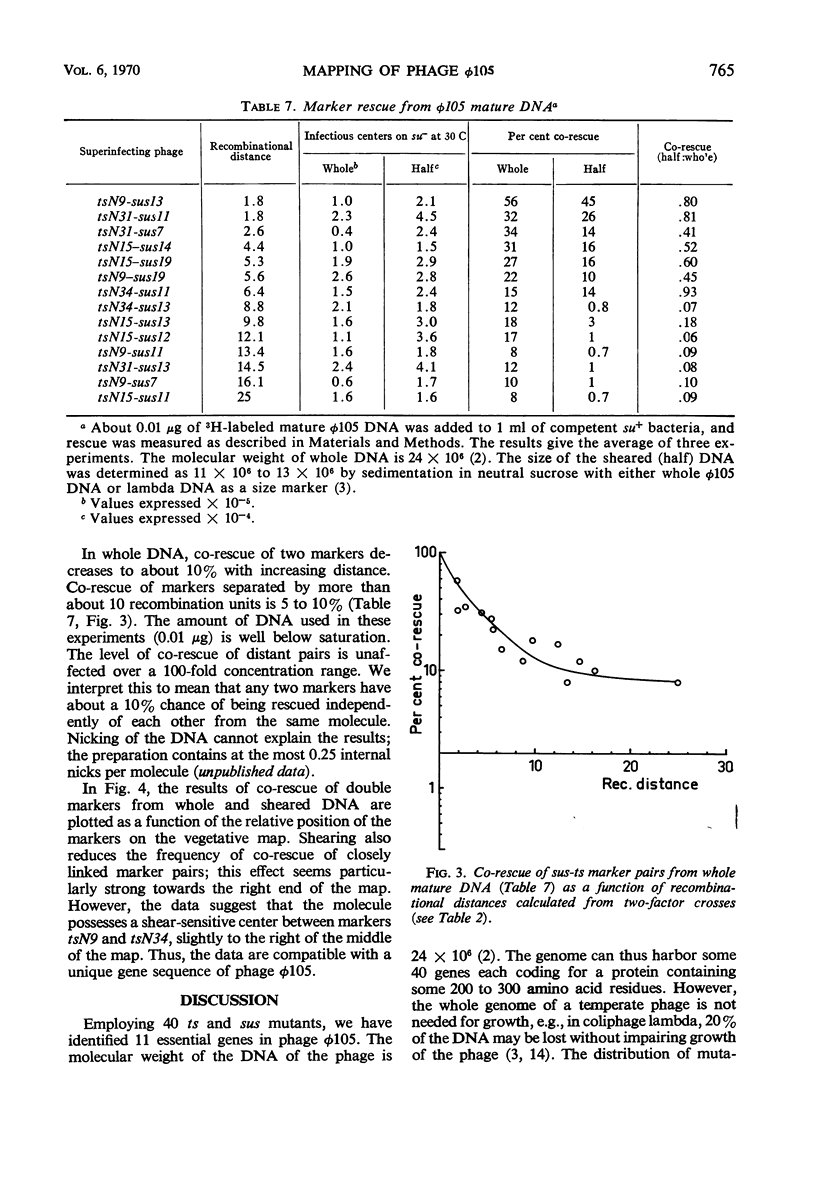
By using temperature-sensitive (ts) and suppressor-sensitive (sus) mutants, 11 essential genes have been identified in phage φ105. The order of the genes has been established in two- and three-factor crosses. The genes can be arranged in a linear order; this order is identical in the vegetative phage and in the prophage. One gene essential for phage deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) synthesis has been found. Marker rescue from prophage and mature DNA, taken up by competent bacteria, was studied by superinfection with phage carrying one sus and one ts mutation. In prophage DNA, all single markers studied are rescued at similar frequencies. The frequency of co-rescue of two markers is proportional to the recombinational distance between the markers. Thus, colinearity between the genetic map and the position on the DNA molecule of those mutations used to establish the map is demonstrated. The results indicate that the recombination frequencies observed in vegetative crosses are a relative measure of the physical distance between markers. All single markers are not rescued at equal frequencies from mature DNA. The frequency of co-rescue of two markers is related to the recombinational distance only over a distance about one-fourth or less of the genetic map. Markers separated by 10% recombination, or more, are co-rescued at 5 to 10% of the frequency of rescue of single markers. Shearing of mature DNA into half-sized molecules reduces the efficiency by which single markers are rescued by a factor of 5 to 10. The results of experiments on co-rescue of two markers from half-sized mature DNA indicate a preferred break-point near the middle of the genetic map; the results are compatible with a nonpermuted sequence in mature DNA. It is pointed out and discussed that mature DNA exhibits several anomalies in marker rescue experiments.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amati P, Meselson M. Localized Negative Interference in Bacteriophage. Genetics. 1965 Mar;51(3):369–379. doi: 10.1093/genetics/51.3.369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURGI E. Changes in molecular weight of DNA accompanying mutations in phage. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Feb 15;49:151–155. doi: 10.1073/pnas.49.2.151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURGI E., HERSHEY A. D. A relative molecular weight series derived from the nucleic acid of bacteriophage T2. J Mol Biol. 1961 Aug;3:458–472. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(61)80058-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birdsell D. C., Hathaway G. M., Rutberg L. Characterization of Temperate Bacillus Bacteriophage phi105. J Virol. 1969 Sep;4(3):264–270. doi: 10.1128/jvi.4.3.264-270.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calendar R., Lindahl G. Attachment of prophage P2: gene order at different host chromosomal sites. Virology. 1969 Dec;39(4):867–881. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90023-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgopoulos C. P. Suppressor system in Bacillus subtilis 168. J Bacteriol. 1969 Mar;97(3):1397–1402. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.3.1397-1402.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gough M., Levine M. The circularity of the phage P22 linkage map. Genetics. 1968 Feb;58(2):161–169. doi: 10.1093/genetics/58.2.161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogness D. S., Doerfler W., Egan J. B., Black L. W. The position and orientation of genes in lambda and lambda dg DNA. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1966;31:129–138. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1966.031.01.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAISER A. D., HOGNESS D. S. The transformation of Escherichia coli with deoxyribonucleic acid isolated from bacteriophage lambda-dg. J Mol Biol. 1960 Dec;2:392–415. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(60)80050-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLENBERGER G., ZICHICHI M. L., WEIGLE J. A mutation affecting the DNA content of bacteriophage lambda and its lysogenizing properties. J Mol Biol. 1961 Aug;3:399–408. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(61)80053-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl G. Genetic map of bacteriophage P2. Virology. 1969 Dec;39(4):839–860. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90021-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson A. M., Rutberg L. Linked transformation of bacterial and prophage markers in Bacillus subtilis 168 lysogenic for bacteriophage phi 105. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jun;98(3):874–877. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.3.874-877.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutberg L., Armentrout R. W. Low-frequency rescue of a genetic marker in deoxyribonucleic acid from Bacillus bacteriophage phi 105 by superinfecting bacteriophage. J Virol. 1970 Dec;6(6):768–771. doi: 10.1128/jvi.6.6.768-771.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutberg L., Hoch J. A., Spizizen J. Mechanism of transfection with deoxyribonucleic acid from the temperate Bacillus bacteriophage phi-105. J Virol. 1969 Jul;4(1):50–57. doi: 10.1128/jvi.4.1.50-57.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutberg L. Mapping of a temperate bacteriophage active on Bacillus subtilis. J Virol. 1969 Jan;3(1):38–44. doi: 10.1128/jvi.3.1.38-44.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutberg L., Rutberg B. Characterization of infectious deoxyribonucleic acid from temperature Bacillus subtilis bacteriophage phi105. J Virol. 1970 May;5(5):604–608. doi: 10.1128/jvi.5.5.604-608.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STRACK H. B., KAISER A. D. ON THE STRUCTURE OF THE ENDS OF LAMBADA DNA. J Mol Biol. 1965 May;12:36–49. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80280-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STRACK H. B., KAISER A. D. ON THE STRUCTURE OF THE ENDS OF LAMBADA DNA. J Mol Biol. 1965 May;12:36–49. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80280-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Signer E. R. Lysogeny: the integration problem. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1968;22:451–488. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.22.100168.002315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tessman I. Mutagenic treatment of double- and single-stranded DNA phages T4 ans S13 with hydroxylamine. Virology. 1968 Jun;35(2):330–333. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(68)90275-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young E. T., 2nd, Sinsheimer R. L. Vegetative bacteriophage lambda-DNA. I. Infectivity in a spheroplast assay. J Mol Biol. 1967 Nov 28;30(1):147–164. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90250-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


